#include
#include
#include
const int N=5;
// 定义结构体类型struct student,并定义STU为其别名
typedef struct student {
long no;
char name[20];
int score;
}STU;
typedef struct student {
long no;
char name[20];
int score;
}STU;
// 函数声明
void input(STU s[], int n);
int findMinlist(STU s[], STU t[], int n);
void output(STU s[], int n);
void input(STU s[], int n);
int findMinlist(STU s[], STU t[], int n);
void output(STU s[], int n);
int main() {
STU stu[N], minlist[N];
int count;
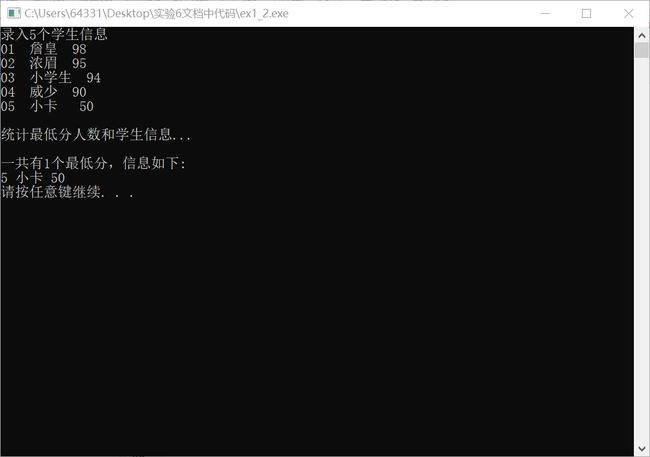
printf("录入%d个学生信息\n", N);
input(stu, N);
printf("\n统计最低分人数和学生信息...\n");
count = findMinlist(stu, minlist, N);
printf("\n一共有%d个最低分,信息如下:\n", count);
output(minlist, count);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
STU stu[N], minlist[N];
int count;
printf("录入%d个学生信息\n", N);
input(stu, N);
printf("\n统计最低分人数和学生信息...\n");
count = findMinlist(stu, minlist, N);
printf("\n一共有%d个最低分,信息如下:\n", count);
output(minlist, count);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
// 输入n个学生信息,存放在结构体数组s中
void input(STU s[], int n) {
int i;
for(i=0; i scanf("%ld %s %d", &s[i].no, s[i].name, &s[i].score);
}
void input(STU s[], int n) {
int i;
for(i=0; i
}
// 输出结构体s中n个元素信息
void output(STU s[], int n) {
int i;
for(i=0; i printf("%ld %s %d\n", s[i].no, s[i].name, s[i].score);
}
void output(STU s[], int n) {
int i;
for(i=0; i
}
// 在结构体数组s中,查找最低分学生的记录,将其存入结构体数组s中
// 形参n是结构体数组s中元素个数
// 函数返回最低分的学生人数
int findMinlist(STU s[], STU t[], int n) {
// 补足函数实现
// ×××
int i,j,m=0;
j=s[0].score;
for(i=0;i {
if(s[i].score j=s[i].score;
}
for(i=0;i {
if(j==s[i].score)
t[m++]=s[i];
}
return m;
}
// 形参n是结构体数组s中元素个数
// 函数返回最低分的学生人数
int findMinlist(STU s[], STU t[], int n) {
// 补足函数实现
// ×××
int i,j,m=0;
j=s[0].score;
for(i=0;i
if(s[i].score
}
for(i=0;i
if(j==s[i].score)
t[m++]=s[i];
}
return m;
}
#include
#include
#include
const int N = 10;
#include
#include
const int N = 10;
// 定义结构体类型struct student,并定义其别名为STU
typedef struct student {
long int id;
char name[20];
float objective; /*客观题得分*/
float subjective; /*操作题得分*/
float sum;
char level[10];
}STU;
typedef struct student {
long int id;
char name[20];
float objective; /*客观题得分*/
float subjective; /*操作题得分*/
float sum;
char level[10];
}STU;
// 函数声明
void input(STU s[], int n);
void output(STU s[], int n);
void process(STU s[], int n);
void input(STU s[], int n);
void output(STU s[], int n);
void process(STU s[], int n);
int main() {
STU stu[N];
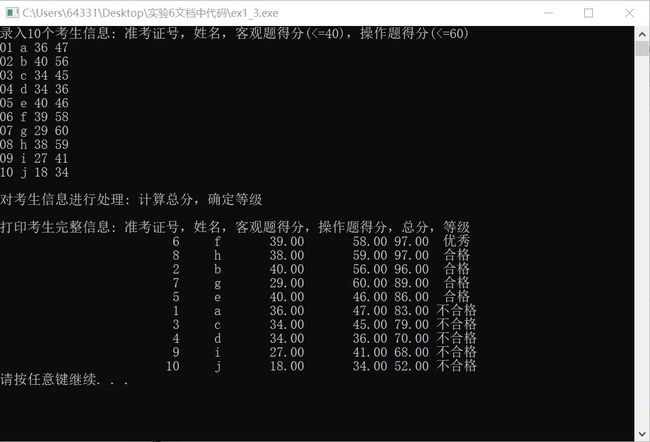
printf("录入%d个考生信息: 准考证号,姓名,客观题得分(<=40),操作题得分(<=60)\n", N);
input(stu, N);
printf("\n对考生信息进行处理: 计算总分,确定等级\n");
process(stu, N);
printf("\n打印考生完整信息: 准考证号,姓名,客观题得分,操作题得分,总分,等级\n");
output(stu, N);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
STU stu[N];
printf("录入%d个考生信息: 准考证号,姓名,客观题得分(<=40),操作题得分(<=60)\n", N);
input(stu, N);
printf("\n对考生信息进行处理: 计算总分,确定等级\n");
process(stu, N);
printf("\n打印考生完整信息: 准考证号,姓名,客观题得分,操作题得分,总分,等级\n");
output(stu, N);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
// 录入考生信息:准考证号,姓名,客观题得分,操作题得分
void input(STU s[], int n) {
// 补足代码
// ×××
int i;
for(i=0; i scanf("%ld %s %f %f",&s[i].id,s[i].name,&s[i].objective,&s[i].subjective);
}
void input(STU s[], int n) {
// 补足代码
// ×××
int i;
for(i=0; i
}
//输出考生完整信息: 准考证号,姓名,客观题得分,操作题得分,总分,等级
void output(STU s[], int n) {
// 补足代码
// ×××
int i;
for(i=0; i printf("%26ld %5s %11.2f %11.2f %3.2f %5s\n",s[i].id,s[i].name,s[i].objective,s[i].subjective,s[i].sum,s[i].level);
}
void output(STU s[], int n) {
// 补足代码
// ×××
int i;
for(i=0; i
}
// 对考生信息进行处理:计算总分,排序,确定等级
void process(STU s[], int n) {
// 补足代码
// ×××
int i,j;
STU k;
for(i=0; i s[i].sum=s[i].objective+s[i].subjective;
for(i=0; i {
for(j=0; j {
if(s[j].sum {
k=s[j];
s[j]=s[j+1];
s[j+1]=k;
}
}
void process(STU s[], int n) {
// 补足代码
// ×××
int i,j;
STU k;
for(i=0; i
for(i=0; i
for(j=0; j
if(s[j].sum
k=s[j];
s[j]=s[j+1];
s[j+1]=k;
}
}
}
for(i=0;i {
switch(i)
{
case 0:strcpy(s[i].level,"优秀");break;
case 1:
case 2:
case 3:
case 4:strcpy(s[i].level,"合格");break;
case 5:
case 6:
case 7:
case 8:
case 9:strcpy(s[i].level,"不合格");break;
}
}
}
for(i=0;i
switch(i)
{
case 0:strcpy(s[i].level,"优秀");break;
case 1:
case 2:
case 3:
case 4:strcpy(s[i].level,"合格");break;
case 5:
case 6:
case 7:
case 8:
case 9:strcpy(s[i].level,"不合格");break;
}
}
}

结构体可以同时存储多种变量类型,而共同体同一个时间只能存储和使用多个变量类型的一种,且同一个数据项可以使用多种格式,可以节省空间。
枚举类型用于描述一系列命名的整型常量。
可以直接输出,但不能直接输入。
不能把一个int型数据直接赋值给枚举变量,若要赋值必须进行强制类型转换;反之,一个枚举变量可以直接赋值给int型数据。