前言
前段时间看了一些vue-cli的源码,收获颇深。本想找个时间更新一篇文章,但是最近事情比较多,没有时间去整理这些东西。趁这两天闲了下来,便整理了一下,然后跟大家分享一下。如果小伙伴们读完之后,跟我一样收获很多的话,还望各位小伙伴们多多点赞收藏支持一下哦。
Vue-cli介绍
Vue-cli是一款非常优秀的用于迅速构建基于Vue的Web应用工具。他不同于creat-react-app这样的工具,开发者只需要关注项目逻辑的代码,而不需要关心webpack打包、启动Node服务等等诸如此类的这些问题。Vue-cli是一款基于模板化的开发工具,等于就是把别人的项目结构给照搬过来,所有的配置都是暴露出来的,你可以根据实际情况去做一些配置的修改,更加灵活自由一点。当然这对前端工程师提出更高的要求,考虑的东西也变多了。不过Vue-cli即将发布3.0的版本,整个Vue-cli发生了翻天覆地的变化,它采用跟creat-react-app这类工具的模式,开发者只需要关注项目逻辑的代码即可。不过目前3.0还没有出来,所以这次源码分析我采用的v2.9.3的源码,也就是2.0的代码。后面小伙们在阅读的时候要注意以下。
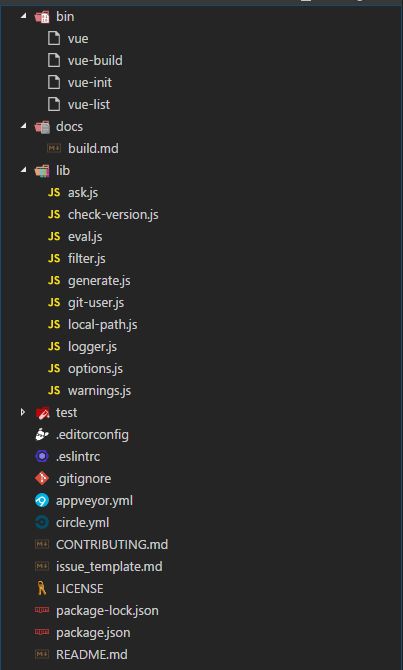
Vue-cli项目结构
整个项目的目录结构如上图所示,下面我大概介绍每个文件夹的东西大致都是干嘛的。
bin (这里放的vue的一些命令文件,比如vue init这样的命令都是从由这里控制的。)
docs (一些注意事项啥的,不重要的目录,可以直接忽略。)
lib (这里存放着一些vue-cli需要的一些自定义方法。)
node_modules (这里应该就不用我多说了,相信大家都知道了,不知道的话可以去面壁去了!●-● )
test (单元测试 开发vue-cli工具时会用到,我们读源码的时候可以直接忽略掉。)
一些杂七杂八的东西 (比如eslint配置、.gitignore、LICENSE等等诸如此类这些东西,不影响我们阅读源码,可以直接忽略掉。)
package.json/README.md (这个不知道也可以去面壁了!●-●)
综合来说,我们阅读源码所要关注的只有bin和lib下面即可,其他的都可忽略。下面开始阅读之旅吧
Vue-cli源码阅读之旅
在开始读源码之前,首先我要介绍一个工具(commander),这是用来处理命令行的工具。具体的使用方法可查看github的README.md https://github.com/tj/commander.js 。小伙伴们再阅读后面的内容之前,建议先去了解一下commander,方便后续的理解。这里我们对commander就不做详细介绍了。这里vue-cli采用了commander的git风格的写法。vue文件处理vue命令,vue-init处理vue init命令以此类推。接着我们一个一个命令看过去。
vue
引入的包:
- commander (用于处理命令行。)
作用: vue这个文件代码很少,我就直接贴出来了。
#!/usr/bin/env node
require('commander')
.version(require('../package').version)
.usage(' [options]')
.command('init', 'generate a new project from a template')
.command('list', 'list available official templates')
.command('build', 'prototype a new project')
.parse(process.argv)
这个文件主要是在用户输入“vue”时,终端上显示参数的使用说明。具体的写法可参考 https://github.com/tj/commander.js 上面的说明。
vue build
引入的包:
- chalk (用于高亮终端打印出来的信息。)
作用: vue build命令在vue-cli之中已经删除了,源码上做了一定的说明。代码不多,我就直接贴出来。
const chalk = require('chalk')
console.log(chalk.yellow(
'\n' +
' We are slimming down vue-cli to optimize the initial installation by ' +
'removing the `vue build` command.\n' +
' Check out Poi (https://github.com/egoist/poi) which offers the same functionality!' +
'\n'
))
vue list
#!/usr/bin/env node
const logger = require('../lib/logger')
const request = require('request')
const chalk = require('chalk')
/**
* Padding.
*/
console.log()
process.on('exit', () => {
console.log()
})
/**
* List repos.
*/
request({
url: 'https://api.github.com/users/vuejs-templates/repos',
headers: {
'User-Agent': 'vue-cli'
}
}, (err, res, body) => {
if (err) logger.fatal(err)
const requestBody = JSON.parse(body)
if (Array.isArray(requestBody)) {
console.log(' Available official templates:')
console.log()
requestBody.forEach(repo => {
console.log(
' ' + chalk.yellow('★') +
' ' + chalk.blue(repo.name) +
' - ' + repo.description)
})
} else {
console.error(requestBody.message)
}
})
引入的包:
- request (发送http请求的工具。)
- chalk (用于高亮console.log打印出来的信息。)
- logger (自定义工具-用于日志打印。)
作用: 当输入"vue list"时(我们测试时,可以直接在当前源码文件目录下的终端上输入“bin/vue-list”),vue-cli会请求接口,获取官方模板的信息,然后做了一定处理,在终端上显示出来模板名称和对应的说明。
效果如下:
Available official templates:
★ browserify - A full-featured Browserify + vueify setup with hot-reload, linting & unit testing.
★ browserify-simple - A simple Browserify + vueify setup for quick prototyping.
★ pwa - PWA template for vue-cli based on the webpack template
★ simple - The simplest possible Vue setup in a single HTML file
★ webpack - A full-featured Webpack + vue-loader setup with hot reload, linting, testing & css extraction.
★ webpack-simple - A simple Webpack + vue-loader setup for quick prototyping.
vue init
“vue init”是用来构建项目的命令,也是vue-cli的核心文件,上面的三个都是非常简单的命令,算是我们阅读源码的开胃菜,真正的大餐在这里。
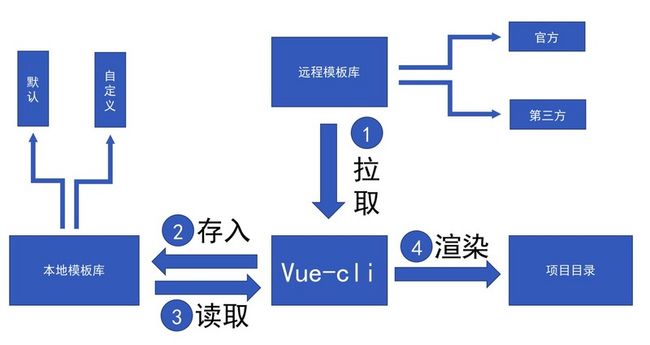
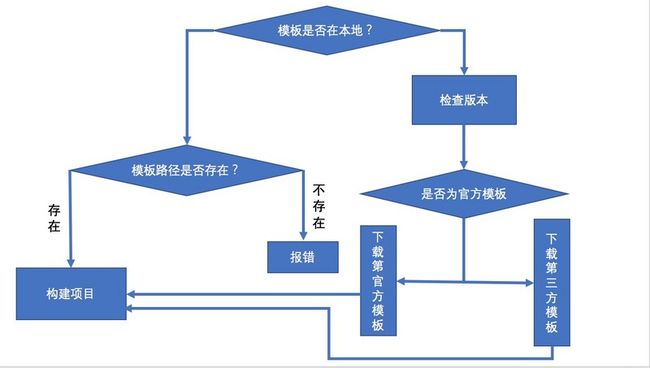
工作流程
在讲代码之前,首先我们要讲一下整个vue-cli初始项目的流程,然后我们沿着流程一步一步走下去。
整个vue init大致流程如我上图所示,应该还是比较好理解的。这里我大致阐述一下大致的流程。
vue-cli会先判断你的模板在远程github仓库上还是在你的本地某个文件里面,若是本地文件夹则会立即跳到第3步,反之则走第2步。
第2步会判断是否为官方模板,官方模板则会从官方github仓库中下载模板到本地的默认仓库下,即根目录下.vue-templates文件夹下。
第3步则读取模板目录下meta.js或者meta.json文件,根据里面的内容会询问开发者,根据开发者的回答,确定一些修改。
根据模板内容以及开发者的回答,渲染出项目结构并生成到指定目录。
源码内容
这里vue-init文件的代码比较多,我这里就拆分几块来看。首先我先把整个文件的结构列出来,方便后续的阅读。
/**
* 引入一大堆包
*/
const program = require('commander')
...
/**
* 配置commander的使用方法
*/
program
.usage(' [project-name]')
.option('-c, --clone', 'use git clone')
.option('--offline', 'use cached template')
/**
* 定义commander的help方法
*/
program.on('--help', () => {
console.log(' Examples:')
console.log()
console.log(chalk.gray(' # create a new project with an official template'))
console.log(' $ vue init webpack my-project')
console.log()
console.log(chalk.gray(' # create a new project straight from a github template'))
console.log(' $ vue init username/repo my-project')
console.log()
})
function help () {
program.parse(process.argv)
if (program.args.length < 1) return program.help() //如果没有输入参数,终端显示帮助
}
help()
/**
* 定义一大堆变量
*/
let template = program.args[0]
...
/**
* 判断是否输入项目名 是 - 直接执行run函数 否- 询问开发者是否在当前目录下生成项目,开发者回答“是” 也执行run函数 否则不执行run函数
*/
/**
* 定义主函数 run
*/
function run (){
...
}
/**
* 定义下载模板并生产项目的函数 downloadAndGenerate
*/
function downloadAndGenerate(){
...
}
整个文件大致的东西入上面所示,后面我们将一块一块内容来看。
引入的一堆包
const download = require('download-git-repo') //用于下载远程仓库至本地 支持GitHub、GitLab、Bitbucket
const program = require('commander') //命令行处理工具
const exists = require('fs').existsSync //node自带的fs模块下的existsSync方法,用于检测路径是否存在。(会阻塞)
const path = require('path') //node自带的path模块,用于拼接路径
const ora = require('ora') //用于命令行上的加载效果
const home = require('user-home') //用于获取用户的根目录
const tildify = require('tildify') //将绝对路径转换成带波浪符的路径
const chalk = require('chalk')// 用于高亮终端打印出的信息
const inquirer = require('inquirer') //用于命令行与开发者交互
const rm = require('rimraf').sync // 相当于UNIX的“rm -rf”命令
const logger = require('../lib/logger') //自定义工具-用于日志打印
const generate = require('../lib/generate') //自定义工具-用于基于模板构建项目
const checkVersion = require('../lib/check-version') //自定义工具-用于检测vue-cli版本的工具
const warnings = require('../lib/warnings') //自定义工具-用于模板的警告
const localPath = require('../lib/local-path') //自定义工具-用于路径的处理
const isLocalPath = localPath.isLocalPath //判断是否是本地路径
const getTemplatePath = localPath.getTemplatePath //获取本地模板的绝对路径
定义的一堆变量
let template = program.args[0] //模板名称
const hasSlash = template.indexOf('/') > -1 //是否有斜杠,后面将会用来判定是否为官方模板
const rawName = program.args[1] //项目构建目录名
const inPlace = !rawName || rawName === '.' // 没写或者“.”,表示当前目录下构建项目
const name = inPlace ? path.relative('../', process.cwd()) : rawName //如果在当前目录下构建项目,当前目录名为项目构建目录名,否则是当前目录下的子目录【rawName】为项目构建目录名
const to = path.resolve(rawName || '.') //项目构建目录的绝对路径
const clone = program.clone || false //是否采用clone模式,提供给“download-git-repo”的参数
const tmp = path.join(home, '.vue-templates', template.replace(/[\/:]/g, '-')) //远程模板下载到本地的路径
主逻辑
if (inPlace || exists(to)) {
inquirer.prompt([{
type: 'confirm',
message: inPlace
? 'Generate project in current directory?'
: 'Target directory exists. Continue?',
name: 'ok'
}]).then(answers => {
if (answers.ok) {
run()
}
}).catch(logger.fatal)
} else {
run()
}
对着上面代码,vue-cli会判断inPlace和exists(to),true则询问开发者,当开发者回答“yes”的时候执行run函数,否则直接执行run函数。这里询问开发者的问题有如下两个:
Generate project in current directory? //是否在当前目录下构建项目
Target directory exists. Continue? //构建目录已存在,是否继续
这两个问题依靠变量inPlace来选择,下面我看一下变量inPlace是怎么得来的。
const rawName = program.args[1] //rawName为命令行的第二个参数(项目构建目录的相对目录)
const inPlace = !rawName || rawName === '.' //rawName存在或者为“.”的时候,视为在当前目录下构建
通过上面的描述可知,变量inPlace用于判断是否在当前目录下构建,因此变量inPlace为true时,则会提示Generate project in current directory? ,反之当变量inPlace为false时,此时exists(to)一定为true,便提示Target directory exists. Continue?。
Run函数
逻辑:
源码:
function run () {
// check if template is local
if (isLocalPath(template)) { //是否是本地模板
const templatePath = getTemplatePath(template) //获取绝对路径
if (exists(templatePath)) { //判断模板所在路径是否存在
//渲染模板
generate(name, templatePath, to, err => {
if (err) logger.fatal(err)
console.log()
logger.success('Generated "%s".', name)
})
} else {
//打印错误日志,提示本地模板不存在
logger.fatal('Local template "%s" not found.', template)
}
} else {
checkVersion(() => { //检查版本号
if (!hasSlash) { //官方模板还是第三方模板
// use official templates
// 从这句话以及download-git-repo的用法,我们得知了vue的官方的模板库的地址:https://github.com/vuejs-templates
const officialTemplate = 'vuejs-templates/' + template
if (template.indexOf('#') !== -1) { //模板名是否带"#"
downloadAndGenerate(officialTemplate) //下载模板
} else {
if (template.indexOf('-2.0') !== -1) { //是都带"-2.0"
//发出警告
warnings.v2SuffixTemplatesDeprecated(template, inPlace ? '' : name)
return
}
// warnings.v2BranchIsNowDefault(template, inPlace ? '' : name)
downloadAndGenerate(officialTemplate)//下载模板
}
} else {
downloadAndGenerate(template)//下载模板
}
})
}
}
downloadAndGenerate函数
function downloadAndGenerate (template) {
const spinner = ora('downloading template')
spinner.start()//显示加载状态
// Remove if local template exists
if (exists(tmp)) rm(tmp) //当前模板库是否存在该模板,存在就删除
//下载模板 template-模板名 tmp- 模板路径 clone-是否采用git clone模板 err-错误短信
download(template, tmp, { clone }, err => {
spinner.stop() //隐藏加载状态
//如果有错误,打印错误日志
if (err) logger.fatal('Failed to download repo ' + template + ': ' + err.message.trim())
//渲染模板
generate(name, tmp, to, err => {
if (err) logger.fatal(err)
console.log()
logger.success('Generated "%s".', name)
})
})
}
lib
generate.js (★)
lib文件下最重要的js文件,他是我们构建项目中最重要的一环,根据模板渲染成我们需要的项目。这块内容是需要我们重点关注的。
const chalk = require('chalk')
const Metalsmith = require('metalsmith')
const Handlebars = require('handlebars')
const async = require('async')
const render = require('consolidate').handlebars.render
const path = require('path')
const multimatch = require('multimatch')
const getOptions = require('./options')
const ask = require('./ask')
const filter = require('./filter')
const logger = require('./logger')
// register handlebars helper 注册handlebars的helper
Handlebars.registerHelper('if_eq', function (a, b, opts) {
return a === b
? opts.fn(this)
: opts.inverse(this)
})
Handlebars.registerHelper('unless_eq', function (a, b, opts) {
return a === b
? opts.inverse(this)
: opts.fn(this)
})
/**
* Generate a template given a `src` and `dest`.
*
* @param {String} name
* @param {String} src
* @param {String} dest
* @param {Function} done
*/
module.exports = function generate (name, src, dest, done) {
const opts = getOptions(name, src) //获取配置
const metalsmith = Metalsmith(path.join(src, 'template')) //初始化Metalsmith对象
const data = Object.assign(metalsmith.metadata(), {
destDirName: name,
inPlace: dest === process.cwd(),
noEscape: true
})//添加一些变量至metalsmith中,并获取metalsmith中全部变量
//注册配置对象中的helper
opts.helpers && Object.keys(opts.helpers).map(key => {
Handlebars.registerHelper(key, opts.helpers[key])
})
const helpers = { chalk, logger }
//配置对象是否有before函数,是则执行
if (opts.metalsmith && typeof opts.metalsmith.before === 'function') {
opts.metalsmith.before(metalsmith, opts, helpers)
}
metalsmith.use(askQuestions(opts.prompts)) //询问问题
.use(filterFiles(opts.filters)) //过滤文件
.use(renderTemplateFiles(opts.skipInterpolation)) //渲染模板文件
//配置对象是否有after函数,是则执行
if (typeof opts.metalsmith === 'function') {
opts.metalsmith(metalsmith, opts, helpers)
} else if (opts.metalsmith && typeof opts.metalsmith.after === 'function') {
opts.metalsmith.after(metalsmith, opts, helpers)
}
metalsmith.clean(false)
.source('.') // start from template root instead of `./src` which is Metalsmith's default for `source`
.destination(dest)
.build((err, files) => {
done(err)
if (typeof opts.complete === 'function') {
//配置对象有complete函数则执行
const helpers = { chalk, logger, files }
opts.complete(data, helpers)
} else {
//配置对象有completeMessage,执行logMessage函数
logMessage(opts.completeMessage, data)
}
})
return data
}
/**
* Create a middleware for asking questions.
*
* @param {Object} prompts
* @return {Function}
*/
function askQuestions (prompts) {
return (files, metalsmith, done) => {
ask(prompts, metalsmith.metadata(), done)
}
}
/**
* Create a middleware for filtering files.
*
* @param {Object} filters
* @return {Function}
*/
function filterFiles (filters) {
return (files, metalsmith, done) => {
filter(files, filters, metalsmith.metadata(), done)
}
}
/**
* Template in place plugin.
*
* @param {Object} files
* @param {Metalsmith} metalsmith
* @param {Function} done
*/
function renderTemplateFiles (skipInterpolation) {
skipInterpolation = typeof skipInterpolation === 'string'
? [skipInterpolation]
: skipInterpolation //保证skipInterpolation是一个数组
return (files, metalsmith, done) => {
const keys = Object.keys(files) //获取files的所有key
const metalsmithMetadata = metalsmith.metadata() //获取metalsmith的所有变量
async.each(keys, (file, next) => { //异步处理所有files
// skipping files with skipInterpolation option
// 跳过符合skipInterpolation的要求的file
if (skipInterpolation && multimatch([file], skipInterpolation, { dot: true }).length) {
return next()
}
//获取文件的文本内容
const str = files[file].contents.toString()
// do not attempt to render files that do not have mustaches
//跳过不符合handlebars语法的file
if (!/{{([^{}]+)}}/g.test(str)) {
return next()
}
//渲染文件
render(str, metalsmithMetadata, (err, res) => {
if (err) {
err.message = `[${file}] ${err.message}`
return next(err)
}
files[file].contents = new Buffer(res)
next()
})
}, done)
}
}
/**
* Display template complete message.
*
* @param {String} message
* @param {Object} data
*/
function logMessage (message, data) {
if (!message) return //没有message直接退出函数
render(message, data, (err, res) => {
if (err) {
console.error('\n Error when rendering template complete message: ' + err.message.trim()) //渲染错误打印错误信息
} else {
console.log('\n' + res.split(/\r?\n/g).map(line => ' ' + line).join('\n'))
//渲染成功打印最终渲染的结果
}
})
}
引入的包:
- chalk (用于高亮终端打印出来的信息。)
- metalsmith (静态网站生成器。)
- handlebars (知名的模板引擎。)
- async (非常强大的异步处理工具。)
- consolidate (支持各种模板引擎的渲染。)
- path (node自带path模块,用于路径的处理。)
- multimatch ( 可以支持多个条件的匹配。)
- options (自定义工具-用于获取模板配置。)
- ask (自定义工具-用于询问开发者。)
- filter (自定义工具-用于文件过滤。)
- logger (自定义工具-用于日志打印。)
主逻辑:
获取模板配置 -->初始化Metalsmith -->添加一些变量至Metalsmith -->handlebars模板注册helper -->配置对象中是否有before函数,有则执行 -->询问问题 -->过滤文件 -->渲染模板文件 -->配置对象中是否有after函数,有则执行 -->最后构建项目内容 -->构建完成,成功若配置对象中有complete函数则执行,否则打印配置对象中的completeMessage信息,如果有错误,执行回调函数done(err)
其他函数:
- askQuestions: 询问问题
- filterFiles: 过滤文件
- renderTemplateFiles: 渲染模板文件
- logMessage: 用于构建成功时,打印信息
Metalsmith插件格式:
function {
return (files,metalsmith,done)=>{
//逻辑代码
...
}
}
options.js
const path = require('path')
const metadata = require('read-metadata')
const exists = require('fs').existsSync
const getGitUser = require('./git-user')
const validateName = require('validate-npm-package-name')
/**
* Read prompts metadata.
*
* @param {String} dir
* @return {Object}
*/
module.exports = function options (name, dir) {
const opts = getMetadata(dir)
setDefault(opts, 'name', name)
setValidateName(opts)
const author = getGitUser()
if (author) {
setDefault(opts, 'author', author)
}
return opts
}
/**
* Gets the metadata from either a meta.json or meta.js file.
*
* @param {String} dir
* @return {Object}
*/
function getMetadata (dir) {
const json = path.join(dir, 'meta.json')
const js = path.join(dir, 'meta.js')
let opts = {}
if (exists(json)) {
opts = metadata.sync(json)
} else if (exists(js)) {
const req = require(path.resolve(js))
if (req !== Object(req)) {
throw new Error('meta.js needs to expose an object')
}
opts = req
}
return opts
}
/**
* Set the default value for a prompt question
*
* @param {Object} opts
* @param {String} key
* @param {String} val
*/
function setDefault (opts, key, val) {
if (opts.schema) {
opts.prompts = opts.schema
delete opts.schema
}
const prompts = opts.prompts || (opts.prompts = {})
if (!prompts[key] || typeof prompts[key] !== 'object') {
prompts[key] = {
'type': 'string',
'default': val
}
} else {
prompts[key]['default'] = val
}
}
function setValidateName (opts) {
const name = opts.prompts.name
const customValidate = name.validate
name.validate = name => {
const its = validateName(name)
if (!its.validForNewPackages) {
const errors = (its.errors || []).concat(its.warnings || [])
return 'Sorry, ' + errors.join(' and ') + '.'
}
if (typeof customValidate === 'function') return customValidate(name)
return true
}
}
引入的包:
- path (node自带path模块,用于路径的处理。)
- read-metadata (用于读取json或者yaml元数据文件并返回一个对象。)
- fs.existsSync (node自带fs模块的existsSync方法,用于检测路径是否存在。)
- git-user (获取本地的git配置。)
- validate-npm-package-name (用于npm包的名字是否是合法的。)
作用:
- 主方法: 第一步:先获取模板的配置文件信息;第二步:设置name字段并检测name是否合法;第三步:只是author字段。
- getMetadata: 获取meta.js或则meta.json中的配置信息
- setDefault: 用于向配置对象中添加一下默认字段
- setValidateName: 用于检测配置对象中name字段是否合法
git-user.js
const exec = require('child_process').execSync
module.exports = () => {
let name
let email
try {
name = exec('git config --get user.name')
email = exec('git config --get user.email')
} catch (e) {}
name = name && JSON.stringify(name.toString().trim()).slice(1, -1)
email = email && (' <' + email.toString().trim() + '>')
return (name || '') + (email || '')
}
引入的包:
- child_process.execSync (node自带模块child_process中的execSync方法用于新开一个shell并执行相应的command,并返回相应的输出。)
作用: 用于获取本地的git配置的用户名和邮件,并返回格式 姓名<邮箱> 的字符串。
eval.js
const chalk = require('chalk')
/**
* Evaluate an expression in meta.json in the context of
* prompt answers data.
*/
module.exports = function evaluate (exp, data) {
/* eslint-disable no-new-func */
const fn = new Function('data', 'with (data) { return ' + exp + '}')
try {
return fn(data)
} catch (e) {
console.error(chalk.red('Error when evaluating filter condition: ' + exp))
}
}
引入的包:
- chalk (用于高亮终端打印出来的信息。)
作用: 在data的作用域执行exp表达式并返回其执行得到的值
ask.js
const async = require('async')
const inquirer = require('inquirer')
const evaluate = require('./eval')
// Support types from prompt-for which was used before
const promptMapping = {
string: 'input',
boolean: 'confirm'
}
/**
* Ask questions, return results.
*
* @param {Object} prompts
* @param {Object} data
* @param {Function} done
*/
/**
* prompts meta.js或者meta.json中的prompts字段
* data metalsmith.metadata()
* done 交于下一个metalsmith插件处理
*/
module.exports = function ask (prompts, data, done) {
//遍历处理prompts下的每一个字段
async.eachSeries(Object.keys(prompts), (key, next) => {
prompt(data, key, prompts[key], next)
}, done)
}
/**
* Inquirer prompt wrapper.
*
* @param {Object} data
* @param {String} key
* @param {Object} prompt
* @param {Function} done
*/
function prompt (data, key, prompt, done) {
// skip prompts whose when condition is not met
if (prompt.when && !evaluate(prompt.when, data)) {
return done()
}
//获取默认值
let promptDefault = prompt.default
if (typeof prompt.default === 'function') {
promptDefault = function () {
return prompt.default.bind(this)(data)
}
}
//设置问题,具体使用方法可去https://github.com/SBoudrias/Inquirer.js上面查看
inquirer.prompt([{
type: promptMapping[prompt.type] || prompt.type,
name: key,
message: prompt.message || prompt.label || key,
default: promptDefault,
choices: prompt.choices || [],
validate: prompt.validate || (() => true)
}]).then(answers => {
if (Array.isArray(answers[key])) {
//当答案是一个数组时
data[key] = {}
answers[key].forEach(multiChoiceAnswer => {
data[key][multiChoiceAnswer] = true
})
} else if (typeof answers[key] === 'string') {
//当答案是一个字符串时
data[key] = answers[key].replace(/"/g, '\\"')
} else {
//其他情况
data[key] = answers[key]
}
done()
}).catch(done)
}
引入的包:
- async (异步处理工具。)
- inquirer (命令行与用户之间的交互。)
- eval (返回某作用下表达式的值。)
作用: 将meta.js或者meta.json中的prompts字段解析成对应的问题询问。
filter.js
const match = require('minimatch')
const evaluate = require('./eval')
/**
* files 模板内的所有文件
* filters meta.js或者meta.json的filters字段
* data metalsmith.metadata()
* done 交于下一个metalsmith插件处理
*/
module.exports = (files, filters, data, done) => {
if (!filters) {
//meta.js或者meta.json没有filters字段直接跳过交于下一个metalsmith插件处理
return done()
}
//获取所有文件的名字
const fileNames = Object.keys(files)
//遍历meta.js或者meta.json没有filters下的所有字段
Object.keys(filters).forEach(glob => {
//遍历所有文件名
fileNames.forEach(file => {
//如果有文件名跟filters下的某一个字段匹配上
if (match(file, glob, { dot: true })) {
const condition = filters[glob]
if (!evaluate(condition, data)) {
//如果metalsmith.metadata()下condition表达式不成立,删除该文件
delete files[file]
}
}
})
})
done()
}
引入的包:
- minimatch (字符匹配工具。)
- eval (返回某作用下表达式的值。)
作用: 根据metalsmith.metadata()删除一些不需要的模板文件,而metalsmith.metadata()主要在ask.js中改变的,也就是说ask.js中获取到用户的需求。
logger.js
const chalk = require('chalk')
const format = require('util').format
/**
* Prefix.
*/
const prefix = ' vue-cli'
const sep = chalk.gray('·')
/**
* Log a `message` to the console.
*
* @param {String} message
*/
exports.log = function (...args) {
const msg = format.apply(format, args)
console.log(chalk.white(prefix), sep, msg)
}
/**
* Log an error `message` to the console and exit.
*
* @param {String} message
*/
exports.fatal = function (...args) {
if (args[0] instanceof Error) args[0] = args[0].message.trim()
const msg = format.apply(format, args)
console.error(chalk.red(prefix), sep, msg)
process.exit(1)
}
/**
* Log a success `message` to the console and exit.
*
* @param {String} message
*/
exports.success = function (...args) {
const msg = format.apply(format, args)
console.log(chalk.white(prefix), sep, msg)
}
引入的包:
- chalk (用于高亮终端打印出来的信息。)
- format (node自带的util模块中的format方法。)
作用: logger.js主要提供三个方法log(常规日志)、fatal(错误日志)、success(成功日志)。每个方法都挺简单的,我就不错过多的解释了。
local-path.js
const path = require('path')
module.exports = {
isLocalPath (templatePath) {
return /^[./]|(^[a-zA-Z]:)/.test(templatePath)
},
getTemplatePath (templatePath) {
return path.isAbsolute(templatePath)
? templatePath
: path.normalize(path.join(process.cwd(), templatePath))
}
}
引入的包:
- path (node自带的路径处理工具。)
作用:
- isLocalPath: UNIX (以“.”或者"/"开头) WINDOWS(以形如:“C:”的方式开头)。
- getTemplatePath: templatePath是否为绝对路径,是则返回templatePath 否则转换成绝对路径并规范化。
check-version.js
const request = require('request')
const semver = require('semver')
const chalk = require('chalk')
const packageConfig = require('../package.json')
module.exports = done => {
// Ensure minimum supported node version is used
if (!semver.satisfies(process.version, packageConfig.engines.node)) {
return console.log(chalk.red(
' You must upgrade node to >=' + packageConfig.engines.node + '.x to use vue-cli'
))
}
request({
url: 'https://registry.npmjs.org/vue-cli',
timeout: 1000
}, (err, res, body) => {
if (!err && res.statusCode === 200) {
const latestVersion = JSON.parse(body)['dist-tags'].latest
const localVersion = packageConfig.version
if (semver.lt(localVersion, latestVersion)) {
console.log(chalk.yellow(' A newer version of vue-cli is available.'))
console.log()
console.log(' latest: ' + chalk.green(latestVersion))
console.log(' installed: ' + chalk.red(localVersion))
console.log()
}
}
done()
})
}
引入的包:
- request (http请求工具。)
- semver (版本号处理工具。)
- chalk (用于高亮终端打印出来的信息。)
作用:
- 第一步:检查本地的node版本号,是否达到package.json文件中对node版本的要求,若低于nodepackage.json文件中要求的版本,则直接要求开发者更新自己的node版本。反之,可开始第二步。
- 第二步: 通过请求https://registry.npmjs.org/vue-cli来获取vue-cli的最新版本号,跟package.json中的version字段进行比较,若本地的版本号小于最新的版本号,则提示有最新版本可以更新。这里需要注意的是,这里检查版本号并不影响后续的流程,即便本地的vue-cli版本不是最新的,也不影响构建,仅仅提示一下。
warnings.js
const chalk = require('chalk')
module.exports = {
v2SuffixTemplatesDeprecated (template, name) {
const initCommand = 'vue init ' + template.replace('-2.0', '') + ' ' + name
console.log(chalk.red(' This template is deprecated, as the original template now uses Vue 2.0 by default.'))
console.log()
console.log(chalk.yellow(' Please use this command instead: ') + chalk.green(initCommand))
console.log()
},
v2BranchIsNowDefault (template, name) {
const vue1InitCommand = 'vue init ' + template + '#1.0' + ' ' + name
console.log(chalk.green(' This will install Vue 2.x version of the template.'))
console.log()
console.log(chalk.yellow(' For Vue 1.x use: ') + chalk.green(vue1InitCommand))
console.log()
}
}
引入的包:
- chalk (用于高亮终端打印出来的信息。)
作用:
- v2SuffixTemplatesDeprecated:提示带“-2.0”的模板已经弃用了,官方模板默认用2.0了。不需要用“-2.0”来区分vue1.0和vue2.0了。
- v2BranchIsNowDefault: 这个方法在vue-init文件中已经被注释掉,不再使用了。在vue1.0向vue2.0过渡的时候用到过,现在都是默认2.0了,自然也就不用了。
总结
由于代码比较多,很多代码我就没有一一细讲了,一些比较简单或者不是很重要的js文件,我就单单说明了它的作用了。但是重点的js文件,我还是加了很多注解在上面。其中我个人认为比较重点的文件就是vue-init、generate.js、options.js、ask.js、filter.js,这五个文件构成了vue-cli构建项目的主流程,因此需要我们花更多的时间在上面。另外,我们在读源码的过程中,一定要理清楚整个构建流程是什么样子的,心里得有一个谱。我自己在读完整个vue-cli之后,我自己根据vue-cli的流程也动手搞了一个脚手架工具,仅供大家参考学习一下。地址如下:
https://github.com/ruichengping/asuna-cli
最后祝愿大家可以在前端的道路上越走越好!如果喜欢我的文章,请记得关注我哦!后续会推出更多的优质的文章哦,敬请期待!