1. long tail: refers to the strategy of selling a large number of unique items to penetrate market niches.
2. Development Budget: Firms thus often use capital rationing: they set a fixed R&D budget and rank order projects to support.(R&D budget is often a percentage of previous year’s sales. Percentage is typically determined through industry benchmarking, or historical benchmarking of firm’s performance.)
3. Financing New Technology Venture s: “angel investors” (typically seed stage and <$1 million) or venture capitalists (multiple early stages, >$1 million).
4. Quantitative Methods for Choosing Projects:
1) Discounted Cash Flow (DCF):
Net Present Value (NPV): Expected cash inflows are discounted and compared to outlays.
Internal Rate of Return (IRR): The discount rate that makes the net present value of investment zero.
2) Real Options: Applies stock option model to nonfinancial resource investments.
5. Qualitative Methods:
1) Screening Questions: may be used to assess different dimensions of the project decision including
•Role of customer(market, use, compatibility and ease of use, distribution and pricing)
•Role of capabilities(existing capabilities, competitors’ capabilities, future capabilities)
•Project timing and cost
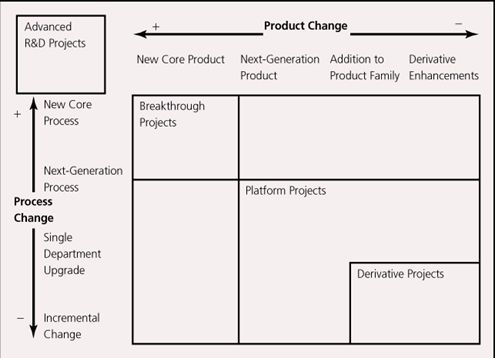
2) The Aggregate Project Planning Framework
•Advanced R&D Projects:
develop cutting-edge technologies; often no immediate commercial application.
•Breakthrough Projects:
incorporate revolutionary new technologies into a commercial application.
•Platform Projects:
not revolutionary, but offer fundamental improvements over preceding generations of products.
•Derivative Projects:
incremental improvements and variety in design features.
(Derivative projects pay off the quickest, and help service the firm’s short-term cash flow needs.Advanced R&D projectstake a long time to pay off (or may not pay off at all), but can position the firm to be a technological leader)
3) Q-Sort is a simple method for ranking ideas on different dimensions.
6. Combining Quantitative and Qualitative Information
1)Conjoint Analysis: estimates the relative value individuals place on attributes of a choice.
(Individuals given a card with products (or projects) with different features and prices.
Individuals rate each in terms of desirability or rank them.
Multiple regression then used to assess the degree to which an attribute influences rating. These weights quantify the trade-offs involved in providing different features.)
2)Data Envelopment Analysis (DEA)useslinear programming to combine measures of projects based on different units(e.g., rank vs. dollars) into an efficiency frontier.