TensorFlow是一个深度学习的库,上层支持Python语言,底层用C++实现具体操作。
它以图graph的方式来建立操作序列,图中的节点表示数学操作,连线表示数据的流动方向。
它以定义和执行分离的方式来编程,用图来定义操作序列,然后建立session来执行,执行时可以把每个操作分配到不同的CPU、GPU上进行,所以速度很快。
具体编程流程:
建立计算图
初始化变量
建立会话
在会话中执行图
关闭会话
注意:需要注意不同版本之间的兼容性不是很好,下面的例子在Python3.5、TensorFlow 1.2版本下编译执行通过。
简单举例
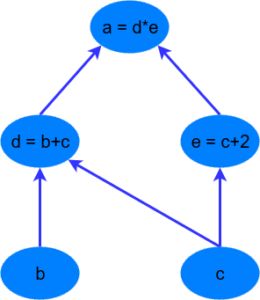
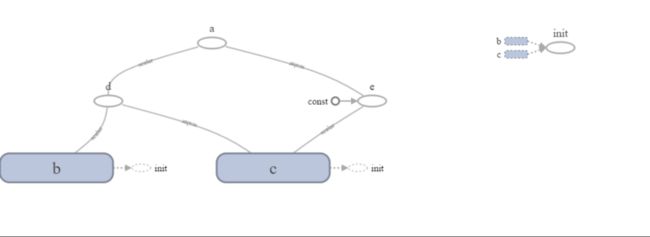
以上面图中a=(b+c)?(c+2)来举例,先导入tensorflow库,然后定义常量,再定义变量。
importtensorflowastf
# first, create a TensorFlow constant
const=tf.constant(2.0,name="const")
# create TensorFlow variables
b=tf.Variable(2.0,name='b')
c=tf.Variable(1.0,name='c')
再建立操作:
# now create some operations
d=tf.add(b,c,name='d')
e=tf.add(c,const,name='e')
a=tf.multiply(d,e,name='a')
再初始化所有变量:
# setup the variable initialisation
init_op=tf.global_variables_initializer()
最后建立并执行session:
# start the session
withtf.Session()assess:
# initialise the variables
sess.run(init_op)
# compute the output of the graph
a_out=sess.run(a)
print("Variable a is {}".format(a_out))
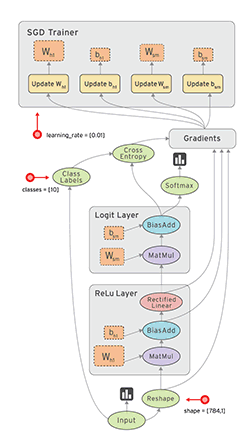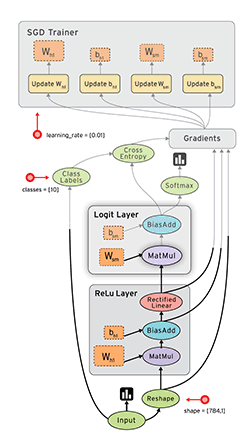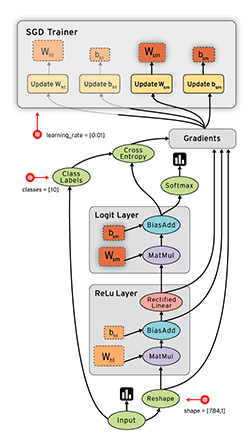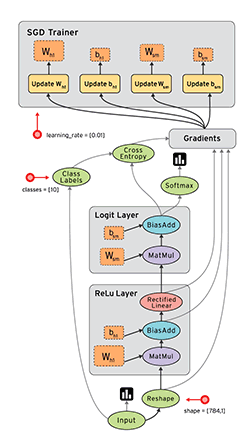
具体执行过程如下图:
最终的执行结果:
Variable a is 9.0
Process finished with exit code 0
神经网络举例
以常见的神经网络基准测试MNIST(图片中阿拉伯数字的识别)为例,祥见注释:
importtensorflowastf
fromtensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnistimportinput_data
mnist=input_data.read_data_sets("MNIST_data/",one_hot=True)# 从官方例子导入训练数据和测试数据,导入后数据保存在当前目录的\MNIST_data目录下。
# Python optimisation variables
learning_rate=0.5
epochs=10# 执行10批次训练
batch_size=100# 每批次100个数据
# declare the training data placeholders
# input x - for 28 x 28 pixels = 784
x=tf.placeholder(tf.float32,[None,784])# 预留训练数据的输入值
# now declare the output data placeholder - 10 digits
y=tf.placeholder(tf.float32,[None,10])# 预留训练数据的输入值对应的输出值
# now declare the weights connecting the input to the hidden layer
W1=tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([784,300],stddev=0.03),name='W1')#定义第一层输入层需要优化的参数变量,计算公式为:y = x * W + b
b1=tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([300]),name='b1')
# and the weights connecting the hidden layer to the output layer
W2=tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([300,10],stddev=0.03),name='W2')#定义第二层隐藏层的参数变量。
b2=tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([10]),name='b2')
# calculate the output of the hidden layer
hidden_out=tf.add(tf.matmul(x,W1),b1)
hidden_out=tf.nn.relu(hidden_out)
# now calculate the hidden layer output - in this case, let's use a softmax activated
# output layer
y_=tf.nn.softmax(tf.add(tf.matmul(hidden_out,W2),b2))# 计算隐藏层输出
y_clipped=tf.clip_by_value(y_,1e-10,0.9999999)
cross_entropy=-tf.reduce_mean(tf.reduce_sum(y*tf.log(y_clipped)+(1-y)*tf.log(1-y_clipped),axis=1))#计算最终评估因子
# add an optimiser
optimiser=tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(learning_rate=learning_rate).minimize(cross_entropy)# 定义一个对参数的BP优化器
# finally setup the initialisation operator
init_op=tf.global_variables_initializer()# 初始化变量
# define an accuracy assessment operation
correct_prediction=tf.equal(tf.argmax(y,1),tf.argmax(y_,1))
accuracy=tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_prediction,tf.float32))# 定义精度
# start the session
withtf.Session()assess:#开始执行
# initialise the variables
sess.run(init_op)
total_batch=int(len(mnist.train.labels)/batch_size)
forepochinrange(epochs):
avg_cost=0
foriinrange(total_batch):
batch_x,batch_y=mnist.train.next_batch(batch_size=batch_size)
_,c=sess.run([optimiser,cross_entropy],
feed_dict={x:batch_x,y:batch_y})
avg_cost+=c/total_batch
print("Epoch:",(epoch+1),"cost =","{:.3f}".format(avg_cost))
print(sess.run(accuracy,feed_dict={x:mnist.test.images,y:mnist.test.labels}))# 最终结果,精度
执行结果,可以看到很不错,精度有0.9742(1.0位为理想值):
Epoch:1 cost=0.768
Epoch:2 cost=0.245
Epoch:3 cost=0.183
Epoch:4 cost=0.152
Epoch:5 cost=0.125
Epoch:6 cost=0.108
Epoch:7 cost=0.090
Epoch:8 cost=0.078
Epoch:9 cost=0.068
Epoch:10 cost=0.060
0.9742
Process finished with exit code 0