1 Spring Boot 简介
简化 Spring 应用开发的一个框架;
整个 Spring 技术栈的一个大整合;
J2EE 开发的一站式解决方案;
2 微服务
微服务:架构风格(服务微化)
一个应用应该是一组小型服务,之间可以通过HTTP的方式进行互通;
之前:单体应用:ALL IN ONE
微服务:每一个功能元素最终都是一个可独立替换和独立升级的软件单元;
详细参照微服务文档
3 环境准备
- 环境约束
jdk1.8:Spring Boot 推荐jdk1.7及以上;java version "1.8.0_112"
maven3.6:maven 3.3以上版本;Apache Maven 3.3.9
IntelliJ IDEA2019:
SpringBoot 2.2.1.RELEASE;
注:在
spring-boot-dependencies-2.2.1.RELEASE.pom中 可以看到 Tomcat 版本为:9.0.27(L222)
(一)MAVEN设置;
给 maven 的 settings.xml 配置文件的
jdk-1.8
true
1.8
1.8
1.8
1.8
4 Spring Boot: HelloWorld实现
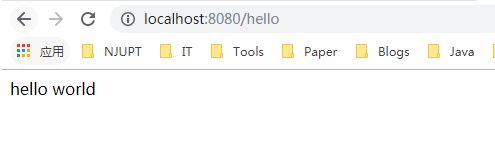
实现的功能:浏览器发送hello请求,服务器接受请求并处理,响应Hello World字符串;
(一)项目搭建
- 方式一:
- 创建一个maven工程;(jar)
- 导入spring boot相关的依赖(maven.xml)
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-parent
1.5.9.RELEASE
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-web
- 方式二:File -> New Project -> Spring initializr (选择jdk版本) -> next -> 填写信息(注意修改最后的 package,同时 Artifact 不能有大写字母 ),然后默认 maven 会自动导入相关的依赖。
(二)在主程序中启动Spring Boot应用
package com.gjxaiou;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
/**
* @SpringBootApplication 来标注一个主程序类,说明这是一个Spring Boot应用
*/
@SpringBootApplication
public class HelloWorldMainApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Spring应用启动起来
SpringApplication.run(HelloWorldMainApplication.class,args);
}
}(三)编写相关的 Controller
package com.gjxaiou.controller;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
@Controller
public class HelloController {
@ResponseBody
@RequestMapping("/hello")
public String hello(){
return "hello world";
}
}(四)运行主程序测试
只要直接执行上面的主程序,就可以直接在浏览器中访问:localhost:8080/hello,结果图如下:
(五)简化部署(直接将项目打成 jar,然后在命令行运行即可)
打成 Jar 包
不在需要将项目导出为 war 包然后部署到服务器中,只需要在 maven 中导入下面插件,然后使用右边的 maven Project -> lifecycle -> pageage(右击:run 项目名[package]) 命令就可以直接将项目打成可执行的 jar 包,默认的 jar 包位置在 项目的 target 文件夹下面;可以直接进入该文件夹,然后在文件路径框输入 cmd;
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-maven-plugin
运行 Jar 包:将这个应用打成 jar 包之后,直接使用 java -jar 的命令进行执行;java -jar Jar包位置和名称
5 Hello World 原理探究
(一)POM文件
1、父项目
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-dependencies
2.2.1.RELEASE
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-dependencies
2.2.1.RELEASE
../spring-boot-dependencies
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-configuration-processor
true
3.测试
测试类的值是否导入:
package com.gjxaiou.springboot;
/**
* SpringBoot单元测试;
* 可以在测试期间很方便的类似编码一样进行自动注入等容器的功能
*/
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest
public class SpringBoot02ConfigApplicationTests {
@Autowired
Person person;
@Autowired
ApplicationContext ioc;
@Test
public void testHelloService(){
boolean b = ioc.containsBean("helloService02");
System.out.println(b);
}
@Test
public void contextLoads() {
System.out.println(person);
}
}10 配置文件说明
(一)@Value 获取值和 @ConfigurationProperties 获取值比较
| @ConfigurationProperties(YAML 形式) | @Value(配置文件形式) | |
|---|---|---|
| 功能 | 批量注入配置文件中的属性 | 需要一个个指定 |
| 松散绑定(松散语法) | 支持(见下面说明) | 不支持 |
| SpEL(例如 # {表达式}) | 不支持 | 支持 |
| JSR303数据校验 | 支持 | 不支持 |
| 复杂类型封装(例如 map 类型) | 支持 | 不支持 |
配置文件 yml 还是 properties 他们都能获取到值;
如果只是在某个业务逻辑中需要获取一下配置文件中的某项值,使用
@Value;如果专门编写了一个 JavaBean 来和配置文件进行映射,我们就直接使用
@ConfigurationProperties;
上面名词解释
- 松散绑定:就是代码中的变量名和 yml 文件中的变量名的对应绑定
以 person.firstName 变量为例,对应的 yml 文件中可以为:person.firstName person.first-name person.first_name PERSON_FIRSTNAME都可以,其中 - 和 _ 都表示大写。
- 数据校验:类上面需要增加:
@Validated注解,同时需要校验的变量名上面加上对应想校验的格式;示例如下:
@Component
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "person")
@Validated
public class Person {
// 表示要校验 lastName 的值是否为邮箱格式
@Email
private String lastName;(二)@PropertySource & @ImportResource & @Bean
@PropertySource:作用是加载指定的配置文件;
因为上面的
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "person")默认从全局配置文件中获取值;如果这两个命令都写并且默认的配置文件和person.properties中都有属性值,则加载全局配置文件中的值;
@PropertySource(value = {"classpath:person.properties"})
@Component
public class Person {
private String lastName;
private Integer age;
private Boolean boss;
对应的 person.properties 文件
person.last-name=李四
person.age=12
person.birth=2017/12/15
person.boss=false
person.maps.k1=v1
person.maps.k2=14
person.lists=a,b,c
person.dog.name=dog
person.dog.age=15@ImportResource:导入 Spring 的配置文件,让配置文件里面的内容生效;
首先可以创建一个 service 类:HelloService.java;
然后创建一个 spring的 xml 配置文件 bean.xml,配置如下:
Spring Boot 里面没有 Spring 的配置文件,而我们自己编写的配置文件(bean.xml),也不能自动识别,因此想让 Spring 的配置文件生效,加载进来;就使用 @ImportResource标注在一个配置类上(这里的注解是标注在主配置类:SpringBootConfigApplication.java 上)
// 导入Spring的配置文件让其生效
@ImportResource(locations = {"classpath:beans.xml"})然后在测试类中:可以验证该类是否在 IOC 容器中
package com.gjxaiou.springboot;
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest
public class SpringBoot02ConfigApplicationTests {
@Autowired
ApplicationContext ioc;
@Test
public void testHelloService(){
boolean b = ioc.containsBean("helloService");
System.out.println(b);
}
}结果为 true.
- @Bean
@Bean 是 SpringBoot 推荐的给容器中添加组件的方式:推荐使用全注解的方式,就是使用配置类代替 xml 配置文件中的
首先要写个配置类,同时加上 @Configuration------>类似于上面的 Spring 配置文件
使用 @Bean 给容器中添加组件
/**
* @Configuration:指明当前类是一个配置类;就是来替代之前的 Spring 配置文件
* 之前在配置文件中用 (三)配置文件占位符
1、随机数
${random.value}、${random.int}、${random.long}
${random.int(10)}、${random.int[1024,65536]}2、占位符获取之前配置的值,如果没有可以是用: 指定默认值
这里的属性值是配置在默认的 application.properties 中,配置在其他之后就是需要在下面的 Java 代码中添加以下位置即可;
person.last-name=张三${random.uuid}
person.age=${random.int}
person.birth=2017/12/15
person.boss=false
person.maps.k1=v1
person.maps.k2=14
person.lists=a,b,c
# 因为这里没有 person.hello ,因此使用 ${person.hello},最终结果显示就是:${person.hello},这里的 : 表示如果没有值,就赋值 hello1 作为默认值
person.dog.name=${person.hello:hello1}_dog
#person.dog.name=${person.last-name}
person.dog.age=15对应的Person 类配置和上面代码一样:
然后测试类为:
package com.gjxaiou.springboot;
import com.gjxaiou.springboot.bean.Person;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringRunner;
/**
* SpringBoot单元测试;
* 可以在测试期间很方便的类似编码一样进行自动注入等容器的功能
*/
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest
public class SpringBoot02ConfigApplicationTests {
@Autowired
Person person;
@Test
public void contextLoads() {
System.out.println(person);
}
}
(四)Profile,是 spring 用于多环境支持的
就是测试、开发等等的配置文件是不相同的,方便进行切换
- 方式一:多 Profile 文件
我们在主配置文件编写的时候,文件名可以是 application-{profile}.properties/yml
例如配置文件为:application-dev.properties/application-product.properties/application.properties
默认使用application.properties的配置;如果想使用使其配置文件,需要在 application.properties 中输入:spring.profiles.active=dev 就激活使用 application-dev.properties 配置文件;
- 方式二:yml 支持多文档块方式
下面都是在 application.yml 中配置,使用 --- 分割成不同的文档块;最上面是默认的,如果想激活其他的,只要在最上面的 里面添加 :active即可
server:
port: 8081
spring:
profiles:
active: prod
---
server:
port: 8083
spring:
profiles: dev
---
server:
port: 8084
spring:
profiles: prod #指定属于哪个环境附:激活指定 profile 方式
(针对方式一)在配置文件中指定
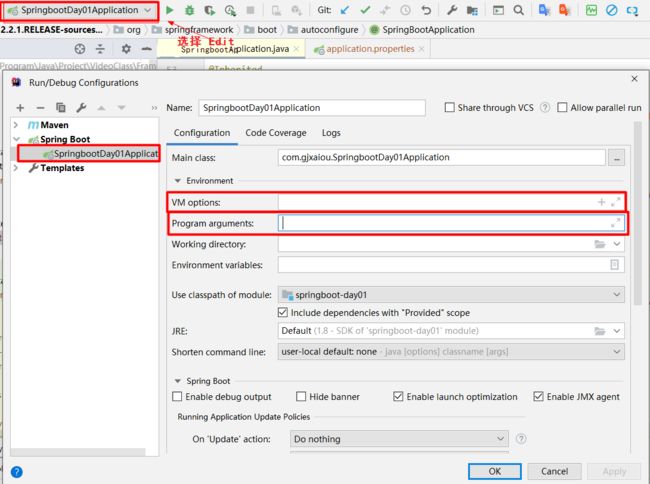
spring.profiles.active=dev(针对 properties 文件)命令行(针对方式一、二):IDEA 中 Run/Debug Configurations 中添加的 SpringBoot 右边对应的:
program arguments中输入下面语句--spring.profiles.active=dev,如果打包之后运行可以使用:java -jar spring-boot-02-config-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar --spring.profiles.active=dev指定
即可以直接在测试的时候,配置传入命令行参数;
- 虚拟机参数(针对方式一、二):IDEA上面配置中的:
VM options中配置:-Dspring.profiles.active=dev
11 内部配置文件加载位置
SpringBoot 启动会按照顺序扫描以下位置的 application.properties 或者 application.yml 文件作为 SpringBoot的默认配置文件:file 表示当前项目的文件夹,classpath:表示类路径,就是 resources 目录下
–file:./config/
–file:./
–classpath:/config/
–classpath:/以上优先级由高到底,高优先级的配置会覆盖低优先级的配置,同时 SpringBoot 会从这四个位置全部加载主配置文件,互补配置;
我们还可以通过
spring.config.location属性来改变默认的配置文件位置项目打包好以后,我们可以使用命令行参数的形式,启动项目的时候来指定配置文件的新位置;指定配置文件和默认加载的这些配置文件共同起作用形成互补配置;
命令为:java -jar spring-boot-02-config-02-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar --spring.config.location=D:/application.properties
12 外部配置加载顺序
SpringBoot也可以从以下位置加载配置; 优先级从高到低;高优先级的配置覆盖低优先级的配置,所有的配置会形成互补配置
命令行参数
因为项目在打包的时候,只会将 main 包下面的 java 和 resources 中的内容进行打包,因此像上面直接在项目根目录下面配置的配置文件是不会被打包的;
所有的配置都可以在命令行上进行指定(也是互补方式),只要多个配置用空格分开,格式均为
--配置项=值,一般适用于小部分的值。示例:
java -jar spring-boot-02-config-02-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar --server.port=8087 --server.context-path=/abc来自 java:comp/env 的 JNDI 属性
Java 系统属性(System.getProperties())
操作系统环境变量
RandomValuePropertySource 配置的 random.* 属性值
由jar包外向jar包内进行寻找;同时优先加载带 profile,然后加载不带 profile
jar包外部设置的的application-{profile}.properties或application.yml(带spring.profile)配置文件(相当于已经将项目打包之后,然后新建一个配置文件放在 jar 包同文件夹下面)
jar包内部的application-{profile}.properties或application.yml(带spring.profile)配置文件
jar包外部的application.properties或application.yml(不带spring.profile)配置文件
jar包内部的application.properties或application.yml(不带spring.profile)配置文件
@Configuration注解类上的@PropertySource通过
SpringApplication.setDefaultProperties指定的默认属性
所有支持的配置加载来源参考官方文档
13 自动配置原理
配置文件到底能写什么?怎么写?自动配置原理;
配置文件能配置的属性参照
(一)自动配置原理
SpringBoot 启动的时候加载主配置类,然后加载主配置类上面的
@SpringBootApplication,该注解(点进去),最主要作用就是开启了自动配置功能 @EnableAutoConfiguration;@EnableAutoConfiguration 作用:(点进去)
利用 @Import 中的
EnableAutoConfigurationImportSelector选择器给容器中导入一些组件;点进去然后查看其父类
AutoConfigurationImportSelector中的selectImports()方法的内容,就知道导入哪些内容了;上面那个
selectImports()方法最终返回
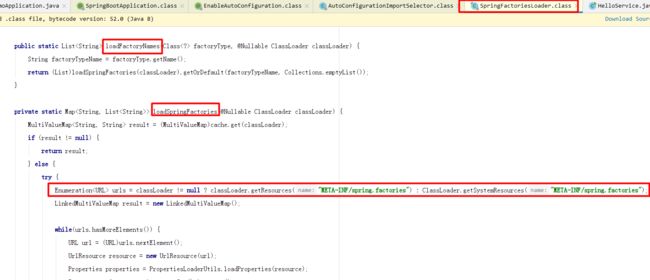
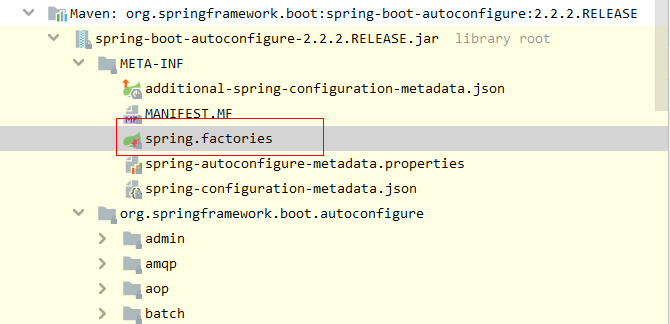
List configurations = getCandidateConfigurations(annotationMetadata, attributes); 获取候选的配置,getCandidateConfiguration 类中最重要的是:SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames() 方法(代码见下),
protected List getCandidateConfigurations(AnnotationMetadata metadata, AnnotationAttributes attributes) {
List configurations = SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(this.getSpringFactoriesLoaderFactoryClass(), this.getBeanClassLoader());
Assert.notEmpty(configurations, "No auto configuration classes found in META-INF/spring.factories. If you are using a custom packaging, make sure that file is correct.");
return configurations;
} 该方法作用(点进去)是从类路径下面得到资源,得到的资源是:扫描所有 jar 包类路径下 META-INF/spring.factories 文件(这部分是 loadFactoryNames() 中调用的 loadSpringFactories() 方法里面)然后扫描文件的 URL 把扫描到的这些文件的内容包装成 properties 对象,从properties中获取到 EnableAutoConfiguration.class 类(类名)对应的值,然后把他们添加在容器中。
下面为 LoadFactoryNames() 方法的具体代码 public static List loadFactoryNames(Class factoryType, @Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {
String factoryTypeName = factoryType.getName();
return (List)loadSpringFactories(classLoader).getOrDefault(factoryTypeName, Collections.emptyList());
}
private static Map> loadSpringFactories(@Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {
MultiValueMap result = (MultiValueMap)cache.get(classLoader);
if (result != null) {
return result;
} else {
try {
// 扫描所有 jar 包类路径下面的 META-INF/spring.factories 文件
Enumeration urls = classLoader != null ? classLoader.getResources("META-INF/spring.factories") : ClassLoader.getSystemResources("META-INF/spring.factories");
LinkedMultiValueMap result = new LinkedMultiValueMap();
// 然后扫描文件的 URL 把扫描到的这些文件的内容包装成 properties 对象
while(urls.hasMoreElements()) {
URL url = (URL)urls.nextElement();
UrlResource resource = new UrlResource(url);
Properties properties = PropertiesLoaderUtils.loadProperties(resource);
Iterator var6 = properties.entrySet().iterator();
while(var6.hasNext()) {
Entry entry = (Entry)var6.next();
String factoryTypeName = ((String)entry.getKey()).trim();
String[] var9 = StringUtils.commaDelimitedListToStringArray((String)entry.getValue());
int var10 = var9.length;
for(int var11 = 0; var11 < var10; ++var11) {
String factoryImplementationName = var9[var11];
result.add(factoryTypeName, factoryImplementationName.trim());
}
}
}
cache.put(classLoader, result);
return result;
} catch (IOException var13) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unable to load factories from location [META-INF/spring.factories]", var13);
}
}
} 因此其作用是:将类路径下 META-INF/spring.factories 里面配置的所有 EnableAutoConfiguration的值添加到容器中;容器中会有以下类(在下面文件中):
# Auto Configure
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration=\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.admin.SpringApplicationAdminJmxAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.aop.AopAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.amqp.RabbitAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.batch.BatchAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.CacheAutoConfiguration,\
...
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.websocket.WebSocketAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.websocket.WebSocketMessagingAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.webservices.WebServicesAutoConfiguration每一个这样的 xxxAutoConfiguration类都是容器中的一个组件,都加入到容器中;用他们来做自动配置;
- 每一个自动配置类进行自动配置功能
以HttpEncodingAutoConfiguration(Http编码自动配置)为例解释自动配置原理;下面就是该类的具体内容
// 表示这是一个配置类,和以前编写的配置文件一样,也可以给容器中添加组件
@Configuration
// 启动指定类(括号中的类,点击这个类就发现该类上面标注了 @configurationProperties 注解,类的内容见下一个代码块)的 ConfigurationProperties 功能;将配置文件中对应的值和 HttpEncodingProperties 绑定起来;并把 HttpEncodingProperties 加入到 ioc 容器中
@EnableConfigurationProperties(HttpEncodingProperties.class)
// 底层是:Spring 的 @Conditional 注解,作用是:根据不同的条件,如果满足指定的条件,整个配置类里面的配置才会生效; 这里作用是:判断当前应用是否是web应用,如果是,当前配置类生效
@ConditionalOnWebApplication
// 判断当前项目有没有这个类(CharacterEncodingFilter);该类是 SpringMVC 中进行乱码解决的过滤器;
@ConditionalOnClass(CharacterEncodingFilter.class)
// 判断配置文件中是否存在某个配置,这里就是:spring.http.encoding.enabled;后面的 matchIfMissing 表示如果不存在,判断也是成立的,即即使我们配置文件中不配置pring.http.encoding.enabled=true,也是默认生效的;
@ConditionalOnProperty(prefix = "spring.http.encoding", value = "enabled", matchIfMissing = true)
public class HttpEncodingAutoConfiguration {
// 它已经和 SpringBoot 的配置文件映射了,它是获取配置文件中的值的
private final HttpEncodingProperties properties;
// 只有一个有参构造器的情况下,参数的值就会从容器中拿,使用上面的 @EnableConfigurationProperties 注解将括号中的类加入 IOC 容器中
public HttpEncodingAutoConfiguration(HttpEncodingProperties properties) {
this.properties = properties;
}
@Bean // @Bean 表示给容器中添加一个组件(这里对应的组件就是 CharacterEncodingFilter),这个组件的某些值需要从 properties 中获取
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(CharacterEncodingFilter.class) //判断容器没有这个组件?
public CharacterEncodingFilter characterEncodingFilter() {
CharacterEncodingFilter filter = new OrderedCharacterEncodingFilter();
filter.setEncoding(this.properties.getCharset().name());
filter.setForceRequestEncoding(this.properties.shouldForce(Type.REQUEST));
filter.setForceResponseEncoding(this.properties.shouldForce(Type.RESPONSE));
return filter;
}上面整个配置类作用就是:根据当前不同的条件判断,决定这个配置类是否生效
一但这个配置类生效;这个配置类就会给容器中添加各种组件;这些组件的属性是从对应的 properties 类中获取的,这些类里面的每一个属性又是和配置文件绑定的;
- 所有在配置文件中能配置的属性都是在 xxxxProperties 类中封装着;例如配置文件(spring.http.encoding)能配置什么就可以参照某个功能对应的这个属性类(HttpEncodingProperties)
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.http.encoding") //从配置文件中获取指定的值和bean的属性进行绑定
public class HttpEncodingProperties {
public static final Charset DEFAULT_CHARSET = Charset.forName("UTF-8");- 精髓:
- SpringBoot 启动会加载大量的自动配置类;
- 看我们需要的功能有没有 SpringBoot 默认写好的自动配置类;
- 如果有,我们再来看这个自动配置类中到底配置了哪些组件;(只要我们要用的组件有,我们就不需要再来配置了)
- 给容器中自动配置类添加组件的时候,会从 properties 类中获取某些属性。我们就可以在配置文件中指定这些属性的值;
- xxxxAutoConfigurartion:自动配置类;作用是给容器中添加组件,同时也会有对应的 xxxxProperties 封装配置文件中相关属性;
示例解释
使用 Ctrl + n 查找:*AutoConfiguration,这里以 CacheAutoconfiguration 为例,有相应的属性自动配置类:`CacheAutoconfiguration.java对应就有相应的属性值的获取:见上面的 @EnableConfigurationProperties 中的括号中类,即 CacheProperties.class,点击之后就可以看出来可以配置哪些属性,属性前缀就是上面的注解@ConfigurationProperties中的内容,后面更上该类的变量名:例如可以在 properties 文件中配置:spring.cache.type
(二)细节
1、@Conditional 派生注解
作用:必须是 @Conditional 指定的条件成立,才给容器中添加组件,配置配里面的所有内容才生效;
还是以上面 HttpEncodingAutoConfiguration 代码为例
@Configuration
@EnableConfigurationProperties(HttpEncodingProperties.class)
// 这里就是三个 Condition 注解判断,只有他们都成立了配置才生效;
// @ConditionOnXX 本质上(点击)就是使用 Spring 的 @condition 注解,@Condition(指定的条件判断类,点击该类,发现该类有一个 match 方法,通过一系列的判断,最终返回 true/false)
@ConditionalOnWebApplication
@ConditionalOnClass(CharacterEncodingFilter.class)
@ConditionalOnProperty(prefix = "spring.http.encoding", value = "enabled", matchIfMissing = true)
public class HttpEncodingAutoConfiguration {
private final HttpEncodingProperties properties;
public HttpEncodingAutoConfiguration(HttpEncodingProperties properties) {
this.properties = properties;
}
// 同样这里注入的时候,进行了Condition的判断
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(CharacterEncodingFilter.class) //判断容器没有这个组件?
public CharacterEncodingFilter characterEncodingFilter() {
CharacterEncodingFilter filter = new OrderedCharacterEncodingFilter();
filter.setEncoding(this.properties.getCharset().name());
filter.setForceRequestEncoding(this.properties.shouldForce(Type.REQUEST));
filter.setForceResponseEncoding(this.properties.shouldForce(Type.RESPONSE));
return filter;
}spring boot 将 @condition 注解扩展了
| @Conditional扩展注解 | 作用(判断是否满足当前指定条件) |
|---|---|
| @ConditionalOnJava | 系统的java版本是否符合要求 |
| @ConditionalOnBean | 容器中存在指定Bean; |
| @ConditionalOnMissingBean | 容器中不存在指定Bean; |
| @ConditionalOnExpression | 满足SpEL表达式指定 |
| @ConditionalOnClass | 系统中有指定的类 |
| @ConditionalOnMissingClass | 系统中没有指定的类 |
| @ConditionalOnSingleCandidate | 容器中只有一个指定的Bean,或者这个Bean是首选Bean |
| @ConditionalOnProperty | 系统中指定的属性是否有指定的值 |
| @ConditionalOnResource | 类路径下是否存在指定资源文件 |
| @ConditionalOnWebApplication | 当前是web环境 |
| @ConditionalOnNotWebApplication | 当前不是web环境 |
| @ConditionalOnJndi | JNDI存在指定项 |
自动配置类必须在一定的条件下才能生效;条件就是上面的一系列 @condition 判断
我们怎么知道哪些自动配置类生效;所有的自动配置类都在 jar 包:spring-boot-autoconfigure 下的 spring.factories,点开每一个配置类都可以看出该控制类有没有生效(因为每个控制类都需要一定的condition,如果里面有冒红就是不生效),但是挨个点击判断太过于麻烦,
我们可以在配置文件 application.properties 通过启用 debug=true 属性,开启 spring boot 的 debug 模式,来让控制台打印自动配置报告,这样我们就可以很方便的知道哪些自动配置类生效,下面是输出示例:
Positive matches:(自动配置类启用的)
-----------------
DispatcherServletAutoConfiguration matched:
- @ConditionalOnClass found required class 'org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet'; @ConditionalOnMissingClass did not find unwanted class (OnClassCondition)
- @ConditionalOnWebApplication (required) found StandardServletEnvironment (OnWebApplicationCondition)
Negative matches:(没有启动,没有匹配成功的自动配置类)
-----------------
ActiveMQAutoConfiguration:
Did not match:
- @ConditionalOnClass did not find required classes 'javax.jms.ConnectionFactory', 'org.apache.activemq.ActiveMQConnectionFactory' (OnClassCondition)
AopAutoConfiguration:
Did not match:
- @ConditionalOnClass did not find required classes 'org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect', 'org.aspectj.lang.reflect.Advice' (OnClassCondition)
..................................14 日志框架
(一)常见日志框架
JUL、JCL、Jboss-logging、logback、log4j、log4j2、slf4j....
(二)日志分类
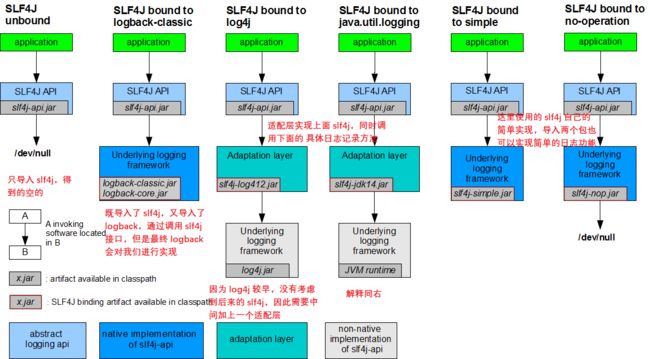
- 日志门面(日志的抽象层)
JCL(Jakarta Commons Logging)- SLF4j(Simple Logging Facade for Java)
jboss-logging
- 日志的实现
- Log4j
- JUL(java.util.logging)
- Log4j2
- Logback
一般选一个门面(抽象层)同时选一个实现;
SpringBoot:底层是 Spring 框架,Spring 框架默认是用 JCL;SpringBoot 选用 SLF4j 和 logback;
15 SLF4j使用
(一)如何在系统中使用SLF4j
开发的时候,日志记录方法的调用,不应该来直接调用日志的实现类(logback),而是调用日志抽象层(slf4j)里面的方法;
- 首先给系统里面导入 slf4j 的 jar 和 logback 的实现 jar
- 然后具体需要日志的类中实现即可;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
public class HelloWorld {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(HelloWorld.class);
logger.info("Hello World");
}
}日志框架搭配方法
每一个日志的实现框架(如以前应用的 log4j)都有自己的配置文件。使用 slf4j 以后,配置文件还是做成日志实现框架自己本身的配置文件;相当于用谁实现就写谁的配置文件,slf4j 只是提供一个接口层;
(二)统一日志记录
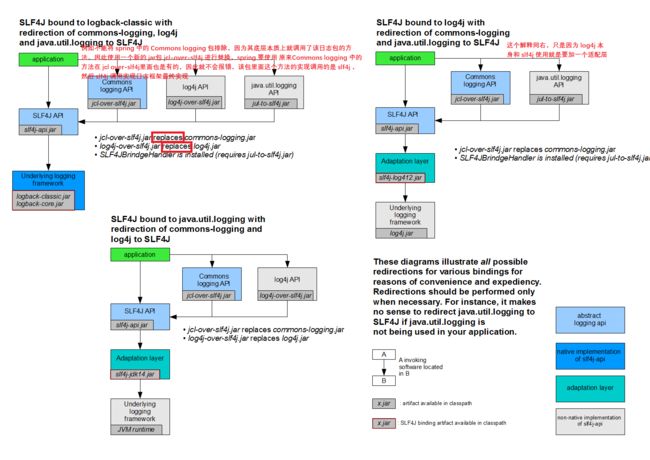
如果系统实现(slf4j + logback): 但是同时该系统依赖 Spring(commons-logging)、Hibernate(jboss-logging)、MyBatis、xxxx等框架,但是框架本身底层就有日志记录还各不相同;
目标:统一日志记录,即别的框架和我一起统一使用 slf4j 进行输出;
如何让系统中所有的日志都统一到slf4j;
将系统中其他日志框架先排除出去;
用中间包来替换原有的日志框架;
导入slf4j 其他的具体实现;
16 SpringBoot日志关系
首先导入 Maven 依赖:
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter
SpringBoot 使用它来做日志功能;下面这个依赖中封装了所有的日志启动场景
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-logging
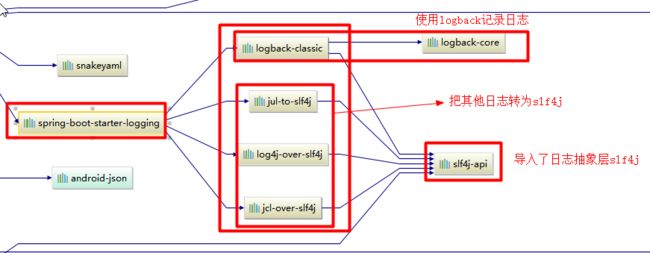
spring boot 底层依赖关系(在项目(这里是 web 项目)的 pom.xml 配置文件上生成)
- 总结:
- SpringBoot 底层也是使用 slf4j + logback 的方式进行日志记录
- SpringBoot 也把其他的日志都替换成了slf4j(因此导入了 jul-to-slf4j 等 Jar包);
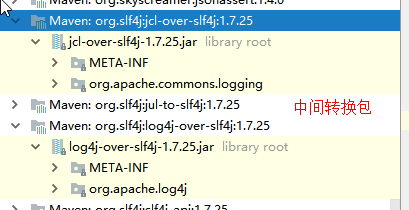
以中间替换包 jcl-over-slf4j.jar 为例:
首先点击 jar 包发现里面的包名仍然还是:org.apache.commons.logging,同时里面的类也是 LogFactory,下面就是该类的部分截图,可以看出该类里面的实现是调用了 SLF4JLogFactory()
@SuppressWarnings("rawtypes")
public abstract class LogFactory {
static String UNSUPPORTED_OPERATION_IN_JCL_OVER_SLF4J = "http://www.slf4j.org/codes.html#unsupported_operation_in_jcl_over_slf4j";
static LogFactory logFactory = new SLF4JLogFactory();- 因此如果我们要引入其他框架,一定要把这个框架的默认日志依赖移除掉
例如Spring框架用的是commons-logging;可以在上面的图中点击:spring-boot-starter-logging,就可以跳到 pom.xml 文件中,可以看到下面的配置,确实排除了 commons-logging
org.springframework
spring-core
commons-logging
commons-logging
SpringBoot能自动适配所有的日志,而且底层使用slf4j+logback的方式记录日志,引入其他框架的时候,只需要把这个框架依赖的日志框架排除掉即可;
17 日志使用
(一)默认配置
SpringBoot 默认帮我们配置好了日志,因此空项目直接运行下面窗口中会有一系列的日志输出;
同时如果自己想配置日志输入示例如下:这里是在 测试类中配置
//日志记录器:logger
Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(getClass());
@Test
public void contextLoads() {
//日志的级别;
//由低到高 trace日志的输出格式含义:
%d 表示日期时间,
%thread 表示线程名,
%-5level: 级别从左显示5个字符宽度
%logger{50} 表示logger名字最长50个字符,否则按照句点分割
%msg: 日志消息
%n 是换行符
示例: %d{yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.SSS} [%thread] %-5level %logger{50} - %msg%nSpringBoot修改日志的默认配置(在 application.properties 配置文件中)
***日志的输出级别可以控制到包/类***
logging.level.com.gjxaiou=trace
***logging.path=***
***当 logging.path 没有值的时候,即不指定路径只是配置 logging.file=日志文件名,就会在当前项目下生成该日志文件名的日志;当然可以指定完整的日志文件输出路径,就会在指定路径下面输出日志文件;***
***logging.file=G:/springboot.log***
***只指定 path 不指定 file 的情况下:使用下面配置就是在当前磁盘的根路径下创建spring文件夹和里面的log文件夹;使用 spring.log 作为默认文件***
logging.path=/spring/log
***在控制台输出的日志的格式***
logging.pattern.console=%d{yyyy-MM-dd} [%thread] %-5level %logger{50} - %msg%n
***指定文件中日志输出的格式***
logging.pattern.file=%d{yyyy-MM-dd} === [%thread] === %-5level === %logger{50} ==== %msg%n| logging.file | logging.path | Example | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| (none) | (none) | 只在控制台输出 | |
| 指定文件名 | (none) | my.log | 输出日志到my.log文件 |
| (none) | 指定目录 | /var/log | 输出到指定目录的 spring.log 文件中 |
(二)指定配置
给类路径下放上每个日志框架自己的配置文件即可,这样SpringBoot就不使用他默认配置的了,文件名如下:
| Logging System | Customization |
|---|---|
| Logback | logback-spring.xml, logback-spring.groovy, logback.xml or logback.groovy |
| Log4j2 | log4j2-spring.xml or log4j2.xml |
| JDK (Java Util Logging) | logging.properties |
logback.xml:直接就被日志框架识别了,相当于绕过了 springboot;
logback-spring.xml:日志框架就不直接加载日志的配置项(因为日志框架只认识 logback.xml),由SpringBoot解析日志配置,就可以使用SpringBoot的高级Profile功能
可以指定某段配置只在某个环境下生效
如在开发环境输入》》》不在开发环境输出》》》:直接运行就行,这里肯定不是开发环境(在 application.properties 中使用 spring.profiles.active=dev 可以进行指定)
%d{yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.SSS} ----> [%thread] ---> %-5level %logger{50} - %msg%n
%d{yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.SSS} ==== [%thread] ==== %-5level %logger{50} - %msg%n
如果使用logback.xml作为日志配置文件,还要使用profile功能,会有以下错误
no applicable action for [springProfile]18 切换日志框架
可以按照slf4j的日志适配图(见上面),进行相关的切换;
slf4j+log4j的方式;不推荐
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-web
logback-classic
ch.qos.logback
log4j-over-slf4j
org.slf4j
org.slf4j
slf4j-log4j12
切换为log4j2:不推荐
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-web
spring-boot-starter-logging
org.springframework.boot
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-log4j2
19 简介
- 使用 SpringBoot 进行 WEB 开发步骤:
- 创建 SpringBoot 应用,选中我们需要的模块;
- SpringBoot 已经默认将这些场景配置好了,只需要在配置文件中指定少量配置就可以运行起来;
- 自己编写业务代码;
自动配置原理
使用自动配置原理还应该考虑一下这个场景 SpringBoot 帮我们配置了什么?能不能修改?能修改哪些配置?能不能扩展?
- xxxxAutoConfiguration:帮我们给容器中自动配置组件;
- xxxxProperties:配置类来封装配置文件的内容;
20 Spring Boot 对静态资源的映射规则
在 SpringBoot 中关于 SpringMVC 的所有配置都在 WebMvcAutoConfiguration.java (使用 Ctrl + n 全局搜索该文件名即可)中,下面仅仅是静态资源配置的相关代码
public void addResourceHandlers(ResourceHandlerRegistry registry) {
if (!this.resourceProperties.isAddMappings()) {
logger.debug("Default resource handling disabled");
} else {
Integer cachePeriod = this.resourceProperties.getCachePeriod();
if (!registry.hasMappingForPattern("/webjars/**")) {
this.customizeResourceHandlerRegistration(
registry.addResourceHandler(new String[]{"/webjars/**"})
.addResourceLocations(new String[]{"classpath:/META-INF/resources/webjars/"})
.setCachePeriod(cachePeriod));
}
String staticPathPattern = this.mvcProperties.getStaticPathPattern();
//静态资源文件夹映射
if (!registry.hasMappingForPattern(staticPathPattern)) {
this.customizeResourceHandlerRegistration(
registry.addResourceHandler(new String[]{staticPathPattern})
.addResourceLocations(this.resourceProperties.getStaticLocations())
.setCachePeriod(cachePeriod));
}
}
}
//配置欢迎页映射
@Bean
public WelcomePageHandlerMapping welcomePageHandlerMapping(
ResourceProperties resourceProperties) {
return new WelcomePageHandlerMapping(resourceProperties.getWelcomePage(),
this.mvcProperties.getStaticPathPattern());
}
//配置喜欢的图标
@Configuration
@ConditionalOnProperty(
value = {"spring.mvc.favicon.enabled"},
matchIfMissing = true
)
public static class FaviconConfiguration {
private final ResourceProperties resourceProperties;
public FaviconConfiguration(ResourceProperties resourceProperties) {
this.resourceProperties = resourceProperties;
}
@Bean
public SimpleUrlHandlerMapping faviconHandlerMapping() {
SimpleUrlHandlerMapping mapping = new SimpleUrlHandlerMapping();
mapping.setOrder(-2147483647);
mapping.setUrlMap(Collections.singletonMap("**/favicon.ico", this.faviconRequestHandler()));
return mapping;
}
@Bean
public ResourceHttpRequestHandler faviconRequestHandler() {
ResourceHttpRequestHandler requestHandler = new ResourceHttpRequestHandler();
requestHandler.setLocations(this.resourceProperties.getFaviconLocations());
return requestHandler;
}
}上面代码中的设置配置在 resourceProperties.java 中,例如下面的部分文件设置(点击resourcesProperties 文件即可) ,可以设置其所有的属性值,例如: 可以设置和静态资源有关的参数,缓存时间等
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.resources", ignoreUnknownFields = false)
public class ResourceProperties implements ResourceLoaderAware {
private static final String[] SERVLET_RESOURCE_LOCATIONS = { "/" };
private static final String[] CLASSPATH_RESOURCE_LOCATIONS = {
"classpath:/META-INF/resources/", "classpath:/resources/",
"classpath:/static/", "classpath:/public/" };
private static final String[] RESOURCE_LOCATIONS;
static {
RESOURCE_LOCATIONS = new String[CLASSPATH_RESOURCE_LOCATIONS.length
+ SERVLET_RESOURCE_LOCATIONS.length];
System.arraycopy(SERVLET_RESOURCE_LOCATIONS, 0, RESOURCE_LOCATIONS, 0,
SERVLET_RESOURCE_LOCATIONS.length);
System.arraycopy(CLASSPATH_RESOURCE_LOCATIONS, 0, RESOURCE_LOCATIONS,
SERVLET_RESOURCE_LOCATIONS.length, CLASSPATH_RESOURCE_LOCATIONS.length);
}
private String[] staticLocations = RESOURCE_LOCATIONS;
private Integer cachePeriod;
private boolean addMappings = true;
private final Chain chain = new Chain();
private ResourceLoader resourceLoader;
(一)映射规则一(WebJars)
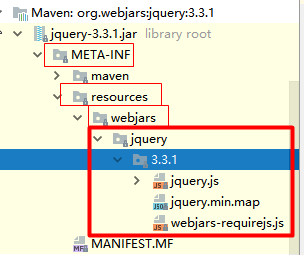
从第一段代码中得出:所有 /webjars/**的请求 ,都去 classpath:/META-INF/resources/webjars/ 找资源;
webjars:以 jar 包的方式引入静态资源,以前是放在 webapp 目录下面即可;
需要使用什么,从官方网站中引入响应的 jar 包即可,这里以 jQuery 为例,需要引入下面的jar包,下图为该jar 包中具体的内容;
在访问的时候只需要写 webjars 下面资源的名称即可
org.webjars
jquery
3.4.1
测试:如果访问:localhost:8080/webjars/jquery/3.3.1/jquery.js 就能访问这里面的 js 了
(二)映射规则二:(项目任意路径)
上述代码块第一个第13行中:mvcProperties 文件中的 staticPathPattern 值为:
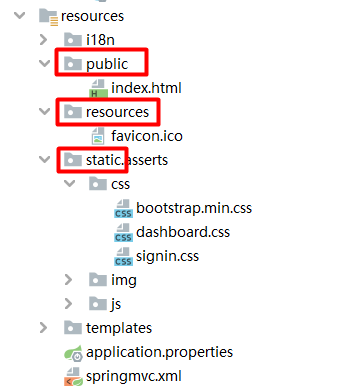
/**(源代码为 WebMvcProperties.java 中对应的代码:private String staticPathPattern = "/**";),这就是第二种映射规则;"/**" 访问当前项目的任何资源,都去(静态资源的文件夹)找映射 即如果该路径没有人进行处理就去下面文件夹中找("/":表示当前项目的根路径)
"classpath:/META-INF/resources/",
"classpath:/resources/",
"classpath:/static/",
"classpath:/public/" 例如访问:localhost:8080/static/asserts/css/signin.css 就是可以访问到资源的;
(三)映射规则三:欢迎页
欢迎页; 静态资源文件夹下的所有index.html页面;被"/**"映射;
localhost:8080/ 找index页面
(四)映射规则四:网页标签的小图标
所有的 **/favicon.ico 都是在静态资源文件下找;
(五)自定义映射规则
当然可以自己在 application.properties 中通过 spring.resource.static-locations=classpath:/hello/设置路径在 /hello/下面
21 模板引擎
因为 springboot 使用内嵌的 tomcat,不支持 jsp 等等,因此可以使用模板引擎。
现有的模板引擎包括:JSP、Velocity、Freemarker、Thymeleaf
SpringBoot 推荐的 Thymeleaf,因为其语法更简单,功能更强大;
(一)引入thymeleaf
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf
3.0.11.RELEASE
3.0.4.RELEASE
3.0.4.RELEASE
2.4.1
(二)Thymeleaf 使用
自动配置规则在 spring-boot-autoconfigure-2.2.1.RELEASE.jar!\org\springframework\boot\autoconfigure\thymeleaf\ThymeleafAutoConfiguration.java中,下面是其对应的 ThymeleafProperties.java 中封装着其默认规则,下面是部分代码
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.thymeleaf")
public class ThymeleafProperties {
private static final Charset DEFAULT_ENCODING = Charset.forName("UTF-8");
private static final MimeType DEFAULT_CONTENT_TYPE = MimeType.valueOf("text/html");
// 默认的前缀和后缀
public static final String DEFAULT_PREFIX = "classpath:/templates/";
public static final String DEFAULT_SUFFIX = ".html";上面的含义:只要我们把HTML页面放在 classpath:/templates/目录下,thymeleaf 就能自动渲染;
例如在 helloController.java 中输入:
package com.gjxaiou.springboot.controller;
@Controller
public class HelloController {
@RequestMapping("/success")
public String success(){
return "success";
}
}上面代码在 templates文件夹下面新建:success.html ,访问:localhost:8080/success就可以到达该页面;
- 在 HTML 中的使用
导入thymeleaf的名称空间(下面两段代码都在在 sucess.html 中)
使用thymeleaf语法;
Title
成功!
这是显示欢迎信息
对应的controller 修改为:
package com.gjxaiou.springboot.controller;
@Controller
public class HelloController {
//查出用户数据,在页面展示
@RequestMapping("/success")
public String success(Map map){
map.put("hello","你好
");
return "success";
}
} (三)语法规则
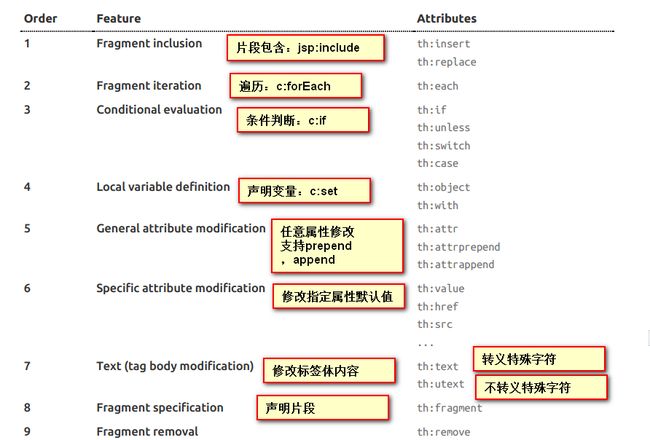
th:任意html属性:来替换原生属性(即 HTML 中默认的属性)的值示例:th:text:改变当前元素里面的文本内容;
- 支持的表达式语法:
Simple expressions:(表达式语法)
Variable Expressions: ${...}:获取变量值;底层就是OGNL;
1)、可以获取对象的属性、调用方法
2)、使用内置的基本对象:(即在 ${}中可以加入下面这些)
#ctx : the context object.
#vars: the context variables.
#locale : the context locale.
#request : (only in Web Contexts) the HttpServletRequest object.
#response : (only in Web Contexts) the HttpServletResponse object.
#session : (only in Web Contexts) the HttpSession object.
#servletContext : (only in Web Contexts) the ServletContext object.
示例:${session.foo}
3)、内置的一些工具对象:
***execInfo : information about the template being processed.***
***messages : methods for obtaining externalized messages inside variables expressions, in the same way as they would be obtained using #{…} syntax.
uris : methods for escaping parts of URLs/URIs
conversions : methods for executing the configured conversion service (if any).
dates : methods for java.util.Date objects: formatting, component extraction, etc.
calendars : analogous to #dates , but for java.util.Calendar objects.
numbers : methods for formatting numeric objects.
strings : methods for String objects: contains, startsWith, prepending/appending, etc.
objects : methods for objects in general.
bools : methods for boolean evaluation.
arrays : methods for arrays.
lists : methods for lists.
sets : methods for sets.
maps : methods for maps.
aggregates : methods for creating aggregates on arrays or collections.
ids : methods for dealing with id attributes that might be repeated (for example, as a result of an iteration).***
Selection Variable Expressions: *{...}:选择表达式:和${}在功能上是一样;
补充功能:配合 th:object="${session.user}:
Name: Sebastian.
Surname: Pepper.
Nationality: Saturn.
对应于使用上面的 ${...}写法为:
Name: Sebastian.
Surname: Pepper.
Nationality: Saturn.
Message Expressions: #{...}:获取国际化内容
Link URL Expressions: @{...}:定义URL;
Fragment Expressions: ~{...}:片段引用表达式
Literals(字面量)
Text literals: 'one text' , 'Another one!' ,…
Number literals: 0 , 34 , 3.0 , 12.3 ,…
Boolean literals: true , false
Null literal: null
Literal tokens: one , sometext , main ,…
Text operations:(文本操作)
String concatenation: +
Literal substitutions: |The name is ${name}|
Arithmetic operations:(数学运算)
Binary operators: + , - , * , / , %
Minus sign (unary operator): -
Boolean operations:(布尔运算)
Binary operators: and , or
Boolean negation (unary operator): ! , not
Comparisons and equality:(比较运算)
Comparators: > , < , >= , <= ( gt , lt , ge , le )
Equality operators: == , != ( eq , ne )
Conditional operators:条件运算(三元运算符)
If-then: (if) ? (then)
If-then-else: (if) ? (then) : (else)
Default: (value) ?: (defaultvalue)
Special tokens:
No-Operation: _ 使用示例:
package com.gjxaiou.springboot.controller;
@Controller
public class HelloController {
//查出用户数据,在页面展示
@RequestMapping("/success")
public String success(Map map){
map.put("hello","你好
");
map.put("users",Arrays.asList("zhangsan","lisi","wangwu"));
return "success";
}
}
对应的 success.html 文件为:
Title
[[${user}]]
22 SpringMVC 自动配置
关于springMVC 的说明
(一)Spring MVC 的 auto-configuration
Spring Boot 自动配置好了 SpringMVC以下是SpringBoot 对 SpringMVC的默认配置(见 Reference 文档 P107/519):下面的所有自动配置都在(WebMvcAutoConfiguration)文件中
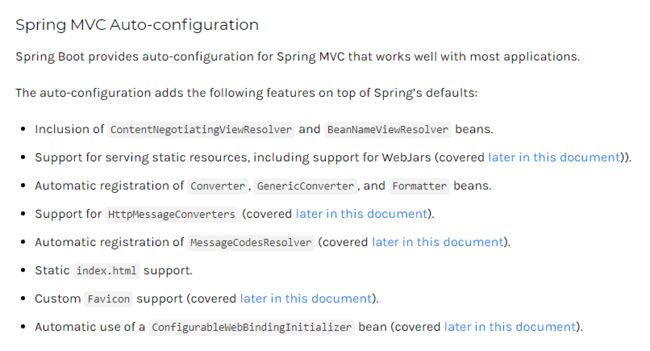
Inclusion(包含) of
ContentNegotiatingViewResolverandBeanNameViewResolverbeans.自动配置了ViewResolver(视图解析器:根据方法的返回值得到视图对象(View),视图对象决定如何渲染(转发?重定向?))
ContentNegotiatingViewResolver:这个类是组合所有的视图解析器的;
如何定制视图解析器:我们可以自己给容器中添加一个视图解析器;然后ContentNegotiatingViewResolver 自动的将其组合进来;
验证:在主类中自定义视图解析器,然后使用 @Bean 就将其加入容器中;
package com.gjxaiou.springboot;
@SpringBootApplication
public class SpringBoot04WebRestfulcrudApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SpringBoot04WebRestfulcrudApplication.class, args);
}
// 添加到容器中
@Bean
public ViewResolver myViewReolver(){
return new MyViewResolver();
}
public static class MyViewResolver implements ViewResolver{
@Override
public View resolveViewName(String viewName, Locale locale) throws Exception {
return null;
}
}
}
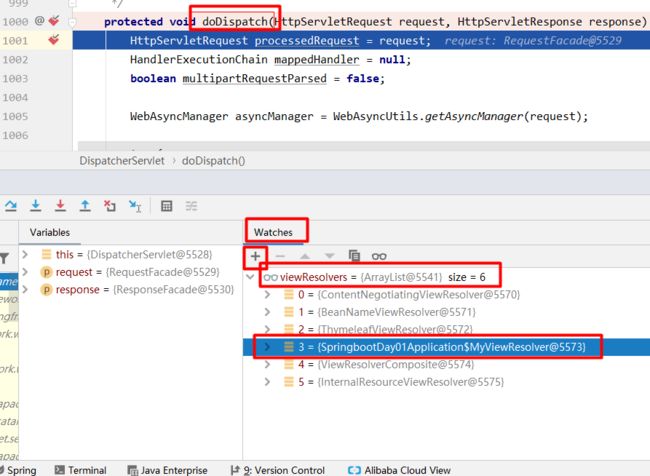
然后全局搜索:DispatcherServlet,来到 1000行(ctrl + G ) 的 doDispatch() 方法上打断点然后调试,访问任意路径看自定义的视图解析器是否在里面;
查看 Valiables 中的 viewResolvers 中就应该有自己定义的视图解析器
Support for serving static resources, including support for WebJars (see below).静态资源文件夹路径,webjars
Static
index.htmlsupport. 静态首页访问Custom
Faviconsupport (see below). 支持 favicon.ico 自定义Automatic use of
Converter,GenericConverter,Formatterbeans;就是页面带来的数据格式要转换成其他格式,例如页面带来一个 18(文本类型)要转换为 integer 类型等等;Converter:转换器; public String hello(User user):类型转换使用 ConverterFormatter格式化器; 2017.12.17===Date;
@Bean
@ConditionalOnProperty(prefix = "spring.mvc", name = "date-format")//在文件中配置日期格式化的规则
public Formatter dateFormatter() {
return new DateFormatter(this.mvcProperties.getDateFormat());//日期格式化组件
} 自己添加的格式化器转换器,我们只需要放在容器中即可,因为它也是遍历 Converter 类型;
Support for
HttpMessageConverters(see below)。HttpMessageConverter:是SpringMVC用来转换Http请求和响应的;如方法返回User对象,想以Json数据形式写出去;
HttpMessageConverters是从容器中确定;获取所有的HttpMessageConverter;自己给容器中添加HttpMessageConverter,只需要将自己的组件注册容器中(@Bean,@Component)
Automatic registration of
MessageCodesResolver(see below).定义错误代码生成规则Automatic use of a
ConfigurableWebBindingInitializerbean (see below).我们可以配置一个ConfigurableWebBindingInitializer来替换默认的;(需要添加到容器中) ,
(二)扩展SpringMVC
Spring MVC 中拓展方式:
Spring Boot 中方式:编写一个配置类(@Configuration),该类是 WebMvcConfigurerAdapter 类型;但是不能标注 @EnableWebMvc;
既保留了所有的自动配置,也能用我们扩展的配置;
// 使用 WebMvcConfigurerAdapter 可以来扩展 SpringMVC 的功能
@Configuration
public class MyMvcConfig extends WebMvcConfigurerAdapter {
@Override
public void addViewControllers(ViewControllerRegistry registry) {
// super.addViewControllers(registry);
//浏览器发送 /gjxaiou 请求来到 success
registry.addViewController("/gjxaiou").setViewName("success");
}
}原理:
WebMvcAutoConfiguration 是 Spring MVC 的自动配置类
在做其他自动配置时会导入:@Import(EnableWebMvcConfiguration.class)
@Configuration
public static class EnableWebMvcConfiguration extends DelegatingWebMvcConfiguration {
private final WebMvcConfigurerComposite configurers = new WebMvcConfigurerComposite();
//从容器中获取所有的WebMvcConfigurer
@Autowired(required = false)
public void setConfigurers(List configurers) {
if (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(configurers)) {
this.configurers.addWebMvcConfigurers(configurers);
//一个参考实现;将所有的WebMvcConfigurer相关配置都来一起调用;
@Override
// public void addViewControllers(ViewControllerRegistry registry) {
// for (WebMvcConfigurer delegate : this.delegates) {
// delegate.addViewControllers(registry);
// }
}
}
} 容器中所有的 WebMvcConfigurer 都会一起起作用;
我们的配置类也会被调用;
效果:SpringMVC 的自动配置和我们的扩展配置都会起作用;
(三)全面接管SpringMVC(不推荐)
SpringBoot 对 SpringMVC 的自动配置都不需要,所有都是我们自己配置;例如基本的静态资源不能使用了,所有路径都需要自己进行配置;
我们需要在配置类中添加@EnableWebMvc即可;
//使用WebMvcConfigurerAdapter可以来扩展SpringMVC的功能
@EnableWebMvc
@Configuration
public class MyMvcConfig extends WebMvcConfigurerAdapter {
@Override
public void addViewControllers(ViewControllerRegistry registry) {
// 浏览器发送 /gjxaiou 请求来到 success
registry.addViewController("/gjxaiou").setViewName("success");
}
}原理:
为什么@EnableWebMvc自动配置就失效了;
- @EnableWebMvc 的代码为:(点击)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Documented
@Import(DelegatingWebMvcConfiguration.class)
public @interface EnableWebMvc {
}- 由上面的 @Import() 中的 DelegatingWebMvcConfiguration.class ,其代码为:
@Configuration
public class DelegatingWebMvcConfiguration extends WebMvcConfigurationSupport {- 下面是 Spring Boot 的自动配置类:WebMvcAutoConfiguration
@Configuration
@ConditionalOnWebApplication
@ConditionalOnClass({ Servlet.class, DispatcherServlet.class,
WebMvcConfigurerAdapter.class })
//容器中没有这个组件的时候,这个自动配置类才生效
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(WebMvcConfigurationSupport.class)
@AutoConfigureOrder(Ordered.HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE + 10)
@AutoConfigureAfter({ DispatcherServletAutoConfiguration.class,
ValidationAutoConfiguration.class })
public class WebMvcAutoConfiguration {总结:
@EnableWebMvc里面的@Import(DelegatingWebMvcConfiguration.class)将 里面类的父类:WebMvcConfigurationSupport组件导入进来,所有相当于@ConditionalOnMissingBean(WebMvcConfigurationSupport.class)就是不符合的,因此自动配置类就失效了 ;导入的WebMvcConfigurationSupport 只是 SpringMVC 最基本的功能;
23 如何修改 SpringBoot 的默认配置
方式一:SpringBoot 在自动配置很多组件的时候,先看容器中有没有用户自己配置的(@Bean、@Component)如果有就用用户配置的,如果没有,才自动配置;如果有些组件可以有多个(ViewResolver)将用户配置的和自己默认的组合起来;
方式二:在 SpringBoot 中会有非常多的 xxxConfigurer 帮助我们进行扩展配置;
方式三:在 SpringBoot 中会有很多的 xxxCustomizer 帮助我们进行定制配置;
24 RestfulCRUD 项目
(一)设置默认访问首页
项目中有两个 index.html 文件,位置分别为:resources.public.index.html 和resources.templates.index.html,要求默认是访问后者的 index.html 文件;
下面的两种方式都是默认使用了 thymeleaf 模板引擎;
- 方法一:编写单独的控制器进行路径映射
@Controller
public class HelloController {
// 不管是访问当前项目还是访问当前项目的 index.html
@RequestMapping({"/","/index.html"})
public String index(){
return "index";
}
} - 方法二:添加视图映射(只需要将组件注册到容器中即可)
@Configuration
public class MyMvcConfig extends WebMvcConfigurerAdapter {
//所有的WebMvcConfigurerAdapter组件都会一起起作用
@Bean //将组件注册在容器
public WebMvcConfigurerAdapter webMvcConfigurerAdapter(){
WebMvcConfigurerAdapter adapter = new WebMvcConfigurerAdapter() {
@Override
public void addViewControllers(ViewControllerRegistry registry) {
registry.addViewController("/").setViewName("index");
registry.addViewController("/index.html").setViewName("index");
}
};
return adapter;
}
}
(二)国际化
- 以前springmvc 配置方式:
- 编写国际化配置文件;
- 使用ResourceBundleMessageSource管理国际化资源文件;
- 在页面使用fmt:message取出国际化内容;
- 使用 Spring Boot 实现步骤:
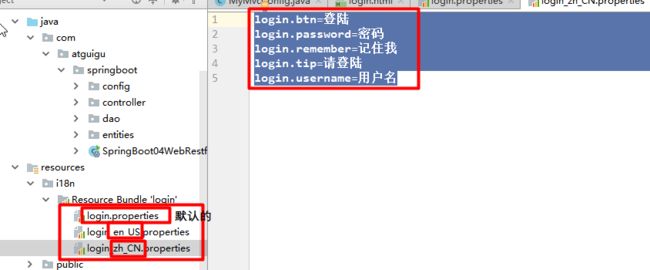
- 首先编写国际化配置文件,抽取页面需要显示的国际化消息(然后分别配置属性文件)
- SpringBoot自动配置好了管理国际化资源文件的组件;@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.messages")
public class MessageSourceAutoConfiguration {
//我们的配置文件可以直接放在类路径下叫messages.properties;(因为默认名为 message)
private String basename = "messages";
@Bean
public MessageSource messageSource() {
ResourceBundleMessageSource messageSource = new ResourceBundleMessageSource();
if (StringUtils.hasText(this.basename)) {
//设置国际化资源文件的基础名(去掉语言国家代码的)
messageSource.setBasenames(StringUtils.commaDelimitedListToStringArray(
StringUtils.trimAllWhitespace(this.basename)));
}
if (this.encoding != null) {
messageSource.setDefaultEncoding(this.encoding.name());
}
messageSource.setFallbackToSystemLocale(this.fallbackToSystemLocale);
messageSource.setCacheSeconds(this.cacheSeconds);
messageSource.setAlwaysUseMessageFormat(this.alwaysUseMessageFormat);
return messageSource;
}因为没有使用系统默认的文件名,因此需要在 application.properties 中配置:`spring.messages.basename=i18n.login`,注意后面是去掉国家代码的部分(即取所有配置文件去掉后面的语言和国家的前面公共部分);
- 在页面获取国际化的值;
在页面中(login.html)取值,例如 19行的:`th:text="#{login.username}"`(如果出现乱码,注意配置在 IDEA 中配置编码)
Signin Template for Bootstrap
效果:根据浏览器语言设置的信息切换了国际化;
- 国际化实现原理:
国际化 Locale(区域信息对象);springMVC 中的LocaleResolver(获取区域信息对象);
springboot 默认也配置了区域信息解析器,如下:默认的就是根据请求头(浏览器 F12 中的Request Header 中的 Accept-Language中可以看出)带来的区域信息获取 Locale 进行国际化
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
@ConditionalOnProperty(prefix = "spring.mvc", name = "locale")
public LocaleResolver localeResolver() {
if (this.mvcProperties
.getLocaleResolver() == WebMvcProperties.LocaleResolver.FIXED) {
return new FixedLocaleResolver(this.mvcProperties.getLocale());
}
AcceptHeaderLocaleResolver localeResolver = new AcceptHeaderLocaleResolver();
localeResolver.setDefaultLocale(this.mvcProperties.getLocale());
return localeResolver;
}
4)、点击链接切换国际化,需要自己写一个 LocalResolver ,以下面的为例:
/**
* 可以在连接上携带区域信息
*/
public class MyLocaleResolver implements LocaleResolver {
@Override
public Locale resolveLocale(HttpServletRequest request) {
String l = request.getParameter("local");
Locale locale = Locale.getDefault();
if(!StringUtils.isEmpty(l)){
String[] split = l.split("_");
// split[0]是语言代码,后面那个是国家代码
locale = new Locale(split[0],split[1]);
}
return locale;
}
@Override
public void setLocale(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Locale locale) {
}
}
// 这里的方法名不能改变
@Bean
public LocaleResolver localeResolver(){
return new MyLocaleResolver();
}
}
对应的 html 也要更改:实现点击 中文显示中文,点击 English 显示英文
© 2017-2018
中文
English
(三)登陆
首先修改 html 中的路径,下面是从 index.html 的15行开始;
开发期间模板引擎页面修改以后,要实时生效
- 禁用模板引擎的缓存(applicationl.properties),否则前端页面修改之后也没有变化
# 禁用缓存
spring.thymeleaf.cache=false - 页面修改完成以后ctrl+f9:重新编译;因为idea在运行期间不会重新编译页面
登陆错误消息的显示
控制器代码:
package com.gjxaiou.springboot.controller;
@Controller
public class LoginController {
// 默认使用下面的方式,但是 springboot 中可以使用 @PostMapping 表示POST 请求,其本质上是里面声明了一个 @RequestMapping(method = {RequestMethod.POST})
//@RequestMapping(value = "/user/login",method = RequestMethod.POST)
@PostMapping(value = "/user/login")
public String login(@RequestParam("username") String username,
@RequestParam("password") String password,
Map map, HttpSession session){
if(!StringUtils.isEmpty(username) && "123456".equals(password)){
//登陆成功,防止表单重复提交,可以重定向到主页
session.setAttribute("loginUser",username);
return "redirect:/main.html";
}else{
//登陆失败
map.put("msg","用户名密码错误");
// 因为要去的页面在 templates 下面,因此有模板引擎的解析,因此前后缀不需要写
return "login";
}
}
}
为了能够解析出上面的 redirect:/main.html,需要在上面的自定义视图配置中添加上对应的语句;
package com.gjxaiou.springboot.config;
@Configuration
public class MyMvcConfig extends WebMvcConfigurerAdapter {
//所有的WebMvcConfigurerAdapter组件都会一起起作用
@Bean //将组件注册在容器
public WebMvcConfigurerAdapter webMvcConfigurerAdapter(){
WebMvcConfigurerAdapter adapter = new WebMvcConfigurerAdapter() {
@Override
public void addViewControllers(ViewControllerRegistry registry) {
registry.addViewController("/main.html").setViewName("dashboard");
}
}
@Bean
public LocaleResolver localeResolver(){
return new MyLocaleResolver();
}
}
(四)拦截器进行登陆检查
首先需要编写拦截器:
package com.gjxaiou.springboot.component;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerInterceptor;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.ModelAndView;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
/**
* 登陆检查,
*/
public class LoginHandlerInterceptor implements HandlerInterceptor {
//目标方法执行之前
@Override
public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception {
Object user = request.getSession().getAttribute("loginUser");
if(user == null){
//未登陆,返回登陆页面
request.setAttribute("msg","没有权限请先登陆");
request.getRequestDispatcher("/index.html").forward(request,response);
return false;
}else{
//已登陆,放行请求
return true;
}
}
@Override
public void postHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, ModelAndView modelAndView) throws Exception {
}
@Override
public void afterCompletion(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, Exception ex) throws Exception {
}
}
注册拦截器
//所有的WebMvcConfigurerAdapter组件都会一起起作用
@Bean //将组件注册在容器
public WebMvcConfigurerAdapter webMvcConfigurerAdapter(){
WebMvcConfigurerAdapter adapter = new WebMvcConfigurerAdapter() {
@Override
public void addViewControllers(ViewControllerRegistry registry) {
registry.addViewController("/").setViewName("login");
registry.addViewController("/index.html").setViewName("login");
registry.addViewController("/main.html").setViewName("dashboard");
}
//注册拦截器
@Override
public void addInterceptors(InterceptorRegistry registry) {
//super.addInterceptors(registry);
//静态资源; *.css , *.js
//SpringBoot已经做好了静态资源映射
registry.addInterceptor(new LoginHandlerInterceptor()).addPathPatterns("/**")
.excludePathPatterns("/index.html","/","/user/login");
}
};
return adapter;
}(五)CRUD-员工列表
实验要求:
- RestfulCRUD:CRUD要满足Rest风格;
Rest风格为:URI: /资源名称/资源标识 并且使用 HTTP请求方式区分对资源CRUD操作
| 普通CRUD(使用urL来区分操作) | RestfulCRUD | |
|---|---|---|
| 查询 | getEmp | emp---GET |
| 添加 | addEmp?xxx | emp---POST |
| 修改 | updateEmp?id=xxx&xxx=xx | emp/{id}---PUT |
| 删除 | deleteEmp?id=1 | emp/{id}---DELETE |
2)、实验的请求架构;
| 实验功能 | 请求URI | 请求方式 |
|---|---|---|
| 查询所有员工 | emps | GET |
| 查询某个员工(来到修改页面) | emp/{id} | GET |
| 来到添加页面 | emp | GET |
| 添加员工 | emp | POST |
| 来到修改页面(查出员工进行信息回显) | emp/{id} | GET |
| 修改员工 | emp | PUT |
| 删除员工 | emp/{id} | DELETE |
功能一:员工列表:
首先 dashboard.html中部分代码修改如下:
Customers
然后对应 /emps 请求需要对应的处理,EmployeeController.java
通过访问:http://localhost:8083/crud/main.html 点击左边的 Employee 就能跳转到员工列表面;
thymeleaf 公共页面元素抽取
例如主页面和员工列表页面的左边和上面都是一样的
1、抽取公共片段
© 2011 The Good Thymes Virtual Grocery
2、引入公共片段(重用)相当于有一个 footer 页面中引入 copy 片段;
insert 之后表达式有两种:这里是第二种;
~{templatename::selector}:模板名::选择器
~{templatename::fragmentname}:模板名::片段名
3、默认效果:
insert的公共片段在div标签中
如果使用th:insert等属性进行引入,可以不用写~{}:
行内写法可以加上:[[~{}]];[(~{})];以顶部为例,使用 F12 看到该部分对应的代码:为 html 中的