一、物理编辑器的使用
在本系列博客的第一篇就介绍了如何使用Box2D内置的几种方式创建刚体的材质,然而我们在开发游戏的时候需要根据很多非常复杂的物体创建对应的形状,使用内置的多边形很难去描出合适的图形,所以Box2D物理游戏引擎支持外部导入文件进行物理刚体的创建。
1.1、根据物理编辑器文件创建物理刚体
首先使用PhysicsEditor物理编辑器将需要创建的材质信息编辑好,然后导出cocos2d支持的plist文件,假设我们将文件保存为“boxEdit.plist”并放在资源目录下的physics文件夹里面。
创建精灵
-- 创建车身精灵
self.car = D.img("common/cars/car_1/carBody_1.png"):p(480, 270):to(self)
-- 创建车轮精灵
self.w1 = D.img("common/cars/car_1/wheel_1.png"):p(430, 210):to(self)
self.w2 = D.img("common/cars/car_1/wheel_1.png"):p(530, 210):to(self)
接下来就要使用物理编辑器导出的文件了:
1、创建刚体
local bodyDef = b2BodyDef()
-- 类型:静态(b2_staticBody),平台(b2_kinematicBody),动态(b2_dynamicBody)
bodyDef.type = b2_dynamicBody
bodyDef.position = b2Vec2(self.car.px() / 32, self.car:py() / 32)
bodyDef.angle = math.rad(0)
-- 用户数据:存储用户的数据,可以是任何类型的数据。一般要求存储的数据的类型是一致的
bodyDef.userData = self.car
-- 创建一个刚体对象,根据刚体定义创建
local body = world:CreateBody(bodyDef)
2、有了刚体,接下来就要创建材质,代码如下:
-- 加载physicsDesigner的.plist格式文件
GB2ShapeCache:sharedGB2ShapeCache():addShapesWithFile("physics/boxEdit.plist")
-- 把生成的刚体和形状绑在一起,key即图片名
GB2ShapeCache:sharedGB2ShapeCache():addFixturesToBody(body, "carBody_1")
可以使用GB2ShapeCache:sharedGB2ShapeCache():addShapesWithFile("plist文件名路径")来加载物理编辑器导出的数据,然后通过GB2ShapeCache:sharedGB2ShapeCache():addFixturesToBody(刚体对象, "精灵列表上的形状名称")来给刚体绑定材质信息。
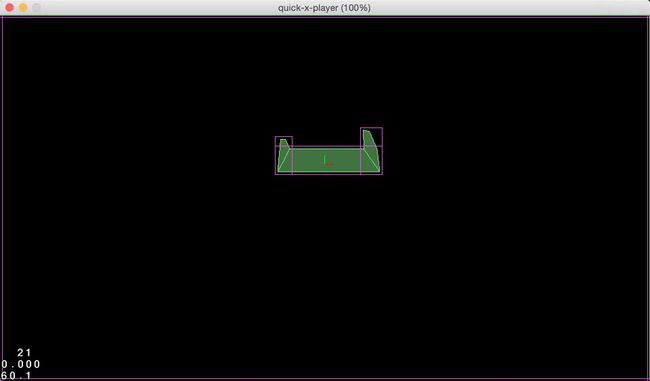
刷新模拟器就可以看到编辑的车身显示在场景中(要开启物理调试模式)。
3、使用同样的方式创建汽车的两个车轮
bodyDef.position = b2Vec2(13.5, 8.5)
bodyDef.userData = self.w1
local bodyWheel1 = world:CreateBody(bodyDef)
GB2ShapeCache:sharedGB2ShapeCache():addFixturesToBody(bodyWheel1, "wheel_1")
bodyDef.position = b2Vec2(16.5, 8.5)
bodyDef.userData = self.w2
local bodyWheel2 = world:CreateBody(bodyDef)
GB2ShapeCache:sharedGB2ShapeCache():addFixturesToBody(bodyWheel2, "wheel_1")
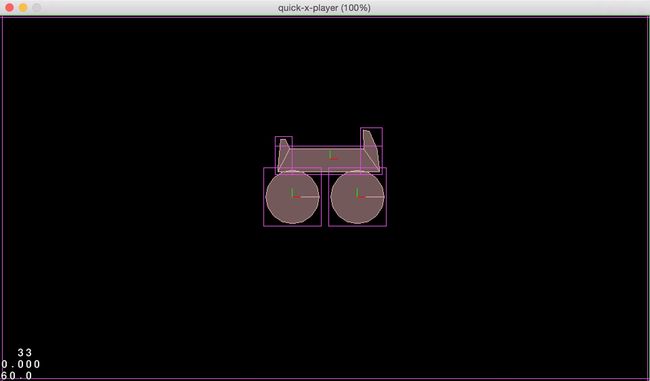
刷新模拟器,可以看到如下画面:
二、物理更新
2.1、物理更新
在这之前,其实物理世界并没有开始进行物理模拟,那么我们可以使用下面这个代码来进行一次物理更新:
-- 更新[物理世界]
function M.tick()
if not world then return end
-- 时间步、速度迭代device、位置迭代
local velocityIterations, positionIterations = 32, 32
-- 物理引擎进行物理模拟,生成模拟后的数据
world:Step(60, velocityIterations, positionIterations)
end
注意:这个函数里面的“world”就是之前创建的物理世界,所以我们可以将world定义成全局的,以保证可以在任何地方访问。
调用物理世界的Step()方法可以进行一次物理模拟,方法的第一个参数是时间步,第二个参数是速度迭代次数,第三个参数是位置迭代参数。
- 时间步用于控制物理模拟的时间间隔,我们一般让其与渲染世界同步,所以设置为60,设备性能较低时可以设置为40。
- 速度迭代:迭代次数越高,模拟越逼真,但是越耗性能。
- 位置迭代:迭代次数越高,模拟越逼真,但是越耗性能。
2.2、开启物理模拟
开启一个调度器来调用上面的这个函数,实现实时模拟:
local timer = SC.open(self.tick, 1.0 / 60)
开启调度进行物理模拟的时候发现车身和车轮开始做只有落地运动,并且它们散架了,这是因为车身和车轮之间没有连接到一起,为了让车身和车轮组成一个整体,可以使用关节(约束)将他们连接到一起。
三、关节(b2Joint)
关节又称之为“约束”,是用于限制刚体运动的一些条件,在box2D中,常用的关节有:鼠标关节、距离关节、移动关节、旋转关节等,其实这些关节的中文名称并非翻译的很准确,很多诸如《Cocos2d-JS 游戏开发》的书籍里面都不进行翻译,而是直接使用关节的类名来进行讲解。
1、关节描述(b2JointDef)
与创建刚体一样,创建关节也需要先创建关节的描述,在box2D中,关节描述b2JointDef的定义如下:
struct b2JointDef
{
b2JointDef()
{
type = e_unknownJoint;
userData = NULL;
bodyA = NULL;
bodyB = NULL;
collideConnected = false;
}
/// The joint type is set automatically for concrete joint types.
b2JointType type;
/// Use this to attach application specific data to your joints.
void* userData;
/// The first attached body.
b2Body* bodyA;
/// The second attached body.
b2Body* bodyB;
/// Set this flag to true if the attached bodies should collide.
bool collideConnected;
};
b2JointDef是一个结构体(struct)类型,包含如下五个属性:
- type:关节类型。
- userData:用户数据(可以存放任意数据)。
- bodyA:被关节约束的第一个刚体对象。
- bodyB:被关节约束的第二个刚体对象。
- collideConnected:被约束的两个刚体是否可以发生碰撞,true表示可以发生碰撞。
1、鼠标关节(b2MouseJoint)
1.1、鼠标关节描述(b2MouseJointDef)
在创建鼠标关节之前,需要先创建对应的关节描述,鼠标关节描述b2MouseJointDef的定义如下:
struct b2MouseJointDef : public b2JointDef
{
b2MouseJointDef()
{
type = e_mouseJoint;
target.Set(0.0f, 0.0f);
maxForce = 0.0f;
frequencyHz = 5.0f;
dampingRatio = 0.7f;
}
/// The initial world target point. This is assumed
/// to coincide with the body anchor initially.
b2Vec2 target;
/// The maximum constraint force that can be exerted
/// to move the candidate body. Usually you will express
/// as some multiple of the weight (multiplier * mass * gravity).
float32 maxForce;
/// The response speed.
float32 frequencyHz;
/// The damping ratio. 0 = no damping, 1 = critical damping.
float32 dampingRatio;
};
b2MouseJointDef继承自b2JointDef,它的type属性值为“e_mouseJoint”,指明使用该关节定义的关节是一个鼠标关节。
b2MouseJointDef相比于b2JointDef多出了如下几个属性:
- maxForce:作用在刚体上的最大的力,力越大拖动刚体越轻松。
- frequencyHz:响应速度,数值越高,关节响应的速度越快,关节看上去越坚固。
- dampingRatio:阻尼率:值越大,关节运动阻尼越大。
典型情况下,关节频率(响应速度)要小于一半的时间步(time step)频率。比如每秒执行60次时间步, 关节的频率就要小于30赫兹。这样做的理由可以参考Nyquist频率理论。
影响关节的弹性(阻尼率无单位,典型是在0到1之间, 也可以更大。1是阻尼率的临界值, 当阻尼率为1时,没有振动。)
1.2、创建鼠标关节描述
-- 创建一个鼠标关节定义
local mouseJointDef = b2MouseJointDef()
-- 要被鼠标关节约束的刚体
mouseJointDef.bodyA = body
-- bodyB设置为世界的边缘刚体
mouseJointDef.bodyB = edgeBody
mouseJointDef.frequencyHz = 30
mouseJointDef.collideConnected = true
mouseJointDef.maxForce = 100
-- 关节的位置
mouseJointDef.target = b2Vec2(11, 10)
可以使用b2MouseJointDef()函数创建一个鼠标关节定义,然后直接设置其属性值。值得注意的是,关节是用于连接两个刚体的,而鼠标关节的主要作用是可以使用鼠标来对刚体进行拖拽操作,作用的是一个刚体,所以我们可以将一个刚体设置为要拖拽的刚体对象,另一个一般设置为世界边缘刚体。
1.3、创建鼠标关节
-- 创建关节,并转换为b2MouseJoint类型
local mouseJoint = tolua.cast(world:CreateJoint(mouseJointDef), "b2MouseJoint")
物理世界对象的CreateJoint(jointDef)方法可以用于创建一个关节,其参数jointDef为要创建的关节对应的关节描述对象,该方法的返回值类型是b2Joint类型,可以通过tolua.cast(obj, typeName)方法来进行类型转换。
1.4、移动刚体
鼠标关节移动刚体的现方式是改变鼠标关节的位置,代码如下:
-- 设置关节的位置
mouseJoint:SetTarget(b2Vec2(10, 10))
只需要在触摸事件的移动回调中改变鼠标关节的位置即可实现刚体的拖拽。
2、焊接关节(b2WeldJoint)
2.1、焊接关节描述(b2WeldJointDef)
struct b2WeldJointDef : public b2JointDef
{
b2WeldJointDef()
{
type = e_weldJoint;
localAnchorA.Set(0.0f, 0.0f);
localAnchorB.Set(0.0f, 0.0f);
referenceAngle = 0.0f;
frequencyHz = 0.0f;
dampingRatio = 0.0f;
}
/// Initialize the bodies, anchors, and reference angle using a world
/// anchor point.
void Initialize(b2Body* bodyA, b2Body* bodyB, const b2Vec2& anchor);
/// The local anchor point relative to bodyA's origin.
b2Vec2 localAnchorA;
/// The local anchor point relative to bodyB's origin.
b2Vec2 localAnchorB;
/// The bodyB angle minus bodyA angle in the reference state (radians).
float32 referenceAngle;
/// The mass-spring-damper frequency in Hertz. Rotation only.
/// Disable softness with a value of 0.
float32 frequencyHz;
/// The damping ratio. 0 = no damping, 1 = critical damping.
float32 dampingRatio;
};
焊接关节的定义如上,其相比与b2JointDef增加的属性有:
- localAnchorA:关节连接在刚体A上的局部锚点,或者就理解成是关节在刚体A上的连接点。
- localAnchorA:关节连接在刚体B上的局部锚点,或者就理解成是关节在刚体B上的连接点。
- referenceAngle:刚体B相对于刚体A的角度,使用弧度制表示。
- frequencyHz:响应速度,数值越高,关节响应的速度越快,关节看上去越坚固。
- dampingRatio:阻尼率:值越大,关节运动阻尼越大。
2.2、创建焊接关节描述
-- 创建一个焊接关节定义
local weldJointDef = b2WeldJointDef()
-- 初始化
weldJointDef:Initialize(bodyA, bodyB, bodyB:GetWorldCenter())
weldJointDef.frequencyHz = 30
weldJointDef.collideConnected = false
创建焊接关节的时候,设置关节约束的两个刚体需要通过调用焊接关节定义的Initialize()方法,该方法有三个参数,分别是:刚体A、刚体B和关节的锚点位置。
2.3、创建焊接关节
local weldJoint = tolua.cast(world:CreateJoint(weldJointDef), "b2WeldJoint")
3、距离关节(b2DistanceJoint)
3.1、距离关节定义(b2DistanceJointDef)
struct b2DistanceJointDef : public b2JointDef
{
b2DistanceJointDef()
{
type = e_distanceJoint;
localAnchorA.Set(0.0f, 0.0f);
localAnchorB.Set(0.0f, 0.0f);
length = 1.0f;
frequencyHz = 0.0f;
dampingRatio = 0.0f;
}
/// Initialize the bodies, anchors, and length using the world
/// anchors.
void Initialize(b2Body* bodyA, b2Body* bodyB,
const b2Vec2& anchorA, const b2Vec2& anchorB);
/// The local anchor point relative to bodyA's origin.
b2Vec2 localAnchorA;
/// The local anchor point relative to bodyB's origin.
b2Vec2 localAnchorB;
/// The natural length between the anchor points.
float32 length;
/// The mass-spring-damper frequency in Hertz. A value of 0
/// disables softness.
float32 frequencyHz;
/// The damping ratio. 0 = no damping, 1 = critical damping.
float32 dampingRatio;
};
距离关节的定义如上,其相比与b2JointDef增加的属性有:
- localAnchorA:关节连接在刚体A上的局部锚点,或者就理解成是关节在刚体A上的连接点。
- localAnchorA:关节连接在刚体B上的局部锚点,或者就理解成是关节在刚体B上的连接点。
- length:锚点之间的自然长度。
3.2、创建距离关节
-- 创建一个距离关节定义
local distanceJointDef = b2DistanceJointDef()
distanceJointDef:Initialize(bodyA, bodyB, bodyA:GetWorldCenter(), bodyB:GetWorldCenter())
distanceJointDef.bodyA = bodyA
distanceJointDef.bodyB = bodyB
-- 距离关节的长度
distanceJointDef.length = 2
distanceJointDef.frequencyHz = 30
-- 是否连续碰撞
distanceJointDef.collideConnected = false
-- 创建关节
lcoal distanceJoint = tolua.cast(world:CreateJoint(distanceJointDef), "b2DistanceJoint")
创建距离关节同样需要调用Initialize()方法,具体参照焊接关节。
4、移动关节(b2PrismaticJoint)
4.1、移动关节定义(b2PrismaticJointDef)
struct b2PrismaticJointDef : public b2JointDef
{
b2PrismaticJointDef()
{
type = e_prismaticJoint;
localAnchorA.SetZero();
localAnchorB.SetZero();
localAxisA.Set(1.0f, 0.0f);
referenceAngle = 0.0f;
enableLimit = false;
lowerTranslation = 0.0f;
upperTranslation = 0.0f;
enableMotor = false;
maxMotorForce = 0.0f;
motorSpeed = 0.0f;
}
/// Initialize the bodies, anchors, axis, and reference angle using the world
/// anchor and unit world axis.
void Initialize(b2Body* bodyA, b2Body* bodyB, const b2Vec2& anchor, const b2Vec2& axis);
/// The local anchor point relative to bodyA's origin.
b2Vec2 localAnchorA;
/// The local anchor point relative to bodyB's origin.
b2Vec2 localAnchorB;
/// The local translation unit axis in bodyA.
b2Vec2 localAxisA;
/// The constrained angle between the bodies: bodyB_angle - bodyA_angle.
float32 referenceAngle;
/// Enable/disable the joint limit.
bool enableLimit;
/// The lower translation limit, usually in meters.
float32 lowerTranslation;
/// The upper translation limit, usually in meters.
float32 upperTranslation;
/// Enable/disable the joint motor.
bool enableMotor;
/// The maximum motor torque, usually in N-m.
float32 maxMotorForce;
/// The desired motor speed in radians per second.
float32 motorSpeed;
};
距离关节的属性会相对多一点,其相比与b2JointDef增加的属性有:
- localAnchorA:关节连接在刚体A上的局部锚点,或者就理解成是关节在刚体A上的连接点。
- localAnchorA:关节连接在刚体B上的局部锚点,或者就理解成是关节在刚体B上的连接点。
- localAxisA:在刚体A中的局部移动单元轴,就是刚体A滑动的方向。
- referenceAngle:参考角度,刚体B减去刚体A的角度值。
- enableLimit:是否启用限制。
- lowerTranslation:移动的最小限制,与方向同向为正,反向为负。启用限制后才有效果。
- upperTranslation:移动的最大限制,与方向同向为正,反向为负。启用限制后才有效果。
- enableMotor:是否启动马达。
- maxMotorForce:马达的最大扭力。
- motorSpeed:马达速度。
4.2、创建移动关节(平移关节)
-- 创建一个移动关节的定义
local prismaticJointDef = b2PrismaticJointDef()
if true then
-- 移动的方向,用矢量来表示可以移动的方向,零向量(0, 0)为任意方向
local directVec = b2Vec2(10, 0)
-- 初始化关节
prismaticJointDef:Initialize(bodyA, bodyB, bodyB:GetWorldCenter(), directVec)
end
prismaticJointDef.lowerTranslation = -1.0
prismaticJointDef.upperTranslation = 1.0
prismaticJointDef.enableLimit = true
prismaticJointDef.collideConnected = false
-- 创建关节
local prismaticJoint = tolua.cast(world:CreateJoint(prismaticJointDef), "b2PrismaticJoint")
5、绳索关节(b2RopeJoint)
5.1、绳索关节定义(b2RopeJointDef)
struct b2RopeJointDef : public b2JointDef
{
b2RopeJointDef()
{
type = e_ropeJoint;
localAnchorA.Set(-1.0f, 0.0f);
localAnchorB.Set(1.0f, 0.0f);
maxLength = 0.0f;
}
/// The local anchor point relative to bodyA's origin.
b2Vec2 localAnchorA;
/// The local anchor point relative to bodyB's origin.
b2Vec2 localAnchorB;
/// The maximum length of the rope.
/// Warning: this must be larger than b2_linearSlop or
/// the joint will have no effect.
float32 maxLength;
};
绳索关节其相比与b2JointDef增加的属性有:
- localAnchorA:关节连接在刚体A上的局部锚点,或者就理解成是关节在刚体A上的连接点。
- localAnchorA:关节连接在刚体B上的局部锚点,或者就理解成是关节在刚体B上的连接点。
- maxLength:绳索的最大长度。
5.2、创建绳索关节
-- 创建一个绳索关节的定义
local ropeJointDef = b2RopeJointDef()
-- 绳索的最大长度
ropeJointDef.maxLength = 4
-- 关节连接的刚体A
ropeJointDef.bodyA = bodyA
-- 关节连接的刚体B
ropeJointDef.bodyB = bodyB
-- 关节连接在刚体A上的锚点,其他关节应该也有,默认在中央
ropeJointDef.localAnchorA = b2Vec2(0.5, 0.5)
-- 关节连接在刚体B上的锚点,其他关节应该也有,默认在中央
ropeJointDef.localAnchorB = b2Vec2(0.5, 0.5)
-- 是否连续碰撞
ropeJointDef.collideConnected = true
-- 创建关节
local ropeJoint = tolua.cast(world:CreateJoint(ropeJointDef), "b2RopeJoint")
6、旋转关节(b2RevoluteJoint)
6.1、旋转关节定义(b2RevoluteJointDef)
struct b2RevoluteJointDef : public b2JointDef
{
b2RevoluteJointDef()
{
type = e_revoluteJoint;
localAnchorA.Set(0.0f, 0.0f);
localAnchorB.Set(0.0f, 0.0f);
referenceAngle = 0.0f;
lowerAngle = 0.0f;
upperAngle = 0.0f;
maxMotorTorque = 0.0f;
motorSpeed = 0.0f;
enableLimit = false;
enableMotor = false;
}
/// Initialize the bodies, anchors, and reference angle using a world
/// anchor point.
void Initialize(b2Body* bodyA, b2Body* bodyB, const b2Vec2& anchor);
/// The local anchor point relative to bodyA's origin.
b2Vec2 localAnchorA;
/// The local anchor point relative to bodyB's origin.
b2Vec2 localAnchorB;
/// The bodyB angle minus bodyA angle in the reference state (radians).
float32 referenceAngle;
/// A flag to enable joint limits.
bool enableLimit;
/// The lower angle for the joint limit (radians).
float32 lowerAngle;
/// The upper angle for the joint limit (radians).
float32 upperAngle;
/// A flag to enable the joint motor.
bool enableMotor;
/// The desired motor speed. Usually in radians per second.
float32 motorSpeed;
/// The maximum motor torque used to achieve the desired motor speed.
/// Usually in N-m.
float32 maxMotorTorque;
};
旋转关节的定义和移动关节差不多,只是没有localAxisA属性,所以被旋转关节约束的两个刚体之间是可以随意方向移动的,将平移关节的移动方向设置为另向量b2Vec2(0, 0),那么平移关节的效果就和旋转关节一致了。
6.2、创建旋转关节
-- 创建一个旋转关节定义
local revoluteJointDef = b2RevoluteJointDef()
revoluteJointDef:Initialize(bodyA, bodyB, bodyB:GetWorldCenter())
revoluteJointDef.bodyA = bodyA
revoluteJointDef.bodyB = bodyB
revoluteJointDef.lowerAngle = 0
revoluteJointDef.upperAngle = 0
-- 是否启用角度限制,类似手臂只能在一定角度内旋转一样。
revoluteJointDef.enableLimit = false
-- 马达的速度
revoluteJointDef.motorSpeed = 0.0
-- 马达的最大扭矩
revoluteJointDef.maxMotorTorque = 11110.0
-- 是否启用旋转马达,启用后关节会自动转动
revoluteJointDef.enableMotor = true
revoluteJointDef.frequencyHz = 32
revoluteJointDef.collideConnected = false
-- 关节长度
revoluteJointDef.length = 0.1
-- 创建关节,并转换为b2RevoluteJoint类型
local revoluteJoint = tolua.cast(world:CreateJoint(revoluteJointDef), "b2RevoluteJoint")
7、摩擦关节
7.1、摩擦关节定义
struct b2FrictionJointDef : public b2JointDef
{
b2FrictionJointDef()
{
type = e_frictionJoint;
localAnchorA.SetZero();
localAnchorB.SetZero();
maxForce = 0.0f;
maxTorque = 0.0f;
}
/// Initialize the bodies, anchors, axis, and reference angle using the world
/// anchor and world axis.
void Initialize(b2Body* bodyA, b2Body* bodyB, const b2Vec2& anchor);
/// The local anchor point relative to bodyA's origin.
b2Vec2 localAnchorA;
/// The local anchor point relative to bodyB's origin.
b2Vec2 localAnchorB;
/// The maximum friction force in N.
float32 maxForce;
/// The maximum friction torque in N-m.
float32 maxTorque;
};
摩擦关节相对于b2JointDef增加的属性是:
- localAnchorA:关节在刚体A上面的作用点。
- localAnchorB:关节在刚体B上面的作用点。
- maxForce:关节的最大摩擦力。
- maxTorque:摩擦关节最大扭力。
7.2、创建摩擦关节
-- 创建一个摩擦关节定义
local frictionJointDef = b2FrictionJointDef()
frictionJointDef:Initialize(bodyA, bodyB, bodyB:GetWorldCenter())
frictionJointDef.frequencyHz = 0.0
frictionJointDef.dampingRatio = 0.0
frictionJointDef.maxForce = 0.0
local frictionJoint = tolua.cast(world:CreateJoint(frictionJointDef), "b2FrictionJoint")
8、齿轮关节(b2GearJoint)
8.1、齿轮关节定义(b2GearJointDef)
struct b2GearJointDef : public b2JointDef
{
b2GearJointDef()
{
type = e_gearJoint;
joint1 = NULL;
joint2 = NULL;
ratio = 1.0f;
}
/// The first revolute/prismatic joint attached to the gear joint.
b2Joint* joint1;
/// The second revolute/prismatic joint attached to the gear joint.
b2Joint* joint2;
/// The gear ratio.
/// @see b2GearJoint for explanation.
float32 ratio;
};
齿轮关节的定义如上,其相比与b2JointDef增加的属性有:
- joint1:齿轮关节上关连的第一个关节(旋转关节/平移关节)。
- joint2:齿轮关节上关连的第二个关节(旋转关节/平移关节)。
- ratio:关节比例(齿轮系数)。
8.2、创建齿轮关节
-- 创建一个齿轮关节
local gearJointDef = b2GearJointDef()
-- 齿轮关节关联的关节1
gearJointDef.joint1 = jointA
-- 齿轮关节关联的关节2
gearJointDef.joint2 = jointB
gearJointDef.bodyA = bodyA
gearJointDef.bodyB = bodyB
-- 关节比例(齿轮系数)
gearJointDef.ratio = 1
local gearJointDef = tolua.cast(world:CreateJoint(gearJointDef), "b2GearJoint")
上面jointA和jointB是预先创建好的旋转关节或者平移关节,**释放这两个关节时需要先释放齿轮关节,否则会引起空指针错误。 **
9、滑轮关节(b2PulleyJoint)
9.1、滑轮关节定义(b2PulleyJointDef)
struct b2PulleyJointDef : public b2JointDef
{
b2PulleyJointDef()
{
type = e_pulleyJoint;
groundAnchorA.Set(-1.0f, 1.0f);
groundAnchorB.Set(1.0f, 1.0f);
localAnchorA.Set(-1.0f, 0.0f);
localAnchorB.Set(1.0f, 0.0f);
lengthA = 0.0f;
lengthB = 0.0f;
ratio = 1.0f;
collideConnected = true;
}
/// Initialize the bodies, anchors, lengths, max lengths, and ratio using the world anchors.
void Initialize(b2Body* bodyA, b2Body* bodyB,
const b2Vec2& groundAnchorA, const b2Vec2& groundAnchorB,
const b2Vec2& anchorA, const b2Vec2& anchorB,
float32 ratio);
/// The first ground anchor in world coordinates. This point never moves.
b2Vec2 groundAnchorA;
/// The second ground anchor in world coordinates. This point never moves.
b2Vec2 groundAnchorB;
/// The local anchor point relative to bodyA's origin.
b2Vec2 localAnchorA;
/// The local anchor point relative to bodyB's origin.
b2Vec2 localAnchorB;
/// The a reference length for the segment attached to bodyA.
float32 lengthA;
/// The a reference length for the segment attached to bodyB.
float32 lengthB;
/// The pulley ratio, used to simulate a block-and-tackle.
float32 ratio;
};
滑轮关节的定义如上,其相比与b2JointDef增加的属性有:
- groundAnchorA:刚体A对应的那个滑轮的位置。
- groundAnchorB:刚体B对应的那个滑轮的位置。
- localAnchorA:关节在刚体A上面的作用点。
- localAnchorB:关节在刚体B上面的作用点。
- lengthA:滑轮到刚体A的线的长度。
- lengthB:滑轮到刚体B的线的长度。
- ratio:比例(关节传动时,滑轮上升和下降的两头的位移比例)。
9.2、创建滑轮关节
-- 创建一个滑轮关节定义
local pulleyJointDef = b2PulleyJointDef()
if true then
local function ccpToVecRatioIfnil(point, defaultVec2, offset)
point = point and M.ccpToVecRatio(point) or b2Vec2(default.x + offset.x, default.y + offset.y)
return point
end
-- 滑轮绳子拉动的点
local bodyWorldPointA = bodyA:GetWorldCenter()
-- 滑轮绳子拉动的点
local bodyWorldPointB = bodyB:GetWorldCenter()
-- 刚体A对应的那个滑轮的位置
local groundPointA = b2Vec2(bodyWorldPointA.x, bodyWorldPointA.y + 2)
-- 刚体B对应的那个滑轮的位置
local groundPointB = b2Vec2(bodyWorldPointB.x, bodyWorldPointB.y + 3)
-- 比例(关节传动时,滑轮上升和下降的两头的位移比例)
local ratio = 1
-- 初始化关节
pulleyJointDef.Initialize(bodyA, bodyB, groundPointA, groundPointB,
bodyWorldPointA, bodyWorldPointB, ratio)
end
-- 绳子可拉动的最大长度
pulleyJointDef.maxLengthA = 5
-- 绳子可拉动的最大长度
pulleyJointDef.maxLengthB = 5
local pulleyJoint = tolua.cast(world:CreateJoint(pulleyJointDef), "b2PulleyJoint")
10、轮子关节(b2WheelJoint)
10.1、轮子关节定义(b2WheelJointDef)
struct b2WheelJointDef : public b2JointDef
{
b2WheelJointDef()
{
type = e_wheelJoint;
localAnchorA.SetZero();
localAnchorB.SetZero();
localAxisA.Set(1.0f, 0.0f);
enableMotor = false;
maxMotorTorque = 0.0f;
motorSpeed = 0.0f;
frequencyHz = 2.0f;
dampingRatio = 0.7f;
}
/// Initialize the bodies, anchors, axis, and reference angle using the world
/// anchor and world axis.
void Initialize(b2Body* bodyA, b2Body* bodyB, const b2Vec2& anchor, const b2Vec2& axis);
/// The local anchor point relative to bodyA's origin.
b2Vec2 localAnchorA;
/// The local anchor point relative to bodyB's origin.
b2Vec2 localAnchorB;
/// The local translation axis in bodyA.
b2Vec2 localAxisA;
/// Enable/disable the joint motor.
bool enableMotor;
/// The maximum motor torque, usually in N-m.
float32 maxMotorTorque;
/// The desired motor speed in radians per second.
float32 motorSpeed;
/// Suspension frequency, zero indicates no suspension
float32 frequencyHz;
/// Suspension damping ratio, one indicates critical damping
float32 dampingRatio;
};
轮子关节相对于b2JointDef增加的属性是:
- localAnchorA:关节在刚体A上面的作用点。
- localAnchorB:关节在刚体B上面的作用点。
- localAxisA:在刚体A中的局部移动单元轴,就是刚体A滑动的方向。
- enableMotor:是否启动马达。
- maxMotorTorque:马达的最大转矩。
- motorSpeed:马达速度。
- frequencyHz:响应速度,数值越高,关节响应的速度越快,关节看上去越坚固。
- dampingRatio:阻尼率:值越大,关节运动阻尼越大。
10.2、创建轮子关节
-- 创建一个轮子关节定义
local wheelJointDef = b2WheelJointDef()
if true then
-- 用坐标表示轮子轴的位置
local axis = b2Vec2(1.0, 0.0)
-- 初始化关节
wheelJointDef:Initialize(bodyA, bodyB, bodyB:GetWorldCenter(), axis)
end
wheelJointDef.enableMotor = false
wheelJointDef.motorSpeed = 0.0
wheelJointDef.maxMotorTorque = 0.0
wheelJointDef.frequencyHz = 32
wheelJointDef.dampingRatio = 0.2
-- 创建关节
local wheelJoint = tolua.cast(world:CreateJoint(wheelJointDef), "b2WheelJoint")
每个关节的用法基本一致,主要的差别都是创建关节定义的时候设置的参数不同而已,上文创建关节的代码里面只是随便设置了几个参数。读者可以使用b2WheelJoint关节将前文的汽车和车轮约束到一起。
三、接触(b2Contact)
在物理游戏中经常会需要实现碰撞检测的逻辑,box2D提供了b2Contact来实现碰撞。
1、接触检测
1.1、创建接触检测监听器
-- 创建接触侦听器
local listener = GB2ContactListener:new_local()
1.2、为接触监听注册回调句柄
-- 为接触注册侦听函数
listener:registerScriptHandler(function(contactType, contact, oldManifold)
if contactType == GB2_CONTACTTYPE_BEGIN_CONTACT then
print("开始接触")
elseif contactType == GB2_CONTACTTYPE_BEGIN_CONTACT then
print("结束接触")
elseif contactType == GB2_CONTACTTYPE_BEGIN_CONTACT then
print("求解前")
elseif contactType == GB2_CONTACTTYPE_BEGIN_CONTACT then
print("求解后")
end
end)
在接触回调里面如果做刚体的销毁工作可能会导致b2Contact对象引用的刚体变成一个空指针,从而造成游戏闪退。所以通常可以延迟一点进行销毁。
1.3、给物理世界设置接触监听
-- 设置物理世界的接触侦听
world:SetContactListener(listener)
2、接触点的获取
刚体在接触的过程中,可以从接触对象(b2Contact)中获取接触点,代码如下:
-- 定义一个b2WorldManifold对象,用来获取并存储碰撞点的全局坐标
local manifold = GB2Util:newWorldManifold()
-- 通过GetWorldManifolde方法,计算出碰撞点的全局坐标,并存储到manifold变量中
contact:GetWorldManifold(manifold)
-- 获取碰撞点
local point = manifold.points[0]
四、渲染世界和物理世界的同步
物理世界只是负责物理效果的模拟,但是真正要反馈给玩家的是游戏的画面,也就是渲染世界。
修改上文的tick()方法如下:
-- 更新[物理世界]
function M.tick()
if not world then return end
-- 时间步、速度迭代device、位置迭代
local velocityIterations, positionIterations = 32, 32
-- 物理引擎进行物理模拟,生成模拟后的数据
world:Step(M.getTimeStep(), velocityIterations, positionIterations)
-- 同步物理世界和渲染世界
local body = world:GetBodyList()
while body do
if body:GetUserData() then
local spr = tolua.cast(body:GetUserData(), "CCSprite")
local x, y = body:GetPosition().x * PTM_RATIO, body:GetPosition().y * PTM_RATIO
-- 更新位置、角度,同步物理世界和渲染世界
spr:setPosition(ccp(x, y))
spr:setRotation(-1 * PT.radians2degrees(body:GetAngle()))
end
-- 获得下一个body
body = body:GetNext()
end
end
实现物理世界和渲染世界的方式就是遍历所有的刚体,然后将刚体的用户数据(userData)绑定的精灵的位置和旋转角度与刚体进行同步。