原题:https://leetcode.com/problems/lfu-cache/?tab=Description
题目要求
设计并实现一个数据结构,满足LFU (Least Frequently Used) Cache特性,实现两种操作:get和put
- get(key):返回指定key对应的value,如果指定key在cache中不存在,返回-1
- put(key, value):设置指定key的value,如果key不存在,则插入该key-value对。如果cache空间已满,则将最少使用的key-value对移除,如果存在多个key-value对的使用次数相同,则将上次访问时间最早的key-value对移除。
public class LFUCache {
public LFUCache(int capacity) {
}
public int get(int key) {
}
public void put(int key, int value) {
}
}
进阶要求
以O(1)时间复杂度实现get和put操作
思路解析
这道题的要求可以分解成两部分
- 实现一个key-value存储结构,能够通过key快速找到对应的value
- 在cache已满时,快速定位到访问次数最低且上次访问时间最早的key,将其移除
上述两种计算都应以O(1)的时间复杂度实现。
对于第1点要求,毫无争议地应使用哈希表来实现,哈希表的插入时间复杂度永远是O(1),在不发生哈希冲突的前提下,查找的时间复杂度也是O(1)。这里我们可以偷个懒,直接把HashMap拿来用。
对于第2点要求,最基本思路是记录每个key的访问次数和上次访问时间,在cache已满时找到访问次数最少的key,如果有多个key访问次数一样,再去找这些key里上次访问时间最早的一个进行移除。
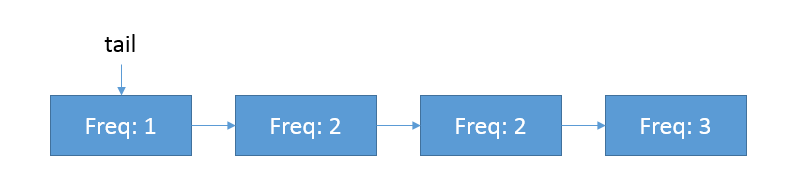
很显然,通过遍历去找访问次数最少的key是不行的,这样时间复杂度就是O(n)了。我们可以考虑构建一个链表,确保访问次数最少的key位于链表的尾部:
设定每次新插入的key的访问次数为0,那么插入时只需要将key置于链表的尾部,同时在移除key时只要移除链表尾部的key就行了,这样插入和移除的时间复杂度都是O(1)了。
然而,可能存在多个key的访问次数一样的情况,这种情况下不得不去遍历这些key,找到上次访问时间最早的一个。这样一来,时间复杂度就超过了O(1)。
对此,我们可以考虑把结构改成两层链表:
外层链表的每个节点代表一组拥有同样访问次数的key,每个节点自身也是一个链表,内层链表确保上次访问时间最早的key位于内层链表的尾部。
在这一数据结构下,我们在插入key时判断外层链表尾部元素的freq是否为0,如果是,将key插入该内层链表的头部,如果否,生成一个只包含key的外层链表,插入到外层链表的尾部。在访问key时,将该key移动到外层链表的下一个节点的头部。这样一来,在移除key时,只需要移除外层链表尾部元素的尾部元素即可,插入、访问、移除的时间复杂度都是O(1)。
代码解析
定义内层链表的元素对象Node:
private static class Node {
int key;
int value;
int frequency = 0; //访问次数
Node next; //下一元素
Node prev; //前一元素
NodeQueue nq; //所属的外层链表元素
Node(int key, int value) {
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
}
}
定义外层链表的元素对象NodeQueue:
private static class NodeQueue {
NodeQueue next; //下一元素
NodeQueue prev; //前一元素
Node tail; //尾部Node
Node head; //头部Node
public NodeQueue(NodeQueue next, NodeQueue prev, Node tail, Node head) {
this.next = next;
this.prev = prev;
this.tail = tail;
this.head = head;
}
}
定义LFU Cache:
import java.util.HashMap;
public class LFUCache {
private NodeQueue tail; //链表尾部的NodeQueue
private int capacity; //容量
private HashMap map; //存储key-value对的HashMap
//构造方法
public LFUCache(int capacity) {
this.capacity = capacity;
map = new HashMap(capacity);
}
}
接下来,实现整个数据结构中最关键的算法:将Node右移
private void oneStepUp(Node n) {
n.frequency++; //访问次数+1
boolean singleNodeQ = false; //为true时,代表此NodeQueue中只有一个Node元素
if(n.nq.head == n.nq.tail)
singleNodeQ = true;
if(n.nq.next != null) {
if(n.nq.next.tail.frequency == n.frequency) {
//右侧NodeQueue的访问次数与Node当前访问次数一样,将此Node置于右侧NodeQueue的头部
removeNode(n); //从当前NodeQueue中删除Node
//把Node插入到右侧NodeQueue的头部
n.prev = n.nq.next.head;
n.nq.next.head.next = n;
n.nq.next.head = n;
n.nq = n.nq.next;
} else if(n.nq.next.tail.frequency > n.frequency) {
//右侧NodeQueue的访问次数大于Node当前访问次数,则需要在两个NodeQueue之间插入一个新的NodeQueue
if(!singleNodeQ) {
removeNode(n);
NodeQueue nnq = new NodeQueue(n.nq.next, n.nq, n, n);
n.nq.next.prev = nnq;
n.nq.next = nnq;
n.nq = nnq;
}
//如果当前NodeQueue中只有一个Node,那么其实不需要任何额外操作了
}
} else {
//此NodeQueue的next == null,说明此NodeQueue已经位于外层链表头部了,这时候需要往外侧链表头部插入一个新的NodeQueue
if(!singleNodeQ) {
removeNode(n);
NodeQueue nnq = new NodeQueue(null, n.nq, n, n);
n.nq.next = nnq;
n.nq = nnq;
}
//同样地,如果当前NodeQueue中只有一个Node,不需要任何额外操作
}
}
移除Node的方法:
private Node removeNode(Node n) {
//如果NodeQueue中只有一个Node,那么移除整个NodeQueue
if(n.nq.head == n.nq.tail) {
removeNQ(n.nq);
return n;
}
if(n.prev != null)
n.prev.next = n.next;
if(n.next != null)
n.next.prev = n.prev;
if(n.nq.head == n)
n.nq.head = n.prev;
if(n.nq.tail == n)
n.nq.tail = n.next;
n.prev = null;
n.next = null;
return n;
}
private void removeNQ(NodeQueue nq) {
if(nq.prev != null)
nq.prev.next = nq.next;
if(nq.next != null)
nq.next.prev = nq.prev;
if(this.tail == nq)
this.tail = nq.next;
}
接下来实现get和put方法:
get方法非常简单了,到HashMap中拿到key对应的Node,并且将该Node右移:
public int get(int key) {
Node n = map.get(key);
if(n == null)
return -1;
oneStepUp(n);
return n.value;
}
put方法:
public void put(int key, int value) {
if(capacity == 0)
return;
Node cn = map.get(key);
//key已存在的情况下,更新value值,并将Node右移
if(cn != null) {
cn.value = value;
oneStepUp(cn);
return;
}
//cache已满的情况下,把外层链表尾部的内层链表的尾部Node移除
if(map.size() == capacity) {
map.remove(removeNode(this.tail.tail).key);
}
//插入新的Node
Node n = new Node(key, value);
if(this.tail == null) {
//tail为null说明此时cache中没有元素,直接把Node封装到NodeQueue里加入
NodeQueue nq = new NodeQueue(null, null, n, n);
this.tail = nq;
n.nq = nq;
} else if(this.tail.tail.frequency == 0) {
//外层链表尾部元素的访问次数是0,那么将Node加入到外层链表尾部元素的头部
n.prev = this.tail.head;
this.tail.head.next = n;
n.nq = this.tail;
this.tail.head = n;
} else {
//外层链表尾部元素的访问次数不是0,那么实例化一个只包含此Node的NodeQueue,加入外层链表尾部
NodeQueue nq = new NodeQueue(this.tail, null, n, n);
this.tail.prev = nq;
this.tail = nq;
n.nq = nq;
}
//最后把key和Node存入HashMap中
map.put(key, n);
}
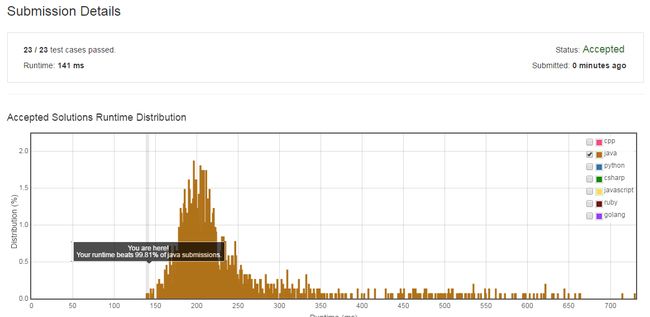
运行结果:
还不错,击败了99.81%的选手。不过LeetCode的代码运行时间统计不太稳定,这段代码跑起来的成绩差不多在140~170ms之间。