性能优化工具知识梳理(1) - TraceView
性能优化工具知识梳理(2) - Systrace
性能优化工具知识梳理(3) - 调试GPU过度绘制 & GPU呈现模式分析
性能优化工具知识梳理(4) - Hierarchy Viewer
性能优化工具知识梳理(5) - MAT
性能优化工具知识梳理(6) - Memory Monitor & Heap Viewer & Allocation Tracker
性能优化工具知识梳理(7) - LeakCanary
性能优化工具知识梳理(8) - Lint
一、概述
LeakCanary提供了一种很便捷的方式,让我们在开发阶段检测内存泄漏问题,我们不需要自己去根据内存快照来分析内存泄漏的原因,所需要做的仅仅是在Debug包中集成它,它会自动地帮我们检测内存泄漏,并给出导致泄漏的引用链。
二、集成
下面,就来看一下如何在项目当中集成它:
- 第一步:需要引入远程依赖,这里我们引入了两个,在
release版本中,所有的调用都是空实现,这样就会避免在release的版本中也在桌面生成一个泄漏检测结果的图标。
dependencies {
//在 debug 版本中才会实现真正的功能
debugCompile 'com.squareup.leakcanary:leakcanary-android:1.3'
//在 release 版本中为空实现
releaseCompile 'com.squareup.leakcanary:leakcanary-android-no-op:1.3'
}
- 第二步:重写
Application,初始化一个全局RefWatcher对象,它负责监视所有应当要被回收的对象:
public class LeakCanaryApplication extends Application {
private RefWatcher mRefWatcher;
@Override
public void onCreate() {
super.onCreate();
mRefWatcher = LeakCanary.install(this);
}
public static RefWatcher getRefWatcher(Context context) {
LeakCanaryApplication application = (LeakCanaryApplication) context.getApplicationContext();
return application.mRefWatcher;
}
}
- 第三步:在需要回收的对象上,添加监测代码,这里我们以
Activity为例就需要在它的onDestory()方法中加入监测的代码,我们通过单例持有Activity的引用,模拟了一种内存泄漏发生的场景:
public class LeakSingleton {
private static LeakSingleton sInstance;
private Context mContext;
public static LeakSingleton getInstance(Context context) {
if (sInstance == null) {
sInstance = new LeakSingleton(context);
}
return sInstance;
}
private LeakSingleton(Context context) {
mContext = context;
}
}
public class LeakCanaryActivity extends Activity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_leak_canary);
//让这个单例对象持有 Activity 的引用
LeakSingleton.getInstance(this);
}
@Override
protected void onDestroy() {
super.onDestroy();
//在 onDestroy 方法中使用 Application 中创建的 RefWatcher 监视需要回收的对象
LeakCanaryApplication.getRefWatcher(this).watch(this);
}
}
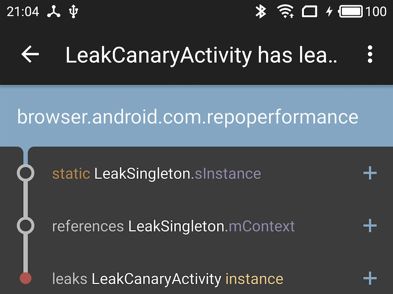
在退出应用程序之后,我们会发现在桌面上生成了一个新的图标,点击图标进入,就是LeakCanary为我们分析出的导致泄漏的引用链:
以上就是把
LeakCanary集成到项目中的方法,下面,我们来讨论一下它的实现原理。
三、原理
当调用了RefWatcher.watch()方法之后,会触发以下逻辑:
- 创建一个
KeyedWeakReference,它内部引用了watch传入的对象:
final KeyedWeakReference reference = new KeyedWeakReference(watchedReference, key, referenceName, this.queue);
- 在后台线程检查引用是否被清除:
this.watchExecutor.execute(new Runnable() {
public void run() {
RefWatcher.this.ensureGone(reference, watchStartNanoTime);
}
});
- 如果没有清除,那么首先调用一次
GC,假如引用还是没有被清除,那么把当前的内存快照保存到.hprof文件当中,并调用heapdumpListener进行分析:
void ensureGone(KeyedWeakReference reference, long watchStartNanoTime) {
long gcStartNanoTime = System.nanoTime();
long watchDurationMs = TimeUnit.NANOSECONDS.toMillis(gcStartNanoTime - watchStartNanoTime);
this.removeWeaklyReachableReferences();
if(!this.gone(reference) && !this.debuggerControl.isDebuggerAttached()) {
this.gcTrigger.runGc();
this.removeWeaklyReachableReferences();
if(!this.gone(reference)) {
long startDumpHeap = System.nanoTime();
long gcDurationMs = TimeUnit.NANOSECONDS.toMillis(startDumpHeap - gcStartNanoTime);
File heapDumpFile = this.heapDumper.dumpHeap();
if(heapDumpFile == null) {
return;
}
long heapDumpDurationMs = TimeUnit.NANOSECONDS.toMillis(System.nanoTime() - startDumpHeap);
this.heapdumpListener.analyze(new HeapDump(heapDumpFile, reference.key, reference.name, watchDurationMs, gcDurationMs, heapDumpDurationMs));
}
}
}
- 上面说到的
heapdumpListener的实现类为ServiceHeapDumpListener,它会启动内部的HeapAnalyzerService:
public void analyze(HeapDump heapDump) {
Preconditions.checkNotNull(heapDump, "heapDump");
HeapAnalyzerService.runAnalysis(this.context, heapDump, this.listenerServiceClass);
}
- 这是一个
IntentService,因此它的onHandlerIntent方法是运行在子线程中的,在通过HeapAnalyzer分析完毕之后,把最终的结果传回给App端展示检测的结果:
protected void onHandleIntent(Intent intent) {
String listenerClassName = intent.getStringExtra("listener_class_extra");
HeapDump heapDump = (HeapDump)intent.getSerializableExtra("heapdump_extra");
AnalysisResult result = this.heapAnalyzer.checkForLeak(heapDump.heapDumpFile, heapDump.referenceKey);
AbstractAnalysisResultService.sendResultToListener(this, listenerClassName, heapDump, result);
}
-
HeapAnalyzer会计算未能回收的引用到Gc Roots的最短引用路径,如果泄漏,那么建立导致泄漏的引用链并通过AnalysisResult返回:
public AnalysisResult checkForLeak(File heapDumpFile, String referenceKey) {
long analysisStartNanoTime = System.nanoTime();
if(!heapDumpFile.exists()) {
IllegalArgumentException snapshot1 = new IllegalArgumentException("File does not exist: " + heapDumpFile);
return AnalysisResult.failure(snapshot1, this.since(analysisStartNanoTime));
} else {
ISnapshot snapshot = null;
AnalysisResult className;
try {
snapshot = this.openSnapshot(heapDumpFile);
IObject e = this.findLeakingReference(referenceKey, snapshot);
if(e != null) {
String className1 = e.getClazz().getName();
AnalysisResult result = this.findLeakTrace(analysisStartNanoTime, snapshot, e, className1, true);
if(!result.leakFound) {
result = this.findLeakTrace(analysisStartNanoTime, snapshot, e, className1, false);
}
AnalysisResult var9 = result;
return var9;
}
className = AnalysisResult.noLeak(this.since(analysisStartNanoTime));
} catch (SnapshotException var13) {
className = AnalysisResult.failure(var13, this.since(analysisStartNanoTime));
return className;
} finally {
this.cleanup(heapDumpFile, snapshot);
}
return className;
}
}
四、自定义处理行为
默认LeakCanary是会在桌面生成一个图标,点击图标之后,会展示导致泄漏的引用链,有时候,我们希望把这些信息上传到服务器中,那么就需要自定义收到结果后的处理的行为,下面,我们看一下要怎么做:
- 第一步:继承
DisplayLeakService,进行自己的处理逻辑,这里我们只是打印出泄漏的信息,heapDump为对应的内存快照,result为分析的结果,leakInfo则是相关的信息:
public class MyLeakUploadService extends DisplayLeakService {
@Override
protected void afterDefaultHandling(HeapDump heapDump, AnalysisResult result, String leakInfo) {
if (!result.leakFound || result.excludedLeak) {
return;
}
Log.d("MyLeakUploadService", "leakInfo=" + leakInfo);
}
}
- 第二步:改变
Application中初始化RefWatcher的方式,第二个参数中传入我们自定义的Service类名:
public class LeakCanaryApplication extends Application {
private RefWatcher mRefWatcher;
@Override
public void onCreate() {
super.onCreate();
mRefWatcher = LeakCanary.install(this, MyLeakUploadService.class);
}
}
- 第三步:在
AndroidManifest.xml中注册自定义的Service:
-
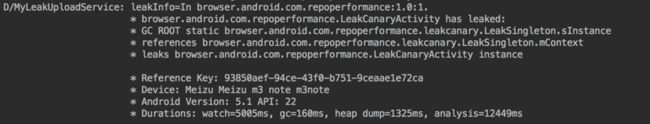
最后,我们运行和之前一样的操作,会看到在输出台上打印出了泄漏的分析结果:
五、小结
在调试阶段,我们可以通过引入LeakCanary,让它帮助我们排查出一些会导致内存泄漏的问题。
六、参考文献
https://www.liaohuqiu.net/cn/posts/leak-canary-read-me/
更多文章,欢迎访问我的 Android 知识梳理系列:
- Android 知识梳理目录:http://www.jianshu.com/p/fd82d18994ce
- 个人主页:http://lizejun.cn
- 个人知识总结目录:http://lizejun.cn/categories/