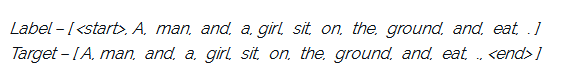深度学习现在发展十分迅猛,每天都会出现多种应用程序。而想要了解深度学习的最好方法就是亲自动手。尽可能尝试自己做项目。这将帮助你更深入地了解它们,并帮助你成为更好的深度学习实践者。
在本文中,我们将结合图像和文本处理来构建一个有用的深度学习应用程序,即图像字幕(Image Captioning)。它是指从图像生成文本描述的过程,主要根据图像中物体和物体的动作。例如:
这个应用在现实生活中有很多潜在的应用场景。要注意保存图像的文本描述,以便在稍后的阶段就可以根据此描述轻松检索。
图像字幕需要做什么?
假设你看到这张照片:
你会首先想到什么呢?也许通常人们可以想出以下几句话:
一个男人和一个女孩坐在地上吃东西。
一个男人和一个小女孩坐在人行道上,靠近一个蓝色的袋子吃东西。
一个穿着黑衬衫的男人和穿橙色连衣裙的小女孩分享一种吃的。
快速浏览一下就足以让你了解和描述图片中发生的事情。从人工系统自动生成这个文本描述就是图像字幕的任务。
任务很简单:生成的输出期望用单个句子描述图像中显示的内容,如物体的存在,它的属性,它正在进行的动作以及对象之间的交互等。但是,要在与任何其他图像处理问题一样,用人工系统复制这种行为是个极为艰巨的任务,因此我们使用复杂和先进的技术(如深度学习)来解决任务。
解决任务的方法
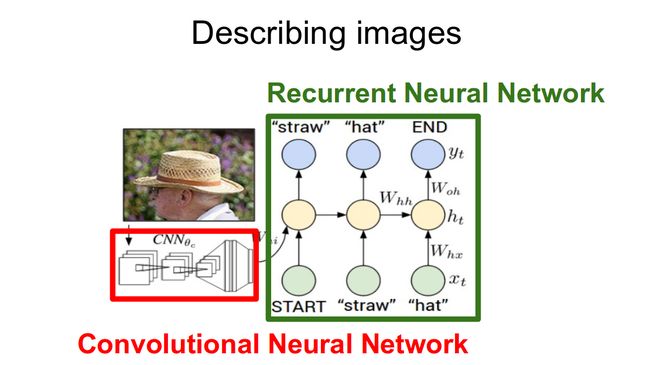
图像字幕的任务从逻辑上可以分为两个模块:一个是基于图像的模型,从图像中提取特征和细微差别,另一个是基于语言的模型,它将第一个模块的所给出的特征和对象转换为的自然语句。
对于我们的基于图像的模型(编码器),我们通常依赖于CNN。对于我们的基于语言的模型(解码器) – 我们依赖于RNN。如下图所示:
在通常情况下,预训练的CNN从我们的输入图像中提取特征。特征向量线性转换后,与RNN/LSTM网络的输入维数相同。这个网络被训练成特征向量的语言模型。
为了训练我们的LSTM模型,我们预定义了我们的标签和目标文本。例如,如果字幕是“A man and a girl sit on the ground and eat”,我们的标签和目标如下:
这样做是为了让我们的模型理解标签序列的开始和结束。
实现
下面我将使用Pytorch进行图像字幕的实现。我们将图像作为输入,并使用深度学习模型预测其描述。
完整代码:https://github.com/yunjey/pytorch-tutorial/tree/master/tutorials/03-advanced/image_captioning
我们使用预训练的resnet-152模型作为编码器,而解码器是LSTM网络。
要运行本例中给出的代码,首先要必须有一个工作的python环境,最好安装了anaconda。然后运行以下命令以安装其他需要的库。
01git clone https://github.com/pdollar/coco.git
02
03cd coco/PythonAPI/
04make
05python setup.py build
06python setup.py install
07
08cd ../../
09
10git clone https://github.com/yunjey/pytorch-tutorial.git
11cd pytorch-tutorial/tutorials/03-advanced/image_captioning/
12
13pip install-r requirements.txt
设置完系统后,应下载训练模型所需的数据集。这里我们将使用MS-COCO数据集。要自动下载数据集,可以运行以下命令:
1chmod+ x download.sh
2./download.sh
现在你可以继续构建你的模型了。首先,你必须处理输入:
1# Search for all the possible words in the dataset and
2# build a vocabulary list
3python build_vocab.py
4
5# resize all the images to bring them to shape 224x224
6python resize.py
现在你可以运行以下命令开始训练模型:
python train.py --num_epochs 10 --learning_rate 0.01
只要查看并查看我们怎样在背后定义我们的模型,可以参考model.py文件中编写的代码 。
01import torch
02import torch.nn as nn
03import torchvision.models as models
04from torch.nn.utils.rnnimport pack_padded_sequence
05from torch.autogradimport Variable
06
07class EncoderCNN(nn.Module):
08 def __init__(self, embed_size):
09 """Load the pretrained ResNet-152 and replace top fc layer."""
10 super(EncoderCNN,self).__init__()
11 resnet= models.resnet152(pretrained=True)
12 modules= list(resnet.children())[:-1] # delete the last fc layer.
13 self.resnet= nn.Sequential(*modules)
14 self.linear= nn.Linear(resnet.fc.in_features, embed_size)
15 self.bn= nn.BatchNorm1d(embed_size, momentum=0.01)
16 self.init_weights()
17
18 def init_weights(self):
19 """Initialize the weights."""
20 self.linear.weight.data.normal_(0.0,0.02)
21 self.linear.bias.data.fill_(0)
22
23 def forward(self, images):
24 """Extract the image feature vectors."""
25 features= self.resnet(images)
26 features= Variable(features.data)
27 features= features.view(features.size(0),-1)
28 features= self.bn(self.linear(features))
29 return features
30
31
32class DecoderRNN(nn.Module):
33 def __init__(self, embed_size, hidden_size, vocab_size, num_layers):
34 """Set the hyper-parameters and build the layers."""
35 super(DecoderRNN,self).__init__()
36 self.embed= nn.Embedding(vocab_size, embed_size)
37 self.lstm= nn.LSTM(embed_size, hidden_size, num_layers, batch_first=True)
38 self.linear= nn.Linear(hidden_size, vocab_size)
39 self.init_weights()
40
41 def init_weights(self):
42 """Initialize weights."""
43 self.embed.weight.data.uniform_(-0.1,0.1)
44 self.linear.weight.data.uniform_(-0.1,0.1)
45 self.linear.bias.data.fill_(0)
46
47 def forward(self, features, captions, lengths):
48 """Decode image feature vectors and generates captions."""
49 embeddings= self.embed(captions)
50 embeddings= torch.cat((features.unsqueeze(1), embeddings),1)
51 packed= pack_padded_sequence(embeddings, lengths, batch_first=True)
52 hiddens, _= self.lstm(packed)
53 outputs= self.linear(hiddens[0])
54 return outputs
55
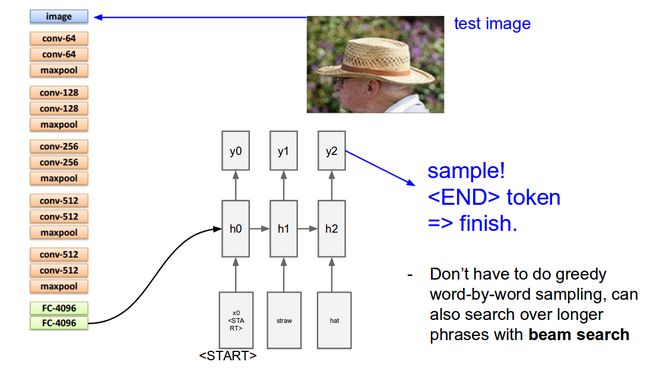
56 def sample(self, features, states=None):
57 """Samples captions for given image features (Greedy search)."""
58 sampled_ids= []
59 inputs= features.unsqueeze(1)
60 for iin range(20): # maximum sampling length
61 hiddens, states= self.lstm(inputs, states) # (batch_size, 1, hidden_size),
62 outputs= self.linear(hiddens.squeeze(1)) # (batch_size, vocab_size)
63 predicted= outputs.max(1)[1]
64 sampled_ids.append(predicted)
65 inputs= self.embed(predicted)
66 inputs= inputs.unsqueeze(1) # (batch_size, 1, embed_size)
67 sampled_ids= torch.cat(sampled_ids,1) # (batch_size, 20)
68 return sampled_ids.squeeze()
现在我们可以使用以下命令进行测试:
1python sample.py--image= ' png / example.png '
对于我们的示例图像,我们的模型给了我们这个输出:
a group of giraffes standing in a grassy area .
我们上面看到的模型只是冰山一角。目前,图像字幕中最先进的模型是微软的CaptionBot。你可以在他们的官方网站上查看系统的演示。
本文为编译作品,转载请注明出处。