原创内容,转载请注明出处:
http://www.jianshu.com/p/0e6eb2f9ed5d
前言
上一篇的时候一直说要把runtime说一遍,后来一直没时间耽误下来了。现在马上要换工作了,腾出时间了,可以把这些东西再过一遍了,一方面做一下复习,另外也还一下以前欠下的嘴债。毕竟,出来混早晚是都要还的。
相信现在还有好多朋友不知道runtime,或者说不太理解,不太会用等等。
总之一句话就是还是用不666,不要紧,看完下面这篇应该就可以用6了。
在这里先放上runtime的源码和runtime官方api:
源码:objc-runtime
官方API:Objective-C Runtime Reference
所谓的runtime,就是运行时。。。
不知道这么说会不会有人打我,并说我废话,但是从字面上理解并没有什么毛病。我们都知道oc是动态语言,所谓的动态语言就是指程序在运行时可以改变其结构:新的函数可以被引进,已有的函数可以被删除等在结构上的变化。的语言。因为它可以在程序执行过程中对类或者变量等等做操作,而不是代码写完了,程序就定型了。
而iOS中的runtime就是可以实现语言动态的一组API.
你可以理解:它就仅仅是一组API而已。
只是这组API看起来比oc长得不太一样,见的少了会觉得它们比较混乱,乱起八糟的。
现在还不会runtime基本上可以归结为下面两条原因:
- 对runtime的api不熟
- 对api的各个部分关系不太熟
看过了这篇,大家应该都没什么问题了。
废话不多说了,开始实质性的东西吧!
runtime的所有知识基本都围绕两个中心(1)类的各个方面的动态配置(2)消息传递
要动态配置类就需要知道类的本质是什么,我们可以从
struct objc_class {
Class isa OBJC_ISA_AVAILABILITY;
#if !__OBJC2__
Class super_class;//父类
const char *name;//类名
long version;//类的版本信息,默认为0
long info;//类信息,供运行期使用的一些位标识
long instance_size;//类的实例变量大小
struct objc_ivar_list *ivars;// 类的成员变量链表
struct objc_method_list **methodLists;// 方法链表
struct objc_cache *cache;//方法缓存
struct objc_protocol_list *protocols;//协议链表
#endif
} OBJC2_UNAVAILABLE;
isa和super_class
不同的类中可以有相同的方法,同一个类中不可以有相同的方法,判断是不是同一个方法只和方法名有关系,和参数没关系。
比如说:
-(void)tableView:(UITableView *)tableView didSelectRowAtIndexPath:(NSIndexPath *)indexPath{}
的方法名为
@selector(tableView:canEditRowAtIndexPath:)
可见方法名里面并没有体现参数的位置,所以是否是同一个方法取决于方法名是否相同,和参数没关系。
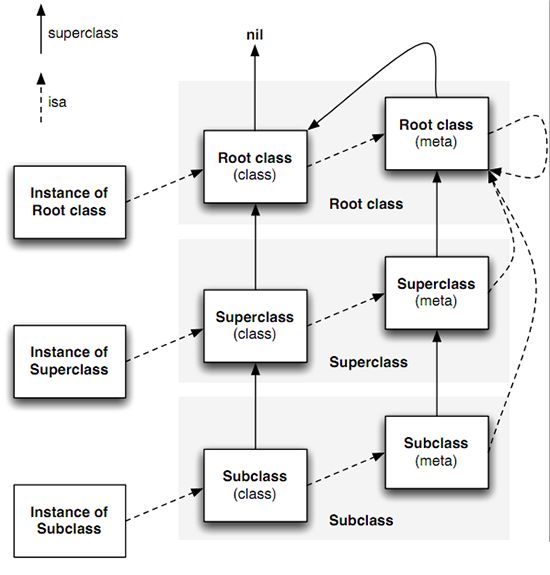
要找到方法首先要先确定是那个类。isa和super_class是找到实现函数的关键映射,决定找到存放在哪个类的方法实现。(isa用于自省确定所属类,super_class确定继承关系)。
实例对象的isa指针指向类,类的isa指针指向其元类(metaClass)。对象就是一个含isa指针的结构体。类存储实例对象的方法列表,元类存储类的方法列表,元类也是类对象。
当创建实例对象时,分配的内存包含一个objc_object数据结构,然后是类到父类直到根类NSObject的实例变量的数据。NSObject类的alloc和allocWithZone:方法使用函数class_createInstance来创建objc_object数据结构。
向一个Objective-C对象发送消息时,运行时库会根据实例对象的isa指针找到这个实例对象所属的类。Runtime库会在类的方法列表由super_class指针找到父类的方法列表直至根类NSObject中去寻找与消息对应的selector指向的方法。找到后即运行这个方法。
- isa:实例对象->类->元类->(不经过父元类)直接到根元类(NSObject的元类),根元类的isa指向自己;
- superclass:类->父类->...->根类NSObject,元类->父元类->...->根元类->根类,NSObject的superclass指向nil。
在正式学习runtime之前你需要知道的
属性概念
- SEL:类成员方法的指针,但不同于C语言中的函数指针,函数指针直接保存了方法的地址,但SEL只是方法编号。
- IMP:一个函数指针,保存了方法的地址
- Method:方法的结构体,其中保存了方法的名字,实现和类型描述字符串
代码
//在runtime.h里面我们可以看到定义
//Method 是一个方法结构体的指针
typedef struct objc_method *Method;
//方法的结构体包含了方法需要的信息
struct objc_method {
SEL method_name;
char *method_types;//方法返回值,和各个参数类型等的字符串描述
IMP method_imp;
}
//根据函数获取函数的SEL
@selector()
//获取函数指针SEL的函数名字符串
NSString *NSStringFromSelector(SEL aSelector);
//根据函数名获取函数指针
SEL NSSelectorFromString(NSString *aSelectorName);
//获取类Class的字符串描述
NSString *NSStringFromClass(Class aClass);
//根据类的字符串描述获取类Class
Class _Nullable NSClassFromString(NSString *aClassName);
//获取协议的字符串描述(协议名字)
NSString *NSStringFromProtocol(Protocol *proto)
//根据协议名字获取协议对象
Protocol * _Nullable NSProtocolFromString(NSString *namestr)
上面的方法我平时用到的频率还不算太低,在这里就暂时不实际跑一下了。知道了上面的那些平常还有些频率用到的函数或概念,那么接下来学习runtime就有些轻松了。
下面会用到的编码值
//下面对应的编码值可以在官方文档里面找到
//编码值 含意
//c 代表char类型
//i 代表int类型
//s 代表short类型
//l 代表long类型,在64位处理器上也是按照32位处理
//q 代表long long类型
//C 代表unsigned char类型
//I 代表unsigned int类型
//S 代表unsigned short类型
//L 代表unsigned long类型
//Q 代表unsigned long long类型
//f 代表float类型
//d 代表double类型
//B 代表C++中的bool或者C99中的_Bool
//v 代表void类型
//* 代表char *类型
//@ 代表对象类型
//# 代表类对象 (Class)
//: 代表方法selector (SEL)
//[array type] 代表array
//{name=type…} 代表结构体
//(name=type…) 代表union
//bnum A bit field of num bits
//^type A pointer to type
//? An unknown type (among other things, this code is used for function pointers)
(语法&API)class-get
//获取类名
//入参:类Class
//返回:类名char数组
const char *class_getName(Class cls)
//获取父类
//入参:类Class
//返回:类Class
Class class_getSuperclass(Class cls)
//获取实例大小(返回size_t)
//入参:实例的类Class
//返回:大小size_t
//深究请看这篇文章http://www.jianshu.com/p/df6b252fbaae
size_t class_getInstanceSize(Class cls)
//获取类中指定名称实例成员变量的信息
//入参:类Class,变量名
//返回:变量信息Ivar
//* 1.实例变量是指变量不是属性.例如某类有个属性为:username 那么它对应的实例变量为_username
//* 2.这个方法可以获取属性的变量,也可以获取私有变量(这点很重要)
//* 3.如果获取的变量为空,那么 ivar_getName和 ivar_getTypeEncoding 获取的值为空,那么[NSString stringWithUTF8String:ivar1Name] 执行崩溃
Ivar class_getInstanceVariable(Class cls, const char *name)
//类成员变量的信息
//入参:类Class,变量名char数组
//返回:Ivar
//* 1.目前没有找到关于Objective-C中类变量的信息,一般认为Objective-C不支持类变量。注意,返回的列表不包含父类的成员变量和属性。
Ivar class_getClassVariable(Class cls, const char *name)
//获取指定的属性
//入参:类Class,属性名char数组
//返回:属性objc_property_t
// * 1.属性不是变量,此方法只能获取属性
// * 2.如果属性不存在那么返回的结构体为0(可以参考下面的判断)
// * 3.属性不存在获取property_getName 和 property_getAttributes 会崩溃
objc_property_t class_getProperty(Class cls, const char *name)
//获取方法实现
//入参:类Class,方法名SEL
//返回:方法实现IMP
IMP class_getMethodImplementation(Class cls, SEL name)
//获取方法实现
//入参:类Class,方法名SEL
//返回:方法实现IMP
IMP class_getMethodImplementation_stret(Class cls, SEL name)
//获取类方法
//入参:类Class,方法名SEL
//返回:方法Method
Method class_getClassMethod(Class cls, SEL name)
(以上API的)运行测试代码地址在这里:TFRumtimeAll:demo-runtime-part0
#import
@interface ViewController ()
@property (nonatomic,strong)NSArray *property0;
@end
@implementation ViewController
- (void)viewDidLoad {
[super viewDidLoad];
//获取类名
//入参:类Class
//返回:类名char数组
const char *result0 = class_getName([ViewController class]);
NSLog(@">>>>>>>>0:%@",[NSString stringWithUTF8String:result0]);
//获取父类
//入参:类Class
//返回:类Class
Class result1 = class_getSuperclass([ViewController class]);
NSLog(@">>>>>>>>1:%@",result1);
//获取实例大小(返回size_t)
//入参:实例的类Class
//返回:大小size_t
//深究请看这篇文章http://www.jianshu.com/p/df6b252fbaae
size_t result2 = class_getInstanceSize([ViewController class]);
NSLog(@">>>>>>>>2:%zu",result2);
//获取类中指定名称实例成员变量的信息
//入参:类Class,变量名
//返回:变量信息Ivar
//* 1.实例变量是指变量不是属性.例如某类有个属性为:username 那么它对应的实例变量为_username
//* 2.这个方法可以获取属性的变量,也可以获取私有变量(这点很重要)
//* 3.如果获取的变量为空,那么 ivar_getName和 ivar_getTypeEncoding 获取的值为空,那么[NSString stringWithUTF8String:ivar1Name] 执行崩溃
const char *result3 = [@"property0" UTF8String];
Ivar result4 = class_getInstanceVariable([ViewController class], result3);
NSLog(@">>>>>>>>3:%@",result4);
//获取指定的属性
//入参:类Class,属性名char数组
//返回:属性objc_property_t
// * 1.属性不是变量,此方法只能获取属性
// * 2.如果属性不存在那么返回的结构体为0(可以参考下面的判断)
// * 3.属性不存在获取property_getName 和 property_getAttributes 会崩溃
const char *result5 = [@"property0" UTF8String];
objc_property_t result6 = class_getProperty([ViewController class], result5);
NSLog(@">>>>>>>>4:%@",[NSString stringWithUTF8String:property_getName(result6)]);
//获取方法实现
//入参:类Class,方法名SEL
//返回:方法实现IMP
IMP result7 = class_getMethodImplementation([ViewController class], @selector(method0));
result7();
//获取方法实现
//入参:类Class,方法名SEL
//返回:方法实现IMP
IMP result8 = class_getMethodImplementation_stret([ViewController class], @selector(method1));
result8();
//获取类方法
//入参:类Class,方法名SEL
//返回:方法Method
Method result9 = class_getClassMethod([ViewController class], @selector(viewDidLoad));
NSLog(@">>>>>>>>7:%@",result9);
}
-(void)method0{
NSLog(@">>>>>>>>5");
}
-(void)method1{
NSLog(@">>>>>>>>6");
}
@end
(以上运行测试的)打印结果
demo-runtime-part0[984:85403] >>>>>>>>0:ViewController
demo-runtime-part0[984:85403] >>>>>>>>1:UIViewController
demo-runtime-part0[984:85403] >>>>>>>>2:768
demo-runtime-part0[984:85403] >>>>>>>>3:(null)
demo-runtime-part0[984:85403] >>>>>>>>4:property0
demo-runtime-part0[984:85403] >>>>>>>>5
demo-runtime-part0[984:85403] >>>>>>>>6
demo-runtime-part0[984:85403] >>>>>>>>7:(null)
(以上打印结果的)解析
#从上面的测试我们可以发现各个函数的作用:
###class_getName:
获取类的字符串描述,由此我们可以想到上面提到的一个OC方法:NSStringFromClass(),这个方法和此函数的作用是一样的。
那么我们可以猜想NSStringFromClass()的上层实现是runtime的class_getName函数(有兴趣的朋友可以反编译验证一下)。
###class_getSuperclass:
获取某个类的父类。同理我们可以想到NSObject里面有个属性:
@property (readonly) Class superclass;那么这个属性的get方法也可能是调用的此函数。
###class_getInstanceSize:
获取实例大小,单位是字节。这个函数暂时不着重说了。有时间可以和其他几个不常用的函数单独细说一下。
###class_getInstanceVariable:
获取实例的变量。在上面打印3我们看到获取到的是nil。从代码中我们命名定义了:
@property (nonatomic,strong)NSArray *property0;
但是为什么找不到?是因为此函数获取的是变量,上面的属性对应的变量是_property0所以以property0变量名找是找不到的。
需要强调的是,此函数可以找到任何属于这个类的变量,包括分类添加的变量,程序动态添加的变量等。
###class_getProperty:
获取类属性。注意这里是属性,不是变量。此函数只能获取类的属性。
该函数返回是是objc_property_t结构体。上面demo代码里面用到了函数:property_getName,这个函数的是获取属性名,下面会说到
###class_getMethodImplementation:
###class_getMethodImplementation_stret:
获取函数的实现。返回函数的实现指针IMP.
从上面代码看到我们获取了method0和method1的函数实现并result7();result8();执行了两个函数,并且函数得到了执行。
###class_getClassMethod:
获取类方法Method结构体。从runtime.h源码里可以找到源码:
typedef struct objc_method *Method;
struct objc_method {
SEL method_name;
char *method_types;
IMP method_imp;
}
总结:
- 从上面部分runtime API可以看出,iOS中所谓的runtime.h只是一组c语音的api,它用的c语言的语法,可以做一些OC做不到的功能.
-
它的语法有一定的规律,这点很重要。比如你可以使用xcode的智能提示,如下图:
知道了上面的规律,那接下来学就方便多了。继续往下看:
class-copy
//获取变量列表
//入参:类Class,int变量指针
//返回:变量信息Ivar列表
//* 1.获取所有私有变量和属性对应的变量
//* 2.获取的私有变量的名和定义的名一样
//* 3.获取的属性的名前面都添加了下划线
//* 4.不能获取Category添加的变量(动态绑定的变量)
Ivar *class_copyIvarList(Class cls, unsigned int *outCount)
//获取属性列表(只获取属性不获取变量)
//入参:类Class,int变量指针
//返回:属性信息objc_property_t列表
//* 1.获取所有属性
//* 2.获取的属性名和你代码写的一样,获取出来的属性名不自动添加下划线
//* 3.不能获取Category添加的属性。
objc_property_t *class_copyPropertyList(Class cls, unsigned int *outCount)
//获取方法列表
//入参:类Class,int变量指针
//返回:方法信息Method列表
//* 1.获取所有实例方法,不包含静态方法
//* 2.不获取父类的方法
//* 3.隐式的get set 方法也能获取到
//* 4.可以获取分类和动态添加的方法。
Method *class_copyMethodList(Class cls, unsigned int *outCount)
//获取协议列表
//入参:类Class,int变量指针
//返回:方法协议Protocol列表
//* 1.不能获取分类实现的协议
Protocol * __unsafe_unretained *class_copyProtocolList(Class cls, unsigned int *outCount)
(以上API的)运行测试代码地址在这里:TFRumtimeAll:demo-runtime-part1
#import "ViewController.h"
#import
@interface ViewController ()
{
NSArray *_property0;
NSArray *property1;
}
@property (nonatomic,strong)UIColor *property2;
@end
@implementation ViewController
- (void)viewDidLoad {
[super viewDidLoad];
//class获取--获取整个成员变量列表
/**
* 1.获取所有私有变量和属性
* 2.获取的私有变量的名和定义的名一模一样
* 3.获取的属性的名前面都添加了下划线
*/
unsigned int copyIvarListCount = 0;
Ivar *ivars = class_copyIvarList([self class], ©IvarListCount);
for (NSInteger i = 0; i< copyIvarListCount; i ++) {
Ivar ivar = ivars[i];
const char *name = ivar_getName(ivar);
NSLog(@">>>>>>>>0:class_copyIvarList:%s",name);
}
free(ivars);//释放
NSLog(@"\n");
//class获取--获取整个属性列表(只获取属性不获取变量)
/**
* 1.获取所有属性
* 2.获取的属性名和你代码写的一样,获取出来的属性名不自动添加下划线
*/
unsigned int copyPropertyListCount = 0;
objc_property_t *propertys = class_copyPropertyList([self class], ©PropertyListCount);
for (NSInteger i = 0; i < copyPropertyListCount; i++) {
objc_property_t property = propertys[i];
const char *name = property_getName(property);
NSLog(@">>>>>>>>1:copyPropertyList:%s",name);
}
free(propertys);//释放
NSLog(@"\n");
//class获取--获取整个类的实例方法的方法列表
/**
* 1.获取所有实例方法,不包含静态方法
* 2.不获取父类的方法
* 3.隐式的get set 方法也能获取到
*/
unsigned int copycopyMethodListCount = 0;
Method *methods = class_copyMethodList([self class], ©copyMethodListCount);
for (NSInteger i = 0; i < copycopyMethodListCount; i++) {
Method method = methods[i];
SEL name = method_getName(method);
NSLog(@">>>>>>>>2:copyMethodList:%@",NSStringFromSelector(name));
}
free(methods);//释放
NSLog(@"\n");
//添加--协议
/**
* 1.class_addProtocol 参数含义:第一个:要添加协议的类,第二个:协议对象
* 2.获取协议列表具体细节参照Class1里的内容
*/
unsigned int copyProtocolListCount = 0;
Protocol * __unsafe_unretained *protocals = class_copyProtocolList([self class], ©ProtocolListCount);
for (NSInteger i = 0; i < copyProtocolListCount; i++) {
Protocol * protocal = protocals[i];
const char *name = protocol_getName(protocal);
NSLog(@">>>>>>>>3:copyProtocolList:%s",name);
}
free(protocals);//释放
NSLog(@"\n");
}
- (NSInteger)tableView:(UITableView *)tableView numberOfRowsInSection:(NSInteger)section{return 0;}
// Row display. Implementers should *always* try to reuse cells by setting each cell's reuseIdentifier and querying for available reusable cells with dequeueReusableCellWithIdentifier:
// Cell gets various attributes set automatically based on table (separators) and data source (accessory views, editing controls)
- (UITableViewCell *)tableView:(UITableView *)tableView cellForRowAtIndexPath:(NSIndexPath *)indexPath{return nil;}
- (void)didReceiveMemoryWarning {
[super didReceiveMemoryWarning];
// Dispose of any resources that can be recreated.
}
@end
(以上运行测试的)打印结果
demo-runtime-part1[3085:698841] >>>>>>>>0:class_copyIvarList:_property0
demo-runtime-part1[3085:698841] >>>>>>>>0:class_copyIvarList:property1
demo-runtime-part1[3085:698841] >>>>>>>>0:class_copyIvarList:_property2
demo-runtime-part1[3085:698841]
demo-runtime-part1[3085:698841] >>>>>>>>1:copyPropertyList:property2
demo-runtime-part1[3085:698841] >>>>>>>>1:copyPropertyList:hash
demo-runtime-part1[3085:698841] >>>>>>>>1:copyPropertyList:superclass
demo-runtime-part1[3085:698841] >>>>>>>>1:copyPropertyList:description
demo-runtime-part1[3085:698841] >>>>>>>>1:copyPropertyList:debugDescription
demo-runtime-part1[3085:698841]
demo-runtime-part1[3085:698841] >>>>>>>>2:copyMethodList:property2
demo-runtime-part1[3085:698841] >>>>>>>>2:copyMethodList:setProperty2:
demo-runtime-part1[3085:698841] >>>>>>>>2:copyMethodList:.cxx_destruct
demo-runtime-part1[3085:698841] >>>>>>>>2:copyMethodList:tableView:numberOfRowsInSection:
demo-runtime-part1[3085:698841] >>>>>>>>2:copyMethodList:tableView:cellForRowAtIndexPath:
demo-runtime-part1[3085:698841] >>>>>>>>2:copyMethodList:didReceiveMemoryWarning
demo-runtime-part1[3085:698841] >>>>>>>>2:copyMethodList:viewDidLoad
demo-runtime-part1[3085:698841]
demo-runtime-part1[3085:698841] >>>>>>>>3:copyProtocolList:UITableViewDelegate
demo-runtime-part1[3085:698841] >>>>>>>>3:copyProtocolList:UITableViewDataSource
demo-runtime-part1[3085:698841]
(以上打印结果的)解析
#从上面的测试我们可以发现各个函数的作用:
###class_copyIvarList:
拷贝变量列表。返回的一个Ivar列表的指针。获取Ivar需要遍历这个列表。
注意:调用copy的函数需要释放资源free();
###class_copyPropertyList:
拷贝属性列表。返回的一个objc_property_t列表的指针。获取objc_property_t需要遍历这个列表。
注意:调用copy的函数需要释放资源free();
###class_copyMethodList:
拷贝方法列表。返回的一个Method列表的指针。获取Method需要遍历这个列表。
注意:调用copy的函数需要释放资源free();
此函数可以获取分类方法。
###class_copyProtocolList:
拷贝协议列表。返回的一个Ivar列表的指针。获取Ivar需要遍历这个列表。
注意:调用copy的函数需要释放资源free();
此函数不能获取分类中添加的协议。
此函数可以获取动态添加的协议。
class-add
//动态添加变量
//入参:类Class,变量名char数组,变量类型大小size_t,变量在内存中的对齐方式,变量的type类型
//返回:添加结果,是否成功。
//* 1.只能给动态创建的类添加变量也就是用 objc_allocateClassPair 创建的类
//* 2.添加变量只能在函数 objc_allocateClassPair 和 class_getInstanceVariable 之间添加才有效
BOOL class_addIvar(Class cls, const char *name, size_t size, uint8_t alignment, const char *types)
//动态添加方法
//入参:类Class,方法名SEL,方法实现IMP,方法返回值各个参数类型等配置字符串
//返回:添加结果,是否成功。
//* 1.添加属性不用再objc_registerClassPair之前,因为添加属性其实就是添加变量的set 和 get方法而已
//* 2.添加的属性和变量不能用kvc设置值和取值
BOOL class_addMethod(Class cls, SEL name, IMP imp, const char *types)
//动态添加协议
//入参:类Class,协议结构体Protocol
//返回:添加结果,是否成功。
BOOL class_addProtocol(Class cls, Protocol *protocol)
//动态添加属性
//入参:类Class,属性名char数组,属性的配置属性,objc_property_attribute_t,属性的属性数量。
//返回:添加结果,是否成功。
BOOL class_addProperty(Class cls, const char *name, const objc_property_attribute_t *attributes, unsigned int attributeCount)
(以上API的)运行测试代码地址在这里:TFRumtimeAll:demo-runtime-part2
#import "ViewController.h"
#import
@interface ViewController ()
{
NSArray *_property0;
NSArray *property1;
}
@property (nonatomic,strong)UIColor *property2;
@end
@implementation ViewController
//get方法
NSString *attribute0Getter(id classInstance, SEL _cmd) {
Ivar ivar = class_getInstanceVariable([classInstance class], "_attribute0");//获取变量,如果没获取到说明不存在
return object_getIvar(classInstance, ivar);
}
//set方法
void attribute0Setter(id classInstance, SEL _cmd, NSString *newName) {
Ivar ivar = class_getInstanceVariable([classInstance class], "_attribute0");//获取变量,如果没获取到说明不存在
id oldName = object_getIvar(classInstance, ivar);
if (oldName != newName) object_setIvar(classInstance, ivar, [newName copy]);
}
- (void)viewDidLoad {
[super viewDidLoad];
//添加--为动态创建类添加变量
/**
* 1.只能给动态创建的类添加变量也就是用 objc_allocateClassPair 创建的类
* 2.添加变量只能在函数 objc_allocateClassPair 和 class_getInstanceVariable 之间添加才有效
*/
Class CreatClass0 = objc_allocateClassPair([NSObject class], "CreatClass0", 0);
class_addIvar(CreatClass0, "_attribute0", sizeof(NSString *), log(sizeof(NSString *)), "i");
Ivar ivar = class_getInstanceVariable(CreatClass0, "_attribute0");//获取变量,如果没获取到说明不存在
NSLog(@">>>>>>>>0:%@",[NSString stringWithUTF8String:ivar_getName(ivar)]);
objc_registerClassPair(CreatClass0);
NSLog(@"\n");
//添加--为动态创建的类添加变量然后添加属性,类和变量和属性都是动态创建的
/**
* 1.各个属性:暂时不知道
* 2.下面这个反驳了上面的第二标,这个证明id不是不会报错,规律是如果id调用的是系统的类的方法,那么就不会报错,
详细介绍:上面的@selector(name) 和 @selector(setName:) name是好多系统类都有方法,所以id会认为本身代表的是那个类
所以不会报错,但是如果你硬写一个完全没有的方法,它就会报错
* 3.添加属性不用再objc_registerClassPair之前,因为添加属性其实就是添加变量的set 和 get方法而已
* 4.添加的属性和变量不能用kvc设置值和取值
*/
objc_property_attribute_t type2 = { "T", "@\"NSString\"" };
objc_property_attribute_t ownership2 = { "C", "" }; // C = copy
objc_property_attribute_t backingivar2 = { "V", "_attribute0" };
objc_property_attribute_t attrs2[] = { type2, ownership2, backingivar2 };
class_addProperty(CreatClass0, "_attribute0", attrs2, 3);
SEL getter = NSSelectorFromString(@"attribute0");
SEL setter = NSSelectorFromString(@"setAttribute0:");
BOOL suc0 = class_addMethod(CreatClass0, getter, (IMP)attribute0Getter, "@@:");
BOOL suc1 = class_addMethod(CreatClass0, setter, (IMP)attribute0Setter, "v@:@");
NSLog(@">>>>>>>>3:%@:%@",@(suc0),@(suc1));
id idclass = [[CreatClass0 alloc]init];
NSLog(@">>>>>>>>1:%@",[idclass performSelector:getter withObject:nil]);
[idclass performSelector:setter withObject:@"为动态创建类先添加变量再添加属性"];
NSLog(@">>>>>>>>2:%@",[idclass performSelector:getter withObject:nil]);
//class获取--获取整个类的实例方法的方法列表
/**
* 1.获取所有实例方法,不包含静态方法
* 2.不获取父类的方法
* 3.隐式的get set 方法也能获取到
* 4.关于Method的更多用法参考Class2类
*/
unsigned int copycopyMethodListCount = 0;
Method *methods = class_copyMethodList([self class], ©copyMethodListCount);
for (NSInteger i = 0; i < copycopyMethodListCount; i++) {
Method method = methods[i];
SEL name = method_getName(method);
NSLog(@">>>>>>>>2:copyMethodList:%@",NSStringFromSelector(name));
}
free(methods);//释放
NSLog(@"\n");
BOOL result0 = class_addProtocol([self class], NSProtocolFromString(@"UITableViewDelegate"));
NSLog(@">>>>>>>>3:添加协议成功");
//添加--协议
/**
* 1.class_addProtocol 参数含义:第一个:要添加协议的类,第二个:协议对象
* 2.获取协议列表具体细节参照Class1里的内容
*/
unsigned int copyProtocolListCount = 0;
Protocol * __unsafe_unretained *protocals = class_copyProtocolList([self class], ©ProtocolListCount);
for (NSInteger i = 0; i < copyProtocolListCount; i++) {
Protocol * protocal = protocals[i];
const char *name = protocol_getName(protocal);
NSLog(@">>>>>>>>4:copyProtocolList:%s",name);
}
free(protocals);//释放
NSLog(@"\n");
}
- (NSInteger)tableView:(UITableView *)tableView numberOfRowsInSection:(NSInteger)section{return 0;}
// Row display. Implementers should *always* try to reuse cells by setting each cell's reuseIdentifier and querying for available reusable cells with dequeueReusableCellWithIdentifier:
// Cell gets various attributes set automatically based on table (separators) and data source (accessory views, editing controls)
- (UITableViewCell *)tableView:(UITableView *)tableView cellForRowAtIndexPath:(NSIndexPath *)indexPath{return nil;}
- (void)didReceiveMemoryWarning {
[super didReceiveMemoryWarning];
// Dispose of any resources that can be recreated.
}
@end
(以上运行测试的)打印结果
demo-runtime-part2[3439:758345] >>>>>>>>0:_attribute0
demo-runtime-part2[3439:758345]
demo-runtime-part2[3439:758345] >>>>>>>>3:1:1
demo-runtime-part2[3439:758345] >>>>>>>>1:(null)
demo-runtime-part2[3439:758345] >>>>>>>>2:为动态创建类先添加变量再添加属性
demo-runtime-part2[3439:758345] >>>>>>>>2:copyMethodList:property2
demo-runtime-part2[3439:758345] >>>>>>>>2:copyMethodList:setProperty2:
demo-runtime-part2[3439:758345] >>>>>>>>2:copyMethodList:.cxx_destruct
demo-runtime-part2[3439:758345] >>>>>>>>2:copyMethodList:tableView:numberOfRowsInSection:
demo-runtime-part2[3439:758345] >>>>>>>>2:copyMethodList:tableView:cellForRowAtIndexPath:
demo-runtime-part2[3439:758345] >>>>>>>>2:copyMethodList:didReceiveMemoryWarning
demo-runtime-part2[3439:758345] >>>>>>>>2:copyMethodList:viewDidLoad
demo-runtime-part2[3439:758345]
demo-runtime-part2[3439:758345] >>>>>>>>3:添加协议成功
demo-runtime-part2[3439:758345] >>>>>>>>4:copyProtocolList:UITableViewDelegate
demo-runtime-part2[3439:758345] >>>>>>>>4:copyProtocolList:UITableViewDataSource
demo-runtime-part2[3439:758345]
(以上打印结果的)解析
#从上面的测试我们可以发现各个函数的作用:
###class_addIvar:
添加变量。添加属性的具体解释和调用注意点上面备注已经写的很清楚。
从打印结果可以看出我们添加属性已经成功。
上面代码中涉及到两个函数objc_allocateClassPair和objc_registerClassPair这两个函数我们后面会继续说。
###class_addProperty:
添加属性。这个函数比较复杂,用到的频率也比较低。有兴趣的朋友可以参考官方文档。
###class_addMethod:
添加方法。这个函数还是比较重要的,后面说几个runtime的几个应用实例会用的到,更多用法也可以去看一下JSPatch源码。
该函数一共需要四个参数,前三个分别是:要添加方法的类,方法名,方法实现。
第四个函数的字符串:
get方法:第一个个@代表返回的类型为非基本数据类型,如果返回的数据是int那么第一个字符应该为i
set方法:第一个个v代表返回的类型为void,如果返回的数据是int那么第一个字符应该为i,最后一个@代表函数的第一个试用参数类型为非基本数据类型
set和get方法的共同部分是@:分别代表方法的两个默认函数target和SEL。
###class_addProtocol:
添加协议。这个函数比较简单,具体上面代码注释已经详细说过了。
class-replace
//属性替换
//入参:
//返回:char数组
//低平率函数,有兴趣的可以看官方文档https://developer.apple.com/reference/objectivec/objective_c_runtime
void class_replaceProperty(Class cls, const char *name, const objc_property_attribute_t *attributes, unsigned int attributeCount)
//方法替换
//入参:要替换方法所在的类Class, 要替换的方法名SEL,方法的实现,方法的描述字符串
//返回:char数组
IMP class_replaceMethod(Class cls, SEL name, IMP imp, const char *types)
(以上API的)运行测试代码地址在这里:TFRumtimeAll:demo-runtime-part3
#import "ViewController.h"
#import
@interface ViewController ()
@end
@implementation ViewController
- (void)viewDidLoad {
[super viewDidLoad];
// Do any additional setup after loading the view, typically from a nib.
[self method0];
BOOL result0 = class_replaceMethod([self class], @selector(method0), (IMP)method1, NULL);
NSLog(@">>>>>>>>2:%@",@(result0));
[self method0];
}
-(void)method0{
NSLog(@">>>>>>>>0");
}
void method1(){
NSLog(@">>>>>>>>1");
}
- (void)didReceiveMemoryWarning {
[super didReceiveMemoryWarning];
// Dispose of any resources that can be recreated.
}
@end
(以上运行测试的)打印结果
demo-runtime-part3[4256:976005] >>>>>>>>0
demo-runtime-part3[4256:976005] >>>>>>>>2:1
demo-runtime-part3[4256:976005] >>>>>>>>1
(以上打印结果的)解析
#从上面的测试我们可以发现各个函数的作用:
###class_replaceMethod:
从上面的代码可以看出。我们第一次调用了[self method0];然后把method0替换成了method1,当我再次调用method0的时候执行的是method1方法。
上面代码只是简单演示基本功能。更多的用法,后面会说几个应用实例。
在篇尾
程序员不需要打赏,只希望自己的项目能帮助更多人,请支持我的git开源框架:TFEasyCoder