参考资料:https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/itAuv86OsTHfBahUrk21DA
我们知道Android的组件化离不开Router,路由的主要主要作用是:消息的中转站,为我们的项目多模块的依赖解耦。,当然市面上有三方路由框架,比如阿里的ARouter就是一个不错的选择,但我们还是要自己自定义一个Router,来研究一下,毕竟自己动手丰衣足食嘛,ok,我们进入正题。
项目分析
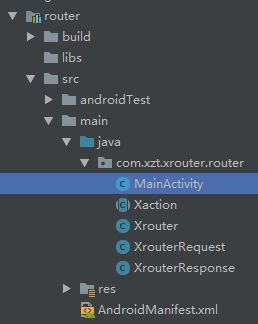
这是我demo的项目结构:
当然凡是用到路由的项目,其依赖关系一定复杂,但我们这里只是为了讲解路由的实现,所以就项目的耦合度并不高。
主要是app,fifferentprocess,sameprocessmodule这三个模块的依赖,通过自定义router实现解耦,common模块就是依赖模块常用的一些静态变量统一存放,便于管理。
router模块的主要代码分析
我们说了router主要作用是消息的中转站,所以我们先看一下其内部的构成类:
没错就是这五个类,其中的MainActivity里啥也没有,也就是Xaction,Xrouter,XrouterRequest,XrouterResponse这四个类,是不是很简单,那我们就来逐一分析一下。
Xrouter
Xrouter是router模块的消息中转类,专门处理消息。我们看其代码:
private static final String TAG = "Xrouter";
//使用volatile关键字的好处是保证线程可见
public static volatile Xrouter mXrouter ;
//使用HashMap初始化一个队列mXactions,用来存储不同种类的消息通道
public static HashMap mXactions ;
private Xrouter() {
mXactions =new HashMap<>();
}
//单例模式,支持多线程。参考:https://www.jianshu.com/p/769f2593c94e
public static Xrouter getInstance(){
if(mXrouter == null){
synchronized (Xrouter.class){
if(mXrouter == null){
mXrouter =new Xrouter();
}
}
}
return mXrouter;
}
//往消息队列插入不同消息通道的方法,这里参数包括通道名称和通道本身Xaction.java
public void registerAction(String actionKey,Xaction xaction){
if(mXactions.containsKey(actionKey)){
Log.e(TAG, "该通道已经注册");
}else{
mXactions.put(actionKey,xaction);
}
}
//对应通道发送消息的方法
public XrouterResponse senMessage(Context context ,XrouterRequest xrouterRequest){
XrouterResponse mXrouterResponse=new XrouterResponse();
Xaction mXaction =getmXAction(xrouterRequest.getActionName());
//Xaction对象不为空,说明该通道存在,之前已经注册,可以正常发送消息
if(mXaction != null){
//将发送的消息内容(xrouterRequest.getData())传递给对应的Xaction的实现类
Object mObject =mXaction.startAction(context,xrouterRequest.getData());
mXrouterResponse.setResponseResult(XrouterResponse.RESPONSE_SUCCESS_CODE,XrouterResponse.RESPONSE_SUCCESS,mObject);
}else{
mXrouterResponse.setResponseResult(XrouterResponse.RESPONSE_FAIL_CODE,XrouterResponse.RESPONSE_FAIL,"该Xaction没有创建");
}
return mXrouterResponse;
}
//返回消息通道对应的对象
public Xaction getmXAction(String actionName){
if(mXactions.containsKey(actionName)){
return mXactions.get(actionName);
}
return null;
}
注释都很详细,主要是三个方法registerAction(),senMessage()和 getmXAction()方法,既然是消息的中转站那么就要存储消息,我们这里用HashMap
分别来说一下这三个方法
registerAction()
我们在用HashMap存消息之前先要注册消息对象,而registerAction方法通过key,value的形式把我们的Xaction放入HashMap存储起来,完成注册。senMessage()
这个方法比较重要,简单来说就是我们发消息给相关的module.,里面涉及的XrouterResponse,Xaction,Xrespinse我们稍后说。getmXAction()
此方法就是查找我们之前在HashMap中注册的消息即Xaction是否已经存在,存在就返回其对象。
Xaction
Xaction是抽象类,里面包含一个抽象方法startAciont,此抽象方法主要是让实现类对发送消息做做一个传递,也就是将发送的消息传递给对应的module,并返回结果(是否成功将消息传递)。
XrouterRequest
public class XrouterRequest {
//消息通道名称
private String mActionName;
//消息通道携带的数据
private HashMap mData;
private XrouterRequest(){
mData =new HashMap<>();
}
public static XrouterRequest create(){
return new XrouterRequest();
}
public XrouterRequest putData(String key, Object value){
mData.put(key,value);
return this;
}
public XrouterRequest putActionName(String actionName){
mActionName=actionName;
return this;
}
public String getActionName(){
return this.mActionName;
}
public HashMap getData(){
return this.mData;
}
}
发送消息的载体,也就是具体消息也携带的内容,包括两个变量一个是mActionName,此mActionName和注册到HashMap中的Xaction的key对应,便于查找到Xaction对象,而其中的mData这是携带传递的内容。
XrouterResponse
public class XrouterResponse {
public static final String RESPONSE_SUCCESS="发送消息成功";
public static final String RESPONSE_FAIL="发送消息失败";
public static final int RESPONSE_SUCCESS_CODE=1;
public static final int RESPONSE_FAIL_CODE=0;
//状态码
private int mcode;
//描述:消息发送成功或失败
private String mdes;
//消息反馈的其他信息
private Object mbody;
//获取响应消息
public JSONObject getResponseResult(){
JSONObject mJSONObject=null;
try {
mJSONObject =new JSONObject();
mJSONObject.put("code",mcode).put("des",mdes).put("content",mbody);
} catch (JSONException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return mJSONObject;
}
//设置响应消息
public void setResponseResult(int code ,String des,Object obj){
this.mcode=code;
this.mdes=des;
this.mbody=obj;
}
}
消息的发送结果的响应类,主要由状态码,描述和其他反馈信息三部分构成。包含一个获取消息结果一个设置消息结果的方法,没啥好说的。
differentprocess和sameprocess模块
从字面意思来看他们一个是和app在一个进程中,一个不再一个进程中。这里主要是为了测试如果不在同一个进程中路由的效果,不再进程中主要是因为我在differentprocess模块的功能清单文件中添加了:
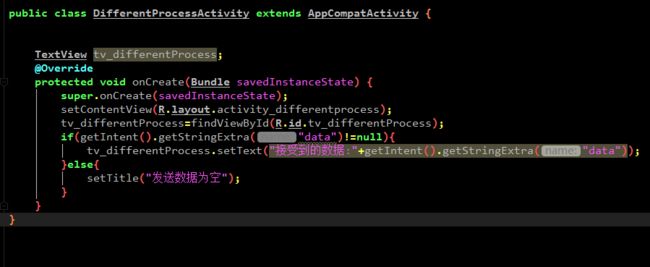
这两个模块(differentprocess和sameprocess)都实现了Xaction的抽象通道方法startAction,j具体如下:
这样就可以将消息通过通道传递给相应的activity了。而在activity中,我们只是对传递的内容进行了展示,如下:
common模块
没事说的,就是几个常量,自己下载demo看。
app模块
该模块中两个类
-MainActivity中
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
Button btn_sameProcess;
Button btn_differentProcess;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
btn_sameProcess=findViewById(R.id.sameprocess);
btn_differentProcess=findViewById(R.id.differnetprocess);
btn_differentProcess.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
//封装传递的请求数据到XrouterRequest
XrouterRequest mXrouterRequest =XrouterRequest.create().putData("data","发给不同进程的数据测试").putActionName(DifferentProcessActionMessage.DIFFERENTPROCESSACTIONNAME);
XrouterResponse mXrouterResponse=Xrouter.getInstance().senMessage(MainActivity.this,mXrouterRequest);
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this,mXrouterResponse.getResponseResult()+"",Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
}
});
btn_sameProcess.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
//封装传递的请求数据到XrouterRequest
XrouterRequest mXrouterRequest =XrouterRequest.create().putData("data","发给同进程的数据测试").putActionName(SameProcessActionMessage.SANEPORICESSBANE);
XrouterResponse mXrouterResponse=Xrouter.getInstance().senMessage(MainActivity.this,mXrouterRequest);
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this,mXrouterResponse.getResponseResult()+"",Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
}
});
}}
MainActivty就是两个按钮一个是跳转到同进程一个跳转到不同进程的module中,将携带的信息存放到XrouterRequest中,同时返回响应对象XrouterResponse,简单toast了一下。
- BaseApplication
Xaction消息的注册建议存放点Application中,如下:
public class BaseApplication extends Application {
@Override
public void onCreate() {
super.onCreate();
//通道的初始化最好放在Application中
initAction();
}
private void initAction() {
Xrouter.getInstance().registerAction(DifferentProcessActionMessage.DIFFERENTPROCESSACTIONNAME,new com.hxzk.bj.differnertprocess.action.DifferentProcessAction());
Xrouter.getInstance().registerAction(SameProcessActionMessage.SANEPORICESSBANE,new com.hxzk.bj.sameprocessmodule.action.SameProcessAction());
}
}
就这么多,建议大家下载demo具体查看,以上传github:点我传送
告辞!