nginx配置解释官网:http://nginx.org/en/docs/http/ngx_http_core_module.html#client_max_body_size
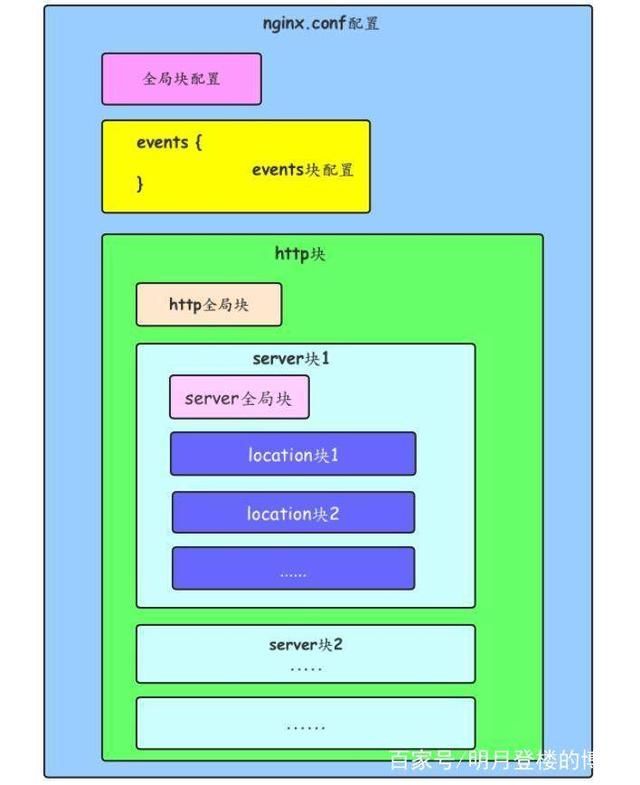
一、Nginx配置文件的整体结构
1.1、全局块
配置影响nginx全局的指令。主要包括:
- 配置运行Nginx服务器用户(组)
- worker process数
- Nginx进程
- PID存放路径错误日志的存放路径
- 配置文件的引入
1.2、events块
配置影响nginx服务器或与用户的网络连接。主要包括:
- 设置网络连接的序列化
- 是否允许同时接收多个网络连接
- 事件驱动模型的选择
- 最大连接数的配置
1.3、http块
可以嵌套多个server,配置代理,缓存,日志定义等绝大多数功能和第三方模块的配置。主要包括:
- 定义MIMI-Type
- 自定义服务日志
- 允许sendfile方式传输文件
- 连接超时时间
- 单连接请求数上限
1.4、server块
配置虚拟主机的相关参数,一个http中可以有多个server。主要包括:
- 配置网络监听
- 基于名称的虚拟主机配置
- 基于IP的虚拟主机配置
1.5、location块
配置请求的路由,以及各种页面的处理情况。主要包括:
- location配置
- 请求根目录配置更改
- location的URI
- 网站默认首页配置
1.6、配置清单例析
二、配置文件详解
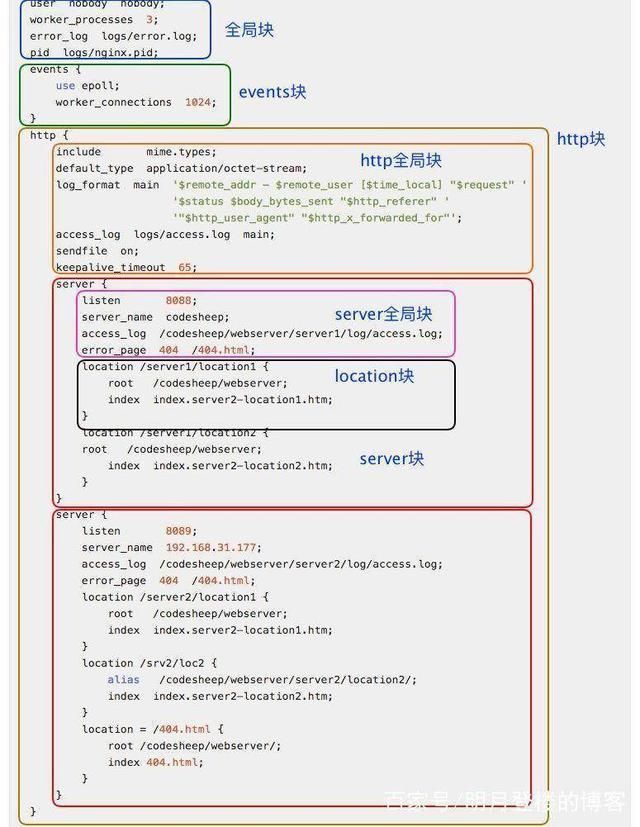
2.1 配置文件1
########### 每个指令必须有分号结束。################# #user administrator administrators; #配置用户或者组,默认为nobody nobody。 #worker_processes 2; #允许生成的进程数,默认为1 #pid /nginx/pid/nginx.pid; #指定nginx进程运行文件存放地址 error_log log/error.log debug; #制定日志路径,级别。这个设置可以放入全局块,http块,server块,级别以此为:debug|info|notice|warn|error|crit|alert|emerg events { accept_mutex on; #设置网路连接序列化,防止惊群现象发生,默认为on multi_accept on; #设置一个进程是否同时接受多个网络连接,默认为off #use epoll; #事件驱动模型,select|poll|kqueue|epoll|resig|/dev/poll|eventport worker_connections 1024; #最大连接数,默认为512 } http { include mime.types; #文件扩展名与文件类型映射表 default_type application/octet-stream; #默认文件类型,默认为text/plain #access_log off; #取消服务日志 log_format myFormat '$remote_addr–$remote_user [$time_local] $request $status $body_bytes_sent $http_referer $http_user_agent $http_x_forwarded_for'; #自定义格式 access_log log/access.log myFormat; #combined为日志格式的默认值 sendfile on; #允许sendfile方式传输文件,默认为off,可以在http块,server块,location块。 sendfile_max_chunk 100k; #每个进程每次调用传输数量不能大于设定的值,默认为0,即不设上限。 keepalive_timeout 65; #连接超时时间,默认为75s,可以在http,server,location块。 upstream mysvr { server 127.0.0.1:7878; server 192.168.10.121:3333 backup; #热备 } error_page 404 https://www.baidu.com; #错误页 server { keepalive_requests 120; #单连接请求上限次数。 listen 4545; #监听端口 server_name 127.0.0.1; #监听地址 location ~*^.+$ { #请求的url过滤,正则匹配,~为区分大小写,~*为不区分大小写。 #root path; #根目录 #index vv.txt; #设置默认页 proxy_pass http://mysvr; #请求转向mysvr 定义的服务器列表 deny 127.0.0.1; #拒绝的ip allow 172.18.5.54; #允许的ip } } }
2.2 配置文件2
#运行用户 user nobody; #启动进程,通常设置成和cpu的数量相等 worker_processes 1; #全局错误日志及PID文件 #error_log logs/error.log; #error_log logs/error.log notice; #error_log logs/error.log info; #pid logs/nginx.pid; #工作模式及连接数上限 events { #epoll是多路复用IO(I/O Multiplexing)中的一种方式, #仅用于linux2.6以上内核,可以大大提高nginx的性能 use epoll; #单个后台worker process进程的最大并发链接数 worker_connections 1024; # 并发总数是 worker_processes 和 worker_connections 的乘积 # 即 max_clients = worker_processes * worker_connections # 在设置了反向代理的情况下,max_clients = worker_processes * worker_connections / 4 为什么 # 为什么上面反向代理要除以4,应该说是一个经验值 # 根据以上条件,正常情况下的Nginx Server可以应付的最大连接数为:4 * 8000 = 32000 # worker_connections 值的设置跟物理内存大小有关 # 因为并发受IO约束,max_clients的值须小于系统可以打开的最大文件数 # 而系统可以打开的最大文件数和内存大小成正比,一般1GB内存的机器上可以打开的文件数大约是10万左右 # 我们来看看360M内存的VPS可以打开的文件句柄数是多少: # $ cat /proc/sys/fs/file-max # 输出 34336 # 32000 < 34336,即并发连接总数小于系统可以打开的文件句柄总数,这样就在操作系统可以承受的范围之内 # 所以,worker_connections 的值需根据 worker_processes 进程数目和系统可以打开的最大文件总数进行适当地进行设置 # 使得并发总数小于操作系统可以打开的最大文件数目 # 其实质也就是根据主机的物理CPU和内存进行配置 # 当然,理论上的并发总数可能会和实际有所偏差,因为主机还有其他的工作进程需要消耗系统资源。 # ulimit -SHn 65535 } http { #设定mime类型,类型由mime.type文件定义 include mime.types; default_type application/octet-stream; #设定日志格式 log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" ' '$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" ' '"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"'; access_log logs/access.log main; #sendfile 指令指定 nginx 是否调用 sendfile 函数(zero copy 方式)来输出文件, #对于普通应用,必须设为 on, #如果用来进行下载等应用磁盘IO重负载应用,可设置为 off, #以平衡磁盘与网络I/O处理速度,降低系统的uptime. sendfile on; #tcp_nopush on; #连接超时时间 #keepalive_timeout 0; keepalive_timeout 65; tcp_nodelay on; #开启gzip压缩 gzip on; gzip_disable "MSIE [1-6]."; #设定请求缓冲 client_header_buffer_size 128k; large_client_header_buffers 4 128k; #设定虚拟主机配置 server { #侦听80端口 listen 80; #定义使用 www.nginx.cn访问 server_name www.nginx.cn; #定义服务器的默认网站根目录位置 root html; #设定本虚拟主机的访问日志 access_log logs/nginx.access.log main; #默认请求 location / { #定义首页索引文件的名称 index index.php index.html index.htm; } # 定义错误提示页面 error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html; location = /50x.html { } #静态文件,nginx自己处理 location ~ ^/(images|javascript|js|css|flash|media|static)/ { #过期30天,静态文件不怎么更新,过期可以设大一点, #如果频繁更新,则可以设置得小一点。 expires 30d; } #PHP 脚本请求全部转发到 FastCGI处理. 使用FastCGI默认配置. location ~ .php$ { fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000; fastcgi_index index.php; fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME $document_root$fastcgi_script_name; include fastcgi_params; } #禁止访问 .htxxx 文件 location ~ /.ht { deny all; } } }
2.3 配置文件3
worker_processes 8; nginx进程数,建议设置为等于CPU总核心数. error_log /var/log/nginx/error.log info; 全局错误日志定义类型,[ debug | info | notice | warn | error | crit ] pid /var/run/nginx.pid; 进程文件 一个nginx进程打开的最多文件描述符数目,理论值应该是最多打开文件数(系统的值ulimit -n)与nginx进程数相除,但是nginx分配请求并不均匀,所以建议与ulimit -n的值保持一致。 worker_rlimit_nofile 65535; 工作模式与连接数上限 events { #参考事件模型,use [ kqueue | rtsig | epoll | /dev/poll | select | poll ]; epoll模型是Linux 2.6以上版本内核中的高性能网络I/O模型,如果跑在FreeBSD上面,就用kqueue模型。 use epoll; #单个进程最大连接数(最大连接数=连接数*进程数) worker_connections 65535; } 设定http服务器 http { include mime.types; #文件扩展名与文件类型映射表 default_type application/octet-stream; #默认文件类型 #charset utf-8; #默认编码 server_names_hash_bucket_size 128; #服务器名字的hash表大小 client_header_buffer_size 32k; #上传文件大小限制 large_client_header_buffers 4 64k; #设定请求缓 client_max_body_size 8m; #设定请求缓 sendfile on; #开启高效文件传输模式,sendfile指令指定nginx是否调用sendfile函数来输出文件,对于普通应用设为 on,如果用来进行下载等应用磁盘IO重负载应用,可设置为off,以平衡磁盘与网络I/O处理速度,降低系统的负载。注意:如果图片显示不正常把这个改成off。 autoindex on; #开启目录列表访问,合适下载服务器,默认关闭。 tcp_nopush on; #防止网络阻塞 tcp_nodelay on; #防止网络阻塞 keepalive_timeout 120; #长连接超时时间,单位是秒 #FastCGI相关参数是为了改善网站的性能:减少资源占用,提高访问速度。下面参数看字面意思都能理解。 fastcgi_connect_timeout 300; fastcgi_send_timeout 300; fastcgi_read_timeout 300; fastcgi_buffer_size 64k; fastcgi_buffers 4 64k; fastcgi_busy_buffers_size 128k; fastcgi_temp_file_write_size 128k; #gzip模块设置 gzip on; #开启gzip压缩输出 gzip_min_length 1k; #最小压缩文件大小 gzip_buffers 4 16k; #压缩缓冲区 gzip_http_version 1.0; #压缩版本(默认1.1,前端如果是squid2.5请使用1.0) gzip_comp_level 2; #压缩等级 gzip_types text/plain application/x-javascript text/css application/xml; #压缩类型,默认就已经包含text/html,所以下面就不用再写了,写上去也不会有问题,但是会有一个warn。 gzip_vary on; #limit_zone crawler $binary_remote_addr 10m; #开启限制IP连接数的时候需要使用 upstream blog.ha97.com { #upstream的负载均衡,weight是权重,可以根据机器配置定义权重。weigth参数表示权值,权值越高被分配到的几率越大。 server 192.168.80.121:80 weight=3; server 192.168.80.122:80 weight=2; server 192.168.80.123:80 weight=3; } 虚拟主机的配置 server { listen 80; #监听端口 server_name aa.cn www.aa.cn ; #server_name end #域名可以有多个,用空格隔开 index index.html index.htm index.php; # 设置访问主页 set $subdomain ''; # 绑定目录为二级域名 bbb.aa.com 根目录 /bbb 文件夹 if ( $host ~* "(?:(\w+\.){0,})(\b(?!www\b)\w+)\.\b(?!(com|org|gov|net|cn)\b)\w+\.[a-zA-Z]+" ) { set $subdomain "/$2"; } root /home/wwwroot/aa.cn/web$subdomain;# 访问域名跟目录 include rewrite/dedecms.conf; #rewrite end #载入其他配置文件 location ~ .*.(php|php5)?$ { fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000; fastcgi_index index.php; include fastcgi.conf; } #图片缓存时间设置 location ~ .*.(gif|jpg|jpeg|png|bmp|swf)$ { expires 10d; } #JS和CSS缓存时间设置 location ~ .*.(js|css)?$ { expiresexpires 1h; } } 日志格式设定 log_format access '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" ' '$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" ' '"$http_user_agent" $http_x_forwarded_for'; #定义本虚拟主机的访问日志 access_log /var/log/nginx/ha97access.log access; #对 "/" 启用反向代理 location / { proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1:88; proxy_redirect off; proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr; #后端的Web服务器可以通过X-Forwarded-For获取用户真实IP proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for; #以下是一些反向代理的配置,可选。 proxy_set_header Host $host; client_max_body_size 10m; #允许客户端请求的最大单文件字节数 client_body_buffer_size 128k; #缓冲区代理缓冲用户端请求的最大字节数, proxy_connect_timeout 90; #nginx跟后端服务器连接超时时间(代理连接超时) proxy_send_timeout 90; #后端服务器数据回传时间(代理发送超时) proxy_read_timeout 90; #连接成功后,后端服务器响应时间(代理接收超时) proxy_buffer_size 4k; #设置代理服务器(nginx)保存用户头信息的缓冲区大小 proxy_buffers 4 32k; #proxy_buffers缓冲区,网页平均在32k以下的设置 proxy_busy_buffers_size 64k; #高负荷下缓冲大小(proxy_buffers*2) proxy_temp_file_write_size 64k; #设定缓存文件夹大小,大于这个值,将从upstream服务器传 } 设定查看Nginx状态的地址 location /NginxStatus { stub_status on; access_log on; auth_basic "NginxStatus"; auth_basic_user_file conf/htpasswd; #htpasswd文件的内容可以用apache提供的htpasswd工具来产生。 } #本地动静分离反向代理配置 #所有jsp的页面均交由tomcat或resin处理 location ~ .(jsp|jspx|do)?$ { proxy_set_header Host $host; proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr; proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for; proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1:8080; } #所有静态文件由nginx直接读取不经过tomcat或resin location ~ .*.(htm|html|gif|jpg|jpeg|png|bmp|swf|ioc|rar|zip|txt|flv|mid|doc|ppt|pdf|xls|mp3|wma)$ { expires 15d; } location ~ .*.(js|css)?$ { expires 1h; } }
2.4 配置文件4
######Nginx配置文件nginx.conf中文详解##### #定义Nginx运行的用户和用户组 user www www; #nginx进程数,建议设置为等于CPU总核心数。 worker_processes 8; #全局错误日志定义类型,[ debug | info | notice | warn | error | crit ] error_log /usr/local/nginx/logs/error.log info; #进程pid文件 pid /usr/local/nginx/logs/nginx.pid; #指定进程可以打开的最大描述符:数目 #工作模式与连接数上限 #这个指令是指当一个nginx进程打开的最多文件描述符数目,理论值应该是最多打开文件数(ulimit -n)与nginx进程数相除,但是nginx分配请求并不是那么均匀,所以最好与ulimit -n 的值保持一致。 #现在在linux 2.6内核下开启文件打开数为65535,worker_rlimit_nofile就相应应该填写65535。 #这是因为nginx调度时分配请求到进程并不是那么的均衡,所以假如填写10240,总并发量达到3-4万时就有进程可能超过10240了,这时会返回502错误。 worker_rlimit_nofile 65535; events { #参考事件模型,use [ kqueue | rtsig | epoll | /dev/poll | select | poll ]; epoll模型 #是Linux 2.6以上版本内核中的高性能网络I/O模型,linux建议epoll,如果跑在FreeBSD上面,就用kqueue模型。 #补充说明: #与apache相类,nginx针对不同的操作系统,有不同的事件模型 #A)标准事件模型 #Select、poll属于标准事件模型,如果当前系统不存在更有效的方法,nginx会选择select或poll #B)高效事件模型 #Kqueue:使用于FreeBSD 4.1+, OpenBSD 2.9+, NetBSD 2.0 和 MacOS X.使用双处理器的MacOS X系统使用kqueue可能会造成内核崩溃。 #Epoll:使用于Linux内核2.6版本及以后的系统。 #/dev/poll:使用于Solaris 7 11/99+,HP/UX 11.22+ (eventport),IRIX 6.5.15+ 和 Tru64 UNIX 5.1A+。 #Eventport:使用于Solaris 10。 为了防止出现内核崩溃的问题, 有必要安装安全补丁。 use epoll; #单个进程最大连接数(最大连接数=连接数*进程数) #根据硬件调整,和前面工作进程配合起来用,尽量大,但是别把cpu跑到100%就行。每个进程允许的最多连接数,理论上每台nginx服务器的最大连接数为。 worker_connections 65535; #keepalive超时时间。 keepalive_timeout 60; #客户端请求头部的缓冲区大小。这个可以根据你的系统分页大小来设置,一般一个请求头的大小不会超过1k,不过由于一般系统分页都要大于1k,所以这里设置为分页大小。 #分页大小可以用命令getconf PAGESIZE 取得。 #[root@web001 ~]# getconf PAGESIZE #4096 #但也有client_header_buffer_size超过4k的情况,但是client_header_buffer_size该值必须设置为“系统分页大小”的整倍数。 client_header_buffer_size 4k; #这个将为打开文件指定缓存,默认是没有启用的,max指定缓存数量,建议和打开文件数一致,inactive是指经过多长时间文件没被请求后删除缓存。 open_file_cache max=65535 inactive=60s; #这个是指多长时间检查一次缓存的有效信息。 #语法:open_file_cache_valid time 默认值:open_file_cache_valid 60 使用字段:http, server, location 这个指令指定了何时需要检查open_file_cache中缓存项目的有效信息. open_file_cache_valid 80s; #open_file_cache指令中的inactive参数时间内文件的最少使用次数,如果超过这个数字,文件描述符一直是在缓存中打开的,如上例,如果有一个文件在inactive时间内一次没被使用,它将被移除。 #语法:open_file_cache_min_uses number 默认值:open_file_cache_min_uses 1 使用字段:http, server, location 这个指令指定了在open_file_cache指令无效的参数中一定的时间范围内可以使用的最小文件数,如果使用更大的值,文件描述符在cache中总是打开状态. open_file_cache_min_uses 1; #语法:open_file_cache_errors on | off 默认值:open_file_cache_errors off 使用字段:http, server, location 这个指令指定是否在搜索一个文件是记录cache错误. open_file_cache_errors on; } #设定http服务器,利用它的反向代理功能提供负载均衡支持 http { #文件扩展名与文件类型映射表 include mime.types; #默认文件类型 default_type application/octet-stream; #默认编码 #charset utf-8; #服务器名字的hash表大小 #保存服务器名字的hash表是由指令server_names_hash_max_size 和server_names_hash_bucket_size所控制的。参数hash bucket size总是等于hash表的大小,并且是一路处理器缓存大小的倍数。在减少了在内存中的存取次数后,使在处理器中加速查找hash表键值成为可能。如果hash bucket size等于一路处理器缓存的大小,那么在查找键的时候,最坏的情况下在内存中查找的次数为2。第一次是确定存储单元的地址,第二次是在存储单元中查找键 值。因此,如果Nginx给出需要增大hash max size 或 hash bucket size的提示,那么首要的是增大前一个参数的大小. server_names_hash_bucket_size 128; #客户端请求头部的缓冲区大小。这个可以根据你的系统分页大小来设置,一般一个请求的头部大小不会超过1k,不过由于一般系统分页都要大于1k,所以这里设置为分页大小。分页大小可以用命令getconf PAGESIZE取得。 client_header_buffer_size 32k; #客户请求头缓冲大小。nginx默认会用client_header_buffer_size这个buffer来读取header值,如果header过大,它会使用large_client_header_buffers来读取。 large_client_header_buffers 4 64k; #设定通过nginx上传文件的大小 client_max_body_size 8m; #开启高效文件传输模式,sendfile指令指定nginx是否调用sendfile函数来输出文件,对于普通应用设为 on,如果用来进行下载等应用磁盘IO重负载应用,可设置为off,以平衡磁盘与网络I/O处理速度,降低系统的负载。注意:如果图片显示不正常把这个改成off。 #sendfile指令指定 nginx 是否调用sendfile 函数(zero copy 方式)来输出文件,对于普通应用,必须设为on。如果用来进行下载等应用磁盘IO重负载应用,可设置为off,以平衡磁盘与网络IO处理速度,降低系统uptime。 sendfile on; #开启目录列表访问,合适下载服务器,默认关闭。 autoindex on; #此选项允许或禁止使用socke的TCP_CORK的选项,此选项仅在使用sendfile的时候使用 tcp_nopush on; tcp_nodelay on; #长连接超时时间,单位是秒 keepalive_timeout 120; #FastCGI相关参数是为了改善网站的性能:减少资源占用,提高访问速度。下面参数看字面意思都能理解。 fastcgi_connect_timeout 300; fastcgi_send_timeout 300; fastcgi_read_timeout 300; fastcgi_buffer_size 64k; fastcgi_buffers 4 64k; fastcgi_busy_buffers_size 128k; fastcgi_temp_file_write_size 128k; #gzip模块设置 gzip on; #开启gzip压缩输出 gzip_min_length 1k; #最小压缩文件大小 gzip_buffers 4 16k; #压缩缓冲区 gzip_http_version 1.0; #压缩版本(默认1.1,前端如果是squid2.5请使用1.0) gzip_comp_level 2; #压缩等级 gzip_types text/plain application/x-javascript text/css application/xml; #压缩类型,默认就已经包含textml,所以下面就不用再写了,写上去也不会有问题,但是会有一个warn。 gzip_vary on; #开启限制IP连接数的时候需要使用 #limit_zone crawler $binary_remote_addr 10m; #负载均衡配置 upstream piao.jd.com { #upstream的负载均衡,weight是权重,可以根据机器配置定义权重。weigth参数表示权值,权值越高被分配到的几率越大。 server 192.168.80.121:80 weight=3; server 192.168.80.122:80 weight=2; server 192.168.80.123:80 weight=3; #nginx的upstream目前支持4种方式的分配 #1、轮询(默认) #每个请求按时间顺序逐一分配到不同的后端服务器,如果后端服务器down掉,能自动剔除。 #2、weight #指定轮询几率,weight和访问比率成正比,用于后端服务器性能不均的情况。 #例如: #upstream bakend { # server 192.168.0.14 weight=10; # server 192.168.0.15 weight=10; #} #2、ip_hash #每个请求按访问ip的hash结果分配,这样每个访客固定访问一个后端服务器,可以解决session的问题。 #例如: #upstream bakend { # ip_hash; # server 192.168.0.14:88; # server 192.168.0.15:80; #} #3、fair(第三方) #按后端服务器的响应时间来分配请求,响应时间短的优先分配。 #upstream backend { # server server1; # server server2; # fair; #} #4、url_hash(第三方) #按访问url的hash结果来分配请求,使每个url定向到同一个后端服务器,后端服务器为缓存时比较有效。 #例:在upstream中加入hash语句,server语句中不能写入weight等其他的参数,hash_method是使用的hash算法 #upstream backend { # server squid1:3128; # server squid2:3128; # hash $request_uri; # hash_method crc32; #} #tips: #upstream bakend{#定义负载均衡设备的Ip及设备状态}{ # ip_hash; # server 127.0.0.1:9090 down; # server 127.0.0.1:8080 weight=2; # server 127.0.0.1:6060; # server 127.0.0.1:7070 backup; #} #在需要使用负载均衡的server中增加 proxy_pass http://bakend/; #每个设备的状态设置为: #1.down表示单前的server暂时不参与负载 #2.weight为weight越大,负载的权重就越大。 #3.max_fails:允许请求失败的次数默认为1.当超过最大次数时,返回proxy_next_upstream模块定义的错误 #4.fail_timeout:max_fails次失败后,暂停的时间。 #5.backup: 其它所有的非backup机器down或者忙的时候,请求backup机器。所以这台机器压力会最轻。 #nginx支持同时设置多组的负载均衡,用来给不用的server来使用。 #client_body_in_file_only设置为On 可以讲client post过来的数据记录到文件中用来做debug #client_body_temp_path设置记录文件的目录 可以设置最多3层目录 #location对URL进行匹配.可以进行重定向或者进行新的代理 负载均衡 } #虚拟主机的配置 server { #监听端口 listen 80; #域名可以有多个,用空格隔开 server_name www.jd.com jd.com; index index.html index.htm index.php; root /data/www/jd; #对******进行负载均衡 location ~ .*.(php|php5)?$ { fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000; fastcgi_index index.php; include fastcgi.conf; } #图片缓存时间设置 location ~ .*.(gif|jpg|jpeg|png|bmp|swf)$ { expires 10d; } #JS和CSS缓存时间设置 location ~ .*.(js|css)?$ { expires 1h; } #日志格式设定 #$remote_addr与$http_x_forwarded_for用以记录客户端的ip地址; #$remote_user:用来记录客户端用户名称; #$time_local: 用来记录访问时间与时区; #$request: 用来记录请求的url与http协议; #$status: 用来记录请求状态;成功是200, #$body_bytes_sent :记录发送给客户端文件主体内容大小; #$http_referer:用来记录从那个页面链接访问过来的; #$http_user_agent:记录客户浏览器的相关信息; #通常web服务器放在反向代理的后面,这样就不能获取到客户的IP地址了,通过$remote_add拿到的IP地址是反向代理服务器的iP地址。反向代理服务器在转发请求的http头信息中,可以增加x_forwarded_for信息,用以记录原有客户端的IP地址和原来客户端的请求的服务器地址。 log_format access '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" ' '$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" ' '"$http_user_agent" $http_x_forwarded_for'; #定义本虚拟主机的访问日志 access_log /usr/local/nginx/logs/host.access.log main; access_log /usr/local/nginx/logs/host.access.404.log log404; #对 "/" 启用反向代理 location / { proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1:88; proxy_redirect off; proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr; #后端的Web服务器可以通过X-Forwarded-For获取用户真实IP proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for; #以下是一些反向代理的配置,可选。 proxy_set_header Host $host; #允许客户端请求的最大单文件字节数 client_max_body_size 10m; #缓冲区代理缓冲用户端请求的最大字节数, #如果把它设置为比较大的数值,例如256k,那么,无论使用firefox还是IE浏览器,来提交任意小于256k的图片,都很正常。如果注释该指令,使用默认的client_body_buffer_size设置,也就是操作系统页面大小的两倍,8k或者16k,问题就出现了。 #无论使用firefox4.0还是IE8.0,提交一个比较大,200k左右的图片,都返回500 Internal Server Error错误 client_body_buffer_size 128k; #表示使nginx阻止HTTP应答代码为400或者更高的应答。 proxy_intercept_errors on; #后端服务器连接的超时时间_发起握手等候响应超时时间 #nginx跟后端服务器连接超时时间(代理连接超时) proxy_connect_timeout 90; #后端服务器数据回传时间(代理发送超时) #后端服务器数据回传时间_就是在规定时间之内后端服务器必须传完所有的数据 proxy_send_timeout 90; #连接成功后,后端服务器响应时间(代理接收超时) #连接成功后_等候后端服务器响应时间_其实已经进入后端的排队之中等候处理(也可以说是后端服务器处理请求的时间) proxy_read_timeout 90; #设置代理服务器(nginx)保存用户头信息的缓冲区大小 #设置从被代理服务器读取的第一部分应答的缓冲区大小,通常情况下这部分应答中包含一个小的应答头,默认情况下这个值的大小为指令proxy_buffers中指定的一个缓冲区的大小,不过可以将其设置为更小 proxy_buffer_size 4k; #proxy_buffers缓冲区,网页平均在32k以下的设置 #设置用于读取应答(来自被代理服务器)的缓冲区数目和大小,默认情况也为分页大小,根据操作系统的不同可能是4k或者8k proxy_buffers 4 32k; #高负荷下缓冲大小(proxy_buffers*2) proxy_busy_buffers_size 64k; #设置在写入proxy_temp_path时数据的大小,预防一个工作进程在传递文件时阻塞太长 #设定缓存文件夹大小,大于这个值,将从upstream服务器传 proxy_temp_file_write_size 64k; } #设定查看Nginx状态的地址 location /NginxStatus { stub_status on; access_log on; auth_basic "NginxStatus"; auth_basic_user_file confpasswd; #htpasswd文件的内容可以用apache提供的htpasswd工具来产生。 } #本地动静分离反向代理配置 #所有jsp的页面均交由tomcat或resin处理 location ~ .(jsp|jspx|do)?$ { proxy_set_header Host $host; proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr; proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for; proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1:8080; } #所有静态文件由nginx直接读取不经过tomcat或resin location ~ .*.(htm|html|gif|jpg|jpeg|png|bmp|swf|ioc|rar|zip|txt|flv|mid|doc|ppt| pdf|xls|mp3|wma)$ { expires 15d; } location ~ .*.(js|css)?$ { expires 1h; } } } ######Nginx配置文件nginx.conf中文详解#####
2.5 配置文件5
user nobody nobody; ## 指定运行用户和组 worker_processes 4; ## 指定worker数量,建议此处auto worker_rlimit_nofile 51200; ## 最大打开文件描述符 error_log logs/error.log notice; pid /var/run/nginx.pid; events { use epoll; ## 使用epoll事件驱动模型 worker_connections 51200; ## 一个worker能处理的最大并发 } http { server_tokens off; ## 隐藏nginx版本 include mime.types; proxy_redirect off; ## 关闭代理重定向 proxy_set_header Host $host; proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr; proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for; client_max_body_size 20m; ## 设置客户端请求body的最大允许大小 client_body_buffer_size 256k; ## 设置客户端请求body的缓冲区大小 proxy_connect_timeout 90; ## 与后端服务器连接的超时时长 proxy_send_timeout 90; ## 把请求发送给后端服务器的超时时长 proxy_read_timeout 90; ## 等待后端服务器发送响应报文的超时时长 proxy_buffer_size 128k; ## 从代理服务器接收的响应的第一部分缓冲区 proxy_buffers 4 64k; ## 从代理服务器读取响应的缓冲区number和size proxy_busy_buffers_size 128k; ## 限制size在响应尚未完全读取时可能忙于向客户端发送响应的缓冲区总数 proxy_temp_file_write_size 128k; ## 该指令设置缓冲临时文件的最大值 default_type application/octet-stream; charset utf-8; ## 字符集 client_body_temp_path /var/tmp/client_body_temp 1 2; ## 请求body临时目录 proxy_temp_path /var/tmp/proxy_temp 1 2; ## 代理服务器接受数据临时目录 fastcgi_temp_path /var/tmp/fastcgi_temp 1 2; ## FastCGI服务器接收临时目录 uwsgi_temp_path /var/tmp/uwsgi_temp 1 2; ## uwsgi 服务器接收临时目录 scgi_temp_path /var/tmp/scgi_temp 1 2; ##scgi服务器接收临时目录 ignore_invalid_headers on; ## 开启控制忽略具有无效名称的标头字段 server_names_hash_max_size 256; ## 服务器名称哈希表的最大值 server_names_hash_bucket_size 64; ## 服务器名称哈希表存储bucket大小 client_header_buffer_size 8k; ## 设置缓冲区以读取客户端请求标头 large_client_header_buffers 4 32k; ## 设置缓冲区以读取客户端请求标头最大值number和size connection_pool_size 256; ## 允许精确调整每个连接的内存分配 request_pool_size 64k; ## 允许精确调整每个请求的内存分配 output_buffers 2 128k; ## 设置用于从磁盘读取响应的缓冲区number和size postpone_output 1460; ## 客户端数据的传输最小值,单位字节 client_header_timeout 1m; ## 定义读取客户端请求标头的超时时长 client_body_timeout 3m; ## 定义读取客户端请求主体的超时时长 send_timeout 3m; ## 设置将响应传输到客户端的超时时长 log_format main '$server_addr $remote_addr [$time_local] $msec+$connection ' '"$request" $status $connection $request_time $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" ' '"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"'; open_log_file_cache max=1000 inactive=20s min_uses=1 valid=1m; access_log logs/access.log main; log_not_found on; sendfile on; tcp_nodelay on; ## 启用长连接马上响应,提高性能 tcp_nopush off; ## 关闭套接字选项 reset_timedout_connection on; ## 启用重置超时连接 keepalive_timeout 10 5; ## 第一个参数设置长连接超时时长,第二个浏览器识别为keep-alive:timeout=5 keepalive_requests 100; ## 设置可通过一个保持活动连接提供的最大请求数 gzip on; ## 开启压缩 gzip_http_version 1.1; ## 启用压缩时协议最小版本 gzip_vary on; gzip_proxied any; ## 为所有代理请求启用压缩 gzip_min_length 1024; ## 设置将被gzip压缩的响应的最小长度 gzip_comp_level 6; ## 设置压缩等级 gzip_buffers 16 8k; ## 设置用于压缩响应的缓冲区number和size gzip_proxied expired no-cache no-store private auth no_last_modified no_etag; gzip_types text/plain application/x-javascript text/css application/xml application/json; gzip_disable "MSIE [1-6]\.(?!.*SV1)"; upstream tomcat8080 { ip_hash; server 172.16.100.103:8080 weight=1 max_fails=2; server 172.16.100.104:8080 weight=1 max_fails=2; server 172.16.100.105:8080 weight=1 max_fails=2; } server { listen 80; server_name www.chan.com; # config_apps_begin root /data/webapps/htdocs; access_log /var/logs/webapp.access.log main; error_log /var/logs/webapp.error.log notice; location / { location ~* ^.*/favicon.ico$ { root /data/webapps; expires 180d; ## 缓存180天 break; } if ( !-f $request_filename ) { proxy_pass http://tomcat8080; break; } } error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html; location = /50x.html { root html; } } server { listen 8088; server_name nginx_status; location / { access_log off; deny all; return 503; } location /status { stub_status on; access_log off; allow 127.0.0.1; allow 172.16.100.71; deny all; } } }
三、按块详解
3.1、全局块
3.1.1、配置运行Nginx服务器用户(组)
指令格式:
user user [group];
user:指定可以运行Nginx服务器的用户
group:可选项,可以运行Nginx服务器的用户组
如果user指令不配置或者配置为user nobody nobody,则默认所有用户都可以启动Nginx进程
3.1.2、worker process数配置
Nginx服务器实现并发处理服务的关键,指令格式: worker_processes number | auto; number:Nginx进程最多可以产生的worker process数 auto:Nginx进程将自动检测 按照上文中的配置清单的实验,我们给worker_processes配置的数目是:3,启动Nginx服务器后,我们可以后台看一下主机上的Nginx进程情况: ps -aux | grep nginx 很明显,理解 worker_processes 这个指令的含义就很容易了
3.1.3、Nginx进程PID存放路径
Nginx进程是作为系统守护进程在运行,需要在某文件中保存当前运行程序的主进程号,Nginx支持该保存文件路径的自定义 指令格式: pid file; file:指定存放路径和文件名称如果不指定默认置于路径 logs/nginx.pid
3.1.4、错误日志的存放路径
指定格式: error_log file | stderr; file:日志输出到某个文件file stderr:日志输出到标准错误输出
3.1.5、配置文件的引入
指令格式: include file; 该指令主要用于将其他的Nginx配置或者第三方模块的配置引用到当前的主配置文件中
3.2、events块
3.2.1、设置网络连接的序列化
指令格式: accept_mutex on | off; 该指令默认为on状态,表示会对多个Nginx进程接收连接进行序列化,防止多个进程对连接的争抢。
说到该指令,首先得阐述一下什么是所谓的 “惊群问题”,可以参考 WIKI百科的解释。就Nginx的场景来解释的话大致的意思就是:当一个新网络连接来到时,多个worker进程会被同时唤醒,但仅仅只有一个进程可以真正获得连接并处理之。如果每次唤醒的进程数目过多的话,其实是会影响一部分性能的。
所以在这里,如果accept_mutex on,那么多个worker将是以串行方式来处理,其中有一个worker会被唤醒;反之若accept_mutex off,那么所有的worker都会被唤醒,不过只有一个worker能获取新连接,其它的worker会重新进入休眠状态
这个值的开关与否其实是要和具体场景挂钩的。
3.2.2、是否允许同时接收多个网络连接
指令格式: multi_accept on | off; 该指令默认为off状态,意指每个worker process 一次只能接收一个新到达的网络连接。若想让每个Nginx的workerprocess都有能力同时接收多个网络连接,则需要开启此配置
3.2.3、事件驱动模型的选择
指令格式: use model; model模型可选择项包括:select、poll、kqueue、epoll、rtsig等......
3.2.4、最大连接数的配置
指令格式:
worker_connections number;
number默认值为512,表示允许每一个worker process可以同时开启的最大连接数
3.3、HTTP块-全局
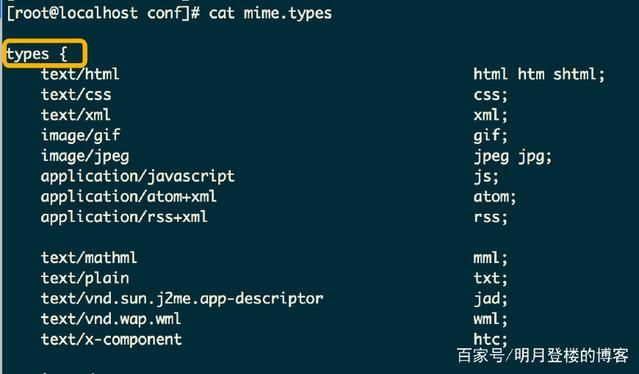
3.3.1 定义MIME-Type
指令格式: include mime.types; default_type mime-type; MIME-Type指的是网络资源的媒体类型,也即前端请求的资源类型
include指令将mime.types文件包含进来 cat mime.types 来查看mime.types文件内容,我们发现其就是一个types结构,里面包含了各种浏览器能够识别的MIME类型以及对应类型的文件后缀名字,如下所示:
3.3.2、自定义服务日志
指令格式: access_log path [format]; path:自定义服务日志的路径 + 名称
format:可选项,自定义服务日志的字符串格式。其也可以使用 log_format 定义的格式
3.3.3、允许sendfile方式传输文件
指令格式: sendfile on | off; sendfile_max_chunk size; 前者用于开启或关闭使用sendfile()传输文件,默认off
后者指令若size>0,则Nginx进程的每个workerprocess每次调用sendfile()传输的数据了最大不能超出此值;若size=0则表示不限制。默认值为0
3.3.4、连接超时时间配置
指令格式:
keepalive_timeout timeout [header_timeout];
timeout 表示server端对连接的保持时间,默认75秒
header_timeout 为可选项,表示在应答报文头部的 Keep-Alive 域设置超时时间:“Keep-Alive :timeout = header_timeout”
3.4、HTTP块-Server
3.4.1、单连接请求数上限
指令格式:
keepalive_requests number;
该指令用于限制用户通过某一个连接向Nginx服务器发起请求的次数
3.4.2、配置网络监听
指令格式:
第一种:配置监听的IP地址: listen IP[:PORT]; 第二种:配置监听的端口: listen PORT; 实际举例: listen192.168.31.177:8080; # 监听具体IP和具体端口上的连接
listen192.168.31.177; # 监听IP上所有端口上的连接
listen 8080; # 监听具体端口上的所有IP的连接
3.4.3、基于名称和IP的虚拟主机配置
指令格式: server_name name1 name2 ...
name可以有多个并列名称,而且此处的name支持正则表达式书写 实际举例: server_name ~^www\d+\.myserver\.com$ 此时表示该虚拟主机可以接收类似域名 www1.myserver.com 等的请求,而拒绝 www.myserver.com 的域名请求,所以说用正则表达式可以实现更精准的控制 至于基于IP的虚拟主机配置比较简单,不再太赘述: 指令格式: server_name IP地址
3.6、HTTP块-location配置
3.6.1、location
指令格式为: location [ = | ~ | ~* | ^~ ] uri {...} 这里的uri分为标准uri和正则uri,两者的唯一区别是uri中是否包含正则表达式 uri前面的方括号中的内容是可选项,解释如下: “=”:用于标准uri前,要求请求字符串与uri严格匹配,一旦匹配成功则停止
“~”:用于正则uri前,并且区分大小写
“~*”:用于正则uri前,但不区分大小写
“^~”:用于标准uri前,要求Nginx找到标识uri和请求字符串匹配度最高的location后,立即使用此location处理请求,而不再使用location块中的正则uri和请求字符串做匹配
3.6.2、请求根目录配置
指令格式:
root path;
path:Nginx接收到请求以后查找资源的根目录路径
当然,还可以通过alias指令来更改location接收到的URI请求路径,指令为:
alias path;
# path为修改后的根路径
3.6.3、设置网站的默认首页
指令格式: index file ...... file可以包含多个用空格隔开的文件名,首先找到哪个页面,就使用哪个页面响应请求
3.6.4、proxy_set_header
目前有一个需求如下:
nginx上配有aaa.example.com的虚拟主机,现在需要将访问http://aaa.example.com/api/x.x/client/的请求转到http://bbb.example.com/api/x.x/client/,bbb.example.com的虚拟主机在另外一台nginx上,其中x.x表示位数不定的版本号,如:1.0或1.20.345都可能。请求转过去要求url保持不变
用rewrite转发的话,url会发生变化的,那就用proxy_pass吧,于是添加了如下的配置:
location ~ ^/api/([0-9]+)(\.[0-9]+)*/client/ { proxy_pass http://bbb.example.com; }
在现有环境的nginx里添加这段配置之后,访问却始终转不过去,查看nginx日志也只能看到是404信息,并没有更多定位问题的信息。检查了许久也没找到原因,于是重新装了一台新nginx,里面只加上面这段配置,结果nginx是能够转发成功的,这说明单独来看这条location的配置是没有问题的,很有可能是现有环境nginx里的某些配置影响到了这个转发。
为了定位问题原因,我将aaa.example.com虚拟主机下的其他配置注意注释掉来调试,最后发现当注释掉proxy_set_header Host $http_host ;这条配置之后,就能成功转发了。这才注意到是反向代理配置的问题。现有环境中原有的配置也不能随便删掉,上网查了下原因,找到下面这种解决方案:
location ~ ^/api/([0-9]+)(\.[0-9]+)*/client/ { proxy_pass http://bbb.example.com; proxy_set_header Host $proxy_host; }
即,在location里面添加一条proxy_set_header Host $proxy_host;配置。当Host设置为$http_host时,则不改变请求头的值,所以当要转发到bbb.example.com的时候,请求头还是aaa.example.com的Host信息,就会有问题;当Host设置为$proxy_host时,则会重新设置请求头为bbb.example.com的Host信息。
另外,关于proxy_pass转发url的参数,可以通过在location中用rewrite来做,所以完善后的配置如下:
location ~ ^/api/([0-9]+)(\.[0-9]+)*/client/ { rewrite /(.*)$ /$1 break; proxy_pass http://bbb.example.com; proxy_set_header Host $proxy_host; }
在location用rewrite改变了URI之后,proxy_pass将使用改变后的URI。上面例子(.*)是将所有参数传给$1,转发时/$1会拼接在http://bbb.example.com后面。
先来看下proxy_set_header的语法
| 语法: | proxy_set_header |
| 默认值: | proxy_set_header Host $proxy_host; proxy_set_header Connection close; |
| 上下文: | http, server, location |
允许重新定义或者添加发往后端服务器的请求头。value可以包含文本、变量或者它们的组合。 当且仅当当前配置级别中没有定义proxy_set_header指令时,会从上面的级别继承配置。 默认情况下,只有两个请求头会被重新定义:
proxy_set_header Host $proxy_host;
proxy_set_header Connection close;
nginx对于upstream默认使用的是基于IP的转发,因此对于以下配置:
upstream backend { server 127.0.0.1:8080; } upstream crmtest { server crmtest.aty.sohuno.com; } server { listen 80; server_name chuan.aty.sohuno.com; proxy_set_header Host $http_host; proxy_set_header x-forwarded-for $remote_addr; proxy_buffer_size 64k; proxy_buffers 32 64k; charset utf-8; access_log logs/host.access.log main; location = /50x.html { root html; } location / { proxy_pass backend ; } location = /customer/straightcustomer/download { proxy_pass http://crmtest; proxy_set_header Host $proxy_host; } }
当匹配到/customer/straightcustomer/download时,使用crmtest处理,到upstream就匹配到crmtest.aty.sohuno.com,这里直接转换成IP进行转发了。假如crmtest.aty.sohuno.com是在另一台nginx下配置的,ip为10.22.10.116,则$proxy_host则对应为10.22.10.116。此时相当于设置了Host为10.22.10.116。如果想让Host是crmtest.aty.sohuno.com,则进行如下设置:
proxy_set_header Host crmtest.aty.sohuno.com;
如果不想改变请求头“Host”的值,可以这样来设置:
proxy_set_header Host $http_host;
但是,如果客户端请求头中没有携带这个头部,那么传递到后端服务器的请求也不含这个头部。 这种情况下,更好的方式是使用$host变量——它的值在请求包含“Host”请求头时为“Host”字段的值,在请求未携带“Host”请求头时为虚拟主机的主域名:
proxy_set_header Host $host;
此外,服务器名可以和后端服务器的端口一起传送:
proxy_set_header Host $host:$proxy_port;
如果某个请求头的值为空,那么这个请求头将不会传送给后端服务器:
proxy_set_header Accept-Encoding "";
nginx配置项,里面的配置项有代理https,http,代理静态文件,H5分发,代理TCP连接,能满足大多数搭建测试环境所要用的nginx的情况,大家碰到要使用nginx的时候可以参考下
#user nobody; worker_processes 1; #error_log logs/error.log; #error_log logs/error.log notice; #error_log logs/error.log info; #pid logs/nginx.pid; events { worker_connections 1024; } #代理TCP连接 stream { upstream tcp_proxy_boc { server 172.16.100.59:8890 ; } server { listen 20080 so_keepalive=on; proxy_connect_timeout 20s; proxy_timeout 30s; proxy_pass tcp_proxy_boc; } upstream tcp_proxy_sls { server 172.16.100.59:8892 ; } server { listen 20081 so_keepalive=on; proxy_connect_timeout 20s; proxy_timeout 30s; proxy_pass tcp_proxy_sls; } upstream tcp_proxy_ccb { server 172.16.100.59:8891 ; } server { listen 20082 so_keepalive=on; proxy_connect_timeout 20s; proxy_timeout 30s; proxy_pass tcp_proxy_ccb; } } http { include mime.types; default_type application/octet-stream; #log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" ' # '$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" ' # '"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"'; #access_log logs/access.log main; sendfile on; #tcp_nopush on; #keepalive_timeout 0; keepalive_timeout 65; client_max_body_size 20m; #gzip on; #liumaAPPH5 server { listen 20074; server_name localhost; location / { root /etc/nginx/xcy/kwl/dist; index index.html index.htm; } location /etcapi { proxy_set_header Host $host; proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for; proxy_pass http://192.168.3.100:8089/; } location /nbapi { proxy_set_header Host $host; proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for; proxy_pass https://nb.nbcolt.com:20059/; } error_log logs/error_www.abc.com.log error; } #中行H5 server { listen 20078; server_name localhost; location / { root /etc/nginx/xcy/hyn/dist; index index.html index.htm; try_files $uri $uri/ @router; } # error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html; # location = /50x.html { # root html; # } location /zjoffice { proxy_set_header Host $host; proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for; proxy_pass http://192.168.3.134:8183/zjoffice/; } location @router { rewrite ^.*$ /index.html last; } } #liumaAPPH5图片服务器 server { listen 20075 ; server_name localhost; location /kwl { root html; index index.html index.htm; proxy_pass http://192.168.3.111/kwl/; } } #liuma server { listen 20079 ssl ; server_name localhost; ssl_certificate /etc/nginx/cert/oit/2441956_nb.nbcolt.com.pem; ssl_certificate_key /etc/nginx/cert/oit/2441956_nb.nbcolt.com.key; ssl_session_timeout 5m; ssl_protocols TLSv1 TLSv1.1 TLSv1.2; ssl_ciphers HIGH:!RC4:!MD5:!aNULL:!eNULL:!NULL:!DH:!EDH:!EXP:+MEDIUM; ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on; location /oitUct { proxy_pass http://192.168.3.134:8040/oitUct; proxy_set_header Host $host; proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr; proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for; } location /oitBaseParam { proxy_pass http://192.168.3.134:8040/oitBaseParam; proxy_set_header Host $host; proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr; proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for; } location /oitBusiness { proxy_pass http://192.168.3.134:8040/oitBusiness; proxy_set_header Host $host; proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr; proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for; } location /oitManage { proxy_pass http://192.168.3.134:8040/oitManage; proxy_set_header Host $host; proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr; proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for; } location /oitManagement { proxy_pass http://192.168.3.134:8040/oitManagement; proxy_set_header Host $host; proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr; proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for; } location /oitPortal { proxy_pass http://192.168.3.134:8040/oitPortal; proxy_set_header Host $host; proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr; proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for; } location /oitFinance { proxy_pass http://192.168.3.134:8042/oitFinance; proxy_set_header Host $host; proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr; proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for; } location /oitMiddleware { proxy_pass http://192.168.3.134:8040/oitMiddleware; proxy_set_header Host $host; proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr; proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for; } location /sso { proxy_pass http://122.224.230.10:17003/sso/; proxy_set_header Host $host; proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr; proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for; } location /dub-webapps-yb { proxy_pass http://122.224.230.26:20019/dub-webapps-yb/; proxy_set_header Host $host; proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr; proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for; } location /member { proxy_pass http://192.168.3.30:5050/member/; proxy_set_header Host $host; proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr; proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for; } location /dub-upload { proxy_pass http://122.224.230.26:20019/dub-upload/; proxy_set_header Host $host; proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr; proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for; } } #代理https并保留源地址 server { listen 20076 ssl ; server_name localhost; ssl_certificate /usr/local/1633691_test.etczj.com.pem; ssl_certificate_key /usr/local/1633691_test.etczj.com.key; ssl_session_timeout 5m; ssl_protocols TLSv1 TLSv1.1 TLSv1.2; ssl_ciphers HIGH:!RC4:!MD5:!aNULL:!eNULL:!NULL:!DH:!EDH:!EXP:+MEDIUM; ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on; location / { proxy_next_upstream http_500 http_502 http_503 http_504 timeout error invalid_header; proxy_pass http://192.168.3.100:8089/; proxy_set_header Host $host; proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr; proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for; } } #代理图片 server { listen 20077; server_name localhost; location / { root /mnt/mfs; index index.html index.htm; } error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html; location = /50x.html { root html; } } # another virtual host using mix of IP-, name-, and port-based configuration # #server { # listen 8000; # listen somename:8080; # server_name somename alias another.alias; # location / { # root html; # index index.html index.htm; # } #} # HTTPS server # #server { # listen 443 ssl; # server_name localhost; # ssl_certificate cert.pem; # ssl_certificate_key cert.key; # ssl_session_cache shared:SSL:1m; # ssl_session_timeout 5m; # ssl_ciphers HIGH:!aNULL:!MD5; # ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on; # location / { # root html; # index index.html index.htm; # } #} }