ssh是Uinx派系系统中通用的管理接口协议,默认端口22。这个协议稳定而且通用性强,过防火墙、过检测、过中间人嗅探那是一等一的尖端,而且,机构内部基本对此协议通行无阻,实乃红队(攻方)穿墙越网之居家必备。
用ssh 命令当做流量和端口转发完全可以利用上面的优势,就是密令复杂了一点。下面介绍的这个工具Sshtunnel,是Python的一个安装包,它不仅能直接以命令行方式实现流量转发,还有更强大的编程功能。
A.安装:
sshtunnel是PyPI维护的包, 也就是说,简单地用python包安装命令就能安装:
pip install sshtunnel
或者
easy_install sshtunnel
或者
conda install -c conda-forge sshtunnel
源码安装,先从这里(https://github.com/pahaz/sshtunnel)下回来,然后运行:
python setup.py install
B.使用场景:
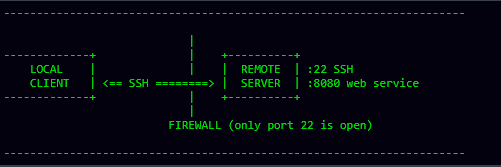
使用sshtunnel的一个经典场景,就如下面图形描述的那样。用户可能需要访问远程服务器(例如8080端口),但是你只能访问这台远程服务器的SSH端口(通常是22端口)
如果能操纵SSH服务器,还可以访问到本地客户端看不到的私有的服务器(远程服务器的角度)
C.用例:
API不仅允许初始化渠道后直接启动,还允许使用“with”语境,这会贯穿从隧道启动到关闭的整个过程。
案例1:
上面图1的例子,假如远程服务器的地址是:"pahaz.urfuclub.ru",使用密码认证,然后随机指定本地绑定的端口。
from sshtunnel import SSHTunnelForwarder
server = SSHTunnelForwarder(
'pahaz.urfuclub.ru',
ssh_username="pahaz",
ssh_password="secret",
remote_bind_address=('127.0.0.1', 8080)
)
server.start()
print(server.local_bind_port) # show assigned local port
# work with `SECRET SERVICE` through `server.local_bind_port`.
server.stop()
案例2:
上面图2的例子,不能直接访问的私有服务端口转发案例,假如只能使用证书访问,远程SSH服务器只有443端口没被左边的防火墙拦截。
import paramiko
import sshtunnel
with sshtunnel.open_tunnel(
(REMOTE_SERVER_IP, 443),
ssh_username="",
ssh_pkey="/var/ssh/rsa_key",
ssh_private_key_password="secret",
remote_bind_address=(PRIVATE_SERVER_IP, 22),
local_bind_address=('0.0.0.0', 10022)
) as tunnel:
client = paramiko.SSHClient()
client.load_system_host_keys()
client.set_missing_host_key_policy(paramiko.AutoAddPolicy())
client.connect('127.0.0.1', 10022)
# do some operations with client session
client.close()
print('FINISH!')
案例3:
Mysql 3306端口转发:
from sshtunnel import open_tunnel
from time import sleep
with open_tunnel(
('localhost', 2222),
ssh_username="vagrant",
ssh_password="vagrant",
remote_bind_address=('127.0.0.1', 3306)
) as server:
print(server.local_bind_port)
while True:
# press Ctrl-C for stopping
sleep(1)
print('FINISH!')
或者简单的一条命令:
(bash)$ python -m sshtunnel -U vagrant -P vagrant -L :3306 -R 127.0.0.1:3306 -p 2222 localhost
案例4:
启动一个跳跨两个隧道的ssh session。SSH 传输和隧道都是以后台形式运行,它不会在连接关闭时退出进程。
import sshtunnel
from paramiko import SSHClient
with sshtunnel.open_tunnel(
ssh_address_or_host=('GW1_ip', 20022),
remote_bind_address=('GW2_ip', 22),
block_on_close=False
) as tunnel1:
print('Connection to tunnel1 (GW1_ip:GW1_port) OK...')
with sshtunnel.open_tunnel(
ssh_address_or_host=('localhost', tunnel1.local_bind_port),
remote_bind_address=('target_ip', 22),
ssh_username='GW2_user',
ssh_password='GW2_pwd',
block_on_close=False
) as tunnel2:
print('Connection to tunnel2 (GW2_ip:GW2_port) OK...')
with SSHClient() as ssh:
ssh.connect('localhost',
port=tunnel2.local_bind_port,
username='target_user',
password='target_pwd',
)
ssh.exec_command(...)
命令行使用帮助:
$ sshtunnel --help
.>勒索软件绕过安全监测的那些套路
.>手把手,远程桌面客户端提取明文账号密码
.> 一种通用的Docker提权方式