最近在看 《Flex & Bison》 这本书, 针对书中的例子进行解读和笔记, 以消化每一个知识细节, 所以本文会持续更新, 直到《Flex & Bison》读完.
因为本文只是针对源码程序进行简单的笔记备忘, 不会完全讲解, 所以为了弄懂每行代码, 建议阅读《Flex & Bison》原文.
运行环境:
- Mac 10.13
- flex 2.5.35 Apple(flex-31)
- bison (GNU Bison) 2.3
单词统计程序
wc.l 源代码:
%{
int chars = 0;
int words = 0;
int lines = 0;
%}
%%
[^ \t\n\r\f\v]+ { words++; chars += strlen(yytext); }
\n { chars++; lines++; }
. { chars++; }
%%
int main(int argc, char **argv) {
yylex();
printf("%8d%8d%8d\n", lines, words, chars);
}
编译命令:
源码备注:
- %{ ... %} 是直接拷贝到 C 文件开头
- %% ... %% 是模式匹配的代码区域, 左边是正则表达式, 右边是匹配的 C 代码
- yytext 代表匹配正则表达式的字符串
- flex 的匹配默认是从最长匹配开始, 如果有多个匹配的正则表达式, 从最早的那个开始匹配, 所以上面的模式匹配, 首先是按照单词 -> 行尾符 -> 剩余字符串的顺序进行匹配的, 不会产生重复统计的问题
- yylex 是调用 flex 的词法分析函数 yylex 进行计算
- Linux 系统上用 -lfl 选项编译, Mac 的编译选项是 -ll
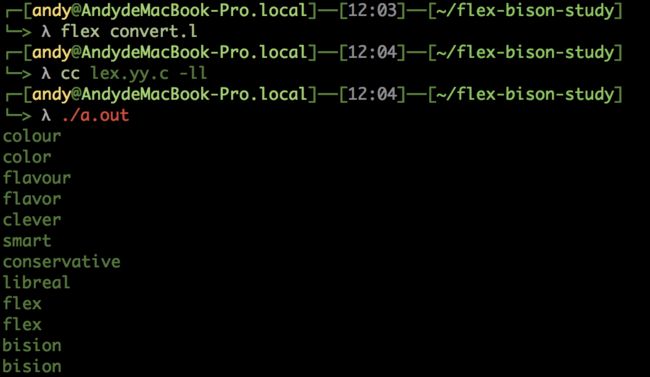
英美式英语转换
convert.l 源代码:
%%
"colour" { printf("color"); }
"flavour" { printf("flavor"); }
"clever" { printf("smart"); }
"conservative" { printf("libreal"); }
. { printf("%s", yytext); }
%%
int main(int argc, char **argv) {
yylex();
}
编译命令:
源码备注:
- 匹配英式单词后, 转换称模式后的美式英语
- 最后的点表示不转换单词
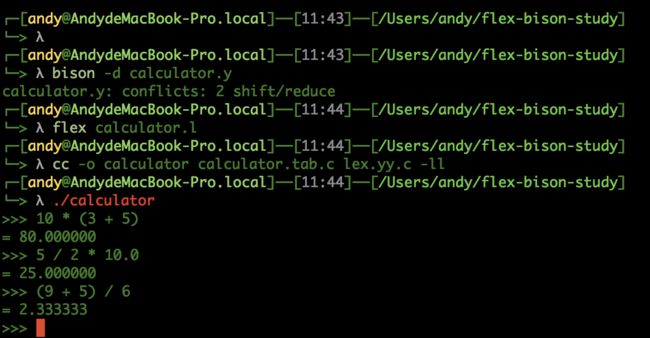
计算器
calculator.y
%{
#define YYSTYPE double
#include
#include
int yylex();
void yyerror(char *s);
%}
%token NUMBER
%token ADD SUB MUL DIV ABS
%token EOL
%token OP CP
%token POW SQRT
%%
calclist:
| calclist exp EOL { printf("= %f\n>>> ", $2); }
| calclist EOL { printf(">>> "); } /* blank line or a comment */
;
exp: factor { $$ = $1; }
| exp ADD factor { $$ = $1 + $3; }
| exp SUB factor { $$ = $1 - $3; }
;
factor: another_factor { $$ =$1; }
| factor MUL another_factor { $$ = $1 * $3; }
| factor DIV another_factor { $$ = $1 / $3; }
;
another_factor: term { $$ = $1; }
| SUB another_factor { $$ = -$2; }
| another_factor POW another_factor { $$ = pow($1,$3); }
;
term: NUMBER { $$ = $1; }
| ABS exp ABS { $$ = fabs($2); }
| OP exp CP { $$ = $2; }
| SQRT OP exp CP { $$ = sqrt($3); }
;
%%
int main(int argc, char **argv) {
printf(">>> ");
yyparse();
}
void yyerror(char *s) {
fprintf(stderr,"error : %s\n",s);
}
calculator.l
%{
#define YYSTYPE double
#include "calculator.tab.h"
#include
YYSTYPE yylval;
%}
%%
"+" { return ADD; }
"-" { return SUB; }
"*" { return MUL; }
"/" { return DIV; }
"|" { return ABS; }
"(" { return OP; }
")" { return CP; }
([0-9]*\.?[0-9]+|[0-9]+\.) { yylval = atof(yytext); return NUMBER;}
"sqrt" { return SQRT; }
"**" { return POW; }
\n { return EOL; }
[ \t] {}
"//".* {}
%%
编译命令:
源码备注:
-
#define YYSTYPE double要放在顶部, 这样就可以把默认的 YYSTYPE 从 int 改成 double 来支持浮点数运算 - calculator.y 顶部定义函数 yylex 和 yyerror 的声明, 避免 cc 编译的时候报警告
- calculator.l 模式中, 只要 { ... } 是空白就表示不处理标记 (token) , 也就可以实现忽略空格和注释字符串的功能
- calculator.y 中越靠下的匹配规则在语法树的优先级越高, 因为它被别人应用的越多, 在语法树中越靠近树枝的部位
Flex 的正则表达式
Flex 有几个正则表达式和传统的正则表达式规则还是有点区别:
- [a-z]{}[jv] 表示 a-z 里面再排除 j 和 v
- / 尾部上下文, 0/1 表示匹配 01 中的 0 , / 后面的只用于尾部模式匹配, 匹配出来的是斜线前面的内容, 但斜线后面的内容并不会消耗掉, 会继续给余下的规则匹配
统计文件中的单词数
wc-file.l 源代码:
%option noyywrap
%{
int chars = 0;
int words = 0;
int lines = 0;
int totchars = 0;
int totwords = 0;
int totlines = 0;
%}
%%
[a-zA-Z]+ { words++; chars += strlen(yytext); }
\n { chars++; lines++; }
. { chars++; }
%%
int main(int argc, char **argv) {
printf("%8s%8s%8s%8s\n", "lines", "words", "chars", "file");
if (argc < 2) {
yylex();
printf("%8d%8d%8d\n", lines, words, chars);
return 0;
}
for (int i = 1; i < argc; i++) {
FILE *f = fopen(argv[i], "r");
if (!f) {
perror(argv[i]);
return 1;
}
yyrestart(f);
yylex();
fclose(f);
printf("%8d%8d%8d %s\n", lines, words, chars, argv[i]);
totchars += chars; chars = 0;
totwords += words; words = 0;
totlines += lines; lines = 0;
}
if (argc > 1) {
printf("%8d%8d%8d total\n", totlines, totwords, totchars);
}
return 0;
}
编译命令:
阅读笔记:
- %option noyywrap 是用于关闭 yywrap 这个鸡肋的函数, yywrap 主要用于调整 yyin 的值来读取新文件的内容
- yyrestart(f) 放在 yylex 之前, 告诉 flex 读取文件 f 的内容