算法
算法内容如下:
- 字符串反转
- 链表反转
- 有序数组合并
- Hash算法
- 查找两个子视图的共同父视图
- 求无序数组当中的中位数
1.字符串反转
给定字符串 "hello,world",实现将其反转
void string_reverse(char* string)
{
//指向第一个字符
char* begin = string;
//指向最后一个字符
char* end = string + strlen(string) -1 ;
while (begin < end){
//交换前后两个字符,同时移动指针
char temp = *begin;
*(begin++) = *end;
*(end--) = temp;
}
}
字符串反转实现
char str[] = "hello,world";
string_reverse(str);
printf("%s",str);
2.链表反转
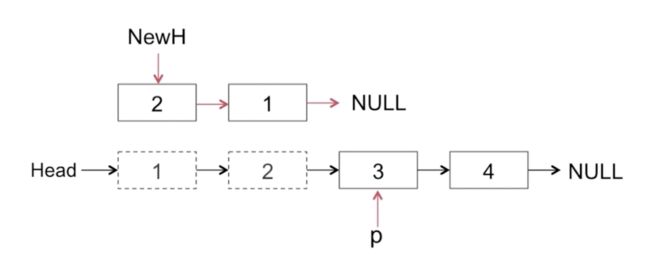
- 链表头结点指向1,2,-3-4
- 我们定义一个新的头结点指针NewH,初始化为NULL
- 定义一个临时变量p指针,进行原有链表的遍历操作
- p现在指向的为1,遍历之后指向2
- 定义NewH指针指向1,1的后面指向NULL
- p现在指向2时,2作为新的头结点,p指向3
- 知道p指针遍历为NULL,整个过程结束
struct Node {
//节点数据
int data;
//链表的下一个节点
struct Node *next;
}
@interface ReverseList:NSObject
//链表反转
struct Node * reverseList(struct Node *head);
//创建链表
struct Node * conList(void);
//打印链表数据
void printList(struct Node *head);
struct Node * reverseList(struct Node *head){
//定义遍历指针,初始化为头结点
struct Node *p = head;
//反转后的链表头部
struct Node *newH = NULL;
//遍历链表
while (p != NULL){
//记录下一个结点
struct Node *temp = p -> next;
//当前结点的next指向新链表头部
p->next = newH;
//更改新链表头部为当前结点
newH = p;
//移动p指针
p = temp;
}
//反转后的链表头结点
return newH;
}
struct Node* conList(void)
{
//头结点定义
struct Node *head = NULL;
//记录当前尾结点
struct Node *cur = NULL;
for (int i = 1 ; i < 5;i++){
struct Node *node = malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
node->data = I ;
//从头结点为空,新结点即为头结点
if (head == NULL){
head = node;
}else{
//当前结点的next为新结点
cur->next = node;
}
//设置当前结点为新结点
cur = node;
}
return head;
}
void printList(struct Node *head){
struct Node *temp = head;
while(temp != NULL){
printf("node = %d",tmep->data);
temp = temp->next;
}
}
链表反转实现
sturct Node *head = conList();
struct Node *newHead = reverseList(head);
printList(newHead);
3.有序数组合并
- 定义两个临时变量指针p,q
- 比较p,q指针内容的大小,按照大小把内容填充到合并数组中
void mergeSortedList(int a[] , int aLenth,int b[] , int bLen ,int res[]){
//遍历数组a的指针
int p = 0;
//遍历数组b的指针
int q = 0;
//记录当前存储位置
int i = 0;
while(p < aLen && q < bLen){
//a数组对应位置的值小于b数组对应位置的值
if(a[p] <= b[q]){
//存储a数组的值
res[i] = a[p];
//移动a数组的遍历指针
p++;
}else{
//存储b数组的值
res[i] = b[q];
//移动b数组的遍历指针
q++;
}
//指向合并结果的下一个存储位置
I++;
}
while( p < aLen){
//a数组有剩余
//将a数组剩余部分拼接到合并结果的后面
res[i] = a[p++];
I++;
}
while(q < bLen){
//b数组剩余部分拼接到合并结果的后面
res[i] = b[q++];
i++;
}
}
有序数组合并实现
int a[6] = {1,6,9,10,12,16};
int b[8] = {2,3,4,6,8,10,20,21};
int res[14];
mergeSortedList(a,6,b,8,res);
4.Hash算法
在一个字符串中找到第一个只出现一次的字符.
比如 aabcbdefg,则为c.
- 字符是一个长度为8的数据类型,因此总共有可能256种可能.
- 每个字母根据其ASCII码值作为数组的下标对应数组的一个数字.
- 数组中存储的是每个字符出现的次数
- char -> f(key) ->index
- f(key) = key
- 存储和查找都通过该函数,有效提高查找效率
char findFirstChar(char* cha)
{
char result = '\0';
// 定义一个数组 用来存储各个字母出现次数
int array[256];
// 对数组进行初始化操作
for (int i=0; i<256; i++) {
array[i] =0;
}
// 定义一个指针 指向当前字符串头部
char* p = cha;
// 遍历每个字符
while (*p != '\0') {
// 在字母对应存储位置 进行出现次数+1操作
array[*(p++)]++;
}
// 将P指针重新指向字符串头部
p = cha;
// 遍历每个字母的出现次数
while (*p != '\0') {
// 遇到第一个出现次数为1的字符,打印结果
if (array[*p] == 1)
{
result = *p;
break;
}
// 反之继续向后遍历
p++;
}
return result;
}
在一个字符串中找到第一个只出现一次的字符实现
char cha[] = "aabcbdefg";
char findchar = findFirstChar(cha);
5.查找两个子视图的共同父视图
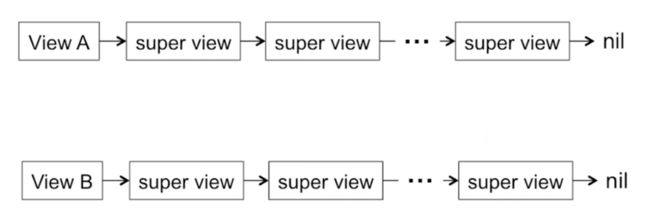
- 查找视图A的所有父视图,保存到数组A中
- 查找视图B的所有父视图,保存到数组B中
- 通过倒序比较父视图是否一样
- (NSArray *)findCommonSuperView:(UIView *)viewOne other:(UIView *)viewOther
{
NSMutableArray *result = [NSMutableArray array];
// 查找第一个视图的所有父视图
NSArray *arrayOne = [self findSuperViews:viewOne];
// 查找第二个视图的所有父视图
NSArray *arrayOther = [self findSuperViews:viewOther];
int i = 0;
// 越界限制条件
while (i < MIN((int)arrayOne.count, (int)arrayOther.count)) {
// 倒序方式获取各个视图的父视图
UIView *superOne = [arrayOne objectAtIndex:arrayOne.count - i - 1];
UIView *superOther = [arrayOther objectAtIndex:arrayOther.count - i - 1];
// 比较如果相等 则为共同父视图
if (superOne == superOther) {
[result addObject:superOne];
I++;
}
// 如果不相等,则结束遍历
else{
break;
}
}
return result;
}
- (NSArray *)findSuperViews:(UIView *)view
{
// 初始化为第一父视图
UIView *temp = view.superview;
// 保存结果的数组
NSMutableArray *result = [NSMutableArray array];
while (temp) {
[result addObject:temp];
// 顺着superview指针一直向上查找
temp = temp.superview;
}
return result;
}
6.求无序数组当中的中位数
排序算法+ 中位数
- 冒泡排序
- 快速排序
- 堆排序
中位数
- n为奇数时,(n+1)/2
- n为偶数时,(n/2 + (n/2)+ 1)/2;
利用快排
- 选取关键字,高低交替扫描
- 找到第一个比关键字大的
- 找到第一个比关键字小的
- 任意选一个元素,以该元素为支点,划分集合为两部分
- 如果左侧集合长度为(n-1)/2,支点为中位数
- 如果左侧长度小于(n-1)/2,中位数在右侧,反之,中位数在左侧
- 进入相应的一侧继续寻找中位点
int findMedian(int a[], int aLen)
{
int low = 0;
int high = aLen - 1;
int mid = (aLen - 1) / 2;
int div = PartSort(a, low, high);
while (div != mid)
{
if (mid < div)
{
//左半区间找
div = PartSort(a, low, div - 1);
}
else
{
//右半区间找
div = PartSort(a, div + 1, high);
}
}
//找到了
return a[mid];
}
int PartSort(int a[], int start, int end)
{
int low = start;
int high = end;
//选取关键字
int key = a[end];
while (low < high)
{
//左边找比key大的值
while (low < high && a[low] <= key)
{
++low;
}
//右边找比key小的值
while (low < high && a[high] >= key)
{
--high;
}
if (low < high)
{
//找到之后交换左右的值
int temp = a[low];
a[low] = a[high];
a[high] = temp;
}
}
int temp = a[high];
a[high] = a[end];
a[end] = temp;
return low;
}
面试题
- 链表反转
- 有序数组合并
- Hash算法
- 查找两个子视图的共同父视图
QQ交流群: 796142709