一.tensorflow中二维卷积函数的参数含义:
def conv2d(input, filter, strides, padding, use_cudnn_on_gpu=True, data_format="NHWC", dilations=[1, 1, 1, 1], name=None)
卷积操作函数:
input:需要做卷积操作的图片;四维tensor张量,类型float32或float64;[batch,in_height,in_width,in_channels]形状(shape):batch训练时一个batch的图片数量,in_height图片高度,in_width图片宽度,in_channels图像通道数
filter:CNN中的卷积核(滤波器),四维tensor张张量,[filter_height,filter_width,in_channels,out_channels]形状(shape):卷积核高度,卷积核宽度,图像通道数,卷积核个数。
strides:卷积时图像每一维的步长。一维向量长度为4 如[1,1,1,1]
padding:决定是否补充0,SAME:填充到滤波器能够到达图像的边缘 VALID:边缘不填充
use_cudnn_on_gpu:bool类型,是否使用cudn加速,默认加速
返回值:featuremap特征图片(tensor张量)
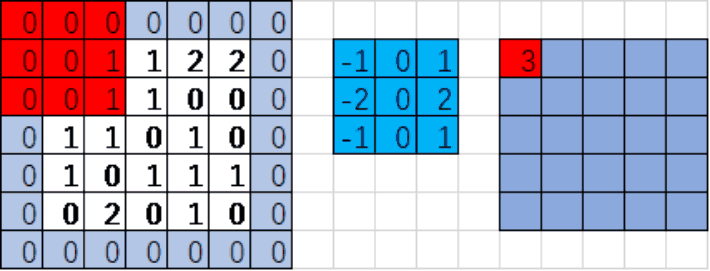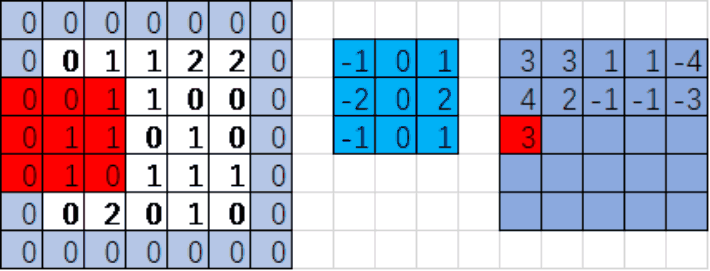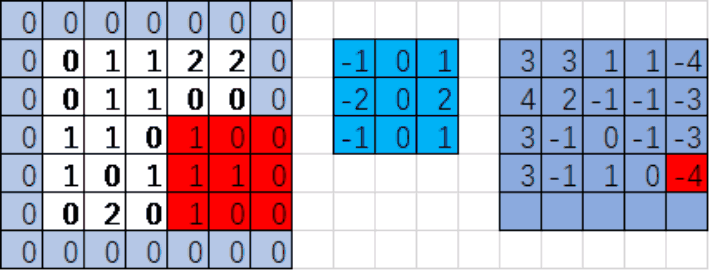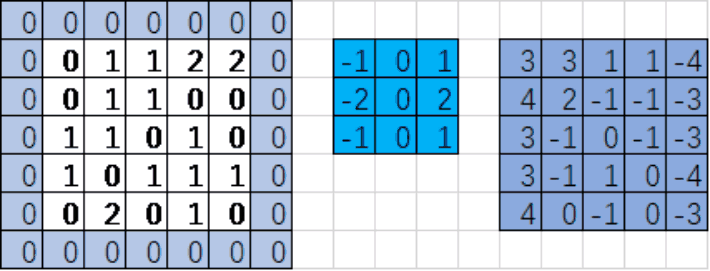
input:输入的图片 如:[1,5,5,1]下图
filter:卷积核或滤波器
strides:步长(注意:图像每一维的步长,input是四维tensor,strides=[1,1,1,1]表示每一维的步长)
padding:padding=‘SAME’补0 当padding='VALID'不补充0
返回值:featuremap特征图片
二.卷积函数的简单实例
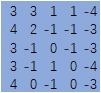
import tensorflow as tf image = [0,1.0,1,2,2,0,1,1,0,0,1,1,0,1,0,1,0,1,1,1,0,2,0,1,0] ##注意:数据类型为float32或float64不能是int,其中需有一个1.0 input = tf.Variable(tf.constant(image,shape=[1,5,5,1])) ###输入一个5*5的图像矩阵 fil1 = [-1.0,0,1,-2,0,2,-1,0,1] ##注意:数据类型为float32或float64不能是int,其中需有一个1.0 filter = tf.Variable(tf.constant(fil1,shape=[3,3,1,1])) ###定义卷积核(滤波器) op = tf.nn.conv2d(input,filter,strides=[1,1,1,1],padding='SAME') ##一个通道输入,输出一个featuremap init = tf.global_variables_initializer() with tf.Session() as sess: sess.run(init) print('input:\n', sess.run(input)) print('op:\n',sess.run(op)) ##输出结果 ''' input: [[[[ 0.] [ 1.] [ 1.] [ 2.] [ 2.]] [[ 0.] [ 1.] [ 1.] [ 0.] [ 0.]] [[ 1.] [ 1.] [ 0.] [ 1.] [ 0.]] [[ 1.] [ 0.] [ 1.] [ 1.] [ 1.]] [[ 0.] [ 2.] [ 0.] [ 1.] [ 0.]]]] op: [[[[ 3.] [ 3.] [ 1.] [ 1.] [-4.]] [[ 4.] [ 2.] [-1.] [-1.] [-3.]] [[ 3.] [-1.] [ 0.] [-1.] [-3.]] [[ 3.] [-1.] [ 1.] [ 0.] [-4.]] [[ 4.] [ 0.] [-1.] [ 0.] [-3.]]]] '''
结果一致:
总结:
1.数据类型 input 和 filter的数据类型都只能是float32 或 float64
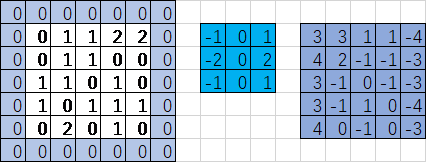
2.strides步长:是指输入数据的每一个维度的步长,输入数据是4维tensor 所以步长[1,1,1,1](一维tensor,长度4)才是和图示步长一致。
3.卷积的实现过程:
红色区域与蓝色区域对应位置的值相乘,之后所有乘积累加
0*(-1)+0*0+0*1+0*(-2)+0*0+1*2+0*(-1)+0*0+1*1=3
注意:对应位置相乘后累加(内积),而不是矩阵乘法
4.padding的规则:
padding=‘VALID’时,边缘不填充。输出的featuremap的高宽
output_width = (in_width-filter_width+1)/strides_width 输出featuremap对的宽度=(输入图片的宽度-卷积核的宽度)/步长宽度 【向上取整:当步长>1时,有可能取值不为整数】
output_height = (in_height-filter_height+1)/strides_height 输出featuremap对的高度=(输入图片的高度-卷积核的高度)/步长高度 【向上取整】 
padding=‘SAME’时的补0的规则。这个很容易理解:补了0的矩阵计算规则一样,用上面的公式(output_width = (in_width-filter_width+1)/strides_width)可以反推得到in_width这时得到的是补了0的矩阵宽度减去实际的输入矩阵宽度,就是多出来的(补0的宽度)。
pad_width = max((out_width-1)*trides_width+filter_width-in_width,0) ##为什么要和0比大小呢?因为小于等于0都是没有补0的情况。
三.卷积操作的参数组合
输入图片:灰度图是1通道输出,彩色图片3通道(RGB 红绿蓝)
卷积核:A.1通道灰度图1个卷积核----1个featuremap输出
B.1通道灰度图2个卷积核----2个featuremap输出
C.3通道彩色图1组(3个卷积核)----1组(3个featuremap)----对应位置相加-----1个featuremap输出
D.3通道彩色图2组(6个卷积核)----2组(6个featuremap)----每组对应位置相加----2个featuremap输出
步长和补0:均适用于ABCD等情况
这里引用一张gif图片(来自博客:https://www.cnblogs.com/duanhx/p/9655223.html)
在tensorflow中实现ABCD四种情况的卷积操作:
import tensorflow as tf image = [0,1.0,1,2,2,0,1,1,0,0,1,1,0,1,0,1,0,1,1,1,0,2,0,1,0] input = tf.Variable(tf.constant(image,shape=[1,5,5,1])) ##1通道输入 fil1 = [-1.0,0,1,-2,0,2,-1,0,1] filter = tf.Variable(tf.constant(fil1,shape=[3,3,1,1])) ##1个卷积核对应1个featuremap输出 op = tf.nn.conv2d(input,filter,strides=[1,1,1,1],padding='SAME') ##SAME补0操作 init = tf.global_variables_initializer() with tf.Session() as sess: sess.run(init) print('input:\n', sess.run(input)) print('filter:\n', sess.run(filter)) print('op:\n',sess.run(op)) ##输出结果 ''' input: [[[[ 0.] [ 1.] [ 1.] [ 2.] [ 2.]] [[ 0.] [ 1.] [ 1.] [ 0.] [ 0.]] [[ 1.] [ 1.] [ 0.] [ 1.] [ 0.]] [[ 1.] [ 0.] [ 1.] [ 1.] [ 1.]] [[ 0.] [ 2.] [ 0.] [ 1.] [ 0.]]]] filter: [[[[-1.]] [[ 0.]] [[ 1.]]] [[[-2.]] [[ 0.]] [[ 2.]]] [[[-1.]] [[ 0.]] [[ 1.]]]] op: [[[[ 3.] [ 3.] [ 1.] [ 1.] [-4.]] [[ 4.] [ 2.] [-1.] [-1.] [-3.]] [[ 3.] [-1.] [ 0.] [-1.] [-3.]] [[ 3.] [-1.] [ 1.] [ 0.] [-4.]] [[ 4.] [ 0.] [-1.] [ 0.] [-3.]]]] '''
import tensorflow as tf image = [0,1.0,1,2,2,0,1,1,0,0,1,1,0,1,0,1,0,1,1,1,0,2,0,1,0] input = tf.Variable(tf.constant(image,shape=[1,5,5,1])) ##1通道输入 fil1 = [-1.0,0,1,-2,0,2,-1,0,1,-1.0,0,1,-2,0,2,-1,0,1] filter = tf.Variable(tf.constant(fil1,shape=[3,3,1,2])) ##2个卷积核对应2个featuremap输出 op = tf.nn.conv2d(input,filter,strides=[1,1,1,1],padding='SAME') init = tf.global_variables_initializer() with tf.Session() as sess: sess.run(init) print('input:\n', sess.run(input)) print('filter:\n', sess.run(filter)) print('op:\n',sess.run(op)) ''' 输出: input: [[[[ 0.] [ 1.] [ 1.] [ 2.] [ 2.]] [[ 0.] [ 1.] [ 1.] [ 0.] [ 0.]] [[ 1.] [ 1.] [ 0.] [ 1.] [ 0.]] [[ 1.] [ 0.] [ 1.] [ 1.] [ 1.]] [[ 0.] [ 2.] [ 0.] [ 1.] [ 0.]]]] filter: [[[[-1. 0.]] [[ 1. -2.]] [[ 0. 2.]]] [[[-1. 0.]] [[ 1. -1.]] [[ 0. 1.]]] [[[-2. 0.]] [[ 2. -1.]] [[ 0. 1.]]]] op: [[[[ 0. 2.] [ 3. 0.] [ 0. 0.] [-1. 0.] [ 0. -2.]] [[ 2. 3.] [ 2. -1.] [-2. 2.] [ 2. -1.] [-2. -4.]] [[ 3. 1.] [-1. 0.] [ 1. -1.] [ 0. -1.] [-1. -1.]] [[ 2. 1.] [ 3. -3.] [-4. 3.] [ 3. -3.] [-3. -1.]] [[ 1. 0.] [ 1. 0.] [-1. 1.] [ 1. -1.] [-1. -2.]]]] '''
import tensorflow as tf image_channel1 = [0,1.0,1,2,2,0,1,1,0,0,1,1,0,1,0,1,0,1,1,1,0,2,0,1,0] image_channel2 = [1,1.0,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1] image_channel3 = [2,2.0,2,2,2,2,2,2,2,2,2,2,2,2,2,2,2,2,2,2,2,2,2,2,2] image = [i for i in zip(image_channel1,image_channel2,image_channel3)] ##生成器表达是生成列表 input = tf.Variable(tf.constant(image,shape=[1,5,5,3])) ##3通道输入 fil1 = [-1.0,0,1,-2,0,2,-1,0,1,-1.0,0,1,-2,0,2,-1,0,1,-1.0,0,1,-2,0,2,-1,0,1] filter = tf.Variable(tf.constant(fil1,shape=[3,3,3,1])) ##1组(3个)卷积核对应1个featuremap输出 op = tf.nn.conv2d(input,filter,strides=[1,1,1,1],padding='SAME') ##SAME补0操作 init = tf.global_variables_initializer() with tf.Session() as sess: sess.run(init) print('input:\n', sess.run(input)) print('filter:\n', sess.run(filter)) print('op:\n',sess.run(op)) ##输出结果 ''' input: [[[[ 0. 1. 2.] [ 1. 1. 2.] [ 1. 1. 2.] [ 2. 1. 2.] [ 2. 1. 2.]] [[ 0. 1. 2.] [ 1. 1. 2.] [ 1. 1. 2.] [ 0. 1. 2.] [ 0. 1. 2.]] [[ 1. 1. 2.] [ 1. 1. 2.] [ 0. 1. 2.] [ 1. 1. 2.] [ 0. 1. 2.]] [[ 1. 1. 2.] [ 0. 1. 2.] [ 1. 1. 2.] [ 1. 1. 2.] [ 1. 1. 2.]] [[ 0. 1. 2.] [ 2. 1. 2.] [ 0. 1. 2.] [ 1. 1. 2.] [ 0. 1. 2.]]]] filter: [[[[-1.] [ 0.] [ 1.]] [[-2.] [ 0.] [ 2.]] [[-1.] [ 0.] [ 1.]]] [[[-1.] [ 0.] [ 1.]] [[-2.] [ 0.] [ 2.]] [[-1.] [ 0.] [ 1.]]] [[[-1.] [ 0.] [ 1.]] [[-2.] [ 0.] [ 2.]] [[-1.] [ 0.] [ 1.]]]] op: [[[[ 10.] [ 10.] [ 8.] [ 8.] [ 6.]] [[ 13.] [ 15.] [ 14.] [ 14.] [ 11.]] [[ 12.] [ 16.] [ 16.] [ 17.] [ 14.]] [[ 11.] [ 15.] [ 16.] [ 16.] [ 13.]] [[ 8.] [ 10.] [ 10.] [ 10.] [ 8.]]]] '''
import tensorflow as tf image_channel1 = [0,1.0,1,2,2,0,1,1,0,0,1,1,0,1,0,1,0,1,1,1,0,2,0,1,0] image_channel2 = [1,1.0,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1] image_channel3 = [2,2.0,2,2,2,2,2,2,2,2,2,2,2,2,2,2,2,2,2,2,2,2,2,2,2] image = [i for i in zip(image_channel1,image_channel2,image_channel3)] ##生成器表达是生成列表 input = tf.Variable(tf.constant(image,shape=[1,5,5,3])) ##3通道输入 fil1 = [-1.0,0,1,-2,0,2,-1,0,1,-1.0,0,1,-2,0,2,-1,0,1,-1.0,0,1,-2,0,2,-1,0,1] filter = tf.Variable(tf.constant(fil1,shape=[3,3,3,2])) ##2组(6个)卷积核对应2个featuremap输出 op = tf.nn.conv2d(input,filter,strides=[1,1,1,1],padding='SAME') ##SAME补0操作 init = tf.global_variables_initializer() with tf.Session() as sess: sess.run(init) print('input:\n', sess.run(input)) print('filter:\n', sess.run(filter)) print('op:\n',sess.run(op)) ##输出结果 ''' input: [[[[ 0. 1. 2.] [ 1. 1. 2.] [ 1. 1. 2.] [ 2. 1. 2.] [ 2. 1. 2.]] [[ 0. 1. 2.] [ 1. 1. 2.] [ 1. 1. 2.] [ 0. 1. 2.] [ 0. 1. 2.]] [[ 1. 1. 2.] [ 1. 1. 2.] [ 0. 1. 2.] [ 1. 1. 2.] [ 0. 1. 2.]] [[ 1. 1. 2.] [ 0. 1. 2.] [ 1. 1. 2.] [ 1. 1. 2.] [ 1. 1. 2.]] [[ 0. 1. 2.] [ 2. 1. 2.] [ 0. 1. 2.] [ 1. 1. 2.] [ 0. 1. 2.]]]] filter: [[[[-1. 0.] [ 1. -2.] [ 0. 2.]] [[-1. 0.] [ 1. -1.] [ 0. 1.]] [[-2. 0.] [ 2. -1.] [ 0. 1.]]] [[[-1. 0.] [ 1. -2.] [ 0. 2.]] [[-1. 0.] [ 1. 1.] [ 1. 1.]] [[ 1. 1.] [ 1. 1.] [ 1. 1.]]] [[[ 1. 1.] [ 1. 1.] [ 1. 1.]] [[ 1. 1.] [ 1. 1.] [ 1. 1.]] [[ 1. 1.] [ 1. 1.] [ 1. 1.]]]] op: [[[[ 14. 14.] [ 18. 20.] [ 18. 21.] [ 16. 20.] [ 6. 11.]] [[ 16. 17.] [ 19. 24.] [ 14. 23.] [ 13. 22.] [ 9. 15.]] [[ 14. 16.] [ 17. 23.] [ 20. 24.] [ 21. 24.] [ 13. 16.]] [[ 13. 16.] [ 20. 24.] [ 20. 25.] [ 19. 23.] [ 10. 15.]] [[ 10. 10.] [ 6. 12.] [ 7. 13.] [ 6. 12.] [ 3. 8.]]]] '''
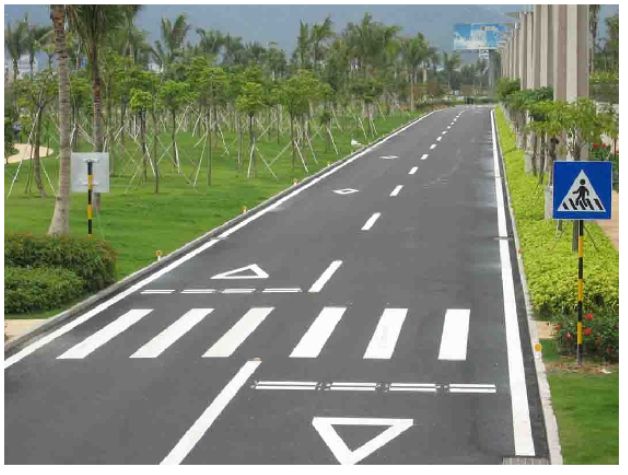
四.对一张道路图片(3通道)进行卷积操作,并且将featuremap转化成灰度图片(1通道)显示出来
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import matplotlib.image as mpimg import numpy as np import tensorflow as tf ##读取图片 myimg = mpimg.imread('road.jpg') plt.imshow(myimg) plt.axis('off') plt.show() print(myimg.shape) # print(myimg) full = np.reshape(myimg,[1,800,1067,3]) # print(full) inputfull = tf.Variable(tf.constant(1.0,shape=[1,800,1067,3])) ##3通道输入 filter = tf.Variable(tf.constant([[-1.0,-1.0,-1.0],[0,0,0],[1.0,1.0,1.0],[-2.0,-2.0,-2.0],[0,0,0], [2.0,2.0,2.0],[-1.0,-1.0,-1.0],[0,0,0],[1.0,1.0,1.0]],shape=[3,3,3,1] )) ##3*3卷积核,3个卷积核,一个featuremap输出 op = tf.nn.conv2d(inputfull,filter,strides=[1,1,1,1],padding="SAME") ##归一化操作数据类型转化成float32 x= 255*(x-min)/(max-min) o = tf.cast(((op-tf.reduce_min(op))/(tf.reduce_max(op)-tf.reduce_min(op)))*255,tf.uint8) with tf.Session() as sess: sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer()) t,f = sess.run([o,filter],feed_dict={inputfull:full}) t = np.reshape(t,[800,1067])##还原图片矩阵 plt.imshow(t,'Greys_r') ###灰度图 plt.axis('off') plt.show() print('t:\n', t)