IPA-task packet002:BGP选路原则
实验二:BGP选路原则
实验目标:调试和观察BGP的选路原则
实验TOP:
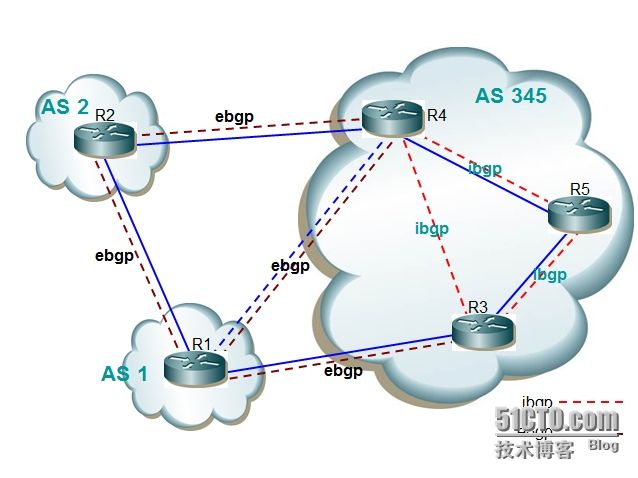
物理拓扑
逻辑拓扑
基本配置:
R1
!
hostname R1
!
no ip domain lookup
!
interface Loopback0
ip address 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.0
!
interface Loopback10
ip address 10.10.10.10 255.255.255.0
ip ospf network point-to-point
!
interface Ethernet0/0
ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.0
!
interface Serial1/0
ip address 12.1.1.1 255.255.255.0
serial restart-delay 0
clock rate 64000
!
interface Serial2/0
ip address 13.1.1.1 255.255.255.0
serial restart-delay 0
!
router ospf 10
router-id 1.1.1.1
log-adjacency-changes
network 10.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
network 10.10.10.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
network 12.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
network 13.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
!
router bgp 1
no synchronization
bgp router-id 1.1.1.1
bgp log-neighbor-changes
network 1.1.1.0 mask 255.255.255.0
neighbor 10.1.1.4 remote-as 345
neighbor 12.1.1.2 remote-as 2
neighbor 13.1.1.3 remote-as 345
no auto-summary
!
ip classless
no ip http server
no ip http secure-server
!
!
line con 0
exec-timeout 0 0
logging synchronous
line aux 0
line vty 0 4
!
end
R2
!
hostname R2
!
no ip domain lookup
!
!
interface Loopback0
ip address 2.2.2.2 255.255.255.0
!
interface Loopback10
ip address 20.20.20.20 255.255.255.0
ip ospf network point-to-point
!
interface Ethernet0/0
no ip address
shutdown
!
interface Serial1/0
ip address 24.1.1.2 255.255.255.0
serial restart-delay 0
clock rate 64000
!
interface Serial2/0
ip address 12.1.1.2 255.255.255.0
serial restart-delay 0
!
router ospf 10
router-id 2.2.2.2
log-adjacency-changes
network 12.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
network 20.20.20.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
network 24.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
!
router bgp 2
no synchronization
bgp router-id 2.2.2.2
bgp log-neighbor-changes
network 2.2.2.0 mask 255.255.255.0
neighbor 12.1.1.1 remote-as 1
neighbor 24.1.1.4 remote-as 345
no auto-summary
!
ip classless
no ip http server
no ip http secure-server
!
!
!
!
!
line con 0
exec-timeout 0 0
logging synchronous
line aux 0
line vty 0 4
!
end
R3
!
hostname R3
!
no ip domain lookup
!
!
interface Loopback0
ip address 3.3.3.3 255.255.255.0
!
interface Loopback10
ip address 30.30.30.30 255.255.255.0
ip ospf network point-to-point
!
interface Ethernet0/0
no ip address
shutdown
!
interface Serial1/0
ip address 13.1.1.3 255.255.255.0
serial restart-delay 0
clock rate 64000
!
interface Serial2/0
ip address 35.1.1.3 255.255.255.0
serial restart-delay 0
!
router ospf 10
router-id 3.3.3.3
log-adjacency-changes
network 13.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
network 30.30.30.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
network 35.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
!
router bgp 345
no synchronization
bgp router-id 3.3.3.3
bgp log-neighbor-changes
network 3.3.3.0 mask 255.255.255.0
neighbor 13.1.1.1 remote-as 1
neighbor 35.1.1.5 remote-as 345
neighbor 45.1.1.4 remote-as 345
no auto-summary
!
ip classless
no ip http server
no ip http secure-server
!
!
!
!
!
line con 0
exec-timeout 0 0
logging synchronous
line aux 0
line vty 0 4
!
End
R4
!
hostname R4
!
no ip domain lookup
!
!
interface Loopback0
ip address 4.4.4.4 255.255.255.0
!
interface Loopback10
ip address 40.40.40.40 255.255.255.0
ip ospf network point-to-point
!
interface Ethernet0/0
ip address 10.1.1.4 255.255.255.0
!
interface Serial1/0
ip address 45.1.1.4 255.255.255.0
serial restart-delay 0
clock rate 64000
!
interface Serial2/0
ip address 24.1.1.4 255.255.255.0
serial restart-delay 0
!
router ospf 10
router-id 4.4.4.4
log-adjacency-changes
network 10.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
network 24.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
network 40.40.40.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
network 45.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
!
router bgp 345
no synchronization
bgp router-id 4.4.4.4
bgp log-neighbor-changes
network 4.4.4.0 mask 255.255.255.0
neighbor 10.1.1.1 remote-as 1
neighbor 24.1.1.2 remote-as 2
neighbor 35.1.1.3 remote-as 345
neighbor 45.1.1.5 remote-as 345
no auto-summary
!
ip classless
no ip http server
no ip http secure-server
!
!
!
!
!
line con 0
exec-timeout 0 0
logging synchronous
line aux 0
line vty 0 4
!
End
R5
!
hostname R5
!
no ip domain lookup
!
!
interface Loopback0
ip address 5.5.5.5 255.255.255.0
!
interface Loopback10
ip address 50.50.50.50 255.255.255.0
ip ospf network point-to-point
!
interface Ethernet0/0
no ip address
shutdown
!
interface Serial1/0
ip address 35.1.1.5 255.255.255.0
serial restart-delay 0
clock rate 64000
!
interface Serial2/0
ip address 45.1.1.5 255.255.255.0
serial restart-delay 0
!
router ospf 10
router-id 5.5.5.5
log-adjacency-changes
network 35.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
network 45.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
network 50.50.50.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
!
router bgp 345
no synchronization
bgp router-id 5.5.5.5
bgp log-neighbor-changes
network 5.5.5.0 mask 255.255.255.0
neighbor 35.1.1.3 remote-as 345
neighbor 45.1.1.4 remote-as 345
no auto-summary
!
ip classless
no ip http server
no ip http secure-server
!
!
!
!
!
line con 0
exec-timeout 0 0
logging synchronous
line aux 0
line vty 0 4
!
End
(注:路由器接口默认是关闭的,所以应将对应的接口开启)
如上配置,已经将R1至R5基本配置完成。
BGP选路规则:
BGP路由信息库(RIB)包括
Adj-RIBs-In:储存未经处理的路由信息,来自对等体接收到的更新消息,所包含的路由信息是可用的
Loc-RIB: 包含的路由是运行BGP的路由器通过对Adj-RIBs-In中的路由使用他的本地路由策略而选择的路由
Adj-RIBs-Out:包含运行BGP的路由器向其对等体公布的路由
三个数据库间的处理方法如下:
1、为每一条可用路由计算优先级,并对BGP update消息中包含的路由信息变更做出处理。
2、将最优路由放入Loc-RIB。
3、将适合的路由放入Adj-RIBs-Out(调用仅在上一步完成后)。
BGP路径选择顺序
1、优选有最大Weight的路由 (范围0到65,535)。
A:weight是CISCO私有的参数,路由器配置了权重后在本地有效。
2、优选有最大LOCAL_PREF值的路由(范围0到4,294,967,295)。
3、优选从本路由器始发的路由(包括本地network配置的重分布,或者在IGP表中已经有一些需要被配置路由聚合的地址,在BGP中用Aggregate命令配置的路由聚合)。
4、优选有最短AS_PATH的路由。
A:如果配置了Bgp bestpath as-path ignore,则这个步骤被忽略。
B:一个AS路径集被当作一个AS,无论在这个集合中有多少AS;AS路径长度中没有包括。AS_CONFED_SEQUENCE。
5、根据Origin属性,优选具有最低起源类型的路由(IGP>EGP>Incomplete)。
6、优选最小MED值的路由(范围0到4,294,967,295)。
A:只有在通过两条路径得到第一个AS(对等体)是同一个AS时才进行MED比较;任何子自治域的联盟系统都会被忽略。也就是说,只有在AS序列号中第一个AS号码一致时,才进行MED比较;任何联盟AS序列号(AS_CONFED_SEQUENCE)都会被忽略。
B:如果路由器上配置了bgp always—compare—med,在全部的路径进行MED比较。但是这需要全体AS都同时启用这个功能,否则有可能发生路由环路。
C:如果路由器上配置了bgp bestpath med confed,将对所有只包括AS_CONFED_SEQUE
NCE的路径进行MED比较(即路径是起源于本地联盟)。
D:如果接收到的路径没有分配MED值,则将此路径分配为0,除非路由器上配置了bestpath missing—is—worst,将被看作MED值为4,294,967,295的路由将在注入到BGP路由选择表之前被改为4,294,967,295。
E:BGP明确的MED值9也可以影响此步骤。
7、外部路由eBGP优先于联盟(confederation)外部路由优于内部路由iBGP(优选eBGP路由)。
注意,路径中包括AS_CONFEND_SEQUENCE属性对联盟只有在本地有效,因此被看作是内部路径。无法区别外部联盟和内部联盟。
8、优选能通过最近的IGP邻居到达的路径(优选对BGP下一跳具有最低IGP度量值的路径)。
9、如果在路由器上配置了maximum—pathsN,而且从同一个对等体自治域/子自治域接收到多条外部/外部联盟的路径,则最多可以将N条最近接收到的路径加入到IP路由选择表中,这可以使得eBGP在多条路径上进行负载分担,目前N所代表的最大数目是6;当没有启用此功能时,缺省数值是1。在输入了showip bgp x.x.x.x后系统输出信息中可以看到最早接收到的路径被标记为最优路径,在将这条最优路径转发到内部对等体之前,需要执行与next_hop_self作用相同的功能。
10、如果是external的路由,优选最老的路由(最先被学习到的路由)。
A:此步骤可以将路由摆动的影响减到最小,因为新接收到的路径不会取代老的,即使这条新接收的路径是通过下面提及到的额外路径选择标准来进行选择的。这使得只在iBGP路径下应用额外的选择步骤更有意义。
B:此步骤可以被bgp bestpath compare_routerid命令语句所关闭。
C:如果路由器标志是一样的,此步骤可以被屏蔽,因为这说明路由器正在从自己那里接收路由。
D:如果当前没有最优路由器,此步骤可以被屏蔽。当提供某个路径的对等体路由器宏机,就会发生丢失当前最优路径的情况。
11、如果在同一时间学习到多条到同一目的地的路由,优选最小BGP-router-ID的路由,注意,如果一个路径包括路由反射器属性,起始者标识将代替路由器标识在路径选择过程中起作用。
12、如果路由从路由反射器上学习到,优选最小Cluster-ID(BGP_IDof the route reflector)长度的路由,而且它运行客户机和其他反射器族中的RR/Clients之间做对等连接,在这种情况下,路由器必须知道BGP协议中的RR的具体配置。
13、优选具有最低对等体地址接收到的路径。这个地址是在BGP对等体上配置并使用的地址,这个地址是本地对等体路由器在其上配置TCP邻居并与远端对等体建立连接时采用的地址。
BGP路径选择顺序:
如果路径不可达或者同步开启后,路径不同步,则该路径不参与选路
1、Weight——权重(越大越优先,Cisco私有属性)
2、Local_Pref——本地优先(越大越优先,本AS内有效)
3、Next_Hop——所传递路由的本地起源优先,即下一跳是0.0.0.0(在BGP表中,当前路由器通告的路由的下一跳为0.0.0.0)
4、AS_Path(越短越优先,对于out与in方向的AS_Path操作产生的效果是不同的)
5、Origin起源(优先:IGP>EGP>Incomplete;IGP指通过在BGP中network通告出来的路由,Incomplete指在BGP 中通过重发布通告出来的路由)
6、MED(越小越优先,影响另一个AS的出站选路)
7、eBGP>iBGP(从eBGP对等体学习的路由优先于从iBGP对等体学习的路由)
8、BGP 优先选择到BGP下一跳的IGP度量最低的路径
9、如果有多条来自相同相邻AS的路由并通过Maximum-paths使多条路径可用,则将所有开销相同的路由加入Loc-RIB
10、Age(eBGP)(Age越大越优先,多条路径具有相同的RID,这个原则不考虑)
11、BGP 邻居的RID(越小越优先)
12、如果多条路径始发路由器ID或路由器ID相同,那么优选Cluster-List最短的路径
13、选择邻居ip地址最小的路由
下面根据观察每台路由器的BGP表并根据BGP的路径选择顺序进行分析:
R1
我们可以通过show ip bgp命令来查看本路由器的BGP表,以下为R1的BGP表。
R1#show ip bgp
BGP table version is 6, local router ID is 1.1.1.1
Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best,i - internal,
r RIB-failure, SStale
Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
*> 1.1.1.0/24 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i
* 2.2.2.0/24 10.1.1.4 0 345 2 i
*> 12.1.1.2 0 0 2 i
* 13.1.1.3 0 345 2 i
* 3.3.3.0/24 10.1.1.4 0 345 i
* 12.1.1.2 0 2 345 i
*> 13.1.1.3 0 0 345 i
* 4.4.4.0/24 10.1.1.4 0 0 345 i
* 12.1.1.2 0 2 345 i
*> 13.1.1.3 0 345 i
* 5.5.5.0/24 10.1.1.4 0 345 i
* 12.1.1.2 0 2 345 i
*> 13.1.1.3 0 345 i
分析:
2.2.2.0/24:从拓扑图中可以看到R1分别从R2、R3和R4三个eBGP对等体学习到2.2.2.0网段,但最后只将从R2学习到的下一跳为12.1.1.2的路由条目作为最优路径装进路由表。
根据BGP的路径选择顺序:
1、Weight(未设置)
2、Local_Perf(未设置)
3、Next_Hop(无)
4、AS_Path
由于从R3和R4学习到的路由条目跨越了AS 345,所以由R3和R4传来的路由条目为2跳,最终选择由R2传来下一跳为12.1.1.2的路由条目装进路由表。
(注意:当BGP协议依据某条选路规则选出最优路径时,将不再考虑后面的规则。)
3.3.3.0/24:R1分别从R2、R3和R4三个eBGP对等体学习到3.3.3.0网段,并将下一跳为13.1.1.3的路由条目装进路由表。
根据BGP的路径选择顺序:
1、Weight(未设置)
2、Local_Perf(未设置)
3、Next_Hop(无)
4、AS_Path
由R2传来的路由条目为2跳,R3和R4相同,都为1跳,所以先排除R2传来的路由条目为最佳路由。
5、Origin起源(无)
6、MED值(未设置)
7、eBGP>iBGP(R3和R4同为R1的eBGP对等体)
8、cost(用于iBGP)
9、Maximum-paths(无)
10、Age(用于eBGP,越大越优先)
这里我们用show ip bgp summary查看R1与R3、R4的老化时间。可以看到R1与R3建立对等体的时间较长,所以选择由R3传来的下一跳为13.1.1.3的路由条目做为最佳路径装进路由表。
R1#show ip bgp summary
BGP router identifier 1.1.1.1, local ASnumber 1
BGP table version is 6, main routing tableversion 6
5 network entries using 505 bytes of memory
13 path entries using 624 bytes of memory
6 BGP path attribute entries using 360bytes of memory
4 BGP AS-PATH entries using 96 bytes ofmemory
0 BGP route-map cache entries using 0 bytesof memory
0 BGP filter-list cache entries using 0bytes of memory
BGP using 1585 total bytes of memory
BGP activity 15/10 prefixes, 39/26 paths,scan interval 60 secs
Neighbor V AS MsgRcvd MsgSent TblVer InQ OutQ Up/Down State/PfxRcd
10.1.1.4 4 345 181 180 6 0 0 02:19:07 4
12.1.1.2 4 2 182 182 6 0 0 02:19:08 4
13.1.1.3 4 345 181 179 6 0 0 02:19:12 4
4.4.4.0/24:情况同R3,所以R1学习4.4.4.0网段并不是通过R4学到,而是由R3传递过来,下一跳为13.1.1.3。
5.5.5.0/24:情况同R3,需要注意的是R4在传递路由时遵循路由传递原则,即从iBGP对等体学来的路由,传递给自身直连的eBGP对等体,下一跳更改,所以下一跳为13.1.1.3。
路由器R2、R3、R4、R5将不在一一赘述,只挑其中比较有代表性的来分析。
R3
R3#show ip bgp
BGP table version is 13, local router ID is3.3.3.3
Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, hhistory, * valid, > best, i - internal,
r RIB-failure, S Stale
Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? -incomplete
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
* i1.1.1.0/24 10.1.1.1 0 100 0 1 i
*> 13.1.1.1 0 0 1 i
* 2.2.2.0/24 13.1.1.1 0 1 2 i
*>i 24.1.1.2 0 100 0 2 i
*> 3.3.3.0/24 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i
*>i4.4.4.0/24 45.1.1.4 0 100 0 i
*>i5.5.5.0/24 35.1.1.5 0 100 0 i
分析:
4.4.4.0/24:从BGP表中可以看到R3只从R4学习到下一跳为45.1.1.4的条目做为最佳路由装进路由表中。但从拓扑中我们知道R1和R5同为R3的对等体,为何R1和R5不向R3传递路由条目?这里需要注意,由于R5与R3、R4都是iBGP对等体的关系,遵循路由传递原则,即从直连iBGP对等体学来的路由,不会再传给直连的另外一个iBGP对等体,所以R5是不会向R3传递R4的路由条目的;再看R1,因为R1是从AS 345学习到R4的4.4.4.0条目,所以R1不会再传回给AS 345,这点很像矢量路由中的“水平分割”。
R4
R4# show ip bgp
BGP table version is 13, local router ID is4.4.4.4
Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, hhistory, * valid, > best, i - internal,
r RIB-failure, S Stale
Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? -incomplete
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
* 1.1.1.0/24 24.1.1.2 0 2 1 i
* i 13.1.1.1 0 100 0 1 i
*> 10.1.1.1 0 0 1 i
* 2.2.2.0/24 10.1.1.1 0 1 2 i
*> 24.1.1.2 0 0 2 i
*>i3.3.3.0/24 35.1.1.3 0 100 0 i
*> 4.4.4.0/24 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i
*>i5.5.5.0/24 45.1.1.5 0 100 0 i
分析:
1.1.1.0/24:R4分别从R1、R2和R3三个对等体学习到1.1.1.0网段,并将下一跳为10.1.1.1的路由条目装进路由表。
根据BGP的路径选择顺序:
1、Weight(未设置)
2、Local_Perf(未设置)
3、Next_Hop(无)
4、AS_Path
由R2传来的路由条目为2跳,R1和R2相同,都为1跳,所以先排除R2传来的路由条目为最佳路由。
5、Origin起源(无)
6、MED值(未设置)
7、eBGP>iBGP
由于R4与R1为eBGP对等体关系,而与R3为iBGP对等体关系,所以R4优选从R1传来的下一跳为10.1.1.1的路由条目做为最佳路由装进路由表。
R5
R5#show ip bgp
BGP table version is 14, local router ID is 5.5.5.5
Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best,i - internal,
r RIB-failure, SStale
Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete
Network NextHop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
* i1.1.1.0/24 13.1.1.1 0 100 0 1 i
*>i 10.1.1.1 0 100 0 1 i
*>i2.2.2.0/24 24.1.1.2 0 100 0 2 i
*>i3.3.3.0/24 35.1.1.3 0 100 0 i
*>i4.4.4.0/24 45.1.1.4 0 100 0 i
*> 5.5.5.0/24 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i
分析:
1.1.1.0/24:R5分别从R3和R4两个对等体学习到1.1.1.0网段,并将下一跳为10.1.1.1的路由条目装进路由表。
根据BGP的路径选择顺序:
1、Weight(未设置)
2、Local_Perf(未设置)
3、Next_Hop(无)
4、AS_Path(同为1跳)
5、Origin起源(无)
6、MED值(未设置)
7、eBGP>iBGP(R3和R4同为R5的iBGP对等体)
8、cost(用于iBGP)
由于整网起OSPF协议,R1与R4之间是用以太网线路连接,因此R5通过R4到R1的cost值为65;而通过R3到R1的cost值为128,所以最终选择R4传来的下一跳为10.1.1.1的路由条目做为最佳路由装进路由表。
(注意:因为这里没有在R4上配置next-hop-self参数,所以R4在传递路由时遵循路由传递原则,即从eBGP对等体学来的路由,传递给自身直连的iBGP对等体,下一跳不改。)
以上我们分析了R1—R5的BGP表,了解到了部分BGP选路原则在网络中是如何工作的,下面我们将配置和调试BGP选路原则种的Weight属性、Local_Pref属性、AS_Path属性及MED属性。
Weight属性的用法和配置方法
基本配置不变,我们到R1上show ip bgp查看一下BGP路由表:
R1#show ip bgp
BGP table version is 12, local router ID is1.1.1.1
Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, hhistory, * valid, > best, i - internal,
r RIB-failure, S Stale
Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? -incomplete
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
*> 1.1.1.0/24 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i
* 2.2.2.0/24 10.1.1.4 0 345 2 i
* 13.1.1.3 0 345 2 i
*> 12.1.1.2 0 0 2 i
* 3.3.3.0/24 10.1.1.4 0 345 i
*> 13.1.1.3 0 0 345 i
* 12.1.1.2 0 2 345 i
* 4.4.4.0/24 10.1.1.4 0 0 345 i
*> 13.1.1.3 0 345 i
* 12.1.1.2 0 2 345 i
* 5.5.5.0/24 12.1.1.2 0 2 345 i
* 13.1.1.3 0 345 i
*> 10.1.1.4 0 345 i
2.2.2.0的路由是从12.1.1.2学到的,也就是从R2学到的,默认的Weight值为0,因为这条路由不是由自己产生的(如果是自己产生的路由,默认为32768,到R2上show ip bgp看到的就会是32768)。下面我们在R1上修改BGP的Weight属性,使从R4传来的下一跳为10.1.1.4的路由为最优路由。
实验配置:
R1(config)#access-list 10 permit 2.2.2.0 0.0.0.255 //创建ACL匹配感兴趣的路由
R1(config)#route-map wei_2 permit 10 //配置策略路由wei_2,序号为10,允许通过
R1(config-route-map)#match ip address 10 //匹配ACL 10定义的路由
R1(config-route-map)#set weight 65535 //设置Weight的值为65535
R1(config-route-map)#exit
R1(config)#router bgp 1
R1(config-router)#neighbor 10.1.1.4 route-map wei_2 in //在邻居10.1.1.4上应用策略路由
R1(config-router)#exit
上面的配置很关键,首先需要定义ACL,用来标记需要使用策略的路由,然后配置策略路由,匹配刚才定义的感兴趣的路由,最后分别应用到邻居上,注意方向为in(Weight属性本地有效),BGP会优先选择Weight值大的路径。
这样配置完成后,我们先在R1上clear ip bgp *,然后再来看看R1的BGP表:
R1#show ip bgp
BGP table version is 9, local router ID is1.1.1.1
Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, hhistory, * valid, > best, i - internal,
r RIB-failure, S Stale
Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? -incomplete
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
*> 1.1.1.0/24 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i
* 2.2.2.0/24 13.1.1.3 0 345 2 i
* 12.1.1.2 0 0 2 i
*> 10.1.1.4 65535 345 2 i
*> 3.3.3.0/24 13.1.1.3 0 0 345 i
* 12.1.1.2 0 2 345 i
*> 4.4.4.0/24 13.1.1.3 0 345 i
* 12.1.1.2 0 2 345 i
*> 5.5.5.0/24 13.1.1.3 0 345 i
* 12.1.1.2 0 2 345 i
可以看到,不仅原来默认的Weight属性值发生了变化,并且也改变了2.2.2.0这个路由的下一跳为10.1.1.4,也就是R4了,成功地实现了用Weight属性来修改BGP的选路。再来看一下R1的路由表:
R1#show ip route bgp
2.0.0.0/24 is subnetted, 1subnets
B 2.2.2.0 [20/0] via10.1.1.4, 00:34:34
3.0.0.0/24 is subnetted, 1 subnets
B 3.3.3.0 [20/0] via 13.1.1.3, 00:34:34
4.0.0.0/24 is subnetted, 1 subnets
B 4.4.4.0 [20/0] via 13.1.1.3, 00:34:34
5.0.0.0/24 is subnetted, 1 subnets
B 5.5.5.0 [20/0] via 13.1.1.3, 00:34:34
Local_Pref属性的用法和配置方法
保持基本配置不变,我们分别到R1、R2和R3上show ip bgp查看它们的BGP路由表表:
R3
R3#show ip bgp
BGP table version is 9, local router ID is 3.3.3.3
Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best,i - internal,
r RIB-failure, SStale
Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
* i1.1.1.0/24 10.1.1.1 0 100 0 1 i
*> 13.1.1.1 0 0 1 i
*>i2.2.2.0/24 24.1.1.2 0 100 0 2 i
*> 3.3.3.0/24 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i
*>i4.4.4.0/24 45.1.1.4 0 100 0 i
*>i5.5.5.0/24 35.1.1.5 0 100 0 i
R4
R4#show ip bgp
BGP table version is 41, local router ID is 4.4.4.4
Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best,i - internal,
r RIB-failure, SStale
Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
* i1.1.1.0/24 13.1.1.1 0 100 0 1 i
* 24.1.1.2 0 2 1 i
*> 10.1.1.1 0 0 1 i
*> 2.2.2.0/24 24.1.1.2 0 0 2 i
*>i3.3.3.0/24 35.1.1.3 0 100 0 i
*> 4.4.4.0/24 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i
*>i5.5.5.0/24 45.1.1.5 0 100 0 i
R5
R5#show ip bgp
BGP table version is 21, local router ID is 5.5.5.5
Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best,i - internal,
r RIB-failure, SStale
Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete
Network NextHop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
*>i1.1.1.0/24 10.1.1.1 0 100 0 1 i
* i 13.1.1.1 0 100 0 1 i
*>i2.2.2.0/24 24.1.1.2 0 100 0 2 i
*>i3.3.3.0/24 35.1.1.3 0 100 0 i
*>i4.4.4.0/24 45.1.1.4 0 100 0 i
*> 5.5.5.0/24 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i
下面我们通过对R3的配置,设置从R1学到的1.1.1.0的本地优先级(Localpref)设置为200,由于缺省的值为100,AS345中所有的路由器都会选择R3到达1.1.1.0。
实验配置:
R3(config)#access-list 10 permit 1.1.1.0 0.0.0.255
R3(config)#route-map local_pref permit 10
R3(config-route-map)#match ip address 10
R3(config-route-map)#set local-preference 200
R3(config-route-map)#exit
R3(config)#router bgp 345
R3(config-router)#neighbor 13.1.1.1 route-map local_pref in
R3(config-router)#end
当配置完成后,我们分别在3台路由器上clear ip bgp * soft,然后在分别看它们的BGP表:
R3
R3#show ip bgp
BGP table version is 10, local router ID is3.3.3.3
Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, hhistory, * valid, > best, i - internal,
r RIB-failure, S Stale
Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? -incomplete
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
*> 1.1.1.0/24 13.1.1.1 0 200 0 1 i
*>i2.2.2.0/24 24.1.1.2 0 100 0 2 i
*> 3.3.3.0/24 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i
*>i4.4.4.0/24 45.1.1.4 0 100 0 i
*>i5.5.5.0/24 35.1.1.5 0 100 0 i
R4
R4#show ip bgp
BGP table version is 42, local router ID is4.4.4.4
Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, hhistory, * valid, > best, i - internal,
r RIB-failure, S Stale
Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? -incomplete
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
*>i1.1.1.0/24 13.1.1.1 0 200 0 1 i
* 24.1.1.2 0 2 1 i
* 10.1.1.1 0 0 1 i
*> 2.2.2.0/24 24.1.1.2 0 0 2 i
*>i3.3.3.0/24 35.1.1.3 0 100 0 i
*> 4.4.4.0/24 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i
*>i5.5.5.0/24 45.1.1.5 0 100 0 i
R5
R5#show ip bgp
BGP table version is 22, local router ID is5.5.5.5
Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, hhistory, * valid, > best, i - internal,
r RIB-failure, S Stale
Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? -incomplete
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
*>i1.1.1.0/24 13.1.1.1 0 200 0 1 i
*>i2.2.2.0/24 24.1.1.2 0 100 0 2 i
*>i3.3.3.0/24 35.1.1.3 0 100 0 i
*>i4.4.4.0/24 45.1.1.4 0 100 0 i
*> 5.5.5.0/24 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i
因为Local_Pref属性作用范围是所在的本AS(这里为AS 345),可以看到,不仅R3原来默认的LocPrf属性值发生了变化,也改变了R4和R5的默认LocPrf属性值,并且R4和R5的1.1.1.0这个路由的下一跳变为13.1.1.1,也就是R3,成功地实现了用LocPrf属性来修改BGP的选路。
这里需要注意的是,R3在修改Local_Pref属性前,是从R1和R4学习到1.1.1.0网段的,而修改Local_Pref属性后,R3只从R1学习到1.1.1.0网段。这是因为在修改前,R4是从R1学得1.1.1.0网段,而修改Local_Pref属性后,根据选路原则,R4将从R3传来的1.1.1.0网段的路由条目做为最优路径,所以R4不会再将自己的次优路径下一跳为10.1.1.1的条目传递给R3。(R5同理)
AS_Path属性的用法和配置方法
保持基本配置不变,我们用show ip bgp查看R1和R2的BGP表:
R1
R1#show ip bgp
BGP table version is 10, local router ID is1.1.1.1
Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, hhistory, * valid, > best, i - internal,
r RIB-failure, S Stale
Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? -incomplete
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
*> 1.1.1.0/24 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i
* 2.2.2.0/24 13.1.1.3 0 345 2 i
* 12.1.1.2 0 0 2 i
*> 10.1.1.4 65535 345 2 i
*> 3.3.3.0/24 13.1.1.3 0 0 345 i
* 12.1.1.2 0 2 345 i
*> 4.4.4.0/24 13.1.1.3 0 345 i
* 12.1.1.2 0 2 345 i
*> 5.5.5.0/24 13.1.1.3 0 345 i
* 12.1.1.2 0 2 345 i
R2
R2#show ip bgp
BGP table version is 9, local router ID is2.2.2.2
Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, hhistory, * valid, > best, i - internal,
r RIB-failure, S Stale
Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? -incomplete
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
* 1.1.1.0/24 24.1.1.4 0 345 1 i
*> 12.1.1.1 0 0 1 i
*> 2.2.2.0/24 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i
* 3.3.3.0/24 12.1.1.1 0 1 345 i
*> 24.1.1.4 0 345 i
* 4.4.4.0/24 12.1.1.1 0 1 345 i
*> 24.1.1.4 0 0 345 i
* 5.5.5.0/24 12.1.1.1 0 1 345 i
*> 24.1.1.4 0 345 i
根据选路原则,BGP总是优先选择具有最短AS路径的路由。接下来我们将配置R1,将1.1.1.0通告给R2之前预先添加两个额外的AS路径到1.0.0.0上(AS100、AS200)。
实验配置:
R1(config)#access-list 10 permit 1.1.1.00.0.0.255
R1(config)#route-map aspath 10
R1(config-route-map)#match ip address 10
R1(config-route-map)#set as-path prepend100 200
R1(config-route-map)#exit
R1(config)#router bgp 1
R1(config-router)#neighbor 12.1.1.2route-map aspath out
R1(config-router)#exit
当配置完成后,我们分别在R1和R2路由器上clear ip bgp * soft,然后在分别看它们的BGP表:
R1
R1#show ip bgp
BGP table version is 10, local router ID is1.1.1.1
Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, hhistory, * valid, > best, i - internal,
r RIB-failure, S Stale
Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? -incomplete
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
*> 1.1.1.0/24 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i
* 2.2.2.0/24 13.1.1.3 0 345 2 i
* 12.1.1.2 0 0 2 i
*> 10.1.1.4 65535 345 2 i
*> 3.3.3.0/24 13.1.1.3 0 0 345 i
* 12.1.1.2 0 2 345 i
*> 4.4.4.0/24 13.1.1.3 0 345 i
* 12.1.1.2 0 2 345 i
*> 5.5.5.0/24 13.1.1.3 0 345 i
* 12.1.1.2 0 2 345 i
R2
R2#show ip bgp
BGP table version is 10, local router ID is2.2.2.2
Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, hhistory, * valid, > best, i - internal,
r RIB-failure, S Stale
Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? -incomplete
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
*> 1.1.1.0/24 24.1.1.4 0 345 1 i
* 12.1.1.1 0 0 1 100 200 i
*> 2.2.2.0/24 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i
*> 3.3.3.0/24 24.1.1.4 0 345 i
*> 4.4.4.0/24 24.1.1.4 0 0 345 i
*> 5.5.5.0/24 24.1.1.4 0 345 i
我们发现R2的BGP表发生了变化,在下一跳为12.1.1.1的条目中,Path属性值增加了2跳(100 200),所以根据选路原则,R2最终将从R4学来的下一跳为24.1.1.4的路由条目做为最优路径。
注意: R1的BGP表在做了路由策略前后没有任何变化,因为对R1做的路由策略是out方向,所以只影响出站的路由条目。
反过来,我们也可以在R2的in方向做路由策略修改AS_Path属性值。首先,清除之前对R1所做的配置,使其保持基本配置,接下来在R2上进行配置,配置如下:
实验配置:
R2(config)#access-list 10 permit 1.1.1.00.0.0.255
R2(config)#route-map aspath 10
R2(config-route-map)#match ip address 10
R2(config-route-map)#set as-path prepend100 200
R2(config-route-map)#exit
R2(config)#router bgp 2
R2(config-router)#neighbor 12.1.1.1route-map aspath in
R2(config-router)#end
当配置完成后,我们分别在R2路由器上clear ip bgp * soft,然后在分别看它的BGP表:
R2#show ip bgp
BGP table version is 10, local router ID is2.2.2.2
Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, hhistory, * valid, > best, i - internal,
r RIB-failure, S Stale
Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? -incomplete
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
*> 1.1.1.0/24 24.1.1.4 0 345 1 i
* 12.1.1.1 0 0 100 200 1 i
*> 2.2.2.0/24 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i
*> 3.3.3.0/24 24.1.1.4 0 345 i
*> 4.4.4.0/24 24.1.1.4 0 0 345 i
*> 5.5.5.0/24 24.1.1.4 0 345 i
这时我们发现,R2收到的下一跳为12.1.1.1的条目依然为2跳,与out方向有所不同的是,我们所增加的AS100和AS200在AS1之前。
总结:修改AS_Path参数,对于out与in方向的AS_Path操作产生的效果是不同的。
MED属性的作用和配置方法
保持基本的BGP配置不变,然后在R1上show ip bgp查看一下BGP的路由表:
R1#show ip bgp
BGP table version is 6, local router ID is1.1.1.1
Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, hhistory, * valid, > best, i - internal,
r RIB-failure, S Stale
Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? -incomplete
Network NextHop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
*> 1.1.1.0/24 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i
* 2.2.2.0/24 13.1.1.3 0 345 2 i
*> 12.1.1.2 0 0 2 i
* 10.1.1.4 0 345 2 i
* 3.3.3.0/24 13.1.1.3 0 0 345 i
* 12.1.1.2 0 2 345 i
*> 10.1.1.4 0 345 i
* 4.4.4.0/24 13.1.1.3 0 345 i
* 12.1.1.2 0 2 345 i
*> 10.1.1.4 0 0 345 i
* 5.5.5.0/24 13.1.1.3 0 345 i
* 12.1.1.2 0 2 345 i
*> 10.1.1.4 0 345 i
可以看到到3.3.3.0和4.4.4.0的路由都是从10.1.1.4学到的,也就是从R4学到的,默认的Metric为0,从拓扑图中可以看到,从R4学到下一跳为10.1.1.4的3.3.3.0网段是一条次优路径,我们希望R1从R3直接学习到3.3.3.0网段。
下面我们来配置BGP的Metric属性来把3.3.3.0的流量分担到R3上:
实验配置:
R3
R3(config)#access-list 10 permit 3.3.3.00.0.0.255
R3(config)#access-list 20 permit 4.4.4.00.0.0.255
R3(config)#route-map med permit 10
R3(config-route-map)#match ip address 10
R3(config-route-map)#set metric 10
R3(config-route-map)#exit
R3(config)#route-map med permit 20
R3(config-route-map)#match ip address 20
R3(config-route-map)#set metric 20
R3(config-route-map)#exit
R3(config)#router bgp 345
R3(config-router)#neighbor 13.1.1.1route-map med out
R3(config-router)#end
R4
R4(config)#access-list 10 permit 3.3.3.00.0.0.255
R4(config)#access-list 20 permit 4.4.4.00.0.0.255
R4(config)#route-map med permit 10
R4(config-route-map)#match ip address 10
R4(config-route-map)#set metric 20
R4(config-route-map)#exit
R4(config)#route-map med permit 20
R4(config-route-map)#match ip address 20
R4(config-route-map)#set metric 10
R4(config-route-map)#exit
R4(config)#router bgp 345
R4(config-router)#neighbor 10.1.1.1route-map med out
R4(config-router)#end
配置好后,在R1上clear ip bgp * soft软重启一下BGP的进程,然后再show ip bgp查看BGP的路由表:
R1#show ip bgp
BGP table version is 9, local router ID is1.1.1.1
Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, hhistory, * valid, > best, i - internal,
r RIB-failure, S Stale
Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? -incomplete
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
*> 1.1.1.0/24 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i
*> 2.2.2.0/24 12.1.1.2 0 0 2 i
*> 3.3.3.0/24 13.1.1.3 10 0 345 i
* 12.1.1.2 0 2 345 i
* 10.1.1.4 20 0 345 i
* 4.4.4.0/24 13.1.1.3 20 0 345 i
* 12.1.1.2 0 2 345 i
*> 10.1.1.4 10 0 345 i
*> 5.5.5.0/24 12.1.1.2 0 2 345 i
这时我们发现Metric属性值变了,从13.1.1.3学到3.3.3.0的Metric变为10,而4.4.4.0的Metric变为20,同样,从10.1.1.4学到的3.3.3.0的Metric变成了20,4.4.4.0的Metric变成了10,这样的话R1上学到的3.3.3.0的路由就是通过R3学到的,4.4.4.0学到的路由是从R4学到的,这样就有效的分担了R4上的流量。
再来看一下R1的路由表:
R1#show ip route bgp
2.0.0.0/24 is subnetted, 1 subnets
B 2.2.2.0 [20/0] via 12.1.1.2, 00:30:13
3.0.0.0/24 is subnetted, 1 subnets
B 3.3.3.0 [20/10] via13.1.1.3, 00:19:05
4.0.0.0/24 is subnetted, 1 subnets
B 4.4.4.0 [20/10] via10.1.1.4, 00:19:05
5.0.0.0/24 is subnetted, 1 subnets
B 5.5.5.0 [20/0] via 12.1.1.2, 00:19:05
总结:配置MED属性值后,会影响另一个AS的出站选路。