今天看到群里有人提到open***,刚好放假在家,就顺带的研究了下。
2年前自己还是小白的时候就在老单位连总部OA时用过open***这个客户端,感觉还挺好用,而且觉得以后项目应该也能用得上,SO google了网上大量零碎资料,折腾了大半天,按照自己的理解就整理了如下文档,给有兴趣的朋友分享一下。
最近一直想把自己的短板,也就是LINUX编程这块好好研究下。。
不扯了,开始干活。。
-------------------华丽的分割线-----------------------
我的博客新站已经建好,更多新的内容即将在新站更新。。
欢迎访问 http://www.showerlee.com
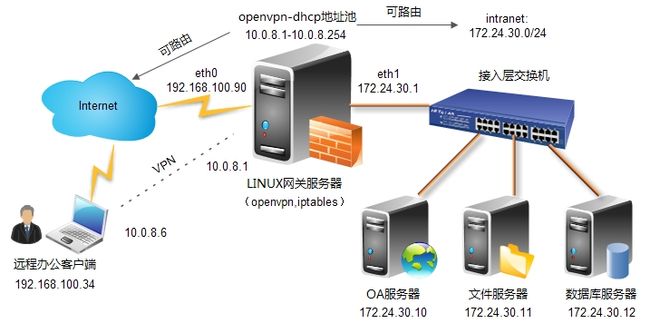
open***是一款在LINUX网关服务器使用的开源的×××软件,顾名思义,其实就是用来打通一条安全的虚拟专用通道,实现用户远程办公,获取内网资源。
该软件可跨平台在在Linux、xBSD、Mac OS X与Windows间使用,并利用openssl作为加密库,使用加密证书或用户名/密码来实现身份验证,是一款不可多得的开源×××解决方案。
我们做这个实验的目的就是模拟线上常见的公司外出人员在外需要访问公司内网OA,实现远程办公自动化。
解决方案:
系统环境:centos6.3 x64
OPEN×××: open***-2.3.0(附件有下载)
*** server: eth0:192.168.100.90,eth1:172.24.30.1
*** client: 192.168.100.34
intranet server: 172.24.30.10
部署环境:
1.清空默认策略并重启iptables
# iptables -t NAT -F
# iptables -F
# service iptables save
# service iptables restart
2.关闭SELINUX
# setenforce 0
# vi /etc/sysconfig/selinux
---------------
SELINUX=disabled
---------------
server端(路由模式):
一.网络设置
1.开启服务器端路由转发功能
# vi /etc/sysctl.conf
---------------------
net.ipv4.ip_forward = 1
---------------------
# sysctl -p
2.设置nat转发:
注:保证×××地址池可路由出外网
# iptables -t nat -A POSTROUTING -s 10.8.0.0/24 -o eth0 -j MASQUERADE
3.设置open***端口通过:
# iptables -A INPUT -p TCP --dport 1194 -j ACCEPT
# iptables -A INPUT -m state --state ESTABLISHED,RELATED -j ACCEPT
重启iptables:
注:这里提一下,INPUT策略是执行后即时生效的,POSTROUTING需要保存并重启服务才能生效
# service iptables save
# service iptables restart
注:若想让该服务器只提供open***等基本服务,可参照本文档附件iptables脚本
3.时间同步(重要):
# ntpdate asia.pool.ntp.org
二.安装依赖库
# yum install -y openssl openssl-devel lzo lzo-devel pam pam-devel automake pkgconfig
三.安装open***:
# wget -c http://swupdate.open***.org/community/releases/open***-2.3.0.tar.gz
# tar zxvf open***-2.3.0.tar.gz
# cd open***-2.3.0
# ./configure --prefix=/usr/local/open***
# make && make install
# mkdir -p /etc/open***
复制模板到open***配置目录:
# cp -rf sample /etc/open***/
复制open***配置文件到主目录:
# cp /etc/open***/sample/sample-config-files/server.conf /etc/open***/
# cd ..
四.下载easy-rsa:
注:该包用来制作ca证书,服务端证书,客户端证书,open***2.3.0该版本源码不包含easy-rsa,所以需要单独下载安装用来配合open***实现证书生成。
# wget -c http://www.showerlee.com/down/easy-rsa-master.zip
# unzip easy-rsa-master.zip
# mv easy-rsa-master easy-rsa
# cp -rf easy-rsa /etc/open***
# cd /etc/open***/easy-rsa/easy-rsa/2.0
修改_证书变量
# vi vars
修改如下参数
注:在后面生成服务端ca证书时,这里的配置会作为缺省配置
---------------------
export KEY_COUNTRY="CN"
export KEY_PROVINCE="SX"
export KEY_CITY="Xian"
export KEY_ORG="example"
export KEY_EMAIL="[email protected]"
---------------------
做SSL配置文件软链:
# ln -s openssl-1.0.0.cnf openssl.cnf
修改vars文件可执行并调用
# chmod +x vars
# source ./vars
-----------------
NOTE: If you run ./clean-all, I will be doing a rm -rf on /etc/open***/easy-rsa/easy-rsa/2.0/keys
-----------------
注:也就是如果执行./clean-all,就会清空/etc/open***/easy-rsa/easy-rsa/2.0/keys下所有文件
开始配置证书:
1.清空原有证书:
# ./clean-all
注:下面这个命令在第一次安装时可以运行,以后在添加完客户端后慎用,因为这个命令会清除所有已经生成的证书密钥,和上面的提示对应
2.生成服务器端ca证书
# ./build-ca
注:由于之前做过缺省配置,这里一路回车即可
3.生成服务器端密钥证书, 后面这个open***.example.com就是服务器名,也可以自定义
# ./build-key-server open***.example.com
---------------------------
Generating a 2048 bit RSA private key
...................................................+++
..................................+++
writing new private key to 'open***.example.com.key'
-----
You are about to be asked to enter information that will be
incorporated
into your certificate request.
What you are about to enter is what is called a Distinguished Name or
a DN.
There are quite a few fields but you can leave some blank
For some fields there will be a default value,
If you enter '.', the field will be left blank.
-----
Country Name (2 letter code) [CN]:
State or Province Name (full name) [SX]:
Locality Name (eg, city) [Xian]:
Organization Name (eg, company) [example]:
Organizational Unit Name (eg, section) []:
Common Name (eg, your name or your server's hostname)
[open***.example.com]:
Name [EasyRSA]:
Email Address [[email protected]]:
Please enter the following 'extra' attributes
to be sent with your certificate request
A challenge password []:123456
An optional company name []:example
Using configuration from /etc/open***/easy-rsa/easy-rsa/2.0/openssl-1.0.0.cnf
Check that the request matches the signature
Signature ok
The Subject's Distinguished Name is as follows
countryName :PRINTABLE:'CN'
stateOrProvinceName :PRINTABLE:'SX'
localityName :PRINTABLE:'Xian'
organizationName :PRINTABLE:'example'
commonName :PRINTABLE:'open***.example.com'
name :PRINTABLE:'EasyRSA'
emailAddress :IA5STRING:'[email protected]'
Certificate is to be certified until Jun 10 21:58:49 2023 GMT (3650 days)
Sign the certificate? [y/n]:y
1 out of 1 certificate requests certified, commit? [y/n]y
Write out database with 1 new entries
Data Base Updated
---------------------------
4.生成所需客户端证书密钥文件(名字任意,建议写成你要发给的人的姓名,方便管理):
# ./build-key client1
# ./build-key client2
注:这里与生成服务端证书配置类似,中间一步提示输入服务端密码,其他按照缺省提示一路回车即可。
5.再生成diffie hellman参数,用于增强open***安全性(生成需要漫长等待)
# ./build-dh
6.打包keys
# tar zcvf keys.tar.gz keys/
7.终端发送到客户端备用
# yum install lrzsz -y
# sz keys.tar.gz
五.配置open*** server:
# vi /etc/open***/server.conf
注:可按照默认模板配置,本例为自定义配置文件:
--------------------------
# 设置监听IP,默认是监听所有IP
;local a.b.c.d
# 设置监听端口,必须要对应的在防火墙里面打开
port 1194
# 设置用TCP还是UDP协议?
;proto tcp
proto tcp
# 设置创建tun的路由IP通道,还是创建tap的以太网通道
# 路由IP容易控制,所以推荐使用它;但如果如IPX等必须
# 使用第二层才能通过的通讯,则可以用tap方式,tap也
# 就是以太网桥接
;dev tap
dev tun
# Windows需要给网卡一个名称,这里设置,linux不需要
;dev-node MyTap
# 这里是重点,必须指定SSL/TLS root certificate (ca),
# certificate(cert), and private key (key)
# ca文件是服务端和客户端都必须使用的,但不需要ca.key
# 服务端和客户端指定各自的.crt和.key
# 请注意路径,可以使用以配置文件开始为根的相对路径,
# 也可以使用绝对路径
# 请小心存放.key密钥文件
ca /etc/open***/easy-rsa/easy-rsa/2.0/keys/ca.crt
cert /etc/open***/easy-rsa/easy-rsa/2.0/keys/open***.example.com.crt
key /etc/open***/easy-rsa/easy-rsa/2.0/keys/open***.example.com.key
# This file should be kept secret
# 指定Diffie hellman parameters.
dh /etc/open***/easy-rsa/easy-rsa/2.0/keys/dh2048.pem
# 配置×××使用的网段,Open×××会自动提供基于该网段的DHCP
# 服务,但不能和任何一方的局域网段重复,保证唯一
server 10.8.0.0 255.255.255.0
# 维持一个客户端和virtual IP的对应表,以方便客户端重新
# 连接可以获得同样的IP
ifconfig-pool-persist ipp.txt
# 配置为以太网桥模式,但需要使用系统的桥接功能
# 这里不需要使用
;server-bridge 10.8.0.4 255.255.255.0 10.8.0.50 10.8.0.100
# 为客户端创建对应的路由,以另其通达公司网内部服务器
# 但记住,公司网内部服务器也需要有可用路由返回到客户端
;push "route 192.168.20.0 255.255.255.0"
push "route 172.24.30.0 255.255.255.0"
# 为特定的客户端指定IP或指定路由,该路由通常是客户端后面的
# 内网网段,而不是服务端连接的网段
# ccd是/etc/open***下的目录,其中建有希望限制的客户端Common
# Name为文件名的文件,并通过下面的命令写入固定IP地址
# 例如Common Name为client1,则在/etc/open***/ccd/client1写有:
# ifconfig-push 10.9.0.1 10.9.0.2
;client-config-dir ccd
;route 192.168.40.128 255.255.255.248
# 为可以对不同的客户端设置防火墙等权限
# 可以让其自动运行对应脚本,可参考man
;learn-address ./script
# 若客户端希望所有的流量都通过×××传输,则可以使用该语句
# 其会自动改变客户端的网关为×××服务器,推荐关闭
# 一旦设置,请小心服务端的DHCP设置问题
;push "redirect-gateway"
# 用Open×××的DHCP功能为客户端提供指定的DNS、WINS等
;push "dhcp-option DNS 10.8.0.1"
;push "dhcp-option WINS 10.8.0.1"
# 默认客户端之间是不能直接通讯的,除非把下面的语句注释掉
client-to-client
# 如果您希望有相同Common Name的客户端都可以登陆
# 也可以注释下面的语句,推荐每个客户端都使用不用的Common Name
# 常用于测试
;duplicate-cn
# 设置服务端检测的间隔和超时时间
keepalive 10 120
# 下面是一些对安全性增强的措施
# For extra security beyond that provided
# by SSL/TLS, create an "HMAC firewall"
# to help block DoS attacks and UDP port flooding.
#
# Generate with:
# open*** --genkey --secret ta.key
#
# The server and each client must have
# a copy of this key.
# The second parameter should be 0
# on the server and 1 on the clients.
;tls-auth ta.key 0 # This file is secret
# Select a cryptographic cipher.
# This config item must be copied to
# the client config file as well.
;cipher BF-CBC # Blowfish (default)
;cipher AES-128-CBC # AES
;cipher DES-EDE3-CBC # Triple-DES
# 使用lzo压缩的通讯,服务端和客户端都必须配置
comp-lzo
# 设置最大用户数
;max-clients 100
# 让Open×××以nobody用户和组来运行(安全)
;user nobody
;group nobody
# The persist options will try to avoid
# accessing certain resources on restart
# that may no longer be accessible because
# of the privilege downgrade.
persist-key
persist-tun
# 输出短日志,每分钟刷新一次,以显示当前的客户端
status /var/log/open***/open***-status.log
# 缺省日志会记录在系统日志中,但也可以导向到其他地方
# 建议调试的使用先不要设置,调试完成后再定义
log /var/log/open***/open***.log
log-append /var/log/open***/open***.log
# 设置日志的级别
#
# 0 is silent, except for fatal errors
# 4 is reasonable for general usage
# 5 and 6 can help to debug connection problems
# 9 is extremely verbose
verb 3
# Silence repeating messages. At most 20
# sequential messages of the same message
# category will be output to the log.
;mute 20
--------------------------
创建日志目录:
# mkdir -p /var/log/open***/
启动open*** server
# /usr/local/open***/sbin/open*** --config /etc/open***/server.conf &
设置开机启动:
# echo "/usr/local/open***/sbin/open*** --config /etc/open***/server.conf > /dev/null 2>&1 &" >> /etc/rc.local
client端:
六.安装WINDOWS客户端(WIN7 64bit)
1.下载客户端,并默认安装:
http://***tech.googlecode.com/files/open***-2.1.1-gui-1.0.3-install-cn-64bit.zip
2.将服务端打包文件解压,并将包内ca.crt、client1.crt、client1.key复制到客户端C:\Program Files\Open×××\config下.
3.在C:\Program Files\Open×××\config下创建client.o***文件
内容如下:
-----------------------
# 定义是一个客户端
client
# 定义使用路由IP模式,与服务端一致
;dev tap
dev tun
# 定义Windows下使用的网卡名称,linux不需要
;dev-node MyTap
# 定义使用的协议,与服务端一致
;proto tcp
proto tcp
# 指定服务端地址和端口,可以用多行指定多台服务器
# 实现负载均衡(从上往下尝试)
remote 192.168.100.90 1194
;remote my-server-2 1194
# 若上面配置了多台服务器,让客户端随机连接
;remote-random
# 解析服务器域名
# Keep trying indefinitely to resolve the
# host name of the Open××× server. Very useful
# on machines which are not permanently connected
# to the internet such as laptops.
resolv-retry infinite
# 客户端不需要绑定端口
# Most clients do not need to bind to
# a specific local port number.
nobind
# 也是为了让Open***也nobody运行(安全)
# 注意:Windows不能设置
;user nobody
;group nobody
# Try to preserve some state across restarts.
persist-key
persist-tun
# 若客户端通过HTTP Proxy,在这里设置
# 要使用Proxy,不能使用UDP为×××的通讯协议
;http-proxy-retry # retry on connection failures
;http-proxy [proxy server] [proxy port #]
# 无线网络有很多多余的头文件,设置忽略它
;mute-replay-warnings
# 重点,就是指定ca和客户端的证书
ca ca.crt
cert client1.crt
key client1.key
# 如果服务端打开了PAM认证模块,客户端需要另其有效
;auth-user-pass
# 一些安全措施
# Verify server certificate by checking
# that the certicate has the nsCertType
# field set to "server". This is an
# important precaution to protect against
# a potential attack discussed here:
# http://open***.net/howto.html#mitm
#
# To use this feature, you will need to generate
# your server certificates with the nsCertType
# field set to "server". The build-key-server
# script in the easy-rsa folder will do this.
;ns-cert-type server
# If a tls-auth key is used on the server
# then every client must also have the key.
;tls-auth ta.key 1
# Select a cryptographic cipher.
# If the cipher option is used on the server
# then you must also specify it here.
;cipher x
# 使用lzo压缩,与服务端一致
comp-lzo
# Set log file verbosity.
verb 3
# Silence repeating messages
;mute 20
-----------------------
5.连接:
在右下角的open***图标上右击,选择“Connect”,若能正常分配IP,则连接成功。
6.最终测试:
C:\Users\Administrator>ipconfig/all
---------------------------------------
...............
以太网适配器 本地连接* 12:
连接特定的 DNS 后缀 . . . . . . . :
描述. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . : TAP-Win32 Adapter V9
物理地址. . . . . . . . . . . . . : 00-FF-45-FB-F5-E2
DHCP 已启用 . . . . . . . . . . . : 是
自动配置已启用. . . . . . . . . . : 是
本地链接 IPv6 地址. . . . . . . . : fe80::848d:bd1d:c1f4:fb51%27(首选)
IPv4 地址 . . . . . . . . . . . . : 10.8.0.6(首选)
子网掩码 . . . . . . . . . . . . : 255.255.255.252
获得租约的时间 . . . . . . . . . : 2013年6月15日 22:36:59
租约过期的时间 . . . . . . . . . : 2014年6月15日 22:36:59
默认网关. . . . . . . . . . . . . :
DHCP 服务器 . . . . . . . . . . . : 10.8.0.5
DHCPv6 IAID . . . . . . . . . . . : 453050181
.....................
----------------------------------
在*** client上ping intranet server 主机IP:172.24.30.10
C:\Users\Administrator>ping 172.24.30.10
-------------------------
正在 Ping 172.24.30.10 具有 32 字节的数据:
来自 172.24.30.10 的回复: 字节=32 时间=2ms TTL=63
来自 172.24.30.10 的回复: 字节=32 时间<1ms TTL=63
来自 172.24.30.10 的回复: 字节=32 时间<1ms TTL=63
来自 172.24.30.10 的回复: 字节=32 时间<1ms TTL=63
--------------------------
大功告成。。。
七.注意事项:
(这里参考并感谢酒哥的“构建高可用LINUX服务器”一书)
1.公司如果有同事离职,如何注销该用户×××证书:
注:这里需保持open***服务正常开启
# cd /etc/open***/easy-rsa/easy-rsa/2.0
# ./revoke-full client2
如果报错,则注释掉该目录下openssl.cnf文件若干行内容,如下:
(实际情况执行上面的操作,直接可注销该用户)
-------------------------
#[pkcs11_section]
#engine_id = pkcs11
#dynamic_path = /usr/lib/engines/engine_pkcs11.so
#MODULE_PATH = $EVN::PKCS11_MODULE_PATH
#PIN = $ EVN::PKCS!!_PIN
#init =0
-------------------------
重新注销:
# ./revoke-full client2
若末行返回error23则账号注销成功,但需完全注销掉还需做如下配置:
# vi /etc/open***/server.conf
末行添加如下内容保证每次在重启加载open***配置文件时都会重新加载crl.pem文件:
-----------------------
crl-verify /etc/open***/easy-rsa/easy-rsa/2.0/keys/crl.pem
-----------------------
注:crl.pem为注销的用户的黑名单,可以理解为每次启动open***时,加载一次黑名单操作,保证最新被吊销的证书无法使用。
重启open***:
# killall open***
# /usr/local/open***/sbin/open*** --config /etc/open***/server.conf &
在客户端服务器使用client2证书验证该证书是否能够使用
最终确定该证书无法连接open***服务器
2.更改证书有效期,提高证书的安全性:
默认_证书的有效期是3650天,也就是10年
# cd /etc/open***/easy-rsa/easy-rsa/2.0
# vi pkitool
搜索到两处默认有效期天数"3650",修改该为你需要设置的天数保存即可
下次执行该脚本制作客户端证书时,期限就会更改为新的天数。
进阶:
open***作为内网server提供远程×××服务解决方案:
有充裕预算的公司可以搭建open***的负载均衡,这里可以把两台服务器挂到内网交换机上,利用一台防火墙隔离内外网,并做分别作到内网这两台open***服务器的两条端口映射,保证两台服务器与其他内网服务器同网段,且两台open***配置相同。
这个方案其实适用于在项目后期,如果已经架设好防火墙,在既保留现有防火墙的情况下又想远程客户端访问内网资源,其实就可以利用原有防火墙做一个到内网open***服务器1194端口的映射,只要能保证open***服务器与其他内网资源在同一网段,或者可路由网段,就能起到远程×××访问功能。
(open***-server)
1.打开ip_forward(略)
2.做open***地址池网段数据可转发出eth0口的策略
# iptables -t nat -A POSTROUTING -s 10.8.0.0/24 -o eth0 -j MASQUERADE
3.保证open***配置文件做了到内网的路由
---------------------
push "route 192.168.100.0 255.255.255.0"
---------------------
其他配置与网关open***模式一致。
最后在客户端配置文件(C:\Program Files\Open×××\config\client.o***)里添加如下内容:
------------------
remote 172.24.30.40 1194
remote 172.24.30.40 1195
.....
remote-random
------------------
这行客户端会随机连接这2台服务器地址,从而利用其作为代理访问网内其他资源。
--------大功告成----------