一、页面渲染,初查找逻辑
ViewGroup:
1、->ViewGroup.requestFocus(intdirection, Rect previouslyFocusedRect)
2、->ViewGroup.onRequestFocusInDescendants(intdirection, Rect previouslyFocusedRect)
protected boolean onRequestFocusInDescendants(int direction,
Rect previouslyFocusedRect) {
int index;
int increment;
int end;
int count = mChildrenCount;
if ((direction & FOCUS_FORWARD) != 0) {
index = 0;
increment = 1;
end = count;
} else {
index = count - 1;
increment = -1;
end = -1;
}
final View[] children = mChildren;
for (int i = index; i != end; i += increment) {
View child = children[I];
if ((child.mViewFlags & VISIBILITY_MASK) == VISIBLE) {
if (child.requestFocus(direction, previouslyFocusedRect)) {
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
二、焦点查找逻辑计算分析
2.1 现象
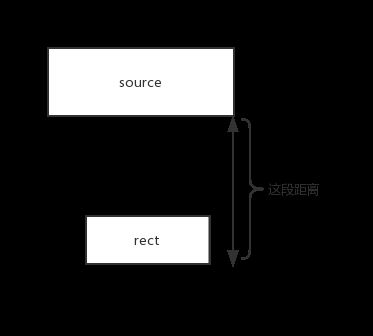
我们在页面开发中出现了类似于下图的现象,问题描述:当前聚焦在source上,按向下键,我们期望的是焦点会到rect1上,但是实际上焦点会到rect2上,下面我们来一步步的探索原因
2.2原因剖析
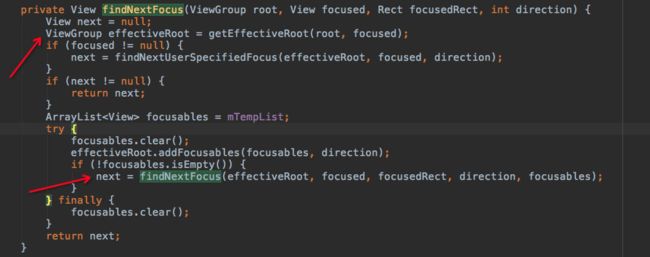
我们可以得出先看FocusFinder的findNextFocus,
我们可以看到最终调用它的findNextFocus,接下来我们看这个方法:
2.2.1 findNextFocus
private View findNextFocus(ViewGroup root, View focused, Rect focusedRect,
int direction, ArrayList focusables) {
if (focused != null) {
if (focusedRect == null) {
focusedRect = mFocusedRect;
}
// fill in interesting rect from focused
//焦点Rect,该Rect是相对focused视图本身的
focused.getFocusedRect(focusedRect);
//将当前focused视图的坐标系,转换到root的坐标系中,统一坐标,以便进行下一步的计算
root.offsetDescendantRectToMyCoords(focused, focusedRect);
} else {
if (focusedRect == null) {
focusedRect = mFocusedRect;
// make up a rect at top left or bottom right of root
switch (direction) {
case View.FOCUS_RIGHT:
case View.FOCUS_DOWN:
setFocusTopLeft(root, focusedRect);
break;
case View.FOCUS_FORWARD:
if (root.isLayoutRtl()) {
setFocusBottomRight(root, focusedRect);
} else {
setFocusTopLeft(root, focusedRect);
}
break;
case View.FOCUS_LEFT:
case View.FOCUS_UP:
setFocusBottomRight(root, focusedRect);
break;
case View.FOCUS_BACKWARD:
if (root.isLayoutRtl()) {
setFocusTopLeft(root, focusedRect);
} else {
setFocusBottomRight(root, focusedRect);
break;
}
}
}
}
switch (direction) {
case View.FOCUS_FORWARD:
case View.FOCUS_BACKWARD:
return findNextFocusInRelativeDirection(focusables, root, focused, focusedRect,
direction);
case View.FOCUS_UP:
case View.FOCUS_DOWN:
case View.FOCUS_LEFT:
case View.FOCUS_RIGHT:
return findNextFocusInAbsoluteDirection(focusables, root, focused,
focusedRect, direction);
default:
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unknown direction: " + direction);
}
}
我们可以看到根据我们的方向按键,接下来进入到方法findNextFocusInAbsoluteDirection()中
2.2.2 findNextFocusInAbsoluteDirection
View findNextFocusInAbsoluteDirection(ArrayList focusables, ViewGroup root, View focused,
Rect focusedRect, int direction) {
// 首先将mBestCandidateRect初始化为不可能的Rect
mBestCandidateRect.set(focusedRect);
switch(direction) {
case View.FOCUS_LEFT:
mBestCandidateRect.offset(focusedRect.width() + 1, 0);
break;
case View.FOCUS_RIGHT:
mBestCandidateRect.offset(-(focusedRect.width() + 1), 0);
break;
case View.FOCUS_UP:
mBestCandidateRect.offset(0, focusedRect.height() + 1);
break;
case View.FOCUS_DOWN:
mBestCandidateRect.offset(0, -(focusedRect.height() + 1));
}
View closest = null;
int numFocusables = focusables.size();
for (int i = 0; i < numFocusables; i++) {
View focusable = focusables.get(i);
// only interested in other non-root views
if (focusable == focused || focusable == root) continue;
// get focus bounds of other view in same coordinate system
focusable.getFocusedRect(mOtherRect);
root.offsetDescendantRectToMyCoords(focusable, mOtherRect);
if (isBetterCandidate(direction, focusedRect, mOtherRect, mBestCandidateRect)) {
mBestCandidateRect.set(mOtherRect);
closest = focusable;
}
}
return closest;
}
通过上面的代码我们会发现,这段是核心代码即遍历focusables集合,拿出每个view的rect属性和当前focused view的rect进行“距离”的比较,最终得到“距离”最近的候选者并返回。至此,整个寻焦逻辑结束。
接下来我们来看这段比较:
(1)首先将mBestCandidateRect初始化为不可能的Rect
当direction为:View.FOCUS_DOWN,即rect的left和right保持不变,会偏移-(focusedRect.height() + 1)的值即,初始mBestCandidateRect会比focusedRect至少高1px;
public void offset(int dx, int dy) {
left += dx;
top += dy;
right += dx;
bottom += dy;
}
(2)接下来我们看for循环里面寻找最优焦点的逻辑,主要是方法isBetterCandidate()
2.2.3 isBetterCandidate()
boolean isBetterCandidate(int direction, Rect source, Rect rect1, Rect rect2) {
// to be a better candidate, need to at least be a candidate in the first
// place :)
if (!isCandidate(source, rect1, direction)) {
return false;
}
// we know that rect1 is a candidate.. if rect2 is not a candidate,
// rect1 is better
if (!isCandidate(source, rect2, direction)) {
return true;
}
// if rect1 is better by beam, it wins
if (beamBeats(direction, source, rect1, rect2)) {
return true;
}
// if rect2 is better, then rect1 cant' be :)
if (beamBeats(direction, source, rect2, rect1)) {
return false;
}
// otherwise, do fudge-tastic comparison of the major and minor axis
return (getWeightedDistanceFor(
majorAxisDistance(direction, source, rect1),
minorAxisDistance(direction, source, rect1))
< getWeightedDistanceFor(
majorAxisDistance(direction, source, rect2),
minorAxisDistance(direction, source, rect2)));
}
通过上面我们会发现isBetterCandidate()方法的流程:
2.2.4 isCandidate()
isCandidate()方法判断是否在source对应的方向上
/**
* Is destRect a candidate for the next focus given the direction? This
* checks whether the dest is at least partially to the direction of (e.g left of)
* from source.
*
* Includes an edge case for an empty rect (which is used in some cases when
* searching from a point on the screen).
*/
boolean isCandidate(Rect srcRect, Rect destRect, int direction) {
switch (direction) {
case View.FOCUS_LEFT:
return (srcRect.right > destRect.right || srcRect.left >= destRect.right)
&& srcRect.left > destRect.left;
case View.FOCUS_RIGHT:
return (srcRect.left < destRect.left || srcRect.right <= destRect.left)
&& srcRect.right < destRect.right;
case View.FOCUS_UP:
return (srcRect.bottom > destRect.bottom || srcRect.top >= destRect.bottom)
&& srcRect.top > destRect.top;
case View.FOCUS_DOWN:
return (srcRect.top < destRect.top || srcRect.bottom <= destRect.top)
&& srcRect.bottom < destRect.bottom;
}
throw new IllegalArgumentException("direction must be one of "
+ "{FOCUS_UP, FOCUS_DOWN, FOCUS_LEFT, FOCUS_RIGHT}.");
}
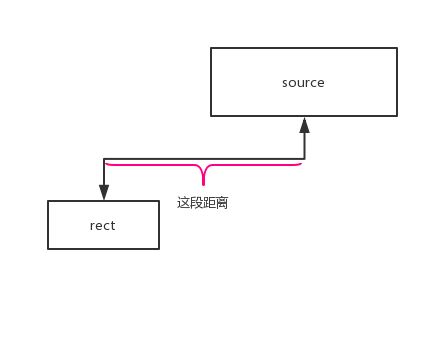
例如:当direction为View.FOCUS_DOWN时,需要满足的是destRect.top比srcRect的顶部或底部大并且destRect.bottom比srcRect的底部大,即如下图所示rect1和rect2对于source都是符合,return ture。
2.2.5 beamBeats()
beamBeats()方法判断rect1是否优于rect2,比较从三个维度展开:
1、是否有重叠
2、rect1有重叠,rect2无重叠,再从rect2是否完全在source的对应方向上。比如direction为FOCUS_LEFT,rect2.right<=source.left表示rect2完全在source左边
3、离source在direction方向上的距离
/**
* One rectangle may be another candidate than another by virtue of being
* exclusively in the beam of the source rect.
* @return Whether rect1 is a better candidate than rect2 by virtue of it being in src's
* beam
*/
boolean beamBeats(int direction, Rect source, Rect rect1, Rect rect2) {
final boolean rect1InSrcBeam = beamsOverlap(direction, source, rect1);
final boolean rect2InSrcBeam = beamsOverlap(direction, source, rect2);
// if rect1 isn't exclusively in the src beam, it doesn't win
if (rect2InSrcBeam || !rect1InSrcBeam) {
return false;
}
// we know rect1 is in the beam, and rect2 is not
// if rect1 is to the direction of, and rect2 is not, rect1 wins.
// for example, for direction left, if rect1 is to the left of the source
// and rect2 is below, then we always prefer the in beam rect1, since rect2
// could be reached by going down.
if (!isToDirectionOf(direction, source, rect2)) {
return true;
}
// for horizontal directions, being exclusively in beam always wins
if ((direction == View.FOCUS_LEFT || direction == View.FOCUS_RIGHT)) {
return true;
}
// for vertical directions, beams only beat up to a point:
// now, as long as rect2 isn't completely closer, rect1 wins
// e.g for direction down, completely closer means for rect2's top
// edge to be closer to the source's top edge than rect1's bottom edge.
return (majorAxisDistance(direction, source, rect1)
< majorAxisDistanceToFarEdge(direction, source, rect2));
}
1、在给定的方向上是否有重叠
/**
* Do the "beams" w.r.t the given direction's axis of rect1 and rect2 overlap?
* @param direction the direction (up, down, left, right)
* @param rect1 The first rectangle
* @param rect2 The second rectangle
* @return whether the beams overlap
*/
boolean beamsOverlap(int direction, Rect rect1, Rect rect2) {
switch (direction) {
case View.FOCUS_LEFT:
case View.FOCUS_RIGHT:
return (rect2.bottom >= rect1.top) && (rect2.top <= rect1.bottom);
case View.FOCUS_UP:
case View.FOCUS_DOWN:
return (rect2.right >= rect1.left) && (rect2.left <= rect1.right);
}
throw new IllegalArgumentException("direction must be one of "
+ "{FOCUS_UP, FOCUS_DOWN, FOCUS_LEFT, FOCUS_RIGHT}.");
}
例:direction == View.FOCUS_DOWN
结论:示例图中:rect1有重叠,rect2无重叠;
2、rect1有重叠,rect2无重叠,再从rect2是否完全在source的对应方向上。比如direction为FOCUS_LEFT,rect2.right<=source.left表示rect2完全在source左边
/**
* e.g for left, is 'to left of'
*/
boolean isToDirectionOf(int direction, Rect src, Rect dest) {
switch (direction) {
case View.FOCUS_LEFT:
return src.left >= dest.right;
case View.FOCUS_RIGHT:
return src.right <= dest.left;
case View.FOCUS_UP:
return src.top >= dest.bottom;
case View.FOCUS_DOWN:
return src.bottom <= dest.top;
}
throw new IllegalArgumentException("direction must be one of "
+ "{FOCUS_UP, FOCUS_DOWN, FOCUS_LEFT, FOCUS_RIGHT}.");
}
例:direction为FOCUS_DOWN时,rect1有重叠,rect2无重叠,再看rect2是否完全在source的下方,如果不是则isToDirectionOf()return false, beamBeats() return ture,
(3)距离source在direction方向上的距离
/**
* @return The distance along the major axis w.r.t the direction from the
* edge of source to the far edge of dest. If the
* dest is not in the direction from source, return 1 (to break ties with
* {@link #majorAxisDistance}).
*/
static int majorAxisDistanceToFarEdge(int direction, Rect source, Rect dest) {
return Math.max(1, majorAxisDistanceToFarEdgeRaw(direction, source, dest));
}
static int majorAxisDistanceToFarEdgeRaw(int direction, Rect source, Rect dest) {
switch (direction) {
case View.FOCUS_LEFT:
return source.left - dest.left;
case View.FOCUS_RIGHT:
return dest.right - source.right;
case View.FOCUS_UP:
return source.top - dest.top;
case View.FOCUS_DOWN:
return dest.bottom - source.bottom;
}
throw new IllegalArgumentException("direction must be one of "
+ "{FOCUS_UP, FOCUS_DOWN, FOCUS_LEFT, FOCUS_RIGHT}.");
}
例:当direction == View_FOCUS_DOWN
结论:由示例图,可以得出:
rect1.buttom - source.buttom = 300;(390 - 90 = 300)
rect2.buttom - source.buttom = 105;(195 - 90 = 105)
即return 300<105; 即return false;
2.2.6 最后就是通过距离去比较
return (getWeightedDistanceFor(
majorAxisDistance(direction, source, rect1),
minorAxisDistance(direction, source, rect1))
< getWeightedDistanceFor(
majorAxisDistance(direction, source, rect2),
minorAxisDistance(direction, source, rect2)));
/**
* Fudge-factor opportunity: how to calculate distance given major and minor
* axis distances. Warning: this fudge factor is finely tuned, be sure to
* run all focus tests if you dare tweak it.
*/
int getWeightedDistanceFor(int majorAxisDistance, int minorAxisDistance) {
return 13 * majorAxisDistance * majorAxisDistance
+ minorAxisDistance * minorAxisDistance;
}
/**
* Find the distance on the minor axis w.r.t the direction to the nearest
* edge of the destination rectangle.
* @param direction the direction (up, down, left, right)
* @param source The source rect.
* @param dest The destination rect.
* @return The distance.
*/
static int minorAxisDistance(int direction, Rect source, Rect dest) {
switch (direction) {
case View.FOCUS_LEFT:
case View.FOCUS_RIGHT:
// the distance between the center verticals
return Math.abs(
((source.top + source.height() / 2) -
((dest.top + dest.height() / 2))));
case View.FOCUS_UP:
case View.FOCUS_DOWN:
// the distance between the center horizontals
return Math.abs(
((source.left + source.width() / 2) -
((dest.left + dest.width() / 2))));
}
throw new IllegalArgumentException("direction must be one of "
+ "{FOCUS_UP, FOCUS_DOWN, FOCUS_LEFT, FOCUS_RIGHT}.");
}
结论:
majorAxisDistance(direction, source, rect1)
= 300
minorAxisDistance(direction, source, rect1)=
Math.abs( ((source.left + source.width() / 2) - ((dest.left + dest.width() / 2))))
= Math.abs( ((225+150/2) -((225+150/2))))
= Math.abs( 0 )
= 0
getWeightedDistanceFor(300,0)
= 13300*300+00
= 1170000
majorAxisDistance(direction, source, rect2)
= 105
minorAxisDistance(direction, source, rect2)=
Math.abs( ((source.left + source.width() / 2) - ((dest.left + dest.width() / 2))))
= Math.abs( ((225 +150/2) -((38+150/2))))
= Math.abs( 187 )
= 187
getWeightedDistanceFor(105,187)
= 13105*105+187187
= 178294
return 1170000<178294 即 return false;
最终结论:
closest 是 rect2