用了好久SQLAlchemy,作为Python ORM里的重量级module,用得很爽。
真是人生苦短,请用Python的一个极好例子。
原来一直只用了SQLAlchemy基本功能CRUD:增加(Create)、读取查询(Retrieve)、更新(Update)和删除(Delete)。最近在开发实际Flask网站时,遇到复杂的数据库处理,感觉要从头好好再深入学习一遍。
注: 这是初稿,会持续更新(20171027)
官网:http://docs.sqlalchemy.org
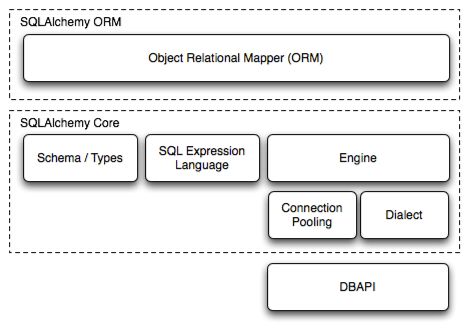
两大核心: SQLAlchemy ORM, SQLAlchemy Core
SQLAlchemy ORM
创建基本框架:
(建议复制到Jupyter Notebook里实际运行和尝试,加深理解!)
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
from sqlalchemy import Sequence, Column, DateTime, String, Integer, ForeignKey, func
from sqlalchemy.orm import relationship, backref
from sqlalchemy.ext.declarative import declarative_base
from sqlalchemy import create_engine
# 在内存中创建临时表
engine = create_engine('sqlite:///:memory:', echo=True)
Base.metadata.create_all(engine)
from sqlalchemy.orm import sessionmaker
session = sessionmaker(bind=engine)
s = session()
定义第一个表:
Base = declarative_base()
class User(Base):
__tablename__ = 'users'
id = Column(Integer, Sequence('user_id_seq'), primary_key=True)
name = Column(String)
fullname = Column(String)
password = Column(String)
def __repr__(self):
return "" % (
self.name, self.fullname, self.password)
Session操作:
- add
u = User(name='ed', fullname='edward jack', password='23r23sdfa')
s.add(u)
# add之后,query(),已经能查到,因为会触发Flush
# 没有commit之前,可以任意修改 u
s.dirty # 查看修改的
s.commit()
- update
- delete
Configuring delete/delete-orphan Cascade
class User(Base):
... __tablename__ = 'users'
... id = Column(Integer, primary_key=True)
... name = Column(String)
... fullname = Column(String)
... password = Column(String)
... addresses = relationship("Address", back_populates='user',
... cascade="all, delete, delete-orphan")
class Address(Base):
... __tablename__ = 'addresses'
... id = Column(Integer, primary_key=True)
... email_address = Column(String, nullable=False)
... user_id = Column(Integer, ForeignKey('users.id'))
... user = relationship("User", back_populates="addresses")
- query
s.query(User).filter_by(name='ed').first()
Query API
http://docs.sqlalchemy.org/en/rel_1_1/orm/query.html
Query是最常用的操作,建议深入学,提高Web App访问数据库的效率
filter操作符
query.filter(User.name == 'ed')
query.filter(User.name != 'ed')
query.filter(User.name.like('%ed%'))
ColumnOperators.ilike() 忽略大小写查找
NOT IN:
query.filter(~User.name.in_(['ed', 'wendy', 'jack']))
User.name == None
User.name != None
AND: 等同于:“, ”
or_
is_
isnot
text(): 直接写SQL
filter(text("id<224")).
order_by(text("id")).all():
has()
get(Primary_key)
Flask-sqlalchemy:
- get_or_404()
- first_or_404()
提高查询效率:to reduce the number of queries (dramatically, in many cases)
Eager Loading:
- orm.subqueryload()
- Joined Load
- Explicit Join + Eagerload
from sqlalchemy.orm import subqueryload
jack = session.query(User).\
... options(subqueryload(User.addresses)).\
... filter_by(name='jack').one()
jack
#
jack.addresses
#[, ]
One to Many:
- joined eager loading only makes sense when the size of the collections are relatively small
- subquery load makes sense when the collections are larger.
Many to One:
- using the default of lazy=’select’ is by far the most efficient way to go
- For a load of objects where there are many possible target references which may have not been loaded already, joined loading with an INNER JOIN is extremely efficient.
Load Only Cols
query = session.query(Book, Author).join(Book.author)
query = query.options(
Load(Book).load_only("summary", "excerpt"),
Load(Author).defer("bio")
)
Relationship Operators 关系表操作符
Operators:
contains()
==, !=, has()
Query.with_parent()
Join查询:
先查关联表,然后Join主表,用主表的column再二次过滤
session.query(RelationTable1).filter(XXX).join(MasterTable1).filter(MT1.XXX)
To access data from other tables, join the other tables and pass the desired columns to the add_columns() function.
Employee.query.join(Person).add_columns(Employee.id, Person.name).paginate(...)
Join From
主表是Address,但用关联表User字段过滤
q = session.query(Address).select_from(User).
join(User.addresses).
filter(User.name == 'ed')
直接读出ourbits_users表+Ob表:order_by(), paginate()
ss.query(ourbits_users, Ob).select_from(User).join(User.ob_seeding).filter(ourbits_users.c.user_id==User.id, ourbits_users.c.ourbits_id==Ob.id).all()
[(1, 56229, 2, 8, 0, 0.0, 9.71, '', '3天06:31:46', '3天7时',), (3, 56369, 1, 0, 0, 0.0, 0.0, '', '1天00:01:40', '2月2天', ), (3, 42951, 1, 0, 0, 0.0, 0.0, '', '1天00:01:12', '3月14天', )]
Many to Many
先定义两张表(db.Model),再定义第三张表作为M2M的联系表。虽然可以用(db.Model) type,而且本地sqlite没问题。但部署到Heroku postgressql(psycopg)上就出错:
2017-10-03T13:09:08.233301+00:00 app[web.1]: [2017-10-03 13:09:08,222] ERROR in app: Exception on /admin/user/edit/ [GET]
2017-10-03T13:09:08.233312+00:00 app[web.1]: Traceback (most recent call last):
2017-10-03T13:09:08.233314+00:00 app[web.1]: File "/app/.heroku/python/lib/python3.6/site-packages/flask/app.py", line 1982, in wsgi_app
2017-10-03T13:09:08.233315+00:00 app[web.1]: response = self.full_dispatch_request()
...
2017-10-03T13:09:08.233853+00:00 app[web.1]: File "/app/.heroku/python/lib/python3.6/site-packages/flask_admin/contrib/sqla/fields.py", line 169, in
iter_choices
2017-10-03T13:09:08.233854+00:00 app[web.1]: yield (pk, self.get_label(obj), obj in self.data)
2017-10-03T13:09:08.233916+00:00 app[web.1]: TypeError: argument of type 'AppenderBaseQuery' is not iterable
查了很久,后来发现,把联系表,db.Model改成db.Table定义就好了!
查询 http://pythoncentral.io/sqlalchemy-faqs/
#To find all the employees in the IT department, we can write it in ORM:
s.query(Employee).filter(Employee.departments.any(Department.name == 'IT')).one().name
#To find marry, i.e., all the employees who belong to at least two departments, we use group_by and having in an ORM query:
from sqlalchemy import func
s.query(Employee).join(Employee.departments).group_by(Employee.id).having(func.count(Department.id) > 1).one().name
http://docs.sqlalchemy.org/en/latest/orm/query.html#sqlalchemy.orm.query.Query
Multiple criteria may be specified as comma separated; the effect is that they will be joined together using the and_() function:
session.query(MyClass).\ filter(MyClass.name == 'some name', MyClass.id > 5)
session.query(MyClass).\
filter_by(name = 'some name', id = 5)
Model:
String to Model对象:
sort = eval('Ob.%s.%s()' % (sort_field, sort_order))
Table对象,使用paginate:
pagination = Ob.query.filter(or_(Ob.tag_gf==True, Ob.tag_gffbz==True)).
filter(and_(Ob.ob_seeding.contains(u),not_(Ob.ourbits_ac.contains(u)), not_(Ob.ourbits_as.contains(u)))).\ order_by(sort).paginate(page=int(paras['page']),per_page=int(paras['per_page']),error_out=False)
查找某User做种的种子Ob,一并返回第三表的某些列:
(这时,可以选择三张表的任意字段排序order_by)
(注1:这里用了join()+group_by(),只会返回联结表里有值的Ob行。如果想返回所有的Ob行,则用outerjoin(),这样即可以用第三表排序,又不会漏掉联结表里无值的Ob行)
(注2:Postgres比MySQL、SQLite严格,很多你本地调试成功的SQL语句,部署到postgres会报错。比如:Group_by时,会强制把你query的所有表或字段,都需要加进来。)
ss.query(Ob.id).join(ourbits_users, User).filter(User.ob_username=='kevinqqnj').group_by(Ob.id).add_columns(User.ob_username, ourbits_users.c.download_size, ourbits_users.c.download_duration).all()
[(56229, 'kevinqqnj', 9.71, ''), (56335, 'kevinqqnj', 4.98, ''), (56369, 'kevinqqnj', 36.61, ''), (61, 'kevinqqnj', 47.7, '')]
查找User和联结表ourbits_users,所有有种子下载<50的User
ss.query(User).join(ourbits_users).group_by(User.id).having(ourbits_users.c.download_size<50).all()
[, ]
查找种子,绑定联结表ourbits_users,所有种子大小>5的Ob,一并返回第三表的某些列
ss.query(Ob).join(ourbits_users).group_by(Ob.id).having(ourbits_users.c.download_size>5).add_columns(ourbits_users.c.download_size, ourbits_users.c.download_duration).first()
(, 47.7, '')
查找种子,哪些有多于一人做种(ourbits_users.c.user_id)的:
ss.query(Ob).join(ourbits_users).group_by(Ob.id).having(func.count(ourbits_users.c.user_id)>1).add_columns(ourbits_users.c.download_size, ourbits_users.c.download_duration).all()
[(, 0.0, ''), (, 0.0, '')]
求和:某个User,所有认领种子的总大小:
ss.query(func.sum(Ob.size_f), User).group_by(User.id).filter(ourbits_users_ac.c.ourbits_id==Ob.id, ourbits_users_ac.c.user_id==User.id).all()
[(1364.7000000000005, ), (223.86, )]
Testing:
注意:测试时,如果Postgres报错
sqlalchemy.exc.InternalError: (psycopg2.InternalError) current transaction is aborted, commands ignored until end of transaction block
当前Shell环境下,必须重启Session,不然,不能执行query!!
ss.close()
ss = db.session()
Table:
Table 操作:insert(), update(), select(), delete()
db.session.execute(ourbits_users.delete()) # ==> delete all
db.session.commit()
db.session.query(ourbits_users_as).paginate()
#
db.session.query(ourbits_users_as).filter_by(ourbits_id=60147).paginate().items
db.session.execute(ourbits_users_as.select().order_by(ourbits_users_as.c.ourbits_id.desc())).fetchall()
# [(1, 60150, None), (1, 60149, None), (1, 60148, None), (1, 60147, None), (1, 60146, None)]