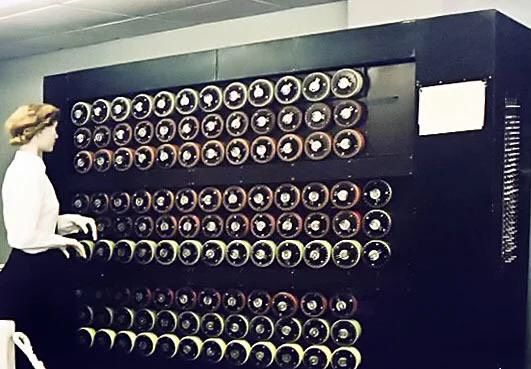
The first Bombe is completed
Built as an electromechanical mechanical means of decrypting Nazi ENIGMA-based military communications during World War II, the British Bombe is conceived of by computer pioneer Alan Turing and Harold Keen of the British Tabulating Machine Company. Hundreds of bombes were built, their purpose to ascertain the daily rotor start positions of Enigma cipher machines, which in turn allowed the Allies to decrypt German messages.
Public unveiling of ENIAC
Started in 1943, the ENIAC computing system was built by John Mauchly and J. Presper Eckert at the Moore School of Electrical Engineering of the University of Pennsylvania. Because of its electronic, as opposed to electromechanical, technology, it is over 1,000 times faster than any previous computer. ENIAC used panel-to-panel wiring and switches for programming, occupied more than 1,000 square feet, used about 18,000 vacuum tubes and weighed 30 tons. It was believed that ENIAC had done more calculation over the ten years it was in operation than all of humanity had until that time.
HP introduces the HP 2116A
The 2116A is HP’s first computer. It was developed as a versatile instrument controller for HP's growing family of programmable test and measurement products. It interfaced with a wide number of standard laboratory instruments, allowing customers to computerize their instrument systems. The 2116A also marked HP's first use of integrated circuits in a commercial product.
Xerox PARC Alto introduced
The Alto is a groundbreaking computer with wide influence on the computer industry. It was based on a graphical user interface using windows, icons, and a mouse, and worked together with other Altos over a local area network. It could also share files and print out documents on an advanced Xerox laser printer. Applications were also highly innovative: a WYSISYG word processor known as “Bravo,” a paint program, a graphics editor, and email for example. Apple’s inspiration for the Lisa and Macintosh computers came from the Xerox Alto.
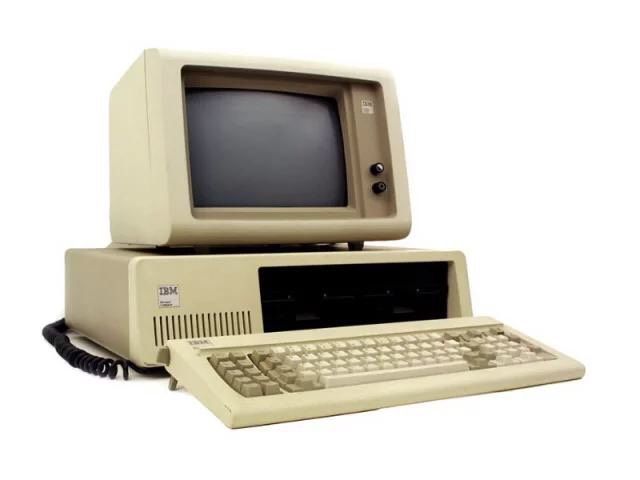
IBM introduces its Personal Computer (PC)
IBM's brand recognition, along with a massive marketing campaign, ignites the fast growth of the personal computer market with the announcement of its own personal computer (PC). The first IBM PC, formally known as the IBM Model 5150, was based on a 4.77 MHz Intel 8088 microprocessor and used Microsoft´s MS-DOS operating system. The IBM PC revolutionized business computing by becoming the first PC to gain widespread adoption by industry. The IBM PC was widely copied (“cloned”) and led to the creation of a vast “ecosystem” of software, peripherals, and other commodities for use with the platform.
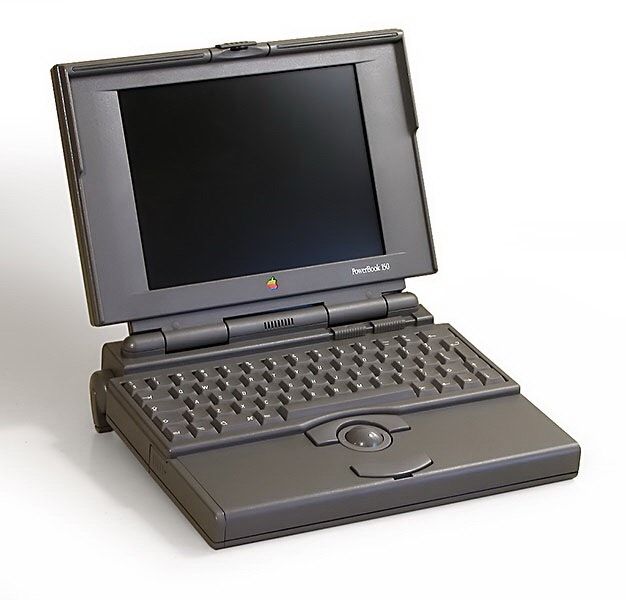
PowerBook series of laptops is introduced
Apple's Macintosh Portable meets with little success in the marketplace and leads to a complete redesign of Apple's line of portable computers. All three PowerBooks introduced featured a built-in trackball, internal floppy drive, and palm rests, which would eventually become typical of 1990s laptop design. The PowerBook 100 was the entry-level machine, while the PowerBook 140 was more powerful and had a larger memory. The PowerBook 170 was the high-end model, featuring an active matrix display, faster processor, as well as a floating point unit. The PowerBook line of computers was discontinued in 2006.
The Amazon Kindle is released
Many companies have attempted to release electronic reading systems dating back to the early 1990s. Online retailer Amazon released the Kindle, one of the first to gain a large following among consumers. The first Kindle featured wireless access to content via Amazon.com, along with an SD card slot allowing increased storage. The first release proved so popular there was a long delay in delivering systems on release. Follow-on versions of the Kindle added further audio-video capabilities.
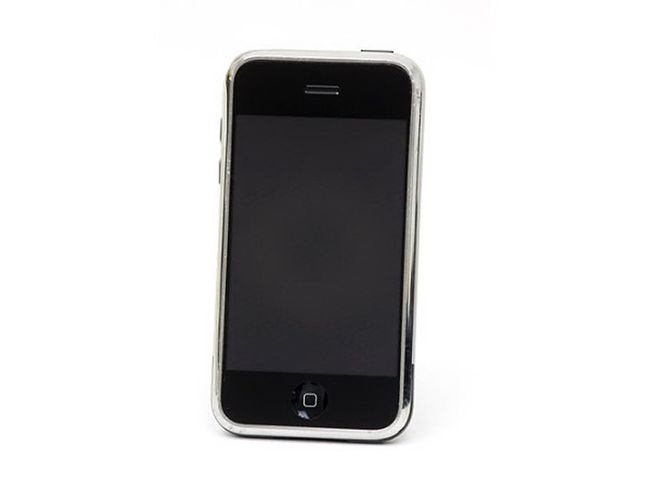
The Apple iPhone is released
Apple launches the iPhone - a combination of web browser, music player and cell phone - which could download new functionality in the form of "apps" (applications) from the online Apple store. The touchscreen enabled smartphone also had built-in GPS navigation, high-definition camera, texting, calendar, voice dictation, and weather reports.
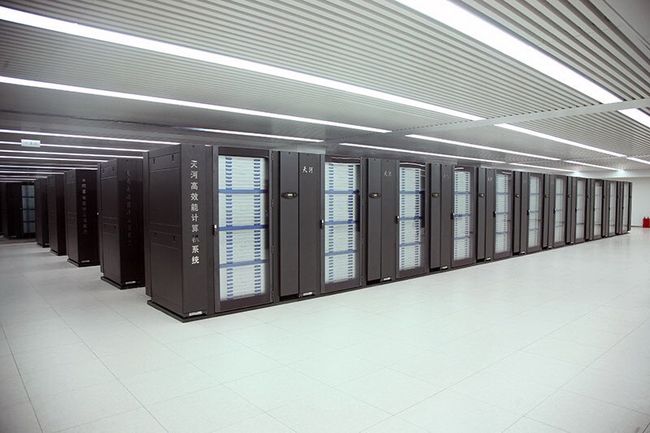
China's Tianhe supercomputers are operational
With a peak speed of over a petaflop (one thousand trillion calculations per second), the Tianhe 1 (translation: Milky Way 1) is developed by the Chinese National University of Defense Technology using Intel Xeon processors combined with AMD graphic processing units (GPUs). The upgraded and faster Tianhe-1A used Intel Xeon CPUs as well, but switched to nVidia's Tesla GPUs and added more than 2,000 Fei-Tang (SPARC-based) processors. The machines were used by the Chinese Academy of Sciences to run massive solar energy simulations, as well as some of the most complex molecular studies ever undertaken.
作文:some people believe that the technology is developing so fast that it might destroy us in the future. Others suggest that with the help of fast developing innovative industry, the mankind would be more successful in any future may come.
Discuss both views and give your own opinion. Write NO LESS THAN 250 words