简介:
inotify的优点:
(1) 监控文件系统时间的变化,通过同步工具实现实时同步数据
inotify的缺点:
(1) 并发如果大于200个文件(10-100K),同步就会有延迟
(2)我们前面写的脚本,每次都是全部推送一次,但确实是增量备份额
也可以只同步变化的文件 不变化的文件不理
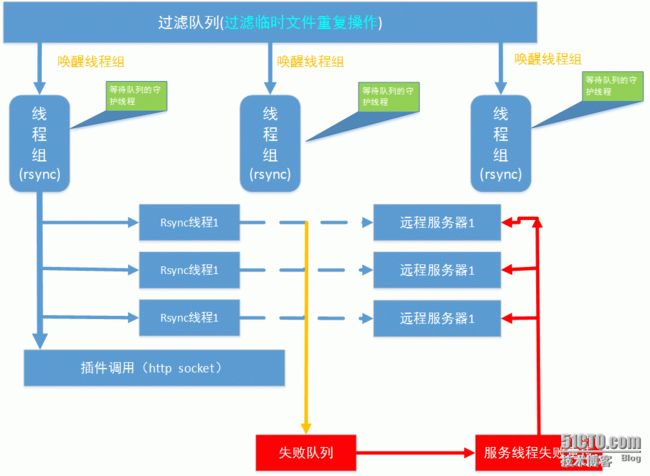
(3) 监控到事件后,调用rsync同步是单线程的(加&并发)。sersync是多线程同步的
既然有了inotify-tools,为什么还要开发sersync
sersync的功能多
(1)配置文件
(2) 真正的守护进程socket
(3)可以对失败的文件定时重传
(4)第三方的http接口
(5) 默认是多线程的同步
sersync原理图解
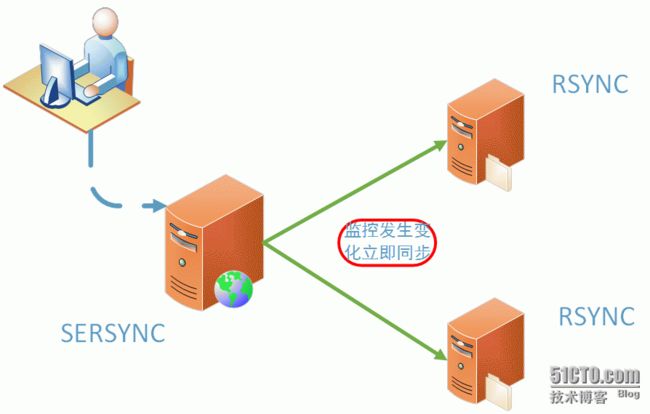
本次实战的图解
1.Rsync服务(S1和S2的配置,都一样),这个配置文件默认是不存在的(得新建)
[root@S2-SERVER ~]# vim /etc/rsyncd.conf
#QQ 31333741 blog:http://oldboy.blog.51cto.com
##rsyncd.conf start##
uid = rsync
gid = rsync
use chroot = no
max connections = 200
timeout = 300
pid file = /var/run/rsyncd.pid
lock file = /var/run/rsync.lock
log file = /var/log/rsyncd.log
ignore errors
read only = false
list = false
hosts allow = 10.0.0.0/24
hosts deny = 0.0.0.0/32
auth users = rsync_backup
secrets file = /etc/rsync.password
[www]
comment = "write by sanlang"
path = /data0/www/www
[bbs]
comment = "write by sanlang"
path = /data0/www/bbs
[blog]
comment = "write by sanlang"
path = /data0/www/blog
"/etc/rsyncd.conf" 27L, 604C 已写入
[root@S2-SERVER ~]#
2. Rsync服务(S1和S2的配置,都一样)添加用户
[root@S2-SERVER ~]# useradd rsync -s /sbin/nologin -M
3.修改/或者密码文件(默认是不存的)
[root@S2-SERVER ~]# vim /etc/rsync.password
rsync_backup:oldboy
[root@S2-SERVER ~]# cat /etc/rsync.password
rsync_backup:oldboy
[root@S2-SERVER ~]# chmod 600 /etc/rsync.password
[root@S2-SERVER ~]#
4. Rsync服务(S1和S2的配置,都一样)创建目录,并把目录赋予相应的权限
[root@S2-SERVER ~]# mkdir /data0/www/www -p
[root@S2-SERVER ~]# mkdir -p /data0/www/bbs
[root@S2-SERVER ~]# mkdir -p /data0/www/blog
[root@S2-SERVER ~]# chown -R rsync.rsync /data0
5.以守护进程的方式启动rsync
[root@S1-SERVER ~]# rsync --daemon
[root@S1-SERVER ~]# echo "/usr/bin/rsync --daemon">>/etc/rc.local
可能会出错错误:
[root@S1-SERVER ~]# rsync --daemon
[root@S1-SERVER ~]# failed to create pid file /var/run/rsyncd.pid: File exists
解决方法:
[root@S1-SERVER ~]# rm -f /var/run/rsyncd.pid
6.Sersync服务(M)端的配置(默认文件不存在自己指定)
[root@M-SERVER ~]# cat /etc/rsync.password
oldboy
[root@M-SERVER ~]# chmod 600 /etc/rsync.password
[root@M-SERVER ~]# ll /etc/rsync.password
-rw-------. 1 root root 7 4月 22 16:18 /etc/rsync.password
[root@M-SERVER ~]#
7.测试(M-SERVER 上执行OK)
[root@M-SERVER ~]# cd /backup
[root@M-SERVER backup]# ls
sanlang01.txt sanlang03.txt sanlang05.txt sanlang07.txt sanlang09.txt
sanlang02.txt sanlang04.txt sanlang06.txt sanlang08.txt sanlang10.txt
[root@M-SERVER backup]# cd
[root@M-SERVER ~]# rsync -avz /backup/ [email protected]::www/ --password-file=/etc/rsync.password
sending incremental file list
./
sanlang01.txt
sanlang02.txt
sanlang03.txt
sanlang04.txt
sanlang05.txt
sanlang06.txt
sanlang07.txt
sanlang08.txt
sanlang09.txt
sanlang10.txt
sent 508 bytes received 201 bytes 1418.00 bytes/sec
total size is 0 speedup is 0.00
[root@M-SERVER ~]#
6.Sersync服务(M)端的配置(可以不加,主要是把安装包放在自己的家目录下)
[root@M-SERVER ~]# useradd oldboy
[root@M-SERVER ~]# passwd oldboy
更改用户 oldboy 的密码 。
新的 密码:
无效的密码: 过于简单化/系统化
无效的密码: 过于简单
重新输入新的 密码:
passwd: 所有的身份验证令牌已经成功更新。
[root@M-SERVER ~]#
新建一个目录用于sersync的安装
[root@M-SERVER ~]# mkdir -p /home/oldboy/tools
[root@M-SERVER ~]#
7.Sersync服务(M)端开始安装sersync
[root@M-SERVER tools]# rz
rz waiting to receive.
zmodem trl+C
[root@M-SERVER tools]# rz
rz waiting to receive.
zmodem trl+C
100% 710 KB 710 KB/s 00:00:01 0 Errorsary_stable_final.tar.gz...
[root@M-SERVER tools]# ls
sersync2.5.4_64bit_binary_stable_final.tar.gz
[root@M-SERVER tools]#
8.Sersync服务(M)端.解压文件(解压到/usr/local/ 下面)
[root@M-SERVER tools]# tar -zxvf sersync2.5.4_64bit_binary_stable_final.tar.gz -C /usr/local/
GNU-Linux-x86/
GNU-Linux-x86/sersync2
GNU-Linux-x86/confxml.xml
[root@M-SERVER tools]# cd /usr/local/
[root@M-SERVER local]# ls
bin etc games GNU-Linux-x86 include lib lib64 libexec sbin share src
[root@M-SERVER local]#
9.Sersync服务(M)端.改名解压文件的名称
[root@M-SERVER local]# mv GNU-Linux-x86 sersync
[root@M-SERVER local]#
[root@M-SERVER local]# tree sersync/
sersync/
├── confxml.xml
└── sersync2
0 directories, 2 files
[root@M-SERVER local]#
10.规范安装包(在 /usr/local/sersync 下操作)
[root@M-SERVER sersync]# mkdir conf bin logs
[root@M-SERVER sersync]# mv confxml.xml conf/
[root@M-SERVER sersync]# mv sersync2 bin/sersync
[root@M-SERVER local]# tree sersync/
sersync/
├── bin
│ └── sersync
├── conf
│ └── confxml.xml
└── logs
3 directories, 2 files
[root@M-SERVER local]#
11.备份配置文件并且配置
[root@M-SERVER sersync]# cd /usr/local/sersync/conf/
[root@M-SERVER conf]# cp confxml.xml confxml.xml.org
[root@M-SERVER conf]# ls
confxml.xml confxml.xml.org
[root@M-SERVER conf]#
①编辑confxml.xml
24
25
26
27
28
改成:
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
②修改认证的部分
40
41
42
43
44
45
改成:
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
③修fail队列日志
改成(这个目录是自己提前创建好的)
最后保存配置文件
12.配置sersync的命令
[root@M-SERVER conf]# echo "export PATH=$PATH:/usr/local/sersync/bin">>/etc/profile
[root@M-SERVER conf]# tail -n 1 /etc/profile
export PATH=/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/sbin:/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/root/bin:/usr/local/sersync/bin
[root@M-SERVER conf]# which rersync
/usr/bin/which: no rersync in (/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/sbin:/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/root/bin)
[root@M-SERVER conf]# source /etc/profile
[root@M-SERVER conf]# which sersync
/usr/local/sersync/bin/sersync
[root@M-SERVER conf]#
13.启动命令
[root@M-SERVER ~]# sersync -r -d -o /usr/local/sersync/conf/confxml.xml
set the system param
execute:echo 50000000 > /proc/sys/fs/inotify/max_user_watches
execute:echo 327679 > /proc/sys/fs/inotify/max_queued_events
parse the command param
option: -r rsync all the local files to the remote servers before the sersync work
option: -d run as a daemon
option: -o config xml name: /usr/local/sersync/conf/confxml.xml
daemon thread num: 10
parse xml config file
host ip : localhost host port: 8008
daemon start,sersync run behind the console
use rsync password-file :
user is rsync_backup
passwordfile is /etc/rsync.password
config xml parse success
please set /etc/rsyncd.conf max connections=0 Manually
sersync working thread 12 = 1(primary thread) + 1(fail retry thread) + 10(daemon sub threads)
Max threads numbers is: 32 = 12(Thread pool nums) + 20(Sub threads)
please according your cpu ,use -n param to adjust the cpu rate
------------------------------------------
rsync the directory recursivly to the remote servers once
working please wait...
execute command: cd /data0/www/www && rsync -artuz -R --delete ./ --timeout=100 [email protected]::www --password-file=/etc/rsync.password >/dev/null 2>&1
run the sersync:
watch path is: /data0/www/www
[root@M-SERVER ~]#
-r 客户端和服务端可能第一次数据不一样 开启先做一次同步
-d 在后台以守护进程的方式启动
-o 指定xml 文件
14.测试以后发现,在第11步骤写的模块(localpath )只识别第一个
这个时候进行多实例传送,每个推送数据的目录给一个配置文件下面三个文件,每个文件都有自己的单独日志和
[root@M-SERVER conf]# ls
bbs_confxml.xml blog_confxml.xml tmp www_confxml.xml
[root@M-SERVER conf]#
以blog_confxml.xml 为例
其余的密码文件如果自己想修该的话在自行修改
15启动三个配置文件
先杀掉原来配置
[root@M-SERVER conf]# ps -ef |grep rsync
root 2147 1 0 17:30 ? 00:00:00 sersync -r -d -o /usr/local/sersync/conf/confxml.xml
root 2289 2232 0 17:53 pts/1 00:00:00 grep rsync
[root@M-SERVER conf]# pkill sersync
[root@M-SERVER conf]# ps -ef |grep rsync
root 2292 2232 0 17:53 pts/1 00:00:00 grep rsync
[root@M-SERVER conf]#
多实例启动
sersync -r -d -o /usr/local/sersync/conf/www_confxml.xml
sersync -r -d -o /usr/local/sersync/conf/bbs_confxml.xml
sersync -r -d -o /usr/local/sersync/conf/blog_confxml.xml
检查:可以查出总共起了三个进程,每个进行都对应一个文件
[root@M-SERVER conf]# ps -ef |grep sersync
root 2300 1 0 17:57 ? 00:00:00 sersync -r -d -o /usr/local/sersync/conf/www_confxml.xml
root 2320 1 0 17:57 ? 00:00:00 sersync -r -d -o /usr/local/sersync/conf/bbs_confxml.xml
root 2340 1 0 17:58 ? 00:00:00 sersync -r -d -o /usr/local/sersync/conf/blog_confxml.xml
root 2411 2232 0 18:00 pts/1 00:00:00 grep sersync
[root@M-SERVER conf]#
最后主服务器Sersync服务(M)端可能也会重启
所以:防止重启(吧配置文件放在/etc/rc.local中,这个时候可以不加-r文件比较大,没有必要只要第一次即可)
[root@M-SERVER tmp]# cat >>/etc/rc.local< > sersync -d -o /usr/local/sersync/conf/www_confxml.xml > sersync -d -o /usr/local/sersync/conf/bbs_confxml.xml > sersync -d -o /usr/local/sersync/conf/blog_confxml.xml > EOF [root@M-SERVER tmp]# 测试(Sersync服务(M)端)(测试成功) [root@M-SERVER ~]# cd /data0 [root@M-SERVER data0]# ls www [root@M-SERVER data0]# cd www [root@M-SERVER www]# ls bbs blog www [root@M-SERVER www]# cd bbs [root@M-SERVER bbs]# touch succes.log [root@M-SERVER bbs]# cd .. [root@M-SERVER www]# cd blog/ [root@M-SERVER blog]# touch success.log [root@M-SERVER blog]# cd .. [root@M-SERVER www]# cd www [root@M-SERVER www]# touch success.log [root@M-SERVER www]# S2-SERVER端查看 [root@S2-SERVER ~]# tree /data0 /data0 └── www ├── bbs │ ├── bbs.log │ ├── bbs.txt │ ├── hello │ ├── succes.log │ └── world ├── blog │ ├── blog.log │ ├── blog.txt │ └── success.log └── www ├── success.log ├── www.log └── www.txt 4 directories, 11 files [root@S2-SERVER ~]# 经验 2710服务器千兆网 每秒可以同步10-100K 能同步 40-50 张 大量文件同步也是受限制的 sersync的参数 -r 开启第一次进行一次完全的同步,保持一致 -o 指定confxml.xml 的文件 -n 指定默认线程池的线程总数,如果不指定默认启动线程池的数量是10,CPU使用过高,可以通过这个参数进行调整 -d 参数为后台启动 -m 不同步,只运行插件 ./sersync --help 进行压力测试 监控是否同步不同步报警![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![P0Y7R@OAFKV~($9RCB6J]RV.png rsync+sersync实战_第3张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info3/33d2f33aa3fc43ef86f0864fc08657bd.gif)