一、Runtime简介
什么是Runtime?
OC = C + Runtime
OC是基于C语言的扩展,不仅增加了面向对象的功能,而且增加了强大的动态特性,这一切都要归功于OC的Runtime。
OC语言将很多原本需要编译或链接时决定的特性延迟到运行时决定,它会尽可能的动态处理一些事情,这就是我们为什么说OC是一门动态语言。
OC的动态性让其如此强大和灵活:
- 动态类型,直到运行时才会决定一个对象的类型。动态类型保证了多态,有了抽象和多态,才有了美妙的设计模式~
- 动态绑定,在运行时决定哪个方法被真正调用。这样,方法的调用过程不会在被接收者的类型限制,甚至不会被方法名限制,开发者可以更灵活的设计。
- 动态访问和调整,我们可以随时获取应用的运行信息,并能跟踪、干预应用的运行过程。各种Hook,各种Patch,让我们为所欲为~
为了支持OC的动态性,光有一个编译器是不够的,还需要一个运行时系统去执行编译后的代码。运行时系统就像是OC语言的操作系统,可以保证OC语言特性的正常表现。OC运行时是以动态库的形式,参与所有OC应用的链接过程。
如何学习Runtime
学习就要学最官方的资料:
Programming with Objective-C
Object-Oriented Programming with Objective-C
Objective-C Runtime Programming Guide
Objective-C Runtime Reference
Objective-C Runtime 源代码下载
Runtime--动态类型
NSObject定义
OC中所有的类都最终继承自NSObject,因此所有的OC对象都可以看成NSObject类型的。先看看NSObject的相关定义:
@interface NSObject {
Class isa OBJC_ISA_AVAILABILITY;
}
// An opaque type that represents an Objective-C class.
typedef struct objc_class *Class;
struct objc_class {
Class isa OBJC_ISA_AVAILABILITY;
#if !__OBJC2__
Class super_class OBJC2_UNAVAILABLE;
const char *name OBJC2_UNAVAILABLE;
long version OBJC2_UNAVAILABLE;
long info OBJC2_UNAVAILABLE;
long instance_size OBJC2_UNAVAILABLE;
struct objc_ivar_list *ivars OBJC2_UNAVAILABLE;
struct objc_method_list **methodLists OBJC2_UNAVAILABLE;
struct objc_cache *cache OBJC2_UNAVAILABLE;
struct objc_protocol_list *protocols OBJC2_UNAVAILABLE;
#endif
}
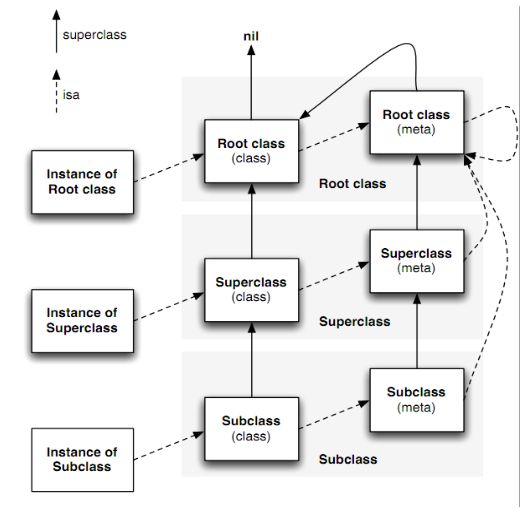
isa是什么?
每个对象都有一个isa的实例变量,它继承自NSObject,是对象连接到运行时系统的桥梁。isa标示了对象的类型,它指向了一个编译时定义好的的类结构(objc_class)。通过isa,一个对象可以找到所有它在运行时需要的信息,比如它在继承层次中的位置,实例变量的大小和结构,以及所有方法实现的位置。
我们发现,objc_class结构体中也有一个isa,它是什么作用呢?
类对象的isa指向了metaclass(元类,可以理解为类的类)。通过它我们可以找到类中的静态变量和方法。
下图解释了isa在继承层次中的作用:
动态类型原理
答案就是运行时通过isa指针判断当前对象所属的类
/// Represents an instance of a class.
struct objc_object {
Class isa OBJC_ISA_AVAILABILITY;
};
/// A pointer to an instance of a class.
typedef struct objc_object *id;
由id类型的结构可以得知,id可以指向任意的NSObject及其子类对象。
在源代码中,我们用id类型的变量指向一个对象,编译器是无法得知这个对象的真实类型的。而运行时通过id指向对象的isa属性,可以访问到该对象的真实类型信息。
如何获取类型
object_getClass(obj)返回的是obj中的isa指针,因此能得到最正确的类型
[obj class]则分两种情况:一是当obj为实例对象时,[obj class]中class是实例方法:- (Class)class,返回的obj对象中的isa指针;二是当obj为类对象(包括元类)时,调用的是类方法:+ (Class)class,返回的结果为其本身。
+ (Class)class {
return self;
}
- (Class)class {
return object_getClass(self);
}
动态类型应用
动态类型最常见的应用就是多态。多态就是相似但不同的两个对象对同一事件的响应不一样,这就要求二者不是同一个类但最终继承自同一个类。因此我们可以用父类指针指向子类对象,不同的场景下指向不同的子类对象,这样调用对象方法时会执行不同的逻辑。 谈到多态,C++也是有多态的,通过虚函数表实现,语法上有限制。而OC在原理上完全支持多态,用起来更方便(还要配合动态绑定来讲解)。
特殊情况下,isa会被修改,指向另一个类对象。比如KVO的原理:当一个类型为T的对象O的属性P被观察时,会在运行时创建一个新的类型NSNotifying_T,NSNotifying_T继承了T,并重新实现P的set方法,注入了通知触发的逻辑。同时会将O的isa指针指向了NSNotifying_T,因此给O设置P时,调用的是NSNotifying_T中的方法。而这一切对开发者而言都是透明的,多么神奇的黑魔法。
Runtime--动态绑定
消息传递
调用一个对象的方法,实际上就是给这个对象发送一条消息,在运行时系统会根据消息去查找对应的方法,然后执行。
调用一个对象的方法,到底发生了什么呢?我们可以测试一下:
@implementation RuntimeObject
- (void)method1{
}
- (void)method2{
[self method1];
}
@end
通过编译器命令xcrun -sdk iphonesimulator clang -rewrite-objc RuntimeObject.m将以上OC代码转成C++代码:
static void _I_RuntimeObject_method1(RuntimeObject * self, SEL _cmd) {
}
static void _I_RuntimeObject_method2(RuntimeObject * self, SEL _cmd) {
((void (*)(id, SEL))(void *)objc_msgSend)((id)self, sel_registerName("method1"));
}
objc_msgSend是什么鬼?我们看看message.h中的声明
/*
* @note When it encounters a method call, the compiler generates a call to one of the
* functions \c objc_msgSend, \c objc_msgSend_stret, \c objc_msgSendSuper, or \c objc_msgSendSuper_stret.
* Messages sent to an object’s superclass (using the \c super keyword) are sent using \c objc_msgSendSuper;
* other messages are sent using \c objc_msgSend. Methods that have data structures as return values
* are sent using \c objc_msgSendSuper_stret and \c objc_msgSend_stret.
*/
OBJC_EXPORT id objc_msgSend(id self, SEL op, ...)
OBJC_AVAILABLE(10.0, 2.0, 9.0, 1.0);
这里我们知道OC中的方法调用会在编译过程中被转成objc_msgSend的调用方式:
- objc_msgSend: 调用一个返回非结构体的方法
- objc_msgSend_stret:调用一个返回结构体的方法
- objc_msgSendSuper:调用super的方法
那objc_msgSend到底做了什么?
objc_msgSend最终会调用lookUpImpOrForward,它会在运行时查找具体要调用的方法实现:
- 缓存中有对应的方法实现,则直接返回
- 如果类还没有完整构建(isRealized),则去构建
- 如果类还没有初始化(isInitialized),则初始化,这里会调用
+initialize方法 - 从当前类的缓存中查找,若找到则结束
- 从当前类的方法列表中查找,若找到则缓存起来并结束
- 一层层的从父类的缓存和方法列表中查找,若找到则缓存起来并结束
- 如果还没尝试过动态解决方法,则调用动态解决,并跳入第4步重新查找
- 返回消息转发流程的IMP
_objc_msgForward_impcache
/***********************************************************************
* lookUpImpOrForward.
* The standard IMP lookup.
* initialize==NO tries to avoid +initialize (but sometimes fails)
* cache==NO skips optimistic unlocked lookup (but uses cache elsewhere)
* Most callers should use initialize==YES and cache==YES.
* inst is an instance of cls or a subclass thereof, or nil if none is known.
* If cls is an un-initialized metaclass then a non-nil inst is faster.
* May return _objc_msgForward_impcache. IMPs destined for external use
* must be converted to _objc_msgForward or _objc_msgForward_stret.
* If you don't want forwarding at all, use lookUpImpOrNil() instead.
**********************************************************************/
IMP lookUpImpOrForward(Class cls, SEL sel, id inst,
bool initialize, bool cache, bool resolver)
{
IMP imp = nil;
bool triedResolver = NO;
runtimeLock.assertUnlocked();
// Optimistic cache lookup
if (cache) {
imp = cache_getImp(cls, sel);
if (imp) return imp;
}
// runtimeLock is held during isRealized and isInitialized checking
// to prevent races against concurrent realization.
// runtimeLock is held during method search to make
// method-lookup + cache-fill atomic with respect to method addition.
// Otherwise, a category could be added but ignored indefinitely because
// the cache was re-filled with the old value after the cache flush on
// behalf of the category.
runtimeLock.read();
if (!cls->isRealized()) {
// Drop the read-lock and acquire the write-lock.
// realizeClass() checks isRealized() again to prevent
// a race while the lock is down.
runtimeLock.unlockRead();
runtimeLock.write();
realizeClass(cls);
runtimeLock.unlockWrite();
runtimeLock.read();
}
if (initialize && !cls->isInitialized()) {
runtimeLock.unlockRead();
_class_initialize (_class_getNonMetaClass(cls, inst));
runtimeLock.read();
// If sel == initialize, _class_initialize will send +initialize and
// then the messenger will send +initialize again after this
// procedure finishes. Of course, if this is not being called
// from the messenger then it won't happen. 2778172
}
retry:
runtimeLock.assertReading();
// Try this class's cache.
imp = cache_getImp(cls, sel);
if (imp) goto done;
// Try this class's method lists.
{
Method meth = getMethodNoSuper_nolock(cls, sel);
if (meth) {
log_and_fill_cache(cls, meth->imp, sel, inst, cls);
imp = meth->imp;
goto done;
}
}
// Try superclass caches and method lists.
{
unsigned attempts = unreasonableClassCount();
for (Class curClass = cls;
curClass != nil;
curClass = curClass->superclass)
{
// Halt if there is a cycle in the superclass chain.
if (--attempts == 0) {
_objc_fatal("Memory corruption in class list.");
}
// Superclass cache.
imp = cache_getImp(curClass, sel);
if (imp) {
if (imp != (IMP)_objc_msgForward_impcache) {
// Found the method in a superclass. Cache it in this class.
log_and_fill_cache(cls, imp, sel, inst, curClass);
goto done;
}
else {
// Found a forward:: entry in a superclass.
// Stop searching, but don't cache yet; call method
// resolver for this class first.
break;
}
}
// Superclass method list.
Method meth = getMethodNoSuper_nolock(curClass, sel);
if (meth) {
log_and_fill_cache(cls, meth->imp, sel, inst, curClass);
imp = meth->imp;
goto done;
}
}
}
// No implementation found. Try method resolver once.
if (resolver && !triedResolver) {
runtimeLock.unlockRead();
_class_resolveMethod(cls, sel, inst);
runtimeLock.read();
// Don't cache the result; we don't hold the lock so it may have
// changed already. Re-do the search from scratch instead.
triedResolver = YES;
goto retry;
}
// No implementation found, and method resolver didn't help.
// Use forwarding.
imp = (IMP)_objc_msgForward_impcache;
cache_fill(cls, sel, imp, inst);
done:
runtimeLock.unlockRead();
return imp;
}
方法决议
如果在类的方法列表中未找到方法实现,则运行时系统会给你第一次补救机会: 方法决议,你可以动态添加方法实现。返回YES表示已决议,否则进入消息转发流程。
方法决议包括类方法和实例方法:
+(BOOL)resolveClassMethod:(SEL)sel;
+(BOOL)resolveInstanceMethod:(SEL)sel;
在obj-class.m中,我们找了消息动态解决的实现
void _class_resolveMethod(Class cls, SEL sel, id inst)
{
if (! cls->isMetaClass()) {
// try [cls resolveInstanceMethod:sel]
_class_resolveInstanceMethod(cls, sel, inst);
}
else {
// try [nonMetaClass resolveClassMethod:sel]
// and [cls resolveInstanceMethod:sel]
_class_resolveClassMethod(cls, sel, inst);
if (!lookUpImpOrNil(cls, sel, inst,
NO/*initialize*/, YES/*cache*/, NO/*resolver*/))
{
_class_resolveInstanceMethod(cls, sel, inst);
}
}
}
static void _class_resolveInstanceMethod(Class cls, SEL sel, id inst)
{
if (! lookUpImpOrNil(cls->ISA(), SEL_resolveInstanceMethod, cls,
NO/*initialize*/, YES/*cache*/, NO/*resolver*/))
{
// Resolver not implemented.
return;
}
BOOL (*msg)(Class, SEL, SEL) = (typeof(msg))objc_msgSend;
bool resolved = msg(cls, SEL_resolveInstanceMethod, sel);
// Cache the result (good or bad) so the resolver doesn't fire next time.
// +resolveInstanceMethod adds to self a.k.a. cls
IMP imp = lookUpImpOrNil(cls, sel, inst,
NO/*initialize*/, YES/*cache*/, NO/*resolver*/);
...
}
常见用到方法决议的场景:@dynamic修饰过的属性不会自动生成访问器方法,我们可以在方法决议时动态添加访问器方法的实现。
消息转发
方法决议失败后,运行时还会给你第二次补救机会:消息转发。可以将消息转发给其他对象,或者直接处理Invocation对象。这也是最后一次机会,如果仍未处理,则抛出异常。
消息转发涉及的方法如下:
-(id)forwardingTargetForSelector:(SEL)aSelector;
- (NSMethodSignature *)methodSignatureForSelector:(SEL)aSelector;
-(void)forwardInvocation:(NSInvocation *)anInvocation;
消息转发的流程:
- 调用
forwardingTargetForSelector尝试转发给另外一个对象,也叫快速转发。返回self或nil则走第2步;默认实现返回nil - 调用
methodSignatureForSelector:获取方法签名(包含方法名、参数、返回类型),以构造NSInvocation对象;返回nil直接抛异常:unrecognized selector sent to instance - 调用
forwardInvocation:并传入构造好的NSInvocation对象,也叫正式转发;默认实现会调用doesNotRecognizeSelector:直接抛出异常
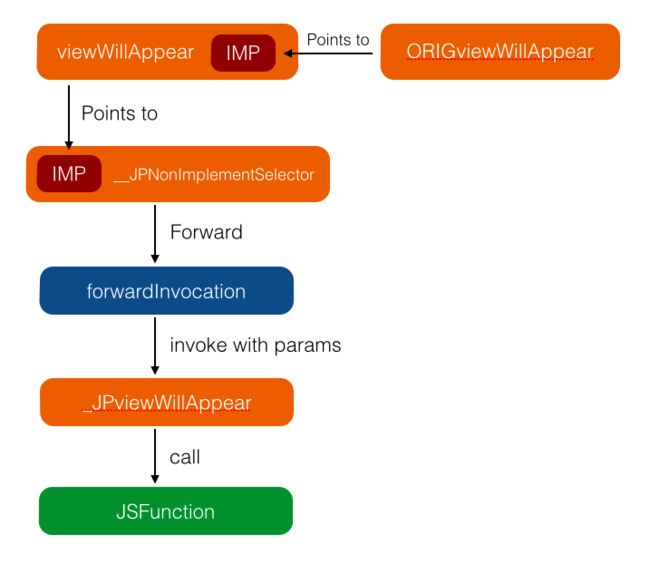
方法决议和消息转发整体流程如下:
消息转发的应用场景最经典的还是JSPatch,它将已有的方法实现直接替换成了消息转发流程,最终在forwardInvocation:中拿到所有调用相关信息(方法名、参数类型等),然后传递给JS代码。
动态访问和调整
访问变量和属性
//获取变量
unsigned int count = 0;
Ivar* varList = class_copyIvarList([RuntimeObject class], &count);
for (int i=0; i访问方法
//获取方法
unsigned int count = 0;
Method* methodList = class_copyMethodList([RuntimeObject class], &count);
for (int i=0; iMethod Swizzle
即交换两个方法的实现,常用于AOP,为已有方法增加功能。
Isa Swizzle
即运行时修改Isa,使其指向另外一个类,比如KVO实现原理。
动态生成类
可以在运行时动态创建一个类,并给它添加变量和方法。注意添加变量的时机必须在 objc_allocateClassPair之后且objc_registerClassPair之前
//创建类
//return Nil if the class could not be created (for example, the desired name is already in use)
Class cls = objc_allocateClassPair([NSObject class], "RuntimeClass", 0);
if (cls) {
//添加成员变量
// * @note This function may only be called after objc_allocateClassPair and before objc_registerClassPair.
// * Adding an instance variable to an existing class is not supported.
// * @note The class must not be a metaclass. Adding an instance variable to a metaclass is not supported.
class_addIvar(cls, "address", sizeof(NSString*), log2(sizeof(NSString*)), @encode(NSString*));
class_addIvar([RuntimeObject class], "sex", sizeof(int), sizeof(int), @encode(int));
//添加方法
// * @note class_addMethod will add an override of a superclass's implementation,
// * but will not replace an existing implementation in this class.
// * To change an existing implementation, use method_setImplementation.
SEL printSEL = sel_registerName("print");
class_addMethod(cls, printSEL, (IMP)print, "v@:");
//注册类
objc_registerClassPair(cls);
}else{
cls = objc_getClass("RuntimeClass");
}
//创建对象
id obj = [[cls alloc] init];
//访问成员变量
Ivar addressVar = class_getInstanceVariable(cls, "address");
object_setIvar(obj, addressVar, @"上海市");
NSLog(@"addressVar %@",object_getIvar(obj, addressVar));
//访问方法
[obj performSelector:@selector(print)];
关联对象
一个已注册的类是不能再添加实例变量了,而关联对象可以为已注册的类增加类似实例变量的存储变量
@implementation RuntimeObject (AddProperty)
static char key;
-(void)setAddress:(NSString *)address{
//key只要是唯一的标示就行,比如一个固定的地址
//objc_setAssociatedObject(self, @selector(address), address, OBJC_ASSOCIATION_RETAIN_NONATOMIC);
objc_setAssociatedObject(self, &key, address, OBJC_ASSOCIATION_RETAIN_NONATOMIC);
}
-(NSString*)address{
return objc_getAssociatedObject(self, &key);
}
@end