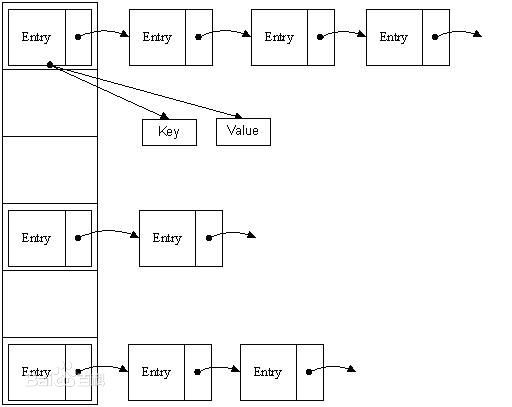
引言:上篇文章中我们学习了List和Set接口下面的集合的实现原理,这篇文章我们主要来学习Map接口下面的各个集合的实现原理。
1、HashMap
1.1、特性
- 采用键值对存储
- 非线程安全的集合
- 允许值为null,只允许一个键为null
- 可以通过Collections.synchronizedMap将其变为线程安全的集合,或者使用ConcurrentHashMap代替。
- 初始容量为16,初始加载因子为0.75
1.2、实现原理
hash作为程序员使用最多的一种键值式的存储集合;它的底层是通过数组+链表+红黑树(JDK8优化之后);它根据键的hashCode值存储数据,大多数情况下可以直接定位到它的值,因而具有很快的访问速度,但遍历顺序却是不确定的。HashMap非线程安全,即任一时刻可以有多个线程同时写HashMap,可能会导致数据的不一致。如果需要满足线程安全,可以用 Collections的synchronizedMap方法使HashMap具有线程安全的能力,或者使用ConcurrentHashMap。
- a、hashMap 的实例有两个参数影响其性能:初始容量和加载因子
-
b、存储数据的格式:通过一个静态内部类Entry存储数据;
static class Entry implements Map.Entry{
}
- c、加载因子:默认为0.75;
主要在扩容时起作用;一般也是扩容为原来的2倍
void resize(int newCapacity) {
Entry[] oldTable = table;
//获取扩容之前的容量
int oldCapacity = oldTable.length;
if (oldCapacity == MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) {
threshold = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
return;
}
Entry[] newTable = new Entry[newCapacity];
//将原来数组的元素拷贝到新的元素中;
transfer(newTable, initHashSeedAsNeeded(newCapacity));
table = newTable;
threshold = (int)Math.min(newCapacity * loadFactor, MAXIMUM_CAPACITY + 1);
}
- d、关于hash函数:
hashMap在存储数据时会先根据它的key值调用一次hash函数;将得到的值作为真实的存储数据的键;当然不排除两个不同的key值产生相同的键值情况;我们称之为hash冲突;常见的解决hash冲突的方式主要有如下:- 拉链法:将冲突的节点组织成一条链表
- 二次hash法:采用另外的散列函数对冲突结果进行处理的方法
- 开发地址法:
- 线性探测:从冲突的位置依次向下移动;
D = H(key);
ND = (D+di)%m; di取1,2,3,……,m-1 - 二次探测:
D = H(key);
ND = (D+di)%m; di取11,-11,22,-22,……,KK,-KK (K≤m/2) - 双散列法
D = H1(key);
p = H2(key);
ND = (D+p)%m;
- 线性探测:从冲突的位置依次向下移动;
int hash = hash(key);
和之前一样,为了方便深入理解hashmap这个数据结构,我们还是针对它的添加元素和删除元素的方法进行详细探讨:
插入元素:
public V put(K key, V value) {
return putVal(hash(key), key, value, false, true);
}
/**
* Implements Map.put and related methods
*
* @param hash hash for key
* @param key the key
* @param value the value to put
* @param onlyIfAbsent if true, don't change existing value
* @param evict if false, the table is in creation mode.
* @return previous value, or null if none
*/
final V putVal(int hash, K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent,
boolean evict) {
Node[] tab; Node p; int n, i;
if ((tab = table) == null || (n = tab.length) == 0)
n = (tab = resize()).length;
if ((p = tab[i = (n - 1) & hash]) == null)
tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
else {
Node e; K k;
if (p.hash == hash &&
((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
e = p;
else if (p instanceof TreeNode)
e = ((TreeNode)p).putTreeVal(this, tab, hash, key, value);
else {
for (int binCount = 0; ; ++binCount) {
if ((e = p.next) == null) {
p.next = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD - 1) // -1 for 1st
treeifyBin(tab, hash);
break;
}
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
break;
p = e;
}
}
if (e != null) { // existing mapping for key
V oldValue = e.value;
if (!onlyIfAbsent || oldValue == null)
e.value = value;
afterNodeAccess(e);
return oldValue;
}
}
++modCount;
if (++size > threshold)
resize();
afterNodeInsertion(evict);
return null;
}
①.判断键值对数组table[i]是否为空或为null,否则执行resize()进行扩容;
②.根据键值key计算hash值得到插入的数组索引i,如果table[i]==null,直接新建节点添加,转向⑥,如果table[i]不为空,转向③;
③.判断table[i]的首个元素是否和key一样,如果相同直接覆盖value,否则转向④,这里的相同指的是hashCode以及equals;
④.判断table[i] 是否为treeNode,即table[i] 是否是红黑树,如果是红黑树,则直接在树中插入键值对,否则转向⑤;
⑤.遍历table[i],判断链表长度是否大于8,大于8的话把链表转换为红黑树,在红黑树中执行插入操作,否则进行链表的插入操作;遍历过程中若发现key已经存在直接覆盖value即可;
⑥.插入成功后,判断实际存在的键值对数量size是否超多了最大容量threshold,如果超过,进行扩容。
删除元素
public V remove(Object key) {
Node e;
return (e = removeNode(hash(key), key, null, false, true)) == null ?
null : e.value;
}
/**
* Implements Map.remove and related methods
*
* @param hash hash for key
* @param key the key
* @param value the value to match if matchValue, else ignored
* @param matchValue if true only remove if value is equal
* @param movable if false do not move other nodes while removing
* @return the node, or null if none
*/
final Node removeNode(int hash, Object key, Object value,
boolean matchValue, boolean movable) {
Node[] tab; Node p; int n, index;
if ((tab = table) != null && (n = tab.length) > 0 &&
(p = tab[index = (n - 1) & hash]) != null) {
Node node = null, e; K k; V v;
//判断链表对应的位置是否为null
if (p.hash == hash &&
((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
node = p;
//是否已经形成链表
else if ((e = p.next) != null) {
//是否已经行为树形结构
if (p instanceof TreeNode)
node = ((TreeNode)p).getTreeNode(hash, key);
else {
do {
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key ||
(key != null && key.equals(k)))) {
node = e;
break;
}
p = e;
} while ((e = e.next) != null);
}
}
if (node != null && (!matchValue || (v = node.value) == value ||
(value != null && value.equals(v)))) {
if (node instanceof TreeNode)
((TreeNode)node).removeTreeNode(this, tab, movable);
else if (node == p)
tab[index] = node.next;
else
p.next = node.next;
++modCount;
--size;
afterNodeRemoval(node);
return node;
}
}
return null;
}
2、TreeMap
2.1、特性
- 插入的元素不能重复
- 插入的元素默认按照key有序(默认按照升序)
2.2、实现原理
底层通过红黑树实现的,
static final class Entry implements Map.Entry {
K key;
V value;
Entry left; // 左孩子
Entry right;//右孩子
Entry parent;// 父亲节点
boolean color = BLACK;
和之前一样我们还是来看看TreeMap的添加元素和删除元素的方法来了解TreeMap的实现原理
添加元素:在树种找到要插入的位置,即该节点的父亲节点,然后根据comp的具体值决定是要插入到left还是right
public V put(K key, V value) {
Entry t = root;
if (t == null) {
compare(key, key); // type (and possibly null) check
root = new Entry<>(key, value, null);
size = 1;
modCount++;
return null;
}
int cmp;
Entry parent;
// split comparator and comparable paths
Comparator cpr = comparator;
if (cpr != null) {
do {
parent = t;
cmp = cpr.compare(key, t.key);
if (cmp < 0)
t = t.left;
else if (cmp > 0)
t = t.right;
else
return t.setValue(value);
} while (t != null);
}
else {
if (key == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Comparable k = (Comparable) key;
do {
parent = t;
cmp = k.compareTo(t.key);
if (cmp < 0)
t = t.left;
else if (cmp > 0)
t = t.right;
else
return t.setValue(value);
} while (t != null);
}
Entry e = new Entry<>(key, value, parent);
if (cmp < 0)
parent.left = e;
else
parent.right = e;
fixAfterInsertion(e);
size++;
modCount++;
return null;
}
删除节点:本质上就是红黑树的节点删除操作,想要理解TreeMap的删除操作最好深入理解红黑树的删除操作
public V remove(Object key) {
Entry p = getEntry(key);
if (p == null)
return null;
V oldValue = p.value;
deleteEntry(p);
return oldValue;
}
/**
* Delete node p, and then rebalance the tree.
*/
private void deleteEntry(Entry p) {
modCount++;
size--;
// If strictly internal, copy successor's element to p and then make p
// point to successor.
if (p.left != null && p.right != null) {
Entry s = successor(p);
p.key = s.key;
p.value = s.value;
p = s;
} // p has 2 children
// Start fixup at replacement node, if it exists.
Entry replacement = (p.left != null ? p.left : p.right);
if (replacement != null) {
// Link replacement to parent
replacement.parent = p.parent;
if (p.parent == null)
root = replacement;
else if (p == p.parent.left)
p.parent.left = replacement;
else
p.parent.right = replacement;
// Null out links so they are OK to use by fixAfterDeletion.
p.left = p.right = p.parent = null;
// Fix replacement
if (p.color == BLACK)
fixAfterDeletion(replacement);
} else if (p.parent == null) { // return if we are the only node.
root = null;
} else { // No children. Use self as phantom replacement and unlink.
if (p.color == BLACK)
fixAfterDeletion(p);
if (p.parent != null) {
if (p == p.parent.left)
p.parent.left = null;
else if (p == p.parent.right)
p.parent.right = null;
p.parent = null;
}
}
}
参考文献:
链接:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/21673805
http://alex09.iteye.com/blog/539549