前言
JSON作为一种轻量级的数据交换格式,在我们日常的开发中使用十分广泛,就Java后端的开发工作中,JSON字符串与Java对象之间相互转换是常常遇到的操作。
虽然平时用到的挺多的,但是因为用于JSON处理的包有很多种,每种工具集的功能和使用方式也都不同,很容易在使用时造成混乱。
本文就结合
FastJson部分源码,简单整理了下常用的API及其使用示例
本文FastJson版本:1.2.54
转换图
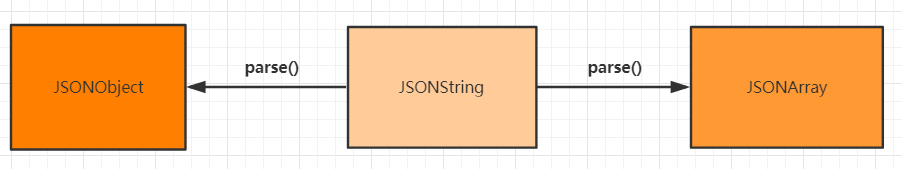
根据FastJson源码大致整理出了这么一张转换图:
可以看到参与转换的对象主要有图中五种:
- JSONString:
json字符串 - JSONObject:
json对象 - JSONArray:
json对象数组 - JavaBean:
java对象 - List :
java对象集合
转化中用到的方法的方法名有如下几种:
- parse:
JSONString ==> JSONObject/JSONArray - parseObject:
JSONString ==> JSONObject/JavaBean - pareseArray:
JSONString ==> JSONObject/List - toJSONString:
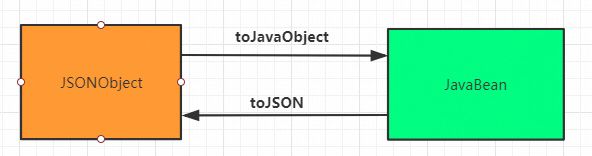
JavaBean/JSONObject ==> JSONString - toJSON:
JavaBean ==> JSONObject - toJavaObject:
JSONObject ==> JavaBean
常用API
本文种仅列举
平常使用频率较高的API,其他的重载方法可参考源码,大都是对序列化/反序列化过程进行定制化。
toJSONString
实现了json对象(
JSONObject)==>json字符串(JSONString),和Java对象(JavaBean)==>json字符串(JSONString)的转化
从源码中可以看到这一方法被重载了多个,我们日常会用到的有如下几个:
| 方法 : 返回值 | 参数说明 | 功能 |
|---|---|---|
| toJSONString(Object object):String | object: 需要进行序列化的对象javaBean或者JSONObject |
将对象序列化为json字符串 |
| toJSONString(Object object, boolean prettyFormat):String | prettyFormat:是否格式化输出json字符串 |
格式化输出json字符串 |
| toJSONString(Object object, SerializerFeature... features):String | features:序列化额外属性配置,非必填 |
根据指定属性进行序列化 |
| toJSONStringWithDateFormat(Object object, String dateFormat, SerializerFeature... features):String | dateFormat:日期格式(yyyy-MM-dd) |
序列化时格式化日期 |
这些方法中最常用的即为:toJSONString(Object object)
parse
实现了json字符串(
JSONString)==>json对象(JSONObject),和json字符串(JSONString)==>json对象数组(JSONArray)的转化
| 方法 : 返回值 | 参数说明 | 功能 |
|---|---|---|
| parse(String text):Object | text:json字符串 |
反序列化json字符串 |
parseObject
实现了json字符串(
JSONString)==>json对象(JSONObject),和json字符串(JSONString)==>Java对象(JavaBean)的转化
| 方法 : 返回值 | 参数说明 | 功能 |
|---|---|---|
| parseObject(String text):JSONObject | text:json字符串 |
反序列化json字符串为Json对象 |
| parseObject(String text, Class clazz):T | clazz:指定反序列化后的类 |
json字符串转java对象 |
| parseObject(String text, TypeReference type, Feature... features):T | type:构造转化类型,features:反序列化额外属性 |
json字符串转java对象 |
parseArray
实现了json字符串(
JSONString)==>json对象数组(JSONArray),和json字符串(JSONString)==>Java对象集合(List `)的转化
| 方法 : 返回值 | 参数说明 | 功能 |
|---|---|---|
| parseArray(String text) :JSONArray | text:json字符串 |
将json字符串反序列化为JSON数组对象 |
| parseArray(String text, Class clazz):List | clazz:指定转化后的类 |
将json字符串反序列化为java对象集合 |
toJSON/toJavaObject
toJSON()实现了Java对象(
JavaBean)==>Json对象(JSONObject)的转换toJavaObject()实现了Json对象(
JSONObject)==>Java对象(JavaBean)的转换
| 方法 : 返回值 | 参数说明 | 功能 |
|---|---|---|
| toJSON(Object javaObject):Object | javaObject:java对象 |
java对象转化为Json对象 |
| toJavaObject(JSON json, Class clazz):T | json:json对象,clazz:要转化的类型 |
json对象转化为java对象 |
代码示例
Student学生类
package com.larscheng.www.jsontest;
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Data;
import java.util.Date;
/**
* 描述:
* 学生类
*
* @author larscheng
* @date 2019/11/19 19:33
*/
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
public class Student {
private String name;
private int age;
private Date birthday;
}
测试类FastJsonTest.java代码如下:
package com.larscheng.www.jsontest.fastJson;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSON;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSONArray;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSONObject;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.TypeReference;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.serializer.SerializerFeature;
import com.larscheng.www.jsontest.Course;
import com.larscheng.www.jsontest.Student;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.List;
/**
* 描述:
* fastJson的api示例
*
* @author larscheng
* @date 2019/11/19 19:37
*/
public class FastJsonTest {
private final static Student LIMING = new Student("liming", 20, new Date());
private final static String LIMING_STR =
"{'age':20,'birthday':1574163958480,'name':'liming'}";
private final static Course MATH = new Course("数学课", "高等代数");
private final static Course CHINESE = new Course("语文课", "大学语文");
private final static List COURSES = Arrays.asList(MATH, CHINESE);
private final static String COURSES_STR =
"[{'desc':'高等代数','name':'数学课'},{'desc':'大学语文','name':'语文课'}]";
private final static JSONObject LIMING_MAP = new JSONObject();
static {
LIMING_MAP.put("name", "liming");
LIMING_MAP.put("age", 20);
LIMING_MAP.put("birthday", new Date());
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
//############ toJSONString ###############
/*JavaBean--->JSONString*/
System.err.println("JavaBean--->JSONString(默认无格式):");
System.out.println(JSON.toJSONString(LIMING));
System.err.println("JavaBean--->JSONString(带格式):");
System.out.println(JSON.toJSONString(LIMING, true));
System.err.println("JavaBean--->JSONString(日期格式化):");
System.out.println(JSON.toJSONStringWithDateFormat(LIMING, "yyyy-MM-dd") + "\n");
/*JSONObject--->JSONString*/
System.err.println("JSONObject--->JSONString(带格式):");
System.out.println(JSON.toJSONString(LIMING_MAP, true) + "\n");
/*List--->JSONString*/
System.err.println("List--->JSONString(默认双引号):");
System.out.println(JSON.toJSONString(COURSES));
System.err.println("List--->JSONString(单引号):");
System.out.println(JSON.toJSONString(COURSES, SerializerFeature.UseSingleQuotes));
System.err.println("List--->JSONString(单引号+带格式):");
System.out.println(JSON.toJSONString(COURSES, SerializerFeature.UseSingleQuotes,SerializerFeature.PrettyFormat) + "\n");
//########## parse/parseObject ###################
/*JSONString--->JSONObject*/
System.err.println("JSONString--->JSONObject(parse):");
JSONObject jsonObject1 = (JSONObject) JSON.parse(LIMING_STR);
System.out.println(jsonObject1.toString());
System.err.println("JSONString--->JSONObject(parseObject):");
System.out.println(JSON.parseObject(LIMING_STR).toString() + "\n");
System.err.println("JSONString--->JavaBean:");
Student student1 = JSON.parseObject(LIMING_STR,Student.class);
System.out.println(student1.hashCode()+"\t"+student1.toString());
System.err.println("JSONString--->JavaBean:");
Student student2 = JSON.parseObject(LIMING_STR,new TypeReference(){});
System.out.println(student2.hashCode()+"\t"+student2.toString());
//########### parse/parseArray ################
/*JSONString--->JSONArray*/
System.err.println("JSONString--->JSONArray(parse):");
JSONArray jsonArray1 = (JSONArray) JSON.parse(COURSES_STR);
System.out.println(jsonArray1.toString());
System.err.println("JSONString--->JSONArray(parseArray):");
System.out.println(JSON.parseArray(COURSES_STR).toString());
System.err.println("JSONString--->List:");
List courses1 = JSON.parseArray(COURSES_STR,Course.class);
System.out.println(courses1.hashCode()+"\t"+courses1.toString()+"\n");
//######### toJSON/toJavaObject ################
System.err.println("JavaBean--->JSONObject:");
System.out.println(JSON.toJSON(LIMING));
System.err.println("JSONObject--->JavaBean:");
System.out.println(JSON.toJavaObject(LIMING_MAP,Student.class));
System.out.println(LIMING_MAP.toJavaObject(Student.class));
System.out.println((Student)LIMING_MAP.toJavaObject(new TypeReference(){}));
System.out.println(LIMING_MAP.toJavaObject(new TypeReference(){}.getType())+"\n");
}
}
总结
基本常用的方法都进行了代码测试,使用过程中可能会出现混淆的情况,但是只要记住了文中的转换图,相信应该会加深印象。
- 文章作者: LarsCheng
- 文章链接: 本文首发于个人博客:https://www.larscheng.com/
- 发布方式:OpenWrite 最懂你的科技自媒体管理平台
- 版权声明: 本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 许可协议。转载请注明来自 LarsCheng's Blog!