ArrayList 概述
ArrayList是JDK容器中的一种列表(List)实现,其实现依赖于数据结构中顺序存储结构(数组),满足了顺序存储结构基本特性。针对 ArrayList 增加改查其实本质就是操作数组.
ArrayList 特性
利于查询。这种存储方式的优点是查询的时间复杂度为O(1),通过首地址和偏移量就可以直接访问到某元素。
不利于修改。插入和删除的时间复杂度最坏能达到O(n),如果你在第一个位置插入一个元素,你需要把数组的每一个元素向后移动一位,如果你在第一个位置删除一个元素,你需要把数组的每一个元素向前移动一位。容量的固定性。就是当你不确定元素的数量时,你开的数组必须保证能够放下元素最大数量,遗憾的是如果实际数量比最大数量少很多时,你开的数组没有用到的内存就只能浪费掉了。
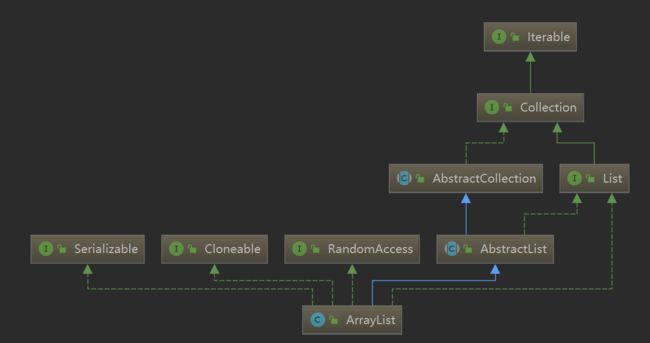
ArrayList类结构
ArrayList内部成员变量
// 内部数组,用 transient 关键字修饰,表示该变量不会被序列化
private transient Object[] elementData;
// 数组中的元素个数
private int size;
通过这两个成员变量表明ArrayList 内部是通过数组来储存元素的.
ArrayList 构造函数
//列表使用默认构造函数的初始容量
private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10;
//标识列表为容量为0
private static final Object[] EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {};
//标识列表为默认构造器构造,第一次添加时会自动扩容到初始容量DEFAULT_CAPACITY
private static final Object[] DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {};
/**
* 默认构造函数
*/
public ArrayList() {
this.elementData = DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;
}
/**
* 指定初始容量的构造函数。
* @param initialCapacity 列表的初始容量
* @throws IllegalArgumentException 如果指定的初始容量为负数
*/
public ArrayList(int initialCapacity) {
if (initialCapacity > 0) {
this.elementData = new Object[initialCapacity];
} else if (initialCapacity == 0) {
this.elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;
} else {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Capacity: "+
initialCapacity);
}
}
/**
* 指定集合,构造一个包含指定集合元素的新列表。
*
* @param c the collection whose elements are to be placed into this list
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified collection is null
*/
public ArrayList(Collection c) {
elementData = c.toArray();
if ((size = elementData.length) != 0) {
// c.toArray might (incorrectly) not return Object[] (see 6260652)
if (elementData.getClass() != Object[].class)
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size, Object[].class);
} else {
// replace with empty array.
this.elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;
}
}
扩容检测
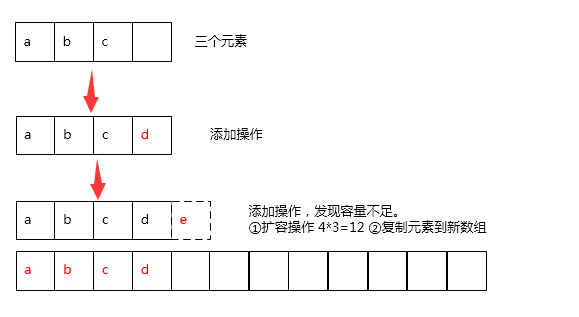
数组有个明显的特点就是它的容量是固定不变的,一旦数组被创建则容量则无法改变。所以在往数组中添加指定元素前,首先要考虑的就是其容量是否饱和。
若接下来的添加操作会时数组中的元素超过其容量,则必须对其进行扩容操作。受限于数组容量固定不变的特性,扩容的本质其实就是创建一个容量更大的新数组,再将旧数组的元素复制到新数组当中去。
这里以 ArrayList 的 添加操作为例,来看下 ArrayList 内部数组扩容的过程。
//添加一个集合元素到列表尾部
public boolean add(E e) {
//关键 -> 扩容检测
ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1);
elementData[size++] = e;
return true;
}
ensureCapacityInternal
minCapacity:表示需要使用的容量
private void ensureCapacityInternal(int minCapacity) {
//列表使用默认构造函数,则直接设置当前需要使用的容量为DEFAULT_CAPACITY(只有大于minCapacity才做此操作)
if (elementData == DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA) {
minCapacity = Math.max(DEFAULT_CAPACITY, minCapacity);
}
ensureExplicitCapacity(minCapacity);
}
判断是否需要扩容 ensureExplicitCapacity
private void ensureExplicitCapacity(int minCapacity) {
//modCount++
modCount++;
// 判断结果数组是否能够容纳当前的容量,返回true说明需要扩容。
if (minCapacity - elementData.length > 0){
// 真正的扩容操作
grow(minCapacity);
}
}
扩容操作 grow
private void grow(int minCapacity) {
// 获取当前数组中容量大小
int oldCapacity = elementData.length;
// 扩容公式 newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity / 2);
int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1);
// 当初始数组容量为0时,newCapacity为0,直接设置新容量为当前需要的容量
if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0)
newCapacity = minCapacity;
// 当扩容后容量大于MAX_ARRAY_SIZE,重新设置扩容容量
if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0)
newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity);
// 构造容量为newCapacity新数组,将原始列表数组保存的原始复制到新数组中.
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity);
}
添加操作
ArrayList 的添加操作,也就是往其内部数组添加元素的过程。首先要确保就是数组有足够的空间来存放元素,因此也就有了扩容检测这一步骤。
添加方式:
- 指定位置(添加到数组指定位置)
- 指定位置时,即将新元素存在到数组的指定位置。若该位置不是数组末尾(即该位置后面还存有元素),则需要将该位置及之后的元素后移一位,以腾出空间来存放新元素。
- 不指定位置(添加到数组末尾)
- 不指定位置时,则默认将新元素存放到数组的末尾位置
不指定位置添加
//不指定位置添加单个元素(添加到数组末尾)
public boolean add(E e) {
//扩容检测
ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1);
//数组中指定size++添加
elementData[size++] = e;
return true;
}
//不指定位置添加集合
public boolean addAll(Collection c) {
Object[] a = c.toArray();
int numNew = a.length;
//扩容检测
ensureCapacityInternal(size + numNew);
//关键:不同于单个,创建新数组
System.arraycopy(a, 0, elementData, size, numNew);
//数组中指定size += numNew添加
size += numNew;
return numNew != 0;
}
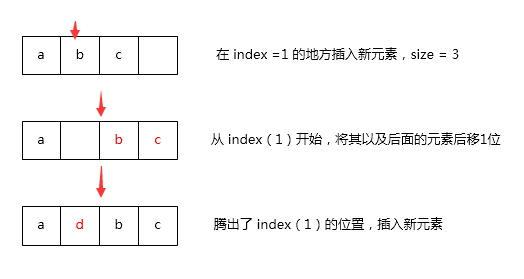
指定位置添加
public void add(int index, E element) {
// 校验添加位置,必须在内部数组的容量范围内
rangeCheckForAdd(index);
//扩容检测
ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1);
// 关键 -> 数组内位置为 index 到 (size-1)的元素往后移动一位,这里仍然采用数组复制实现
System.arraycopy(elementData, index, elementData, index + 1,
size - index);
// 腾出新空间添加新元素
elementData[index] = element;
// 修改数组内的元素数量
size++;
}
private void rangeCheckForAdd(int index) {
if (index > size || index < 0)
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index));
}
public boolean addAll(int index, Collection c) {
// 校验添加位置,必须在内部数组的容量范围内
rangeCheckForAdd(index);
Object[] a = c.toArray();
int numNew = a.length;
//扩容检测
ensureCapacityInternal(size + numNew); // Increments modCount
//如果插入的元素在当前数组内,则需要将原数元素从index向后移动numNew位置
int numMoved = size - index;
if (numMoved > 0)
System.arraycopy(elementData, index, elementData, index + numNew,
numMoved);
//腾出新空间添加新元素
System.arraycopy(a, 0, elementData, index, numNew);
// 修改数组内的元素数量
size += numNew;
return numNew != 0;
}
修改操作
修改操作,就是替换指定位置上的元素。返回原始值
public E set(int index, E element) {
//校验修改位置上必须存在数组元素内
rangeCheck(index);
E oldValue = elementData(index);
elementData[index] = element;
return oldValue;
}
private void rangeCheck(int index) {
if (index >= size)
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index));
}
删除操作
添加方式
- 删除指定位置的元素
- 如果删除位置在数组末尾,直接设置数组尾部为null,不在需要构建新数组数据前移。
-
如果删除位置不在数组末尾,将数组从该位置所有元素前移,在设置数组尾部为null.
- 删除指定元素
删除指定位置的元素
public E remove(int index) {
//校验修改位置上必须存在数组元素内
rangeCheck(index);
//modCount++
modCount++;
// 取得该位置的元素
E oldValue = elementData(index);
// 判断该位置是否为数组末尾
int numMoved = size - index - 1;
// 若是,则将数组中位置为 idnex+1 到 size -1 元素前移一位
if (numMoved > 0)
System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index,
numMoved);
//清空末尾元素让 GC 生效,并修改数组中的元素个数
elementData[--size] = null;
return oldValue;
}
删除指定元素
移除指定元素的过程,与删除指定位置的元素方法相比,该方法主要多了查找指定元素位置的过程,
若存在该元素则删除并返回 true,否则返回 false
public boolean remove(Object o) {
/ 判断是否为空(如果在遍历中判断为空,则每次循环都要判断,会降低效率)
if (o == null) {
//从数组头部开始遍历
for (int index = 0; index < size; index++)
if (elementData[index] == null) {
//删除指定位置元素,不返回原始值
fastRemove(index);
return true;
}
} else {
//从数组头部开始遍历
for (int index = 0; index < size; index++)
if (o.equals(elementData[index])) {
//删除指定位置元素,不返回原始值
fastRemove(index);
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
/*
* 删除指定位置元素,不返回原始值
*/
private void fastRemove(int index) {
modCount++;
int numMoved = size - index - 1;
if (numMoved > 0)
System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index,
numMoved);
elementData[--size] = null; // clear to let GC do its work
}
查询操作
查询指定位置的元素
直接取得数组指定位置的元素
public E get(int index) {
rangeCheck(index);
return elementData(index);
}
查询指定元素
查询指定元素比查询指定位置的元素多了一步确定指定元素位置的过程
public boolean contains(Object o) {
return indexOf(o) >= 0;
}
public int indexOf(Object o) {
if (o == null) {
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
if (elementData[i]==null)
return i;
} else {
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
if (o.equals(elementData[i]))
return i;
}
return -1;
}
public int lastIndexOf(Object o) {
if (o == null) {
for (int i = size-1; i >= 0; i--)
if (elementData[i]==null)
return i;
} else {
for (int i = size-1; i >= 0; i--)
if (o.equals(elementData[i]))
return i;
}
return -1;
}