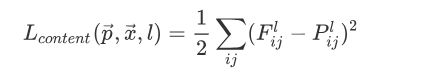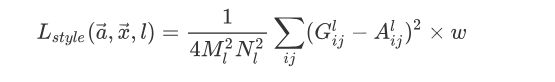TensorFlow实战 8 VGGNet进阶(图像风格迁移)
背景:在上一篇TensorFlow实战 7 VGGNet神经网络中初步了解到VGGNet神经网络模型特点,本次通过使用已经训练好的imagenet-vgg-verydeep-19.mat实现对不同风格画面的迁移运用。
参考博客: 1) TensorFlow练手项目三:使用VGG19迁移学习实现图像风格迁移
2)深度学习实战(一)快速理解实现风格迁移
正文:1)风格迁移原理
a图的style loss与p图的content loss线性组合的最小化loss而求得的x图像即为风格迁移结果:
![]()
得到两个损失函数和内容风格重建的方法:利用了VGG-Network19个卷积层和5个池化层,没有用全连接层,采用的平均池化的方法反向求取输入。
对于内容重建,用了原始网络的五个卷积层,‘conv1_1’ (a), ‘conv2_1’ (b), ‘conv3_1’ (c), ‘conv4_1’ (d) and ‘conv5_1’ (e),即图下方中的a、b、c、d、e。VGG 网络主要用来做内容识别,使用前三层a、b、c已经能够达到比较好的内容重建工作,d、e两层保留了一些比较高层的特征,丢失了一些细节。
对于风格重建,用了卷积层的不同子集:
‘conv1_1’ (a),
‘conv1_1’ and ‘conv2_1’ (b),
‘conv1_1’, ‘conv2_1’ and ‘conv3_1’ (c),
‘conv1_1’, ‘conv2_1’ , ‘conv3_1’and ‘conv4_1’ (d),
‘conv1_1’, ‘conv2_1’ , ‘conv3_1’, ‘conv4_1’and ‘conv5_1’ (e)
这样构建网络可以忽略图像的内容,保留风格。
内容损失函数:
风格损失函数:
其中G为噪声图像的gram特征, A为原始图像的gram特征,w权重值
总的损失函数即为:
2)基于TensorFlow的代码实现:
setting.py
#parameters for artistic style
#set content image
CONTENT_IMAGE = 'images/content.jpg'
#set style image
STYLE_IMAGE = 'images/style.jpg'
#set the output image
OUTPUT_IMAGE = 'images/output'
#set vgg model path
VGG_MODEL_PATH = 'imagenet-vgg-verydeep-19.mat'
#define image height
IMAGE_HEIGHT = 224
#define image width
IMAGE_WIDTH = 224
#define vgg_19 content layer loss parameters [conv_layer, weights]
CONTENT_LOSS_LAYERS = [('conv4_2', 0.5), ('conv5_2', 0.5)]
#define vgg_19 style layer parameters [conv_layer, weights]
STYLE_LOSS_LAYERS = [('conv1_1', 0.2), ('conv2_1', 0.2), ('conv3_1', 0.2), ('conv4_1', 0.2), ('conv5_1', 0.2)]
#define noize rate
NOIZE = 0.5
#define image mean value
IMAGE_MEAN_VALUE = [104, 117, 124]
#define content loss weight
ALPHA = 1
#define style loss weight
BETA = 500
#define train steps
TRAIN_STEPS = 3000models.py
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
import setting
import scipy.io
import scipy.misc
#define model class to build vgg_19 network
class model(object):
'''
description: to build vgg_19 network
Funcs: __init__(self, content_path, style_path): initialize parameters
vggnet(self): construct vgg_19 network
conv_relu(self, x, wb): relu activation
pool(self, x): max_pool operation
get_wb(self, layers, i): get the vgg parameter in i-th layer
get_random_img(self): get noise image
load_img(self, path): load the image form path
'''
def __init__(self, content_path, style_path):
'''
description: to initialize parameters
Args: content_path: content image path
style_path: style image path
Returns: None
'''
#get content image path
self.content = self.load_img(content_path)
#get style image path
self.style = self.load_img(style_path)
#get random noise image
self.random_img = self.get_random_img()
#set up the vgg network
self.net = self.vggnet()
def vggnet(self):
'''
description: to construct vgg_19 network
Args: self
Returns : net: the vgg_19 pretrained network without full connection layers
'''
#get the prtrained vgg-19.mat data
vgg = scipy.io.loadmat(setting.VGG_MODEL_PATH)
vgg_layers = vgg['layers'][0]
#initialize net dict
net = {}
#use vgg19 pretrained model parameters to train input image without full connection layers
net['input'] = tf.Variable(np.zeros([1, setting.IMAGE_HEIGHT, setting.IMAGE_WIDTH, 3]), dtype = tf.float32)
net['conv1_1'] = self.conv_relu(net['input'], self.get_wb(vgg_layers, 0))
net['conv1_2'] = self.conv_relu(net['conv1_1'], self.get_wb(vgg_layers, 2))
net['pool1'] = self.pool(net['conv1_2'])
net['conv2_1'] = self.conv_relu(net['pool1'], self.get_wb(vgg_layers, 5))
net['conv2_2'] = self.conv_relu(net['conv2_1'], self.get_wb(vgg_layers, 7))
net['pool2'] = self.pool(net['conv2_2'])
net['conv3_1'] = self.conv_relu(net['pool2'], self.get_wb(vgg_layers, 10))
net['conv3_2'] = self.conv_relu(net['conv3_1'], self.get_wb(vgg_layers, 12))
net['conv3_3'] = self.conv_relu(net['conv3_2'], self.get_wb(vgg_layers, 14))
net['conv3_4'] = self.conv_relu(net['conv3_3'], self.get_wb(vgg_layers, 16))
net['pool3'] = self.pool(net['conv3_4'])
net['conv4_1'] = self.conv_relu(net['pool3'], self.get_wb(vgg_layers, 19))
net['conv4_2'] = self.conv_relu(net['conv4_1'], self.get_wb(vgg_layers, 21))
net['conv4_3'] = self.conv_relu(net['conv4_2'], self.get_wb(vgg_layers, 23))
net['conv4_4'] = self.conv_relu(net['conv4_3'], self.get_wb(vgg_layers, 25))
net['pool4'] = self.pool(net['conv4_4'])
net['conv5_1'] = self.conv_relu(net['pool4'], self.get_wb(vgg_layers,28))
net['conv5_2'] = self.conv_relu(net['conv5_1'], self.get_wb(vgg_layers, 30))
net['conv5_3'] = self.conv_relu(net['conv5_2'], self.get_wb(vgg_layers, 32))
net['conv5_4'] = self.conv_relu(net['conv5_3'], self.get_wb(vgg_layers, 34))
net['pool5'] = self.pool(net['conv5_4'])
return net
def conv_relu(self, x, wb):
'''
description: to excute relu activation
Args: x: the input data
wb: weights and biases array
Returns: result of relu(x*wb[0] + wb[1])
'''
#excute conv2d operation
conv = tf.nn.conv2d(x, wb[0], strides = [1, 1, 1, 1], padding = 'SAME')
#relu activation
relu = tf.nn.relu(conv + wb[1])
return relu
def pool(self, x):
'''
description: to excute max_pool operation
Args: x: the input data
Returns: the results of max_pool
'''
return tf.nn.max_pool(x, ksize = [1, 2, 2, 1], strides = [1, 2, 2, 1], padding = 'SAME')
def get_wb(self, layers, i):
'''
description: to get weights and biases array
Args: layers: the pretrained vgg_19 layers
i: the i-th layer
Returns: the w and b array
'''
w = tf.constant(layers[i][0][0][0][0][0])
bias = layers[i][0][0][0][0][1]
b = tf.constant(np.reshape(bias, (bias.size)))
return w, b
def get_random_img(self):
'''
description: to generate the random noise image
Args: self:
Returns: random_img
'''
noise_img = np.random.uniform(-20, 20, [1, setting.IMAGE_HEIGHT, setting.IMAGE_WIDTH, 3])
random_img = noise_img * setting.NOIZE + self.content * (1 - setting.NOIZE)
return random_img
def load_img(self, path):
'''
description: to load the image form path
Args: self
path: the file path
Returns: image
'''
img = scipy.misc.imread(path)
img = scipy.misc.imresize(img, [setting.IMAGE_HEIGHT, setting.IMAGE_WIDTH])
img = np.reshape(img, [1, setting.IMAGE_HEIGHT, setting.IMAGE_WIDTH, 3])
return img
if __name__ == '__main__':
model(setting.CONTENT_IMAGE, setting.STYLE_IMAGE)
train.py
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
import setting
import models
import scipy.misc
#define loss function to calculate the sum loss of content loss and style loss
def loss(sess, model):
'''
description: to calculate the sum loss of content loss and style loss
Args: sess: tf Session
model: the vgg_19 model parameters
Returns: the loss sum
'''
#access content layer
content_layers = setting.CONTENT_LOSS_LAYERS
#define the input image as content
sess.run(tf.assign(model.net['input'], model.content))
#calculate the content loss
content_loss = 0.0
#access the weights and biases in layers defined in vgg_19
for layer_name, weights in content_layers:
#extract the feature matrx in layer_name for content image
p = sess.run(model.net[layer_name])
#extract the feature matrx in layer_name for noise image
x = model.net[layer_name]
# M = length * width
M = p.shape[1] * p.shape[2]
# N = channel numbers
N = p.shape[3]
#calculate the content loss
content_loss += (1.0 / (2 * M * N)) * tf.reduce_sum(tf.pow(p - x, 2))*weights
content_loss /= len(content_layers)
#access style layer
style_layers = setting.STYLE_LOSS_LAYERS
#define the input image as style
sess.run(tf.assign(model.net['input'], model.style))
#calculate the style loss
style_loss = 0.0
for layer_name, weights in style_layers:
#extract the feature matrx in layer_name for style image
a = sess.run(model.net[layer_name])
#extract the feature max in layer_name for noise image
x = model.net[layer_name]
# M = length * width
M = a.shape[1] * a.shape[2]
# N = channel numbers
N = a.shape[3]
# A = gram(a) [style image gram feature matrx]
A = gram(a, M, N)
# G = gram(x) [noise image gram feature matrx]
G = gram(x, M, N)
#calculate the style_loss
style_loss += (1.0 / (4 * M * M * N * N)) * tf.reduce_sum(tf.pow(G - A, 2)) * weights
style_loss /= len(style_layers)
#the total loss result
loss = setting.ALPHA * content_loss + setting.BETA * style_loss
return loss
#define gram function to calculate the g = transpose(x)*x
def gram(x, size, deepth):
'''
description: to calculate the gram result
Args: x: the input data
size: the result (length * width)
deepth: the channel numbers
Returns: g = transpose(x) * x
'''
x = tf.reshape(x, (size, deepth))
g = tf.matmul(tf.transpose(x), x)
return g
#define train function to train the model
def train():
'''
description: to train the model
Args: None
Returns: None
'''
model = models.model(setting.CONTENT_IMAGE, setting.STYLE_IMAGE)
with tf.Session() as sess:
#intialize the global variables
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
#define cost
cost = loss(sess, model)
#define optimizer
optimizer = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(1.0).minimize(cost)
#intialize the global variables sine the new operation
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
#train the model with noise image
sess.run(tf.assign(model.net['input'], model.random_img))
#define the train setps
for step in range(setting.TRAIN_STEPS):
#define BP once
sess.run(optimizer)
#output the trainning results
if step % 50 == 0:
print('step{} is done .'.format(step))
#access the generated image
img = sess.run(model.net['input'])
#recover the image with adding the image mean value
img += img + setting.IMAGE_MEAN_VALUE
#get the batch 0 demension
img = img[0]
#recover the float32 image to int image in [0, 255]
img = np.clip(img, 0, 255).astype(np.uint8)
#save the image
scipy.misc.imsave('{}-{}.jpg'.format(setting.OUTPUT_IMAGE, step), img)
#save the finnal result
img = sess.run(model.net['input'])
#recover the image with adding the image mean value
img += img + setting.IMAGE_MEAN_VALUE
#get the batch 0 demension
img = img[0]
#recover the float32 image to int image in [0, 255]
img = np.clip(img, 0, 255).astype(np.uint8)
#save the image
scipy.misc.imsave('{}.jpg'.format(setting.OUTPUT_IMAGE), img)
if __name__ == '__main__':
train()3)最终效果:
通过调整不同权重还可获得更加奇特的效果,还可以进行更多尝试。
practice makes perfect!