在写控制器过程中看到了如下注解:
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface SystemLogger {
String module() default "";
String methods() default "";
String source() default "";
}
以前在SpringBoot的小项目中,Controller与Service并没有完全分离,界限不清晰,因此这个项目帮助我又一次深入理解了AOP。
一、AOP的使用(记录操作日志的例子)
1、自定义注解
@Target({ElementType.METHOD})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Inherited
public @interface OperLog {
//操作类型
String operType() default "";
//操作人
String user() default "";
//操作人下标
int userIndex() default -1;
}
2、拦截器 (切面类)
@Aspect
@Component
public class OperLogInterceptor {
触发条件为:com.opr包下面所有类且注解为OperLog的
@Around("within(com.opr..*) @annotation(operLog)")
public Object doAroundMethod(ProceedingJoinPoint pjd,OperLog operLog) throws Throwable {
long startTime=System.currentTimeMillis();//开始时间
Object[] params = pjd.getArgs();//获取请求参数
System.out.println("监听到传入参数为:");
for(Object param:params) {
System.out.println(param);
}
//###################上面代码为方法执行前#####################
Object result = pjd.proceed();//执行方法,获取返回参数
//###################下面代码为方法执行后#####################
System.out.println("返回参数为:" + result);
String user = operLog.userIndex()==-1?operLog.user():(String)params[operLog.userIndex()];//操作人
String operType = operLog.operType();//操作类型
System.out.println("操作人: " + user +" 操作类型: " + operType);
long endTime=System.currentTimeMillis();//结束时间
float excTime=(float)(endTime-startTime)/1000;
System.out.println("执行时间:"+excTime+"s");
System.out.println("#######################分隔符##########################");
return result;
}
}
3、Service
@Service("userService")
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService {
//设置默认值,模拟登录
private final String userName = "admin";
private final String password = "123456";
@Override
@OperLog(operType="用户登录",userIndex = 0 )//0为下标,代表传入的第一个参数,这里取userName为示例。实际场景可以在session中取操作人!
public boolean userLogin(String userName,String password) {
boolean flag = false;
if(this.userName.equals(userName) && this.password.equals(password)) {
flag = true;
}
return flag;
}
}
4、控制器
@Controller
@RequestMapping("user")
public class UserController {
@Autowired UserService userService;
/***
* 首页
* @param request
* @param response
* @return ModelAndView
*/
@RequestMapping("index")
public ModelAndView index(HttpServletRequest request,HttpServletResponse response) {
return new ModelAndView("index");
}
/***
* 登录
* @param request
* @param response
* @return ModelAndView
*/
@RequestMapping("userLogin")
public ModelAndView userLogin(HttpServletRequest request,HttpServletResponse response,
String userName,String password) {
ModelAndView mv = new ModelAndView();
try {
boolean result = userService.userLogin(userName,password);
if(result) {
mv.setViewName("success");
}else {
mv.setViewName("error");
}
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO: handle exception
e.printStackTrace();
}
return mv;
}
}
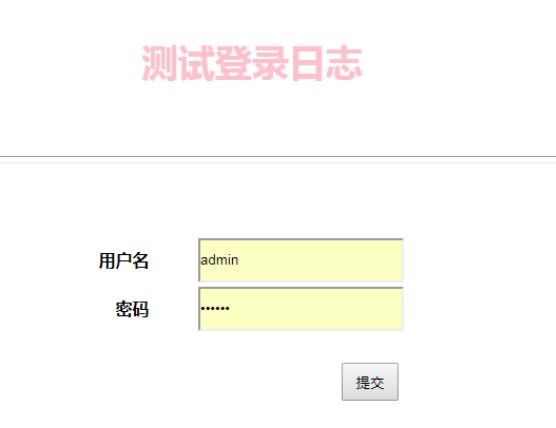
5、运行效果
登陆界面:
前端页面:
后台显示:
使用AOP实现用户登陆验证
@Aspect
@Component
@Slf4j
public class SellerAuthorizeAspect {
@Autowired
private StringRedisTemplate redisTemplate;
//定义一个切入点
@Pointcut("execution(public * com.imooc.controller.Seller*.*(..))" +
"&& !execution(public * com.imooc.controller.SellerUserController.*(..))")
public void verify() {}
@Before("verify()")
public void doVerify() {
ServletRequestAttributes attributes = (ServletRequestAttributes) RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes();
HttpServletRequest request = attributes.getRequest();
//查询cookie
Cookie cookie = CookieUtil.get(request, CookieConstant.TOKEN);
if (cookie == null) {
log.warn("【登录校验】Cookie中查不到token");
throw new SellerAuthorizeException();
}
//去redis里查询
String tokenValue = redisTemplate.opsForValue().get(String.format(RedisConstant.TOKEN_PREFIX, cookie.getValue()));
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(tokenValue)) {
log.warn("【登录校验】Redis中查不到token");
throw new SellerAuthorizeException();
}
}
}
CookieUtil是自己写的获取HttpServletRequest的工具类
ReidsTemplate 与 StringRedisTemplate 的区别:
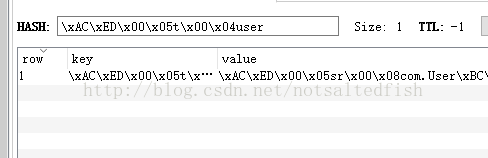
RedisTemplate使用的序列类在在操作数据的时候,比如说存入数据会将数据先序列化成字节数组存入redis数据库:
当Redis当中的数据值是以可读的形式显示出来的时候,只能使用StringRedisTemplate才能获取到里面的数据。
当redis数据库里面存的本来就是字符串数据或者要存取的数据就是字符串类型的时候,那么你就使用StringRedisTemplate即可。
但是如果你的数据是复杂的对象类型,而取出的时候又不想做任何的数据转换,直接从Redis里面取出一个对象,那么使用RedisTemplate是更好的选择。
Q:实体类为什么要序列化:
序列化的实体是对象,结果也是对象。
A:进程间的对象传送:无论是何种类型的数据,都会以二进制序列的形式在网络上传送。发送方需要把这个对象转换为字节序列,才能在网络上传送;接收方则需要把字节序列再恢复为对象。
redis的基本操作:
redisTemplate.opsForValue();//操作字符串String
redisTemplate.opsForHash();//操作hash
redisTemplate.opsForList();//操作list
redisTemplate.opsForSet();//操作set
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set(key,value));
redisTemplate.opsForValue().get(key));
RedisTemplate.opsForSet().isMember("red_123", "1")//根据key查看集合中是否存在指定数据