项目简介
LLDP协议由802.1ab所定义。它是一个二层协议,一般称之为数据链路发现协议。这里对于该协议的实现原理不做详细介绍。具体原理可以参见IEEE 802.1ab文档连接。
OpenLLDP为802.1ab的开源实现,号称支Linux,macOS,FreeBSD,NetBSD等众多类unix系统。参见维基百科对于openlldp的介绍。
下面为OpenLLDP的
项目主页
sourceforge页面。这里要提前指出的是,OpenLLDP的实现的并非非常标准的lldp。可以说它只是简单的实现了最基本的lldp功能。若需要lldp功能更多的实现,恐怕还要自己进行功能的添加了。
LLDP协议可以参考这篇文章
代码总览
关键数据结构
接口管理
每个网络接口都对应了这样一个数据结构,它用来存储网络接口的接口名,接口索引,mac地址,创建的套接字描述符,和邻居信息指针(这里问lldp_msap)以及最为重要的接收和发送端口缓存(具体为lldp_rx_port结构体和lldp_tx_port结构体)等等。
struct lldp_port {
struct lldp_port *next; //用于将接口串为链
int socket; // 该接口的套接字.
char *if_name; // 接口名.
uint32_t if_index; //接口索引 .
uint32_t mtu; // 接口 MTU.
uint8_t source_mac[6]; //接口mac
uint8_t source_ipaddr[4];//接口IP
struct lldp_rx_port rx; //消息接收状态机,接收缓存
struct lldp_tx_port tx; //消息发送状态机,发送缓存
uint8_t portEnabled; //端口使能
uint8_t adminStatus; //端口状态
/* I'm not sure where this goes... the state machine indicates it's per-port */
uint8_t rxChanges;
// I'm really unsure about the best way to handle this...
uint8_t tick;
time_t last_tick;
struct lldp_msap *msap_cache;
// 802.1AB Appendix G flag variables.
uint8_t auto_neg_status;
uint16_t auto_neg_advertized_capabilities;
uint16_t operational_mau_type;
};
LLDP发送状态机
如下所示,该结构体为存储发送缓存以及发送端口状态机相关参数。state在收发报文时根据lldp协议改变状态,从而影响了发送状态机的运转轨,somethingChangedLocal在本端信息改变时被置位。它被置一标志着lldp开启快速发送机制,会将本端信息快速的传递给直连邻居。
struct lldp_tx_port {
uint8_t *frame; /*frame为缓存发送报文的指针 */
uint64_t sendsize; /*待发送的缓存字节数 */
uint8_t state; /*发送状态 */
uint8_t somethingChangedLocal; /*标志本地mib改变*/
uint16_t txTTL; /*< IEEE 802.1AB var (from where?) */
struct lldp_tx_port_timers timers; /*发送记时*/
struct lldp_tx_port_statistics statistics; /**< The lldp tx statistics for this interface */
};
LLDP接收状态机
和tx类似,用于处理接收报文,当收到邻居通告的LLDP后somethingChangedRemote被置1
struct lldp_rx_port {
uint8_t *frame;
ssize_t recvsize;
uint8_t state;
uint8_t badFrame;
uint8_t rcvFrame;
uint8_t rxInfoAge;
uint8_t somethingChangedRemote;
uint8_t tooManyNeighbors;
struct lldp_rx_port_timers timers;
struct lldp_rx_port_statistics statistics;
};
邻居MIB管理
这个数据结构主要是存储一条邻居信息。多个邻居信息,则以链表的形式组织在lldp_port结构体中。id为lldpdu中必填的tlv字段的chassis subtype id和 port subtype id组成。基本上不同的邻居信息会有不同的lldp_msap id。length为经过格式化之后的全部lldp报文tlv长度。rxInfoTTL则为老化时间。tlv_list为存储tlv的链表,每个节点是一个tlv。该tlv经过了“格式化”而非lldpdu中的tlv。只有经过了什么样的格式化,后续会讲述。
struct lldp_msap {
struct lldp_msap *next;
uint8_t *id;
uint8_t length;
struct lldp_tlv_list *tlv_list;
// XXX Revisit this
// A pointer to the TTL TLV
// This is a hack to decrement
// the timer properly for
// lldpneighbors output
struct lldp_tlv *ttl_tlv;
/* IEEE 802.1AB MSAP-specific counters */
uint16_t rxInfoTTL;
};
tlv为一条lldp的tlv,多个tlv被组织为链表的形式。
struct lldp_tlv_list {
struct lldp_tlv_list *next;
struct lldp_tlv *tlv;
};
tlv的数据结构定义,严格的T(type) L(length)V(value)形式。
struct lldp_tlv {
uint8_t type;
uint16_t length;
uint8_t *info_string;
};
结构说明
整体结构
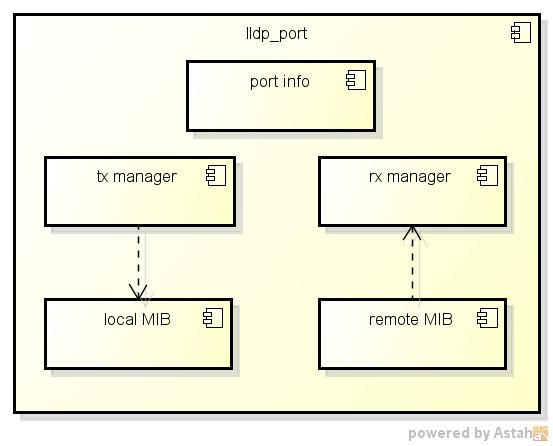
如图1所示
- openlldp整体上是对每个接口独立管理
- 每个接口将保存本地MIB(local MIB),和远程MIB(remote MIB)以及该接口的信息(port info).MIB即是存放LLDP协议获取的信息.
- 此外该接口还有一个发送管理(tx manger)和接收管理(rx manager).
发送管理与本地MIB关联,当本地MIB变化时负责进行通告。接收管理负责接收相邻设备MIB变化时发送来的LLDP信息,存放于远程MIB中。
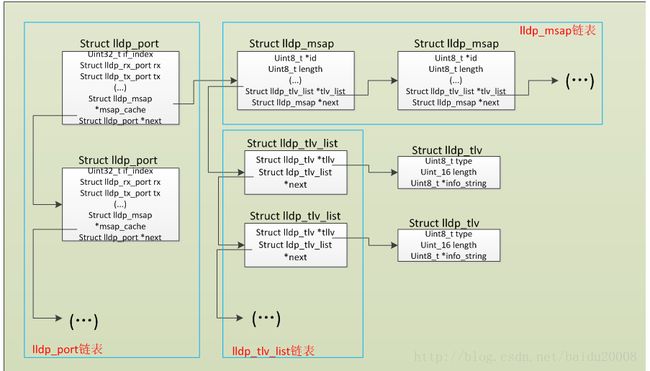
详细结构
如图2所示,具体来组织方式是4层链表嵌套.
- 第一层是lldp_port, 是将各个接口的管理结构链式管理.
- 第二层是lldp_masp , 其存放的是各个接口相邻设备的remote MIB。
- 第三层是lldp_tlv_list, 每一个管理一个相邻设备的tlv。
具体代码分析
了解了上面openlldp的原理可以知道重要的代码集中在以下几处
- 原始套接字封装
- 报文接收处理模块
- 报文发送处理模块
下面就针对上面几点,进行分别说明.注意:...表示省略不重要代码
原始套接字
接口初始化
主要是建立原始套接字,设置广播,初始化缓冲区.
int socketInitializeLLDP(struct lldp_port *lldp_port)
{
struct ifreq *ifr = calloc(1, sizeof(struct ifreq));
struct sockaddr_ll *sll = calloc(1, sizeof(struct sockaddr_ll));
int retval = 0;
...
/* 创建原始套接字,选择协议号0x88cc*/
sll->sll_family = PF_PACKET;
sll->sll_ifindex = lldp_port->if_index;
sll->sll_protocol = htons(0x88CC);
retval = bind(lldp_port->socket, (struct sockaddr *)sll, sizeof(struct sockaddr_ll));
if(retval < 0) {
debug_printf(DEBUG_NORMAL, "Error binding raw socket to interface %s in %s():%d!\n", lldp_port->if_name, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__);
return XENOSOCK;
}
ifr->ifr_ifindex = lldp_port->if_index;
strncpy(ifr->ifr_name, &lldp_port->if_name[0], strlen(lldp_port->if_name));
if(strlen(ifr->ifr_name) == 0) {
debug_printf(DEBUG_NORMAL, "Invalid interface name in %s():%d\n", __FUNCTION__, __LINE__);
return XENOSOCK;
}
if(retval < 0) {
debug_printf(DEBUG_NORMAL, "Error getting hardware (MAC) address for interface '%s' in %s():%d - %d:%s!\n", lldp_port->if_name, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__, errno, strerror(errno));
return retval;
}
retval = _getip(lldp_port);
if (retval < 0) {
debug_printf(DEBUG_NORMAL, "Error getting interface IP address for interface '%s' in %s():%d!\n", lldp_port->if_name, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__);
}*/
refreshInterfaceData(lldp_port);
retval = ioctl(lldp_port->socket, SIOCGIFFLAGS, ifr);
if (retval == -1)
{
debug_printf(DEBUG_NORMAL, "Can't get flags for interface '%s' in %s():%d!\n", lldp_port->if_name, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__);
}
//检查接口是否UP
if ((ifr->ifr_flags & IFF_UP) == 0) {
debug_printf(DEBUG_INT, "Interface '%s' is down. portEnabled = 0.\n", lldp_port->if_name);
lldp_port->portEnabled = 0;
}
// set allmulti on interface
// need to devise a graceful way to turn off allmulti otherwise it is left on for the interface when problem is terminated.
retval = ioctl(lldp_port->socket, SIOCGIFFLAGS, ifr);
...
//由于lldp交互的数据报文为多播报文,故此这里要设置端口接收并处理多播报 文。若不这么设置,端口是接收不到多播报文的.
ifr->ifr_flags |= IFF_ALLMULTI; // allmulti on (verified via ifconfig)
// ifr.ifr_flags &= ~IFF_ALLMULTI; // allmulti off (I think)
retval = ioctl(lldp_port->socket, SIOCSIFFLAGS, ifr);
if (retval == -1)
{
debug_printf(DEBUG_NORMAL, "Can't set flags for interface '%s' in %s():%d!\n", lldp_port->if_name, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__);
}
// Discover MTU of our interface.
retval = ioctl(lldp_port->socket, SIOCGIFMTU, ifr);
if(retval < 0)
{
debug_printf(DEBUG_NORMAL, "Can't determine MTU for interface '%s' in %s():%d!\n", lldp_port->if_name, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__);
return retval;
}
lldp_port->mtu = ifr->ifr_ifru.ifru_mtu;
debug_printf(DEBUG_INT, "[%s] MTU is %d\n", lldp_port->if_name, lldp_port->mtu);
//建立,发送以及接收缓冲区
lldp_port->rx.frame = calloc(1, lldp_port->mtu - 4);
lldp_port->tx.frame = calloc(1, (lldp_port->mtu - 2));
if(!lldp_port->rx.frame) {
debug_printf(DEBUG_NORMAL, "[ERROR] Unable to malloc buffer in %s() at line: %d!\n", __FUNCTION__, __LINE__);
} else {
debug_printf(DEBUG_INT, "Created framebuffer for %s at %x\n", lldp_port->if_name, &lldp_port->rx.frame);
}
if(!lldp_port->tx.frame) {
debug_printf(DEBUG_NORMAL, "[ERROR] Unable to malloc buffer in %s() at line: %d!\n", __FUNCTION__, __LINE__);
} else {
debug_printf(DEBUG_INT, "Created framebuffer for %s at %x\n", lldp_port->if_name, &lldp_port->tx.frame);
}
debug_printf(DEBUG_INT, "Interface (%s) MTU is %d.\n", lldp_port->if_name, lldp_port->mtu);
free(ifr);
free(sll);
return 0;
}
发数据
写数据比较简单,直接向原始套接字发送数据即可
ssize_t lldp_write(struct lldp_port *lldp_port) {
// Write the frame to the wire.
return write(lldp_port->socket, lldp_port->tx.frame, lldp_port->tx.sendsize);
}
收数据
也是直接从原始套接字中获取数据
ssize_t lldp_read(struct lldp_port *lldp_port) {
// allocate the bpf_buf to recieve as many packets as will fit in lldp_port->mtu
// which is the bpf internal buffer size.
struct bpf_hdr *bpf_buf = malloc(lldp_port->mtu);
lldp_port->rx.recvsize = read(lldp_port->socket, bpf_buf, lldp_port->mtu);
// Allocate the buffer to be the length of the captured packet
uint8_t *frame_buffer = malloc(bpf_buf->bh_caplen);
//XXX: BUG HERE - We could actually have more than one packet in bpf_buf
// we should process bpf_buf in a loop until we have processed all
// of the packets in the buffer. This would mean changing lldp_port->rx
// so that there was a linked list of packets in frame so that the next
// code section could process all the packets in the queue.
//
// However the chance of more than one packet being in the buffer is low
// and we can safely drop any other frames as well.
if(frame_buffer) {
debug_printf(DEBUG_INT, "(%s) Raw BPF Frame with BPF header: \n", lldp_port->if_name);
debug_printf(DEBUG_INT, "BPF Header Length: %d\n", bpf_buf->bh_hdrlen);
debug_hex_dump(DEBUG_INT, (uint8_t *)bpf_buf, lldp_port->rx.recvsize);
// Copy the captured data to the buffer, NOTE this may not be the whole packet!!!
memcpy(frame_buffer, ((char*) bpf_buf + bpf_buf->bh_hdrlen), bpf_buf->bh_caplen);
debug_printf(DEBUG_INT, "(%s) Raw BPF Frame without BPF header: \n", lldp_port->if_name);
debug_hex_dump(DEBUG_INT, (uint8_t *)frame_buffer, bpf_buf->bh_caplen);
// Correct the rx.recvsize to reflect the lenght of the packet without the bpf_hdr
lldp_port->rx.recvsize = bpf_buf->bh_caplen;
// Free the tmp buffer
free(bpf_buf);
// Now free the old buffer
free(lldp_port->rx.frame);
// Now assign the new buffer
lldp_port->rx.frame = frame_buffer;
} else {
debug_printf(DEBUG_NORMAL, "Couldn't malloc! Skipping frame to prevent leak...\n");
}
return(lldp_port->rx.recvsize);
}
LLDP协议处理
LLDP接收处理
rxProcessFrame主要是
- 提取tlv检查合法性,解析为对应的lldp_tlv节点,并缓存相应的信息,最终构造lldp_msap结构体。并更新邻居信息。
- 在update_msap_cache函数中,会判断rxProcessFrame函数构造的lldp_msap在本端口的lldp_msap链表中是否存在。若存在,那么直接进行替换(不检查是否完全完全相等,简便的做法)。若不存在,则说明是一个新邻居,那么完成邻居信息结构体lldp_msap的链表插入工作。
- 在lldp报文中tlv被组织为7bit的type字段,9bit的length字段。这种组织方式,在存储tlv时,极为不便。这里将这种组织方式转化为lldp_tlv的组织方式。type和length都可以使用现有的数据类型表示,方便程序的编写。
int rxProcessFrame(struct lldp_port *lldp_port) {
…
…
/*
主要是验证报文的正确性:具体要验证报文的目的地址以及报文类型字段
*/
/* 确定是LLDP */
expect_hdr.dst[0] = 0x01;
expect_hdr.dst[1] = 0x80;
expect_hdr.dst[2] = 0xc2;
expect_hdr.dst[3] = 0x00;
expect_hdr.dst[4] = 0x00;
expect_hdr.dst[5] = 0x0e;
expect_hdr.ethertype = htons(0x88cc);
/*指向接收缓冲区*/
ether_hdr = (struct eth_hdr *)&lldp_port->rx.frame[0];
debug_printf(DEBUG_INT, "LLPDU Dst: ");
debug_hex_printf(DEBUG_INT, (uint8_t *)ether_hdr->dst, 6);
debug_printf(DEBUG_EXCESSIVE, "Expect Dst: ");
debug_hex_printf(DEBUG_EXCESSIVE, (uint8_t *)expect_hdr.dst, 6);
/* Validate the frame's destination */
if(
ether_hdr->dst[0] != expect_hdr.dst[0] ||
ether_hdr->dst[1] != expect_hdr.dst[1] ||
ether_hdr->dst[2] != expect_hdr.dst[2] ||
ether_hdr->dst[3] != expect_hdr.dst[3] ||
ether_hdr->dst[4] != expect_hdr.dst[4] ||
ether_hdr->dst[5] != expect_hdr.dst[5] ) {
debug_printf(DEBUG_NORMAL, "[ERROR] This frame is incorrectly addressed to: ");
debug_hex_printf(DEBUG_NORMAL, (uint8_t *)ether_hdr->dst, 6);
debug_printf(DEBUG_NORMAL, "[ERROR] This frame should be addressed to: ");
debug_hex_printf(DEBUG_NORMAL, (uint8_t *)expect_hdr.dst, 6);
debug_printf(DEBUG_NORMAL, "[ERROR] statsFramesInTotal will *NOT* be incremented\n");
badFrame++;
}
debug_printf(DEBUG_INT, "LLPDU Src: ");
debug_hex_printf(DEBUG_INT, (uint8_t *)ether_hdr->src, 6);
debug_printf(DEBUG_INT, "LLPDU Ethertype: %x\n", htons(ether_hdr->ethertype));
debug_printf(DEBUG_EXCESSIVE, "Expect Ethertype: %x\n", htons(expect_hdr.ethertype));
/* Validate the frame's ethertype */
if(ether_hdr->ethertype != expect_hdr.ethertype) {
debug_printf(DEBUG_NORMAL, "[ERROR] This frame has an incorrect ethertype of: '%x'.\n", htons(ether_hdr->ethertype));
badFrame++;
}
if(!badFrame) {
lldp_port->rx.statistics.statsFramesInTotal ++;
}
…
…
/*
请注意lldp报文TLV的格式,前7个bits为tlv类型字段,后9个为数据长度字段。
*/
/* Grab the first 9 bits */
tlv_length = htons(*tlv_hdr) & 0x01FF;
/* Then shift to get the last 7 bits */
tlv_type = htons(*tlv_hdr) >> 9;
/*
lldp报文中tlv最少为4个,分别为Chasis ID TLV、Port ID TLV、TTL TLV、End TLV
*/
/* Validate as per 802.1AB section 10.3.2*/
if(num_tlvs <= 3) {
if(num_tlvs != tlv_type) {
debug_printf(DEBUG_NORMAL, "[ERROR] TLV number %d should have tlv_type %d, but is actually %d\n", num_tlvs, num_tlvs, tlv_type);
debug_printf(DEBUG_NORMAL, "[ERROR] statsFramesDiscardedTotal and statsFramesInErrorsTotal will be incremented as per 802.1AB 10.3.2\n");
lldp_port->rx.statistics.statsFramesDiscardedTotal++;
lldp_port->rx.statistics.statsFramesInErrorsTotal++;
badFrame++;
}
}
/*
缓存lldp报文中tlv的值
*/
tlv->type = tlv_type;
tlv->length = tlv_length;
if(tlv->length > 0)
tlv->info_string = calloc(1, tlv_length);
/*
如果LLDP中的tlv为TTL,那么则更新rx.timers.rxTTL的值
*/
if(tlv_type == TIME_TO_LIVE_TLV) {
if(tlv_length != 2) {
debug_printf(DEBUG_NORMAL, "[ERROR] TTL TLV has an invalid length! Should be '2', but is '%d'\n", tlv_length);
#ifndef WIN32
#warning We should actually discard this frame and print out an error...
#warning Write a unit test to stress this
#endif // WIN32
} else {
lldp_port->rx.timers.rxTTL = htons(*(uint16_t *)&tlv_info_string[0]);
msap_ttl_tlv = tlv;
debug_printf(DEBUG_EXCESSIVE, "rxTTL is: %d\n", lldp_port->rx.timers.rxTTL);
}
}
if(tlv->info_string) {
memset(tlv->info_string, 0x0, tlv_length);
memcpy(tlv->info_string, tlv_info_string, tlv_length);
}
/* Validate the TLV */
if(validate_tlv[tlv_type] != NULL) {
debug_printf(DEBUG_EXCESSIVE, "Found a validator for TLV type %d.\n", tlv_type);
debug_hex_dump(DEBUG_EXCESSIVE, tlv->info_string, tlv->length);
if(validate_tlv[tlv_type](tlv) != XVALIDTLV) {
badFrame++;
}
} else {
// NOTE: Any organizationally specific TLVs should get processed through validate_generic_tlv
debug_printf(DEBUG_EXCESSIVE, "Didn't find specific validator for TLV type %d. Using validate_generic_tlv.\n", tlv_type);
if(validate_generic_tlv(tlv) != XVALIDTLV) {
badFrame++;
}
}
…
…
/*
将之前缓存的lldp报文中tlv加入到tlv_list中
*/
cached_tlv = initialize_tlv();
if(tlvcpy(cached_tlv, tlv) != 0) {
debug_printf(DEBUG_TLV, "Error copying TLV for MSAP cache!\n");
}
debug_printf(DEBUG_EXCESSIVE, "Adding exploded TLV to MSAP TLV list.\n");
// Now we can start stuffing the msap data... ;)
add_tlv(cached_tlv, &tlv_list);
/*
如果是CHASSIS_ID_TLV和PORT_ID_TLV,那么则缓存它们的值。并将它们拼接为msap_id
*/
if(tlv_type == CHASSIS_ID_TLV) {
debug_printf(DEBUG_NORMAL, "Copying TLV1 for MSAP Processing...\n");
msap_tlv1 = initialize_tlv();
tlvcpy(msap_tlv1, tlv);
} else if(tlv_type == PORT_ID_TLV) {
debug_printf(DEBUG_NORMAL, "Copying TLV2 for MSAP Processing...\n");
msap_tlv2 = initialize_tlv();
tlvcpy(msap_tlv2, tlv);
//Minus 2, for the chassis id subtype and port id subtype...
// IEEE 802.1AB specifies that the MSAP shall be composed of
// The value of the subtypes.
msap_id = calloc(1, msap_tlv1->length - 1 + msap_tlv2->length - 1);
if(msap_id == NULL)
{
debug_printf(DEBUG_NORMAL, "[ERROR] Unable to malloc buffer in %s() at line: %d!\n", __FUNCTION__, __LINE__);
}
// Copy the first part of the MSAP
memcpy(msap_id, &msap_tlv1->info_string[1], msap_tlv1->length - 1);
// Copy the second part of the MSAP
memcpy(&msap_id[msap_tlv1->length - 1], &msap_tlv2->info_string[1], msap_tlv2->length - 1);
msap_length = (msap_tlv1->length - 1) + (msap_tlv2->length - 1);
debug_printf(DEBUG_MSAP, "MSAP TLV1 Length: %d\n", msap_tlv1->length);
debug_printf(DEBUG_MSAP, "MSAP TLV2 Length: %d\n", msap_tlv2->length);
debug_printf(DEBUG_MSAP, "MSAP is %d bytes: ", msap_length);
debug_hex_printf(DEBUG_MSAP, msap_id, msap_length);
debug_hex_dump(DEBUG_MSAP, msap_id, msap_length);
// Free the MSAP pieces
destroy_tlv(&msap_tlv1);
destroy_tlv(&msap_tlv2);
msap_tlv1 = NULL;
msap_tlv2 = NULL;
/* 指示有新的邻居信息到来*/
have_msap = 1;
}
…
…
if(have_msap)
{
#ifndef WIN32
#warning We need to verify whether this is actually the case.
#endif // WIN32
lldp_port->rxChanges = TRUE;
debug_printf(DEBUG_TLV, "We have a(n) %d byte MSAP!\n", msap_length);
/*
创建一条新的保存邻居信息的lldp_msap结构体,并将之前缓存的tlv信息复制到其中。然后更新该端口对应的lldp_port结构体中的lldp_msap信息。亦即更新该底层端口对应的邻居信息。
*/
msap_cache = calloc(1, sizeof(struct lldp_msap));
msap_cache->id = msap_id;
msap_cache->length = msap_length;
msap_cache->tlv_list = tlv_list;
msap_cache->next = NULL;
msap_cache->ttl_tlv = msap_ttl_tlv;
msap_ttl_tlv = NULL;
//debug_printf(DEBUG_MSAP, "Iterating MSAP Cache...\n");
//iterate_msap_cache(msap_cache);
//debug_printf(DEBUG_MSAP, "Updating MSAP Cache...\n");
debug_printf(DEBUG_MSAP, "Setting rxInfoTTL to: %d\n", lldp_port->rx.timers.rxTTL);
msap_cache->rxInfoTTL = lldp_port->rx.timers.rxTTL;
update_msap_cache(lldp_port, msap_cache);
if(msap_tlv1 != NULL) {
debug_printf(DEBUG_NORMAL, "Error: msap_tlv1 is still allocated!\n");
free(msap_tlv1);
msap_tlv1 = NULL;
}
if(msap_tlv2 != NULL) {
debug_printf(DEBUG_NORMAL, "Error: msap_tlv2 is still allocated!\n");
free(msap_tlv2);
msap_tlv2 = NULL;
}
}
else
{
debug_printf(DEBUG_NORMAL, "[ERROR] No MSAP for TLVs in Frame!\n");
}
/* Report frame errors */
if(badFrame) {
rxBadFrameInfo(badFrame);
}
return badFrame;
}
LLDP接收状态机
void rxStatemachineRun(struct lldp_port *lldp_port)
{
debug_printf(DEBUG_NORMAL, "Running RX state machine for %s\n", lldp_port->if_name);
rxGlobalStatemachineRun(lldp_port);
switch(lldp_port->rx.state)
{
case LLDP_WAIT_PORT_OPERATIONAL: //空操作
{
// Do nothing here... we'll transition in the global state machine check
rx_do_lldp_wait_port_operational(lldp_port);
}break;
case DELETE_AGED_INFO: //老化邻居,以及清理
{
rx_do_delete_aged_info(lldp_port);
}break;
case RX_LLDP_INITIALIZE: //初始化remote mib
{
rx_do_rx_lldp_initialize(lldp_port);
}break;
case RX_WAIT_FOR_FRAME: //等待LLDP消息
{
rx_do_rx_wait_for_frame(lldp_port);
}break;
case RX_FRAME: //接收到LLDP消息,并更新remote MIB
{
rx_do_rx_frame(lldp_port);
}break;
case DELETE_INFO: {
rx_do_rx_delete_info(lldp_port); //清理老化邻居
}break;
case UPDATE_INFO: {
rx_do_rx_update_info(lldp_port);
}break;
default:
debug_printf(DEBUG_NORMAL, "[ERROR] The RX State Machine is broken!\n");
};
rx_do_update_timers(lldp_port); //更新时间
}
发送LLDP处理
发送LLDP全是按照下面的伪代码组织
- 对于每个接口在对应的状况下调用对应的tx_do_tx_something_frame,something是该状态对应的行为。
- 该函数将首先构建LLDP然后使用txFrame发送
void tx_do_tx_something_frame(struct lldp_port *lldp_port) {
/* As per 802.1AB 10.5.4.3 */
mibConstrsomethingLLDPDU(lldp_port);
txFrame(lldp_port);
}
LLDP发送状态机
void txStatemachineRun(struct lldp_port *lldp_port)
{
debug_printf(DEBUG_STATE, "%s -> %s\n", lldp_port->if_name, txStateFromID(lldp_port->tx.state));
txGlobalStatemachineRun(lldp_port);
switch(lldp_port->tx.state)
{
case TX_LLDP_INITIALIZE: //初始化时设置部分默认参数
{
tx_do_tx_lldp_initialize(lldp_port);
}break;
case TX_IDLE:
{
tx_do_tx_idle(lldp_port); //idle不作为
}break;
case TX_SHUTDOWN_FRAME: //接口关闭,发送空TLV通告
{
tx_do_tx_shutdown_frame(lldp_port);
}break;
case TX_INFO_FRAME: //LLPD通告本机信息
{
tx_do_tx_info_frame(lldp_port);
}break;
default:
debug_printf(DEBUG_NORMAL, "[ERROR] The TX State Machine is broken!\n");
};
tx_do_update_timers(lldp_port);//仅仅更新本机接口时间
}
顶层代码
ServiceMain模块
主要做了2件事
- 运行状态机
- 建立本地套接字,为其他进程与openlldp交互预留接口
#ifdef BUILD_SERVICE
// We are building as a service, so this should be our ServiceMain()
int ServiceMain(int argc, char *argv[])
#else
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
#endif // BUILD_SERVICE
{
#ifndef WIN32
uid_t uid;
struct timeval timeout;
struct timeval un_timeout;
int fork = 1;
#endif // WIN32
int op = 0;
char *theOpts = "i:d:fshl:o";
int socket_width = 0;
time_t current_time = 0;
time_t last_check = 0;
int result = 0;
struct lldp_port *lldp_port = NULL;
#ifdef BUILD_SERVICE
ServiceStatus.dwServiceType =
SERVICE_WIN32;
ServiceStatus.dwCurrentState =
SERVICE_START_PENDING;
ServiceStatus.dwControlsAccepted =
SERVICE_ACCEPT_STOP |
SERVICE_ACCEPT_SHUTDOWN;
ServiceStatus.dwWin32ExitCode = 0;
ServiceStatus.dwServiceSpecificExitCode = 0;
ServiceStatus.dwCheckPoint = 0;
ServiceStatus.dwWaitHint = 0;
hStatus = RegisterServiceCtrlHandler(
"OpenLLDP",
(LPHANDLER_FUNCTION)ControlHandler);
if (hStatus == (SERVICE_STATUS_HANDLE)0)
{
// Registering Control Handler failed
return -1;
}
/* ServiceStatus.dwCurrentState = SERVICE_STOPPED;
ServiceStatus.dwWin32ExitCode = 0xfe;
SetServiceStatus(hStatus, &ServiceStatus);*/
#endif // BUILD_SERVICE
program = argv[0];
#ifndef WIN32
//获取传入参数
// Process any arguments we were passed in.
while ((op = getopt(argc, argv, theOpts)) != EOF) {
switch (op) {
case 'd':
// Set the debug level.
if ((atoi(optarg) == 0) && (optarg[0] != '0')) {
debug_alpha_set_flags(optarg);
} else {
debug_set_flags(atoi(optarg));
}
break;
case 'i':
iface_filter = 1;
memcpy(iface_list, optarg, strlen(optarg));
iface_list[IF_NAMESIZE - 1] = '\0';
debug_printf(DEBUG_NORMAL, "Using interface %s\n", iface_list);
break;
case 'l':
#ifdef USE_CONFUSE
lci.config_file = optarg;
#else
debug_printf(DEBUG_NORMAL, "OpenLLDP wasn't compiled with libconfuse support.\n");
exit(1);
#endif // USE_CONFUSE
break;
case 'o':
// Turn on the looback interface. :)
process_loopback = 1;
break;
case 'f':
fork = 0;
break;
case 's':
unlink(local.sun_path);
break;
case 'h':
default:
usage();
exit(0);
break;
};
}
//建立域流套接字,为本地其他进程数据
neighbor_local_sd = socket(AF_UNIX, SOCK_STREAM, 0);
if(neighbor_local_sd < 0)
{
debug_printf(DEBUG_NORMAL, "[Error] Unable to open unix domain socket for client registration!\n");
}
local.sun_family = AF_UNIX;
strcpy(local.sun_path, "/var/run/lldpd.sock");
debug_printf(DEBUG_NORMAL, "%s:%d\n", local.sun_path, strlen(local.sun_path));
// Bind to the neighbor list socket.
result = bind(neighbor_local_sd, (struct sockaddr *)&local, sizeof(local));
if(result != 0) {
debug_printf(DEBUG_NORMAL, "[Error] Unable to bind to the unix domain socket for client registration!\n");
}
//监听
result = listen(neighbor_local_sd, 5);
if(result != 0) {
debug_printf(DEBUG_NORMAL, "[Error] Unable to listen to the unix domain socket for client registration!\n");
}
// Set the socket permissions
if(chmod("/var/run/lldpd.sock", S_IWOTH) != 0) {
debug_printf(DEBUG_NORMAL, "[Error] Unable to set permissions for domain socket!\n");
}
/* Needed for select() */
fd_set readfds;
fd_set unixfds;
// get uid of user executing program.
uid = getuid();
if (uid != 0) {
debug_printf(DEBUG_NORMAL, "You must be running as root to run %s!\n", program);
exit(0);
}
#endif // WIN32
lci.config_file = NULL;
/* Initialize2 the LLDP subsystem */
/* This should happen on a per-interface basis */
if(initializeLLDP() == 0) {
debug_printf(DEBUG_NORMAL, "No interface found to listen on\n");
}
get_sys_desc();
get_sys_fqdn();
#ifdef USE_CONFUSE
//read the location config file for the first time!
lci_config ();
#endif // USE_CONFUSE
#ifdef BUILD_SERVICE
// We report the running status to SCM.
ServiceStatus.dwCurrentState =
SERVICE_RUNNING;
SetServiceStatus (hStatus, &ServiceStatus);
while (ServiceStatus.dwCurrentState ==
SERVICE_RUNNING)
{
// Sleep for 1 seconds.
Sleep(1000);
}
#endif // BUILD_SERVICE
#ifndef WIN32
if (fork) {
if (daemon(0,0) != 0)
debug_printf(DEBUG_NORMAL, "Unable to daemonize (%m) at: %s():%d\n",
__FUNCTION__, __LINE__);
}
#endif // WIN32
while(1) {
#ifndef WIN32
/* Set up the neighbor client domain socket */
if(neighbor_local_sd > 0) {
FD_ZERO(&unixfds);
FD_SET(neighbor_local_sd, &unixfds);
} else {
debug_printf(DEBUG_NORMAL, "Couldn't initialize the socket (%d)\n", neighbor_local_sd);
}
/* Set up select() */
FD_ZERO(&readfds);
#endif // WIN32
lldp_port = lldp_ports;
while(lldp_port != NULL) {
// This is not the interface you are looking for...
if(lldp_port->if_name == NULL)
{
debug_printf(DEBUG_NORMAL, "[ERROR] Interface index %d with name is NULL at: %s():%d\n", lldp_port->if_index, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__);
continue;
}
#ifndef WIN32
FD_SET(lldp_port->socket, &readfds);
if(lldp_port->socket > socket_width)
{
socket_width = lldp_port->socket;
}
#endif
lldp_port = lldp_port->next;
}
time(¤t_time);
#ifndef WIN32
// Will be used to tell select how long to wait for...
timeout.tv_sec = 1;
timeout.tv_usec = 0;
// Timeout after 1 second if nothing is ready
result = select(socket_width+1, &readfds, NULL, NULL, &timeout);
#endif // WIN32
// Everything is cool... process the sockets
lldp_port = lldp_ports;
while(lldp_port != NULL) {
// This is not the interface you are looking for...
if(lldp_port->if_name == NULL) {
debug_printf(DEBUG_NORMAL, "[ERROR] Interface index %d with name is NULL at: %s():%d\n", lldp_port->if_index, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__);
continue;
}
#ifndef WIN32
if(result > 0) {
if(FD_ISSET(lldp_port->socket, &readfds)) {
debug_printf(DEBUG_INT, "%s is readable!\n", lldp_port->if_name);
// Get the frame back from the OS-specific frame handler.
lldp_read(lldp_port);
if(lldp_port->rx.recvsize <= 0) {
if(errno != EAGAIN && errno != ENETDOWN) {
printf("Error: (%d) : %s (%s:%d)\n", errno, strerror(errno), __FUNCTION__, __LINE__);
}
} else {
debug_printf(DEBUG_INT, "Got an LLDP frame %d bytes long on %s!\n", lldp_port->rx.recvsize, lldp_port->if_name);
// debug_hex_dump(DEBUG_INT, lldp_port->rx.frame, lldp_port->rx.recvsize);
// Mark that we received a frame so the state machine can process it.
lldp_port->rx.rcvFrame = 1;
rxStatemachineRun(lldp_port);
}
}
}
#endif // WIN32
if((result == 0) || (current_time > last_check)) {
lldp_port->tick = 1;
txStatemachineRun(lldp_port); //运行发送状态机
rxStatemachineRun(lldp_port); //运行接收状态机
#ifndef WIN32
// Will be used to tell select how long to wait for...
un_timeout.tv_sec = 0;
un_timeout.tv_usec = 2;
result = select(neighbor_local_sd+1, &unixfds, NULL, NULL, &un_timeout);
if(result > 0) {
if(FD_ISSET(neighbor_local_sd, &unixfds)) {
debug_printf(DEBUG_NORMAL, "Got a request on the unix domain socket!\n");
socklen_t addrlen = sizeof(remote);
neighbor_remote_sd = accept(neighbor_local_sd, (struct sockaddr *)&remote, &addrlen);
if(neighbor_remote_sd < 0) {
debug_printf(DEBUG_NORMAL, "Couldn't accept remote client socket!\n");
} else {
char *client_msg = lldp_neighbor_information(lldp_ports);
int bytes_tx = strlen(client_msg);
int bytes_sent = 0;
while(bytes_tx > 0) {
debug_printf(DEBUG_NORMAL, "Transmitting %d bytes to client...\n", bytes_tx);
bytes_sent = send(neighbor_remote_sd, client_msg, strlen(client_msg), 0);
debug_printf(DEBUG_NORMAL, "%d bytes left to send. Bytes already sent: %d\n\n", bytes_tx, bytes_sent);
bytes_tx -= bytes_sent;
}
free(client_msg);
close(neighbor_remote_sd);
}
}
}
#endif // WIN32
lldp_port->tick = 0;
}
if(result < 0) {
if(errno != EINTR) {
debug_printf(DEBUG_NORMAL, "[ERROR] %s\n", strerror(errno));
}
}
lldp_port = lldp_port->next;
}
time(&last_check);
}
return 0;
}
lldpneighbors模块
主要是演示如何从ServiceMain获取主机的邻居信息。
*
* OpenLLDP Neighbor
*
* See LICENSE file for more info.
*
* File: lldpneighbors.c
*
* Authors: Terry Simons ([email protected])
*
*******************************************************************/
#ifndef WIN32
#include
#include
#include
#include
#endif
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#define NEIGHBORLIST_SIZE 512
#define DEBUG 0
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
char msg[NEIGHBORLIST_SIZE];
char *buf = NULL;
char *tmp = NULL;
int s = 0;
unsigned int msgSize = 0;
size_t bytes = 0;
int result = 0;
buf = calloc(1, NEIGHBORLIST_SIZE);
memset(&msg[0], 0x0, NEIGHBORLIST_SIZE);
#ifndef WIN32
struct sockaddr_un addr;
s = socket(AF_UNIX, SOCK_STREAM, 0);
addr.sun_family = AF_UNIX;
/*
使用和lldp_main模块一样的unix套接字对象标识
*/
strcpy(addr.sun_path, "/var/run/lldpd.sock");
/*
连接
*/
result = connect(s, (struct sockaddr *)&addr, sizeof(addr));
if(result < 0) {
printf("\n%s couldn't connect to the OpenLLDP transport socket. Is lldpd running?\n", argv[0]);
goto cleanup;
}
/*
接收
*/
while((bytes = recv(s, msg, NEIGHBORLIST_SIZE, 0))) {
if(bytes > 0) {
tmp = calloc(1, msgSize + bytes + 1);
if(buf != NULL) {
memcpy(tmp, buf, msgSize);
free(buf);
buf = NULL;
}
memcpy(&tmp[msgSize], msg, bytes);
msgSize += bytes;
buf = tmp;
tmp = NULL;
} else {
if(DEBUG) {
printf("Error reading %d bytes: %d:%s\n", NEIGHBORLIST_SIZE, errno, strerror(errno));
}
}
if(DEBUG) {
printf("Read %d bytes. Total size is now: %d\n", (int)bytes, msgSize);
printf("Buffer is: 0x%08X and Temporary Buffer is 0x%08X.\n", (int)&buf, (int)&tmp);
}
}
if(buf != NULL) {
printf("%s\n", buf);
}
cleanup:
if(buf != NULL)
{
free(buf);
msgSize = 0;
buf = NULL;
}
close(s);
#endif
return 0;
}
参考文章
- http://blog.csdn.net/baidu20008/article/details/19813201
- http://www.jianshu.com/p/84e4533062d1