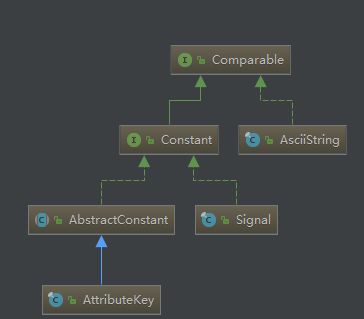
1. attributeKey
1.1 ConstantPool
这个类主要是来缓存一些常量,和我之前写的cache类似的思想。
提供了3个关键的方法,valueOf、exists、newInstance,其中我们真正缓存容器还是jdk提供的 ConcurrentHashMap
1.1.1 valueOf
可以看出最关键的方法是 getOrCreate,这个方法最大的特点是采用类乐观锁的方式,当我们最后发现了 constant != null时,那么我们返回已经插入的 constant。
public T valueOf(Class firstNameComponent, String secondNameComponent) {
return valueOf(firstNameComponent.getName() + '#' + secondNameComponent);
}
public T valueOf(String name) {
return getOrCreate(name);
}
private T getOrCreate(String name) {
T constant = constants.get(name);
if (constant == null) {
final T tempConstant = newConstant(nextId(), name);
constant = constants.putIfAbsent(name, tempConstant);
if (constant == null) {
return tempConstant;
}
}
return constant;
}
1.1.2 newInstance
可以看出最关键的方法是 createOrThrow,这个方法最大的特点是采用类乐观锁的方式,当我们最后发现了 constant != null时,我们直接抛出异常。
public T newInstance(String name) {
return createOrThrow(name);
}
private T createOrThrow(String name) {
T constant = constants.get(name);
if (constant == null) {
final T tempConstant = newConstant(nextId(), name);
constant = constants.putIfAbsent(name, tempConstant);
if (constant == null) {
return tempConstant;
}
}
throw new IllegalArgumentException(String.format("'%s' is already in use", name));
}
1.1.3 valueOf和newInstance 对比
valueOf:如果 name 不存在就创建一个,且多线程随先创建返回谁。
newInstance : 如果name存在就抛出异常,且多线程创建,除了成功创建的那个线程外,其他线程抛出异常。
1.2 AttributeKey
AttributeKey是基于ConstantPool进行缓存的。
1.2.1 创建
可以看出,每个newConstant的id,是nextId,是逐渐递增。
//AttributeKey
private static final ConstantPool> pool = new ConstantPool>() {
@Override
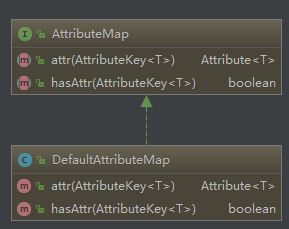
protected AttributeKey 2.AttributeMap
可以看出,唯一的实现类就是DefaultAttributeMap。
就两方法,attr 和 hasAttr。
2.1 DefaultAttributeMap
2.1.1 为啥要自己重新设计一个map类?
作者做出了解释
Not using ConcurrentHashMap due to high memory consumption.
显然,在大量连接数下,ConcurrentHashMap 显得非常吃内存,作者做出一定的抉择。
2.1.1 这个类的优点和缺点
优点:
代码少,简单,占用内存相对较小。
缺点:
- 单利模式没设计好,显然传统的double-check更优秀。
可以看出,在多线程竞争下,attributes 可能创建多次,而传统的 double-check 只会创建一次。
if (attributes == null) {
attributes = new AtomicReferenceArray>(BUCKET_SIZE);
if (!updater.compareAndSet(this, null, attributes)) {
attributes = this.attributes;
}
}
- key在极端情况下可能练成一条线
可以看出,最关键的还是key.id()这个方法,而这个方法是通过每次++一个int生成,在极端情况下,多次不同的key可以得到同一个index,这样结果显然不如直接array数组来的好
int i = index(key);
private static int index(AttributeKey key) {
return key.id() & MASK;
}
2.1.3 设计思想
通过 AttributeKey的id做一个划分,来做个分段锁。使用数组+链表作结构。
客观的评价,这个类写的勉勉强强
2.1.4 attr(AttributeKey key)
这是一个通过AttributeKey 获取 Attribute 的方法。如果找不到对应的Attribute ,就创建一个 Attribute
可以看出一个数组加链表的结构,且链表第一个元素必须为 空的DefaultAttribute元素,用来防止回滚
public Attribute attr(AttributeKey key) {
//我觉得double-check更好
AtomicReferenceArray> attributes = this.attributes;
if (attributes == null) {
// Not using ConcurrentHashMap due to high memory consumption.
attributes = new AtomicReferenceArray>(BUCKET_SIZE);
if (!updater.compareAndSet(this, null, attributes)) {
attributes = this.attributes;
}
}
int i = index(key);
DefaultAttribute head = attributes.get(i);
if (head == null) {
// No head exists yet which means we may be able to add the attribute without synchronization and just
// use compare and set. At worst we need to fallback to synchronization and waste two allocations.
head = new DefaultAttribute();//主要是 attributes.compareAndSet会引起替换操作,这里就是避免替换后还要回滚。
DefaultAttribute attr = new DefaultAttribute(head, key);
head.next = attr;
attr.prev = head;
if (attributes.compareAndSet(i, null, head)) {
// we were able to add it so return the attr right away
return attr;
} else {
head = attributes.get(i);
}
}
synchronized (head) {
DefaultAttribute curr = head;
for (;;) {
DefaultAttribute next = curr.next;
if (next == null) {//如果一直找不到就生成一个
DefaultAttribute attr = new DefaultAttribute(head, key);
curr.next = attr;
attr.prev = curr;
return attr;
}
if (next.key == key && !next.removed) {//遍历过程
return (Attribute) next;
}
curr = next;
}
}
}
2.1.4 hasAttr(AttributeKey key)
判断是否含有这个属性。
public boolean hasAttr(AttributeKey key) {
if (key == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("key");
}
AtomicReferenceArray> attributes = this.attributes;
if (attributes == null) {
// no attribute exists
return false;
}
int i = index(key);
DefaultAttribute head = attributes.get(i);
if (head == null) {
// No attribute exists which point to the bucket in which the head should be located
return false;
}
// We need to synchronize on the head.
synchronized (head) {
// Start with head.next as the head itself does not store an attribute.
DefaultAttribute curr = head.next;
while (curr != null) {
if (curr.key == key && !curr.removed) {
return true;
}
curr = curr.next;
}
return false;
}
}
2.1.5 DefaultAttribute
private static final class DefaultAttribute extends AtomicReference implements Attribute {
private static final long serialVersionUID = -2661411462200283011L;
// The head of the linked-list this attribute belongs to
private final DefaultAttribute head;
private final AttributeKey key;
// Double-linked list to prev and next node to allow fast removal
private DefaultAttribute prev;
private DefaultAttribute next;
// Will be set to true one the attribute is removed via getAndRemove() or remove()
private volatile boolean removed;
DefaultAttribute(DefaultAttribute head, AttributeKey key) {
this.head = head;
this.key = key;
}
// Special constructor for the head of the linked-list.
DefaultAttribute() {
head = this;
key = null;
}
@Override
public AttributeKey key() {
return key;
}
@Override
public T setIfAbsent(T value) {
while (!compareAndSet(null, value)) {
T old = get();
if (old != null) {
return old;
}
}
return null;
}
@Override
public T getAndRemove() {
removed = true;
T oldValue = getAndSet(null);
remove0();
return oldValue;
}
@Override
public void remove() {
removed = true;
set(null);
remove0();
}
private void remove0() {
synchronized (head) {
if (prev == null) {
// Removed before.
return;
}
prev.next = next;
if (next != null) {
next.prev = prev;
}
// Null out prev and next - this will guard against multiple remove0() calls which may corrupt
// the linked list for the bucket.
prev = null;
next = null;
}
}
}