在elastic-job中,有一块很重要的功能,与作业的执行密切相关,但又不影响作业的执行,那就是作业的执行状态和运行轨迹记录,脑子里很容易想到这几个词,观察者模式,发布订阅模式。
在elastic-Job中,是使用guava的EventBus事件总线工具,简单的使用观察者模式来实现。
先看一个简单的demo:
新建一个消息总线的发送者
public class EventBusPoster {
private EventBus eventBus = new EventBus();
public void post(String message) {
eventBus.post(message);
}
public void addListener(EventBusListener eventBusListener) {
eventBus.register(eventBusListener);
}
新建一个监听消息总线的listener
public class EventBusListener {
@Subscribe
public void listener(String message) {
System.out.println("receive eventbus message:" + message);
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
EventBusPoster eventBusPoster = new EventBusPoster();
EventBusListener eventBusListener = new EventBusListener();
eventBusPoster.addListener(eventBusListener);
eventBusPoster.post("hello world!");
eventBusPoster.post("你好,世界!");
}
}
receive eventbus message:hello world!
receive eventbus message:你好,世界!
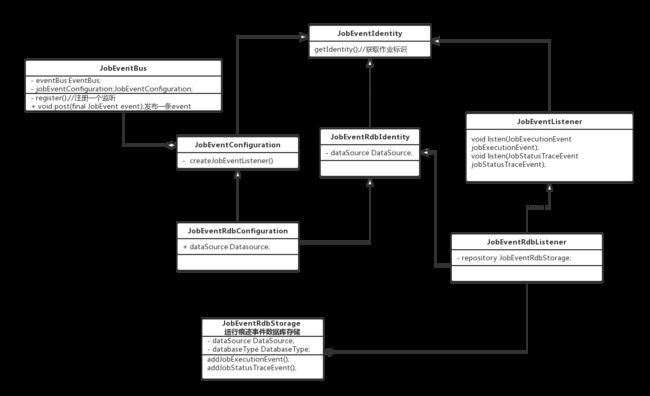
一个很简单的观察者模式就这样实现了。那么,elastic-Job是怎样实现的?先看一下类图:
在elastic-Job启动的过程中,初始化JobScheduler时,就已经将JobEventBus初始化进去了,看代码new JobEventBus():
public JobScheduler(final CoordinatorRegistryCenter regCenter, final LiteJobConfiguration liteJobConfig, final ElasticJobListener... elasticJobListeners) {
this(regCenter, liteJobConfig, new JobEventBus(), elasticJobListeners);
}
public JobScheduler(final CoordinatorRegistryCenter regCenter, final LiteJobConfiguration liteJobConfig, final JobEventConfiguration jobEventConfig,
final ElasticJobListener... elasticJobListeners) {
this(regCenter, liteJobConfig, new JobEventBus(jobEventConfig), elasticJobListeners);
}
而在作业执行过程中,多次调用jobFacade.postJobStatusTraceEvent(..)和postJobExecutionEvent去推送Event,看代码;
//AbstractElasticJobExecutor 抽象执行器
public final void execute() {
try {
jobFacade.checkJobExecutionEnvironment();
} catch (final JobExecutionEnvironmentException cause) {
jobExceptionHandler.handleException(jobName, cause);
}
ShardingContexts shardingContexts = jobFacade.getShardingContexts();
if (shardingContexts.isAllowSendJobEvent()) {
//这里推送Event
jobFacade.postJobStatusTraceEvent(shardingContexts.getTaskId(), State.TASK_STAGING, String.format("Job '%s' execute begin.", jobName));
}
jobFacade.failoverIfNecessary();
//此处省略很多代码
}
private void process(final ShardingContexts shardingContexts, final int item, final JobExecutionEvent startEvent) {
if (shardingContexts.isAllowSendJobEvent()) {
//推送执行情况Event
jobFacade.postJobExecutionEvent(startEvent);
}
log.trace("Job '{}' executing, item is: '{}'.", jobName, item);
JobExecutionEvent completeEvent;
try {
process(new ShardingContext(shardingContexts, item));
completeEvent = startEvent.executionSuccess();
log.trace("Job '{}' executed, item is: '{}'.", jobName, item);
if (shardingContexts.isAllowSendJobEvent()) {
//推送执行情况Event
jobFacade.postJobExecutionEvent(completeEvent);
}
// CHECKSTYLE:OFF
} catch (final Throwable cause) {
// CHECKSTYLE:ON
completeEvent = startEvent.executionFailure(cause);
//推送执行情况Event
jobFacade.postJobExecutionEvent(completeEvent);
itemErrorMessages.put(item, ExceptionUtil.transform(cause));
jobExceptionHandler.handleException(jobName, cause);
}
}
而postJobExecutionEvent和postJobStatusTraceEvent主要是调用jobEventBus去post数据,看代码:
@Override
public void postJobExecutionEvent(final JobExecutionEvent jobExecutionEvent) {
jobEventBus.post(jobExecutionEvent);
}
@Override
public void postJobStatusTraceEvent(final String taskId, final State state, final String message) {
TaskContext taskContext = TaskContext.from(taskId);
jobEventBus.post(new JobStatusTraceEvent(taskContext.getMetaInfo().getJobName(), taskContext.getId(), taskContext.getSlaveId(), Source.LITE_EXECUTOR, taskContext.getType(), taskContext.getMetaInfo().getShardingItems().toString(), state, message));
if (!Strings.isNullOrEmpty(message)) {
log.trace(message);
}
}
在JobEventBus初始化过程中,主要是通过构造线程池初始化一个AsynEventBus,通过register注册监听类,若没有配置类,则不注册监听Listener,且不postEvent。
public final class JobEventBus {
private final JobEventConfiguration jobEventConfig;
private final ExecutorServiceObject executorServiceObject;
private final EventBus eventBus;
private boolean isRegistered;
public JobEventBus() {
jobEventConfig = null;
executorServiceObject = null;
eventBus = null;
}
public JobEventBus(final JobEventConfiguration jobEventConfig) {
this.jobEventConfig = jobEventConfig;
//线程池线程数量为cpu核数的两倍
executorServiceObject = new ExecutorServiceObject("job-event", Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors() * 2);
//异步总线
eventBus = new AsyncEventBus(executorServiceObject.createExecutorService());
register();
}
private void register() {
try {
eventBus.register(jobEventConfig.createJobEventListener());
isRegistered = true;
} catch (final JobEventListenerConfigurationException ex) {
log.error("Elastic job: create JobEventListener failure, error is: ", ex);
}
}
/**
* 发布事件.
* 若没有注册则不发布
* @param event 作业事件
*/
public void post(final JobEvent event) {
if (isRegistered && !executorServiceObject.isShutdown()) {
eventBus.post(event);
}
}
}
而在注册的过程中,主要是注册了一个监听类JobEventRdbListener,看代码:
@Override
public JobEventListener createJobEventListener() throws JobEventListenerConfigurationException {
try {
return new JobEventRdbListener(dataSource);
} catch (final SQLException ex) {
throw new JobEventListenerConfigurationException(ex);
}
}
而JobEventRdbListener类,主要是订阅Event消息。
public final class JobEventRdbListener extends JobEventRdbIdentity implements JobEventListener {
private final JobEventRdbStorage repository;
public JobEventRdbListener(final DataSource dataSource) throws SQLException {
repository = new JobEventRdbStorage(dataSource);
}
@Override
public void listen(final JobExecutionEvent executionEvent) {
repository.addJobExecutionEvent(executionEvent);
}
@Override
public void listen(final JobStatusTraceEvent jobStatusTraceEvent) {
repository.addJobStatusTraceEvent(jobStatusTraceEvent);
}
}
那post的Event事件,Listener是如何感知到的,看接口定义,有两个标签,@Subscribe,代表订阅消息,只要是该方法参数类型的Event,就能够被监听,如果没有合适的类型的Event,则会是DeadEvent,而@AllowConcurrentEvents字面意思就是允许并发,实际原因在于如果是线程安全的,使用该标签会减少同步开销,具体原因可以看AllowConcurrentEvents分析
public interface JobEventListener extends JobEventIdentity {
/**
* 作业执行事件监听执行.
*
* @param jobExecutionEvent 作业执行事件
*/
@Subscribe
@AllowConcurrentEvents
void listen(JobExecutionEvent jobExecutionEvent);
/**
* 作业状态痕迹事件监听执行.
*
* @param jobStatusTraceEvent 作业状态痕迹事件
*/
@Subscribe
@AllowConcurrentEvents
void listen(JobStatusTraceEvent jobStatusTraceEvent);
}