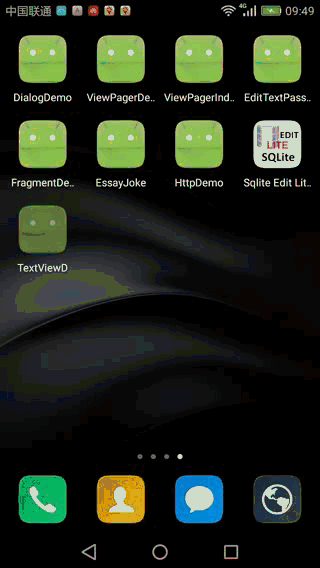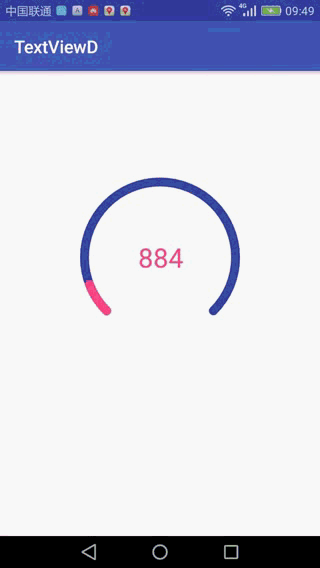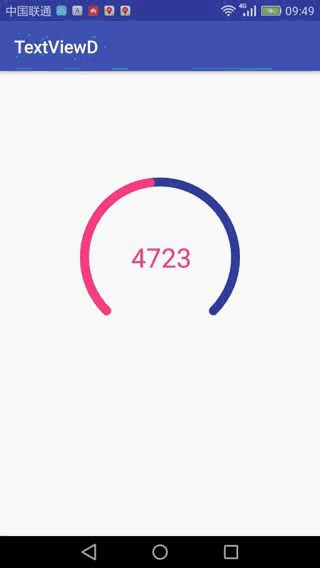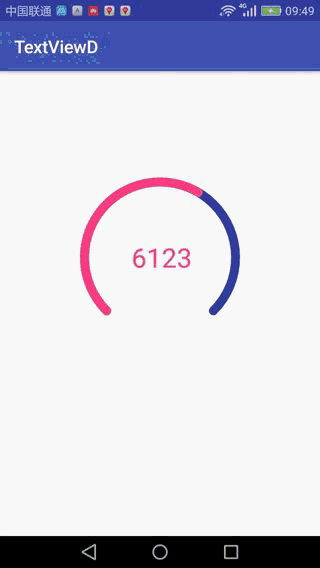
最近在跟大牛在学习自定义view的时候,跟着他们写了一个步数计数,效果如下:
效果实现的大致一个思路:
1:写一个类继承自view
2:自定义一些属性,这样可以在布局文件中直接使用
3:在onMeasure方法中进行测量
4:在onDraw方法中进行绘制
5:提供参数设置的方法
在继承view的时候需要实现一些构造方法:
public QQStepView(Context context) {
this(context, null);
}
public QQStepView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
this(context, attrs, 0);
}
public QQStepView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr);
initAttrs(context, attrs);
initPaint();
}
这里说下这三个构造方法会在什么情况下调用,第一构造方法会在java文件中直接new的时候调用,第二个构造方法是在布局文件中使用的时候调用,第三个构造方法是在布局文件中使用并设有style样式的时候调用,将第一个和第二个改为this,这样不管在什么情况下使用都会统一调用第三个构造方法,接下来在第三个构造方法中初始化自定义属性和画笔;
初始化自定义属性:
private void initAttrs(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
TypedArray array = context.obtainStyledAttributes(attrs, R.styleable.QQStepView);
mOuterColor = array.getColor(R.styleable.QQStepView_outerColor, mOuterColor);
mInnerColor = array.getColor(R.styleable.QQStepView_innerColor, mInnerColor);
mStepTextColor = array.getColor(R.styleable.QQStepView_stepTextColor, mStepTextColor);
mBorderWidth = (int) array.getDimension(R.styleable.QQStepView_borderWidth, mBorderWidth);
mStepTextSize = array.getDimensionPixelSize(R.styleable.QQStepView_stepTextSize, mStepTextSize);
//回收
array.recycle();
}
在初始化属性后要记得回收;
初始化画笔:
private void initPaint(){
outPaint = new Paint();
//抗锯齿
outPaint.setAntiAlias(true);
outPaint.setStrokeWidth(mBorderWidth);
outPaint.setColor(mOuterColor);
//画笔空心
outPaint.setStyle(Paint.Style.STROKE);
outPaint.setStrokeCap(Paint.Cap.ROUND);
innerPaint = new Paint();
innerPaint.setAntiAlias(true);
innerPaint.setStrokeWidth(mBorderWidth);
innerPaint.setColor(mInnerColor);
//画笔空心
innerPaint.setStyle(Paint.Style.STROKE);
innerPaint.setStrokeCap(Paint.Cap.ROUND);
mTextPaint = new Paint();
mTextPaint.setAntiAlias(true);
mTextPaint.setColor(mStepTextColor);
mTextPaint.setTextSize(mStepTextSize);
}
接着就是在onMeasure中进行测量了:
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
//获取宽高模式模式
int modeWidth = MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec);
int modeHeight = MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec);
//获取宽高值
int width = MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec);
int height = MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec);
//判断模式是否是wrap_content
if (modeWidth == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST) {
width = dp2px(80);
}
if (modeHeight == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST) {
height = dp2px(80);
}
//宽度和高度不一致的时候取最小值
width = width > height ? height : width;
height = width > height ? height : width;
setMeasuredDimension(width, height);
}
在这里的做了一个宽高模式的判断,如果是MeasureSpec.AT_MOST也就是wrap_content的时候就将宽和高设置为固定大小,同时如果宽高设置的不一致的时候,取其中的最小值进行测量绘制;
现在可以在onDraw方法中进行绘制了:
@Override
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {
super.onDraw(canvas);
//绘制外弧 描边问题
RectF rectf = new RectF(mBorderWidth / 2, mBorderWidth / 2, getWidth() - mBorderWidth / 2, getHeight() - mBorderWidth / 2);
canvas.drawArc(rectf, 135, 270, false, outPaint);
//绘制内弧
if (mStepMax == 0) {
return;
}
float swweepAngle = (float) mCurrentStep / mStepMax;
canvas.drawArc(rectf, 135, swweepAngle * 270, false, innerPaint);
//绘制文字
String stepText = mCurrentStep + "";
Rect rect = new Rect();
mTextPaint.getTextBounds(stepText, 0, stepText.length(), rect);
int dx = getWidth() / 2 - rect.width() / 2;
//基线
Paint.FontMetricsInt metricsInt = mTextPaint.getFontMetricsInt();
int dy = (metricsInt.bottom - metricsInt.top) / 2 - metricsInt.bottom;
int baseLine = getHeight() / 2 + dy;
canvas.drawText(stepText, dx, baseLine, mTextPaint);
}
因为在布局文件中时候的时候就会调用onDraw方法但是这个时候还没有设置mStepMax 值还为0,在计算
float swweepAngle = (float) mCurrentStep / mStepMax;
就会出错,所以做了下判断,下面还提供了两个方法;
设置最大步数:
public synchronized void setStepMax(int stepMax){
this.mStepMax=stepMax;
}
设置当前步数:
public synchronized void setCurrentStep(int currentStep){
this.mCurrentStep=currentStep;
//不断的去绘制
invalidate();
}
在设置当前步数里面调用invalidate方法就会不停的调用onDraw方法进行绘制,到这里效果就实现的差不多了,在java文件中调用时,设置一些属性动画就可以了;
final QQStepView stepView = (QQStepView) findViewById(R.id.stepView);
stepView.setStepMax(10000);
//属性动画
ValueAnimator valueAnimator = ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(0, 6123);
valueAnimator.setDuration(2000);
//插值器
valueAnimator.setInterpolator(new DecelerateInterpolator());
valueAnimator.addUpdateListener(new ValueAnimator.AnimatorUpdateListener() {
@Override
public void onAnimationUpdate(ValueAnimator animation) {
float animatedValue = (float) animation.getAnimatedValue();
stepView.setCurrentStep((int) animatedValue);
}
});
valueAnimator.start();
在使用属性动画的时候要注意animation.getAnimatedValue();返回的是一个Object,在这里强转成float型,不能转成int要不会报转换异常的错误;
这样就实现上面的效果了,上面写的有什么问题,欢迎交流。
源码地址:http://pan.baidu.com/s/1eSAFa4y