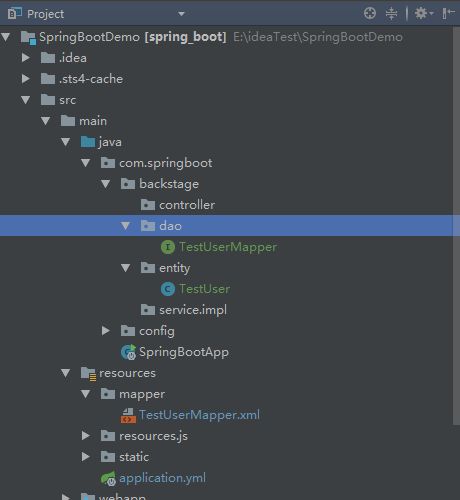
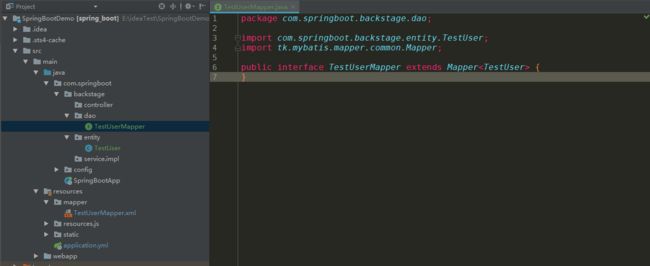
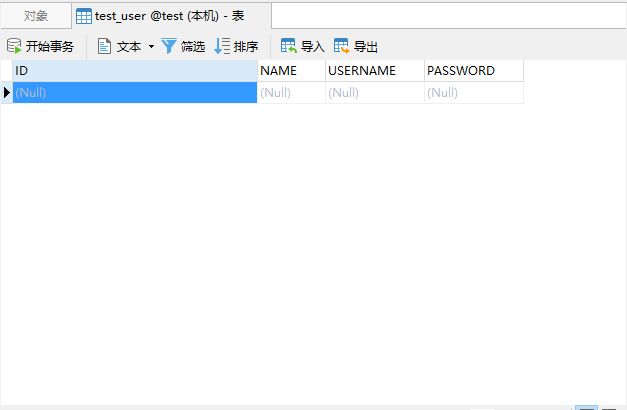
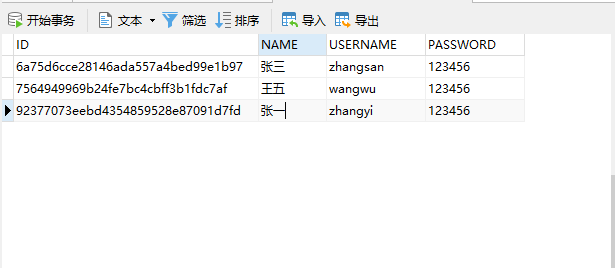
生成文件放到项目
Github地址
用工具把数据库里面的表生成对应的文件放到项目里
SpringBoot集成通用mapper
pom.xml添加依赖
tk.mybatis
mapper-spring-boot-starter
1.1.7
特别注意,如果使用了1.2.0以上版本 @MapperScan 注解,请使用 tk.mybatis.spring.annotation.MapperScan 注解。
application.yml文件配置
mapper:
mappers: tk.mybatis.mapper.common.Mapper
not-empty: false
identity: MYSQL
style: camelhump
可配置参数介绍
- UUID:设置生成UUID的方法,需要用OGNL方式配置,不限制返回值,但是必须和字段类型匹配
- IDENTITY:取回主键的方式
- DB2: VALUES IDENTITY_VAL_LOCAL()
- MYSQL: SELECT LAST_INSERT_ID()
- SQLSERVER: SELECT SCOPE_IDENTITY()
- CLOUDSCAPE: VALUES IDENTITY_VAL_LOCAL()
- DERBY: VALUES IDENTITY_VAL_LOCAL()
- HSQLDB: CALL IDENTITY()
- SYBASE: SELECT @@IDENTITY
- DB2_MF: SELECT IDENTITY_VAL_LOCAL() FROM >> * SYSIBM.SYSDUMMY1
- INFORMIX: select dbinfo('sqlca.sqlerrd1') from systables where tabid=1
- JDBC:这会令 MyBatis 使用 JDBC 的 getGeneratedKeys 方法来取出由数据库内部生成的主键(比如:像 MySQL 和 SQL Server 这样的关系数据库管理系统的自动递增字段)。
- ORDER:
中的order属性,可选值为BEFORE和AFTER - catalog:数据库的catalog,如果设置该值,查询的时候表名会带catalog设置的前缀
- schema:同catalog,catalog优先级高于schema
- seqFormat:序列的获取规则,使用{num}格式化参数,默认值为{0}.nextval,针对Oracle,可选参数一共4个,对应0,1,2,3分别为SequenceName,ColumnName, PropertyName,TableName
- notEmpty:insert和update中,是否判断字符串类型!='',少数方法会用到
- style:实体和表转换时的规则,默认驼峰转下划线,可选值为normal用实体名和字段名;camelhump是默认值,驼峰转下划线;uppercase转换为大写;lowercase转换为小写
- enableMethodAnnotation:可以控制是否支持方法上的JPA注解,默认false。
使用通用Mapper
继承通用的Mapper必须指定泛型
例:
泛型实体类必须符合要求
实体类按照如下规则和数据库表进行转换,注解全部是JPA中的注解:
- 1.表名默认使用类名,驼峰转下划线(只对大写字母进行处理),如TestUser默认对应的表名为test_user
- 2.表名可以使用@Table(name = "tableName")进行指定,对不符合第一条默认规则的可以通过这种方式指定表名.
- 3.字段默认和@Column一样,都会作为表字段,表字段默认为Java对象的Field名字驼峰转下划线形式.
- 4.可以使用@Column(name = "fieldName")指定不符合第3条规则的字段名
- 5.使用@Transient注解可以忽略字段,添加该注解的字段不会作为表字段使用.
- 6.建议一定是有一个@Id注解作为主键的字段,可以有多个@Id注解的字段作为联合主键.
- 7.默认情况下,实体类中如果不存在包含@Id注解的字段,所有的字段都会作为主键字段进行使用(这种效率极低).
- 8.实体类可以继承使用,可以参考测试代码中的tk.mybatis.mapper.model.UserLogin2类.
- 9.由于基本类型,如int作为实体类字段时会有默认值0,而且无法消除,所以实体类中建议不要使用基本类型.
- 10.@NameStyle注解,用来配置对象名/字段和表名/字段之间的转换方式,该注解优先于全局配置style,可选值:
normal:使用实体类名/属性名作为表名/字段名
camelhump:这是默认值,驼峰转换为下划线形式
uppercase:转换为大写
lowercase:转换为小写
重点强调 @Transient 注解 许多人由于不仔细看文档,频繁在这个问题上出错。如果你的实体类中包含了不是数据库表中的字段,你需要给这个字段加上@Transient注解,这样通用Mapper在处理单表操作时就不会将标注的属性当成表字段处理!
主键策略(仅用于insert方法)
通用Mapper还提供了序列(支持Oracle)、UUID(任意数据库,字段长度32)、主键自增(类似Mysql,Hsqldb)三种方式,其中序列和UUID可以配置多个,主键自增只能配置一个。
- 1.@GeneratedValue(generator = "JDBC")
@Id
@GeneratedValue(generator = "JDBC")
private Integer id;
这会令 MyBatis 使用 JDBC 的 getGeneratedKeys 方法来取出由数据库内部生成的主键(比如:像 MySQL 和 SQL Server 这样的关系数据库管理系统的自动递增字段)
- 2.@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
- 这个注解适用于主键自增的情况,支持下面这些数据库:
DB2: VALUES IDENTITY_VAL_LOCAL()
MYSQL: SELECT LAST_INSERT_ID()
SQLSERVER: SELECT SCOPE_IDENTITY()
CLOUDSCAPE: VALUES IDENTITY_VAL_LOCAL()
DERBY: VALUES IDENTITY_VAL_LOCAL()
HSQLDB: CALL IDENTITY()
SYBASE: SELECT @@IDENTITY
DB2_MF: SELECT IDENTITY_VAL_LOCAL() FROM SYSIBM.SYSDUMMY1
INFORMIX: select dbinfo('sqlca.sqlerrd1') from systables where tabid=1
使用GenerationType.IDENTITY需要在全局配置中配置IDENTITY的参数值,并且需要根据数库配置ORDER属性。
- 3.@GeneratedValue(generator = "UUID")
可以用于任意字符串类型长度超过32位的字段
@Id
@GeneratedValue(generator = "UUID")
private Integer id;
接口及使用大全
基础接口
Insert
1.InsertMapper
接口:InsertMapper
方法:int insert(T record);
说明:保存一个实体,null的属性也会保存,不会使用数据库默认值
public int insertTestUser(TestUser testUser) {
return testUserMapper.insert(testUser);
}
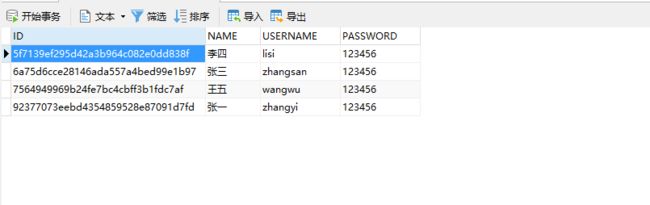
结果:
2.InsertSelectiveMapper
接口:InsertSelectiveMapper
方法:int insertSelective(T record);
说明:保存一个实体,null的属性不会保存,会使用数据库默认值
结果:
请自行实验
Update
1.UpdateByPrimaryKeyMapper
接口:UpdateByPrimaryKeyMapper
方法:int updateByPrimaryKey(T record);
说明:根据主键更新实体全部字段,null值会被更新
结果:
会把没有值的属性变成空请自行实验
2.UpdateByPrimaryKeySelectiveMapper
接口:UpdateByPrimaryKeySelectiveMapper
方法:int updateByPrimaryKeySelective(T record);
说明:根据主键更新属性不为null的值
public int updateTestUser() {
TestUser testUser=new TestUser();
testUser.setId("5f7139ef295d42a3b964c082e0dd838f");
testUser.setName("李四四");
return testUserMapper.updateByPrimaryKeySelective(testUser);
}
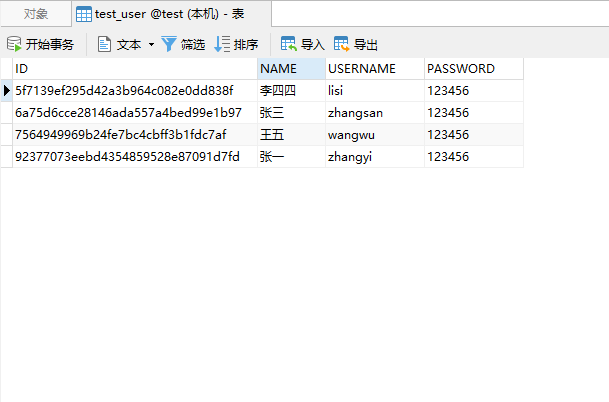
结果:
Delete
1.DeleteMapper
接口:DeleteMapper
方法:int delete(T record);
说明:根据实体属性作为条件进行删除,查询条件使用等号
public int deleteTestUser() {
TestUser testUser=new TestUser();
//根据属性删除会把所有密码是123456的数据删除
testUser.setPassword("123456");
return testUserMapper.delete(testUser);
}
结果:
四个已经全部删除
2.DeleteByPrimaryKeyMapper
接口:DeleteByPrimaryKeyMapper
方法:int deleteByPrimaryKey(Object key);
说明:根据主键字段进行删除,方法参数必须包含完整的主键属性
public int deleteKeyTestUser() {
//根据主键ID删除
return testUserMapper.deleteByPrimaryKey("5f7139ef295d42a3b964c082e0dd838f");
}
结果:
Select
1.SelectMapper
接口:SelectMapper
方法:List
说明:根据实体中的属性值进行查询,查询条件使用等号
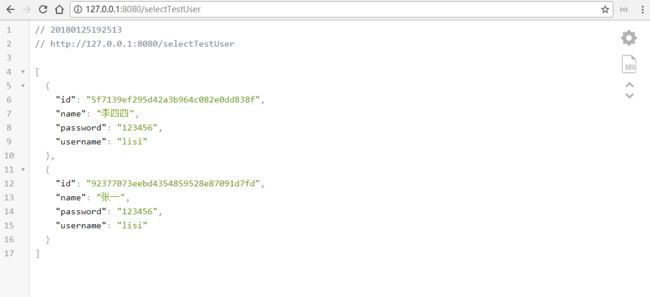
public List selectTestUser() {
TestUser testUser=new TestUser();
testUser.setPassword("123456");
testUser.setUsername("lisi");
return testUserMapper.select(testUser);
}
结果:
2.SelectByPrimaryKeyMapper
接口:SelectByPrimaryKeyMapper
方法:T selectByPrimaryKey(Object key);
说明:根据主键字段进行查询,方法参数必须包含完整的主键属性,查询条件使用等号
结果:
根据主键查询请自行实验
3.SelectAllMapper
接口:SelectAllMapper
方法:List
说明:查询全部结果,select(null)方法能达到同样的效果
结果:
查询所有请自行实验
4.SelectOneMapper
接口:SelectOneMapper
方法:T selectOne(T record);
说明:根据实体中的属性进行查询,只能有一个返回值,有多个结果是抛出异常,查询条件使用等号
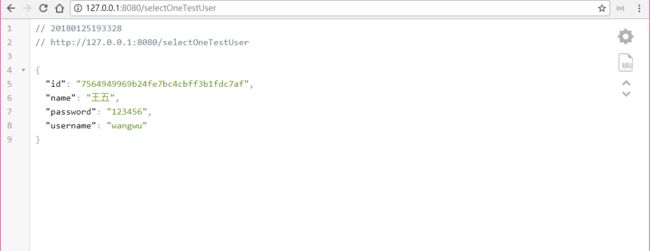
public TestUser selectOneTestUser() {
TestUser testUser=new TestUser();
testUser.setUsername("wangwu");
//结果只能返回一条数据否则会抛出异常
return testUserMapper.selectOne(testUser);
}
结果:
5.SelectCountMapper
接口:SelectCountMapper
方法:int selectCount(T record);
说明:根据实体中的属性查询总数,查询条件使用等号
结果:
返回查询个数请自行实验
Example 方法
Select 方法
1.SelectByExampleMapper
接口:SelectByExampleMapper
方法:List
说明:根据Example条件进行查询
重点:这个查询支持通过Example类指定查询列,通过selectProperties方法指定查询列
public List selectExample() {
Example example = new Example(TestUser.class);
//排序方法setOrderByClause("字段名 ASC")DESC降序
example.setOrderByClause("name ASC");
example.createCriteria()
//添加xxx字段等于value条件
.andEqualTo("password","123456")
//模糊查询xxx字段like value条件
.andLike("name","%四%")
//可以自由拼接SQL
//.andCondition("ID = '5f7139ef295d42a3b964c082e0dd838f' ")
//或者可以这么写
.andCondition("ID =","5f7139ef295d42a3b964c082e0dd838f")
;
return testUserMapper.selectByExample(example);
}
实例解析:
mybatis的逆向工程中会生成实例及实例对应的example,example用于添加条件,相当where后面的部分
Example example = new Example();
Criteria criteria = example.createCriteria();
| 方法 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| example.setOrderByClause(“字段名 ASC”) | 添加升序排列条件,DESC为降序 |
| example.setDistinct(false) | 去除重复,boolean型,true为选择不重复的记录。 |
| criteria.andIsNull("字段") | 添加字段xxx为null的条件 |
| criteria.andIsNotNull("字段") | 添加字段xxx不为null的条件 |
| criteria.andEqualTo("字段",value) | 添加xxx字段等于value条件 |
| criteria.andNotEqualTo("字段",value) | 添加xxx字段不等于value条件 |
| criteria.andGreaterThan("字段",value) | 添加xxx字段大于value条件 |
| criteria.andGreaterThanOrEqualTo("字段",value) | 添加xxx字段大于等于value条件 |
| criteria.andLessThan("字段",value) | 添加xxx字段小于value条件 |
| criteria.andLessThanOrEqualTo("字段",value) | 添加xxx字段小于等于value条件 |
| criteria.andIn("字段",List) | 添加xxx字段值在List条件 |
| criteria.andNotIn("字段",List) | 添加xxx字段值不在List条件 |
| criteria.andLike("字段",“%”+value+”%”) | 添加xxx字段值为value的模糊查询条件 |
| criteria.andNotLike("字段",“%”+value+”%”) | 添加xxx字段值不为value的模糊查询条件 |
| criteria.andBetween(value1,value2) | 添加xxx字段值在value1和value2之间条件 |
| criteria.andNotBetween(value1,value2) | 添加xxx字段值不在value1和value2之间条件 |
| criteria.andCondition("SQL") | 可以写字符串拼接SQL |
| criteria.andCondition("字段 =",value) | 前面可以写SQL后面可以写值 |
还有criteria.orxxxx的方法跟上面一样这里不做解释
2. SelectCountByExampleMapper
接口:SelectCountByExampleMapper
方法:int selectCountByExample(Object example);
说明:根据Example条件进行查询总数
查询总数的方法跟上面的写法一样
Update 方法
UpdateByExampleMapper
接口:UpdateByExampleMapper
方法:int updateByExample(@Param("record") T record, @Param("example") Object example);
说明:根据Example条件更新实体record包含的全部属性,null值会被更新
UpdateByExampleSelectiveMapper
接口:UpdateByExampleSelectiveMapper
方法:int updateByExampleSelective(@Param("record") T record, @Param("example") Object example);
说明:根据Example条件更新实体record包含的不是null的属性值
Delete 方法
DeleteByExampleMapper
接口:DeleteByExampleMapper
方法:int deleteByExample(Object example);
说明:根据Example条件删除数据
结语
- 更新这个文档用的时间很长.终于写完了,以后开发会提高不少效率。也可以把通用mapper整合到spring里详细教程可以看
通用Mapper文档
通用Mapper码云文档