传送门:47. 全排列 II。
给定一个可包含重复数字的序列,返回所有不重复的全排列。
示例:
输入: [1,1,2] 输出: [ [1,1,2], [1,2,1], [2,1,1] ]
同《剑指 Offer》(第 2 版)第 38 题:输入一个字符串,按字典序打印出该字符串中字符的所有排列。例如输入字符串 abc,则打印出由字符 a、b、c 所能排列出来的所有字符串 abc、acb、bac、bca、cab 和 cba 。
- 如何解决重复问题。
- 使用一个数,通过二进制“左移”和“右移”判断一个数是否被使用过。
注意:去除重复结果。
注意:上面这种思路不能处理有重复元素的问题。
Python 代码:首先排序,如果后一个数和前一个数相等,并且前一个数没有使用过,就要 continue 。
class Solution:
def permutation(self, nums):
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:rtype: List[List[int]]
"""
l = len(nums)
res = []
if l == 0:
return res
# 因为含有重复数组,所以先排序
nums.sort()
marked = [False for _ in range(l)]
self.__dfs(nums, 0, [], marked, res)
return res
def __dfs(self, nums, index, path, marked, res):
if index == len(nums):
res.append(path[:])
return
for i in range(len(nums)):
if not marked[i]:
if i > 0 and nums[i] == nums[i - 1] and not marked[i - 1]:
continue
marked[i] = True
path.append(nums[i])
self.__dfs(nums, index + 1, path, marked, res)
path.pop()
marked[i] = False
特别注意:1、首先将数组排序,以便后续去重;
2、就是在遍历的时候:
if i > 0 and nums[i] == nums[i - 1] and not marked[i - 1]:
continue
说明:i > 0 是因为后面要用到索引 i - 1。后一个数等于之前的数,而之前的数又没有用过,这是导致重复的原因,把这种情况排除掉就可以了,可以认为这个操作是一个剪枝。
(以上是最经典的写法,下面的写法有一定技巧性。)
解法2:大雪菜的思路:
由于有重复元素的存在,这道题的枚举顺序和 Permutations 不同。先将所有数从小到大排序,这样相同的数会排在一起;从左到右依次枚举每个数,每次将它放在一个空位上;对于相同数,我们人为定序,就可以避免重复计算:我们在 dfs 时记录一个额外的状态,记录上一个相同数存放的位置 start,我们在枚举当前数时,只枚举 start+1、start+2、...、n 这些位置。
Python 代码:
# 38、数字排列
# 输入一组数字(可能包含重复数字),输出其所有的排列方式。
#
# 样例
# 输入:[1,2,3]
#
# 输出:
# [
# [1,2,3],
# [1,3,2],
# [2,1,3],
# [2,3,1],
# [3,1,2],
# [3,2,1]
# ]
# 参考资料:https://www.acwing.com/solution/AcWing/content/776/
class Solution:
def permutation(self, nums):
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:rtype: List[List[int]]
"""
l = len(nums)
res = []
if l == 0:
return res
# 因为含有重复数组,所以先排序
nums.sort()
path = [0 for _ in range(l)]
self.__dfs(nums, 0, 0, path, 0, res)
return res
def __dfs(self, nums, index, start, path, state, res):
if index == len(nums):
res.append(path[:])
return
if index == 0 or nums[index] != nums[index - 1]:
start = 0
for i in range(start, len(nums)):
if (state >> i & 1) == 0:
# 如果当前的数没有使用过
# 这一句不好理解
path[i] = nums[index]
self.__dfs(nums, index + 1, i + 1, path, state + (1 << i), res)
if __name__ == '__main__':
nums = [1, 1, 2]
solution = Solution()
result = solution.permutation(nums)
print(result)
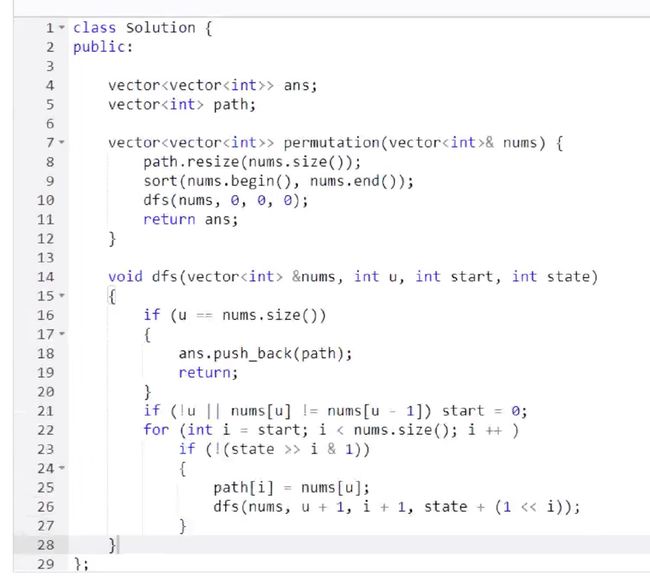
C++ 代码:
时间复杂度分析:搜索树中最后一层共 个节点,前面所有层加一块的节点数量相比于最后一层节点数是无穷小量,可以忽略。且最后一层节点记录方案的计算量是 ,所以总时间复杂度是 。
Python 代码:
# 38、数字排列
# 输入一组数字(可能包含重复数字),输出其所有的排列方式。
#
# 样例
# 输入:[1,2,3]
#
# 输出:
# [
# [1,2,3],
# [1,3,2],
# [2,1,3],
# [2,3,1],
# [3,1,2],
# [3,2,1]
# ]
# 参考资料:https://www.acwing.com/solution/AcWing/content/776/
class Solution:
def permutation(self, nums):
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:rtype: List[List[int]]
"""
l = len(nums)
res = []
if l == 0:
return res
# 因为含有重复数组,所以先排序
nums.sort()
marked = [False for _ in range(l)]
path = [0 for _ in range(l)]
self.__dfs(nums, 0, 0, path, marked, res)
return res
def __dfs(self, nums, index, start, path, marked, res):
if index == len(nums):
res.append(path[:])
return
for i in range(start, len(nums)):
if not marked[i]:
marked[i] = True
# 这一句不好理解
path[i] = nums[index]
if index + 1 < len(nums) and nums[index] != nums[index + 1]:
self.__dfs(nums, index + 1, 0, path, marked, res)
else:
self.__dfs(nums, index + 1, i + 1, path, marked, res)
marked[i] = False
if __name__ == '__main__':
nums = [1, 1, 2]
solution = Solution()
result = solution.permutation(nums)
print(result)
注意:不要忘记递归前和回溯时,对状态进行更新。
(本节完)