字节流
- InputStream 输入字节流
- OutputStream 输出字节流
输入字节流----InputStream
InputStream 是所有的输入字节流的父类,它是一个抽象类。同样的来看它的子类。
FileInputStream 继承自InputStream
构造方法:
//传一个文件路径(字符串)
public FileInputStream(String var1) throws FileNotFoundException {
this(var1 != null?new File(var1):null);
}//如:FileInputStream in=new FileInputStream(String path);
//传一个文件
public FileInputStream(File var1) throws FileNotFoundException {
....
}//如:FileInputStream in=new FileInputStream(new File(String path));
//不常用
public FileInputStream(FileDescriptor var1) {
...
}
主要方法
int read();//返回值int,若返回值为-1,则代表已经读完,是不是和字符流很像,但每次读一个字节,并打印,如果存在中文,可能会乱码
int read(byte[] bytes);//每次读bytes字节
代码演示:
/**
* 需求:控制台输出本文件内容
*/
public class Demo {
//文件地址
public static final String PATH = "/Volumes/huang/studyfromGitHub/JavaForAndroid/JavaForAndroid/series11/src/main/java/com/example/Demo1.java";
//文件名
public static final String NAME = "copyTest1.java";
public static void main(String[] args) {
// read();//测试InputStream 的read()方法
reads();
}
/**
* 测试read(byte[] bytes)
* 可以控制字符集
*/
private static void reads() {
FileInputStream inputStream = null;
try {
inputStream = new FileInputStream(PATH);
byte[] bytes = new byte[inputStream.available()];//inputStream.available()获取文件长度
//读取的字节长度
int len = inputStream.read(bytes);//将数据一次性读取到字节数组中
System.out.println("读取长度" + len + "\n" + new String(bytes, "utf-8"));
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* 测试read()
* 每次读一个字节,并打印,如果存在中文,可能会乱码
*/
private static void read() {
FileInputStream inputStream = null;
try {
inputStream = new FileInputStream(PATH);
int len = 0;
while ((len = inputStream.read()) != -1) {
System.out.print((char) len);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
inputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
结果----read(),出现了乱码.
结果----read(byte[]bytes),设置了字符集,没出现乱码.
有没有觉得都差不多.
输出字节流----OutputStream
OutputStream 是所有的输入字节流的父类,它是一个抽象类。同样的来看它的子类。
FileOutStream 继承自OutputStream
构造方法:
//是不是和FileWriter很像,第一个参数目的是创建一个向指定 File 对象表示的文件中写入数据的文件输出流。如果第二个参数为 true,则将字节写入文件末尾处,而不是写入文件开始处。
public FileOutputStream(String var1) throws FileNotFoundException {
....
}
public FileOutputStream(String var1, boolean var2) throws FileNotFoundException {
.....
}
public FileOutputStream(File var1) throws FileNotFoundException {
this(var1, false);
}
public FileOutputStream(File var1, boolean var2) throws FileNotFoundException {
......
}
public FileOutputStream(FileDescriptor var1) {
.....
}
主要方法
- void write(byte[]bytes);//写字节数组
写纯文本文件-----案例
-
Config类代码:(通用案例1,2,3)
public class Config { public static final String PATH="/Volumes/huang/studyfromGitHub/JavaForAndroid/JavaForAndroid/series11/src/main/java/files"; } -
主要代码
private static final String fileName = "testOutput.java"; /** * */ private static void write() { FileOutputStream outputStream = null; try { outputStream = new FileOutputStream(Config.PATH + fileName); outputStream.write("你好啊,美女".getBytes()); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); }finally { try { outputStream.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } 结果
拷贝纯文本文件-----案例(读,写)
-
代码
/** * 拷贝本类文件 */ private static void copyFile() { String copyName = "copy.java"; String sourcePath = "/Volumes/huang/studyfromGitHub/JavaForAndroid/JavaForAndroid/series11/src/main/java/com/example/Demo2.java"; FileInputStream inputStream = null; FileOutputStream outputStream = null; try { inputStream = new FileInputStream(sourcePath); outputStream = new FileOutputStream(Config.PATH + copyName); byte[] bytes = new byte[inputStream.available()]; inputStream.read(bytes); outputStream.write(bytes); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { try { inputStream.close(); outputStream.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } -
结果
拷贝图片-----案例(读,写)
-
代码
/** * 拷贝图片step1.png */ private static void copyPicture() { String picSource = "/Volumes/huang/studyfromGitHub/JavaForAndroid/JavaForAndroid/series11/src/main/java/images/step1.png"; String copyName = "copyPic.png"; FileInputStream inputStream = null; FileOutputStream outputStream = null; try { inputStream = new FileInputStream(picSource); outputStream = new FileOutputStream(Config.PATH + copyName); //定义缓冲区--字节数组 byte[] bytes=new byte[1024]; //每次最多读取1K节字 int len=-1; //每次读取的字节长度 while((len=inputStream.read(bytes))!=-1){ //-1代表的是文件结尾标识 outputStream.write(bytes, 0, len); } } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { try { inputStream.close(); outputStream.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } -
结果
同样的,字节流也有带缓冲的,基本都是一样的,当读写纯文本的时候优先考虑字符流,读写非纯文本的时候用字节流。下面我们继续看带缓冲的字节流,基本一样。
带缓冲的字节流读写案例(BufferedInputStream 读,BufferedOutputStream 写)没有关闭的流你们自行关闭。
-
Config 类
public class Config { public static final String PATH="/Volumes/huang/studyfromGitHub/JavaForAndroid/JavaForAndroid/series11/src/main/java/files"; } -
测试类
/** * 带缓冲的字节流 ** 需求:使用带缓冲的字节流拷贝文件 */ public class Demo3 { //纯文本源文件路径 private static final String txtPath = "/Volumes/huang/studyfromGitHub/JavaForAndroid/JavaForAndroid/series11/src/main/java/com/example/Demo2.java"; //拷贝后的纯文本文件名 private static final String txtName = "copy.java"; //图片源文件路径 private static String picPath = "/Volumes/huang/studyfromGitHub/JavaForAndroid/JavaForAndroid/series11/src/main/java/images/step1.png"; //拷贝后的图片名 private static String picName = "copyPic.png"; public static void main(String[] args) { //copy(txtPath, txtName); copy(picPath, picName); } /** * 拷贝文件 * Config.PATH 是上面提到的 * * @param sourcePath 源路径 * @param targetName 文件名 */ private static void copy(String sourcePath, String targetName) { //申明变量 FileInputStream inputStream = null; BufferedInputStream bufferedInputStream = null; FileOutputStream outputStream = null; BufferedOutputStream bufferedOutputStream = null; //实例化变量 try { inputStream = new FileInputStream(sourcePath); bufferedInputStream = new BufferedInputStream(inputStream); outputStream = new FileOutputStream(Config.PATH + targetName); bufferedOutputStream = new BufferedOutputStream(outputStream); byte[] bytes = new byte[2048];//大小可以自己指定,但不要非常非常大。 int len = 0; while ((len = bufferedInputStream.read(bytes)) != -1) { bufferedOutputStream.write(bytes, 0, len);//向缓冲区中写入指定长度的数据 bufferedOutputStream.flush();//将数据从内存中写入到文件中 } } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { try { bufferedInputStream.close();//关闭流(处理流),其中的包装流会自动关闭 bufferedOutputStream.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } }
结果
都是一样的。
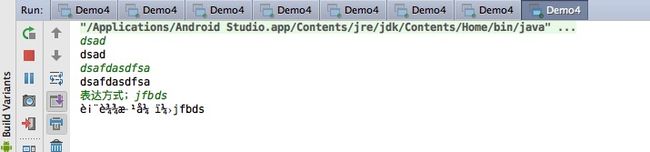
InputStram 绑定System.in 案例
public class Demo4 {
/**
* 打印从键盘输入的字母,直到输入exit结束程序
* @param args
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
InputStream inputStream = System.in;
int num = -1;
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
while (true) {
try {
num = inputStream.read();
//判断字符是否换行
if (num == '\n') {
String line = sb.toString().trim();//去除两边的空格
if (line.equalsIgnoreCase("over")) {
break;
}
System.out.println(line); //打印输入的一行数据(字母是大写)
//重置字符串变量的内容
sb.delete(0, sb.length());
}
sb.append((char) num);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
结果
可是兄弟们,你们看到打印字符串乱码了吗,字节流不能操作Unicode字符,由于Java采用16位的Unicode字符,
所以要使用基于字符的输入输出操作。所以有了字符流,以提供直接的字符输入输出的支持。而字节流怎么转成字符流呢,Java为我们提供了两个类,InputStreamReader,
OutputStreamWriter。作为字节流和字符流的桥接,并可以设置字符编码.
-
InputStreamReader 构造方法
//来自源码 // 接收一个字节流实例 public InputStreamReader(InputStream var1) { super(var1); try { this.sd = StreamDecoder.forInputStreamReader(var1, this, (String)null); } catch (UnsupportedEncodingException var3) { throw new Error(var3); } } //接受一个字节流实例和一个String 类型的参数,再深入看代码可猜测var2和字符集(charset)有关系 public InputStreamReader(InputStream var1, String var2) throws UnsupportedEncodingException { super(var1); if(var2 == null) { throw new NullPointerException("charsetName"); } else { this.sd = StreamDecoder.forInputStreamReader(var1, this, var2); } } //同 public InputStreamReader(InputStream var1, Charset var2) { super(var1); if(var2 == null) { throw new NullPointerException("charset"); } else { this.sd = StreamDecoder.forInputStreamReader(var1, this, var2); } } //基本一样 public InputStreamReader(InputStream var1, CharsetDecoder var2) { super(var1); if(var2 == null) { throw new NullPointerException("charset decoder"); } else { this.sd = StreamDecoder.forInputStreamReader(var1, this, var2); } } -
OutputStreamWriter 构造方法(实参var2作用同InputStreamReader)
public OutputStreamWriter(OutputStream var1, String var2) throws UnsupportedEncodingException { super(var1); if(var2 == null) { throw new NullPointerException("charsetName"); } else { this.se = StreamEncoder.forOutputStreamWriter(var1, this, var2); } } public OutputStreamWriter(OutputStream var1) { super(var1); try { this.se = StreamEncoder.forOutputStreamWriter(var1, this, (String)null); } catch (UnsupportedEncodingException var3) { throw new Error(var3); } } public OutputStreamWriter(OutputStream var1, Charset var2) { super(var1); if(var2 == null) { throw new NullPointerException("charset"); } else { this.se = StreamEncoder.forOutputStreamWriter(var1, this, var2); } } public OutputStreamWriter(OutputStream var1, CharsetEncoder var2) { super(var1); if(var2 == null) { throw new NullPointerException("charset encoder"); } else { this.se = StreamEncoder.forOutputStreamWriter(var1, this, var2); } }
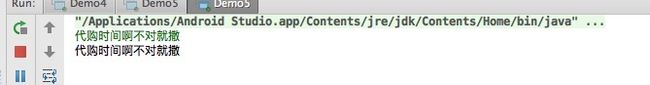
案例优化,接收打印中文字符
/**
* 字节流,字符流转换
*/
public class Demo5 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//输入流绑定键盘输入
InputStream inputStream = System.in;
//字符输入流声明
InputStreamReader inputStreamReader = null;
try {
//实例化带有编码格式的字符流
inputStreamReader = new InputStreamReader(inputStream, "utf-8");
//包装
BufferedReader bufferedReader = new BufferedReader(inputStreamReader);
String line = null;
while (true) {
//判断读取
line = new String(bufferedReader.readLine());
if (line.trim().equalsIgnoreCase("exit")) {
break;
}
//打印输出
System.out.println(line);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
结果
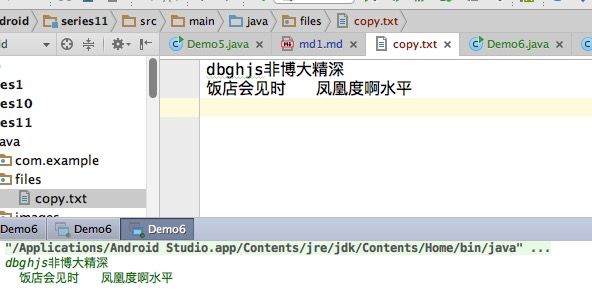
持续深入
/**
* 需求:接收键盘输入的内容,并打印到文件里去
*/
public class Demo6 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1. 通过转换流,获取到读取键盘的字符输入流
BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
String fileName = "copy.txt";//文件名
//涉及到了System.in,System.out,System.setOut(...),PrintWriter
//设置控制输出的数据位置--保存到文件中
try {
//File.separator分隔符
System.setOut(new PrintStream(Config.PATH + File.separator + fileName));
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
//2. 通过转换流,将控制台的字节流转换成缓冲的字符流
BufferedWriter writer = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out));
//3. 开始读取数据
String line = null;
while (true) {
try {
line = reader.readLine().trim();
if (line.equalsIgnoreCase("exit")) {
break;
}
writer.write(line);
writer.newLine();
writer.flush();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}