1 基本图形和属性
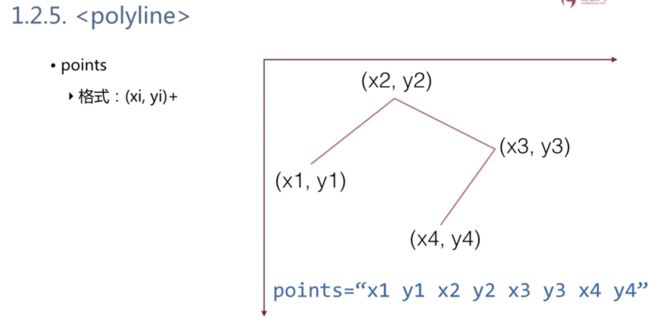
矩形---圆形————椭圆———直线——折线—————多边形
PS:
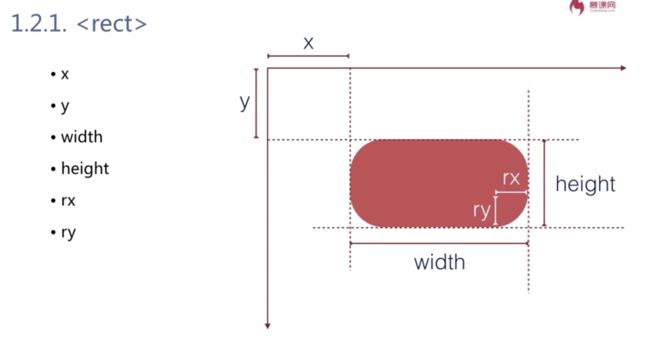
x y 表示左上角的位置
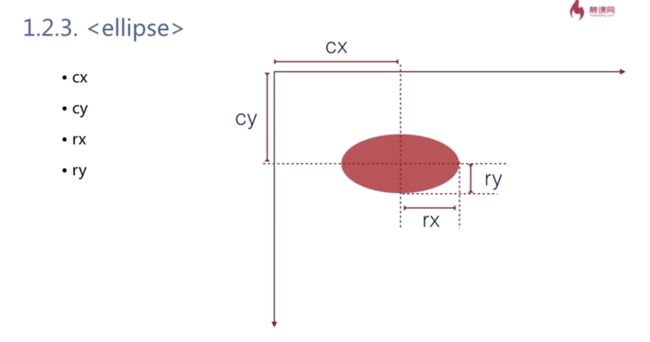
cx cy表示圆心的位置
2 基本属性
fill:填充色
stroke:边框色
stroke-width:边框宽度
transform:偏移量
3 动态创建svg的基本API
创建图形: document.createElementNS(ns,tagName)
添加图形:element.appendChild(childElement)
设置获取属性:element.setAttribute(name,value)
<svg xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg"> <rect x="10" y="10" rx="5" ry="5" width="150" height="150" stroke="red" fill="yellow" >rect> <circle cx="250" cy="60" r="50" stroke="red" fill="green" >circle> <line x1="20" y1="20" x2="200" y2="200" stroke="green" >line> <polyline points=" 100 100 200 400 300 200 " fill="green" stroke="red" stroke-width="5" >polyline> <polygon points=" 250 120 300 220 200 220 100 300 " stroke="red" stroke-width="5" >polygon> svg>
示例2 微笑脸
<svg xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg" width="200" height="200"> <circle cx="100" cy="100" r="90" fill="#39F" /> <circle cx="70" cy="80" r="20" fill="white" /> <circle cx="130" cy="80" r="20" fill="white" /> <circle cx="65" cy="75" r="10" fill="black" /> <circle cx="125" cy="75" r="10" fill="black"/> <path d="M 50 140 A 60 60 0 0 0 150 140" stroke="white" stroke-width="3" fill="none" /> svg>
DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>Documenttitle>
<style>
.box{
width: 200px;
text-align: center;
line-height: 60px;
height: 60px;
background-color: green;
color: red;
}
style>
head>
<body>
<div class="box">按钮div>
<div id="canvas">div>
<script>
var SVG_NS = 'http://www.w3.org/2000/svg';
var defaultAttrs = {
rect: {
x:'10',
y:'10',
width:'200',
height:'100',
rx:'10',
ry:'10',
fill:'red'
},
circle:{
cx:"100",
cy:'100',
r:'50',
fill:'yellow'
}
};
function createSVG() {
var svg = document.createElementNS(SVG_NS, 'svg');
var canvas = document.querySelector('#canvas');
svg.setAttribute('width', '100%');
svg.setAttribute('height', '100%');
for (name in defaultAttrs) {
var shape = document.createElementNS(SVG_NS, name);
for(key in defaultAttrs[name]){
shape.setAttribute(key, defaultAttrs[name][key]);
svg.appendChild(shape);
}
}
canvas.appendChild(svg);
}
document.querySelector('.box').addEventListener('click',function(){
createSVG();
},false)
script>
body>
html>
视野与世界
世界是无穷大的
视野是观察世界的一个矩形区域(viewbox)
width,height—控制视窗,svg用来渲染图像的区域;
SVG代码—定义世界
viewBox preserveAspectORatio—控制视野,也就是决定用户能够观看到的范围;
<svg xmlns="" width="800" height="600" viewBox="0 0 400 300" preserveAspectORatio = "xMidYMid meet" > svg>
一般来说设置 viewBox=”0 0 400 300”
这里的400 300 就是svg的宽度和高度即可
分组的概念
标签来创建分组
属性继承
transform 属性定义坐标变换
可以嵌套使用
示例:锤子分组
<svg xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg" > <line x1="0" y1="0" x2="200" y2="0" stroke="red"> line> <g stroke="green" fill="none" transform="translate(50,50)"> <rect x="100" y="50" width="100" height="50">rect> <rect x="140" y="100" width="20" height="120">rect> g> svg>
笛卡尔直角坐标系
和常规的坐标系是相反的,顺时针角度为正值
transform 属性
rotate(deg)
translate(x,y)
scale(sx,sy)
matrix(a,b,c,d,e,f)
<defs>defs> 标签不会被立即绘出来,但是会在后面被引用,相当于是个组件,提高复用性
<defs> <g id="coord"> <rect>rect> g> defs> <use xlink:href="#coord" stroke="blank"/> <use xlink:href="#coord" stroke="blank"/>
线性渐变(斜对角线方向)
<linearGradient> 和 <stop>
定义方向
关键点位置及颜色
gradientUnits
<svg xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg"> <path d="M100,100A200,100,0,1,0,200,200" stroke="red" fill="none"/> svg>
===
userSpaceOnUse是真实的宽高/objectBoundingBox是按照比例计算的
<svg xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg"> <defs> <linearGradient id="grad1" x1="0" y1="0" x2="1" y2="1"> <stop offset="0" stop-color="red"/> <stop offset="0.5" stop-color="yellow"/> <stop offset="1" stop-color="green"/> linearGradient> defs> <rect x="100" y="100" fill="url(#grad1)" width="200" height="150">rect> svg>
径向渐变(斜对角线方向)
<radialGradient> 和 <stop>
cx1开始位置
定义方向
关键点位置及颜色
gradientUnits
焦点位置fx\fy
<svg xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg"> <defs> <radialGradient id="grad2" cx1="0.5" cy1="0.5" r="0.5" fx="0.6" fy="0.3"> <stop offset="0" stop-color="red"/> <stop offset="0.5" stop-color="yellow"/> <stop offset="1" stop-color="green"/> radialGradient> defs> <rect x="100" y="100" fill="url(#grad2)" width="200" height="150">rect> svg>
笔刷
绘制纹理
标签
patternUnits
patternContentUnits //内容设置
userSpaceOnUse是真实的宽高/objectBoundingBox是按照比例计算的
<svg xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg"> <defs> <pattern id="p1" x="0" y="0" width="0.2" height="0.2"> <circle cx="10" cy="10" r="5" fill="red">circle> <polygon points="30 10 60 50 0 50" fill="green">polygon> pattern> defs> <rect x="100" y="100" fill="url(#p1)" width="200" height="150" stroke="blue">rect> svg>
patternContentUnits = “userSpacePnUse” 表示按照实际宽高计算的而不是按照比例
<svg xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg"> <defs> <pattern id="p1" x="0" y="0" width="0.2" height="0.2"> <circle cx="10" cy="10" r="5" fill="red">circle> <polygon points="30 10 60 50 0 50" fill="green">polygon> pattern> defs> <rect x="100" y="100" fill="url(#p1)" width="200" height="150" stroke="blue">rect> svg>
Path路径
<path d="M0,0L10,20C30-10,40,20,100,100" stroke="red">
其中L表示命令 数字表示参数
参数之间用空格或者逗号隔开,有一种情况例外,就是下一个数值是负数
列举了相关命令;
区分大小写:大写表示坐标参数为绝对位置,小写为相对位置 最后的参数表示最终要到达的位置
上一个命令结束的位置就是下一个命令开始的位置 命令可以重复参数表示重复执行同一个命令
弧线命令
A(rx,ry,xr,laf,sf,x,y)—绘制弧线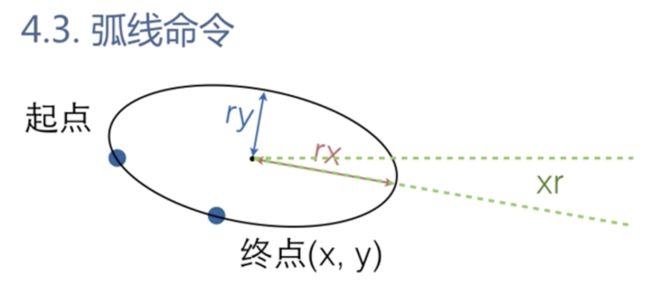
rx 表示弧线所在椭圆的x半轴长
ry 表示弧线所在椭圆的y半轴长
xr 表示弧线所在椭圆的长轴角度,旋转角度
laf 表示是否选择弧长较长的那一段弧线
sf 表示是否选择逆时针方向的那一段弧线
x,y表示弧线要画到那个位置
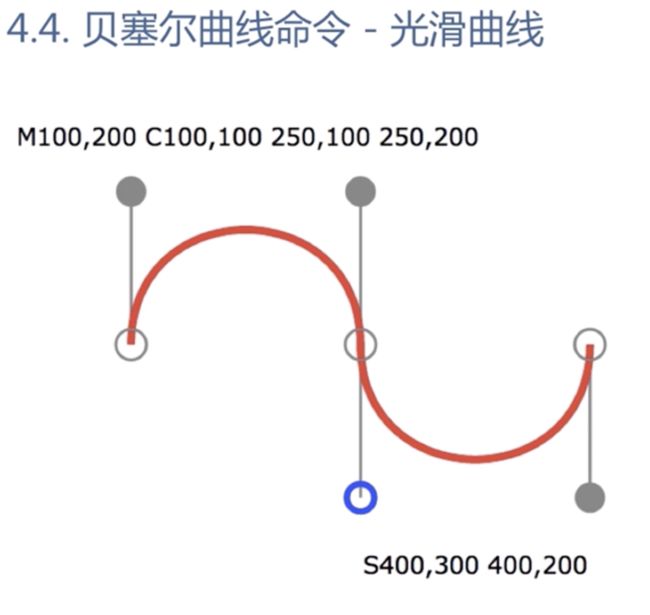
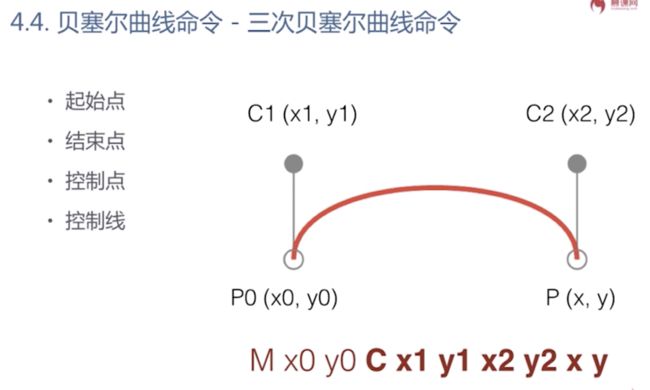
贝塞尔曲线
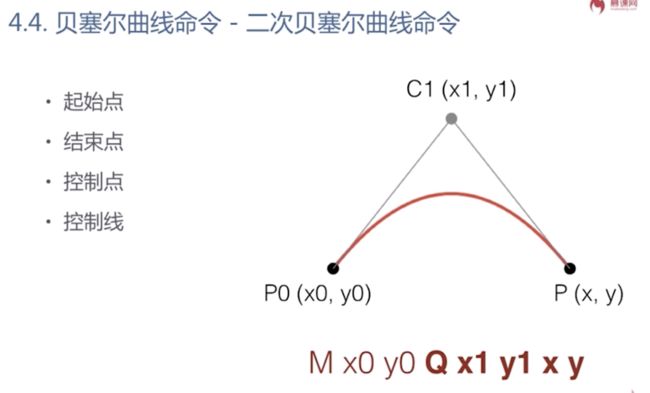
Q是大写的时候 是相对于坐标系的绝对路径
q是小写的时候 是相对于坐标系的相对路径
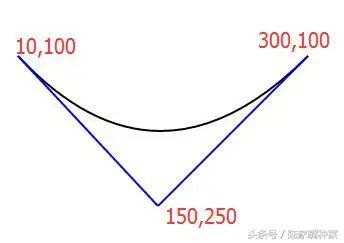
M x0 y0 Q x1 y1 x y
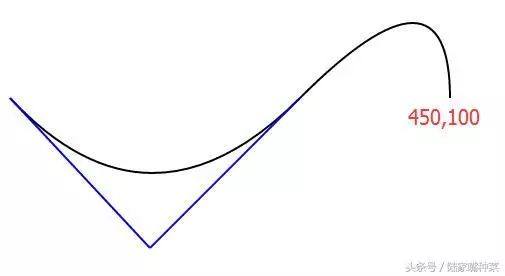
光滑曲线,无需指定第三个控制点的坐标
T指令自动补全对称的控制点(上图蓝色部分),让曲线平滑起来
<svg xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg"> <path d="M10,100 Q150,250 300,100 T450,100" stroke="red" fill="none"/> svg>
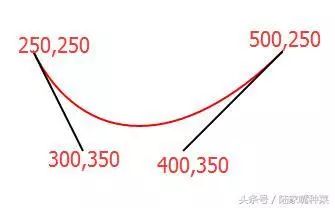
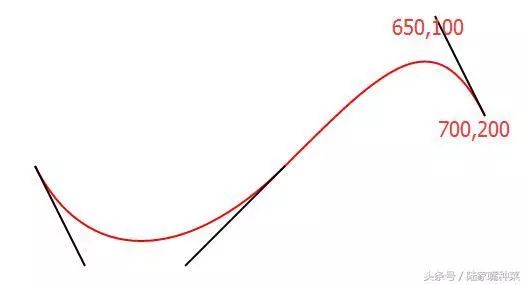
<svg xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg"> <path d="M250,250 C300,350,400,350,500,250" stroke="red" fill="none"/> svg>
<svg xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg"> <path d="M250,250 C300,350,400,350,500,250 S650,100 700,200" stroke="red" fill="none"/> svg>
在SVG中使用文本
<svg xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg"> <defs> <pattern id="grid" x="0" y="0" width="20" height="20" patternUnits="userSpaceOnUse"> <path d="M0,0H20V20" stroke="red" fill="none"/> pattern> defs> <rect width="1200" height="1000" fill="url(#grid)">rect> <text x="100" y="100" style="font-size:50px">你好text> <path d="M100,0V200M0,100H200" stroke="green">path> svg>
可以看出基线是和 英文字母下对齐的。
dx和dy表示在水平方向和垂直方向上的移动,支持数组形式,则表示对每一个数字移动
<svg xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg"> <defs> <pattern id="grid" x="0" y="0" width="20" height="20" patternUnits="userSpaceOnUse"> <path d="M0,0H20V20" stroke="red" fill="none"/> pattern> defs> <rect width="1200" height="1000" fill="url(#grid)">rect> <text x="100" y="100" dx="20 20 20 20" dy="20 20 20 20" style="font-size:50px">ABCDEtext> <path d="M100,0V200M0,100H600" stroke="green">path> svg>
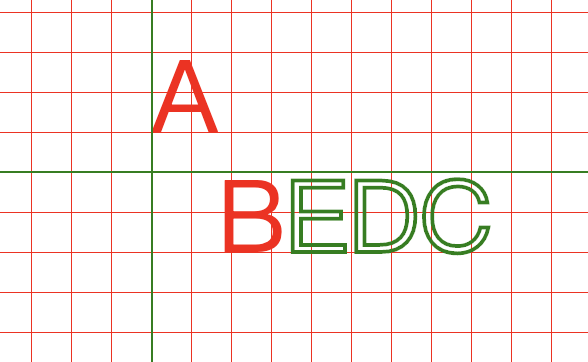
tspan可以用来对文字进行分组
<svg xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg"> <defs> <pattern id="grid" x="0" y="0" width="20" height="20" patternUnits="userSpaceOnUse"> <path d="M0,0H20V20" stroke="red" fill="none"/> pattern> defs> <rect width="1200" height="1000" fill="url(#grid)">rect> <text x="100" y="100" style="font-size:50px"> <tspan fill="red">ABtspan> <tspan fill="none" stroke="green" stroke-width="2">EDCtspan> text> <path d="M100,0V200M0,100H600" stroke="green">path> svg>
其中给第一个tspan设置的dy属性也会应用到剩下的tspan
<svg xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg"> <defs> <pattern id="grid" x="0" y="0" width="20" height="20" patternUnits="userSpaceOnUse"> <path d="M0,0H20V20" stroke="red" fill="none"/> pattern> defs> <rect width="1200" height="1000" fill="url(#grid)">rect> <text x="100" y="100" style="font-size:50px"> <tspan fill="red" dy="-20 60">ABtspan><tspan fill="none" stroke="green" stroke-width="2">EDCtspan> text> <path d="M100,0V200M0,100H600" stroke="green">path> svg>
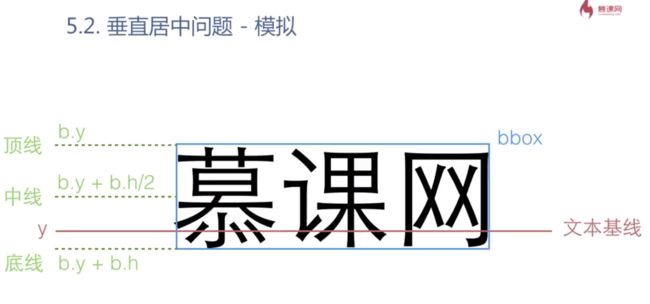
文字居中问题
1 text-anchor 水平居中属性
2 垂直居中 使用dy自己模拟
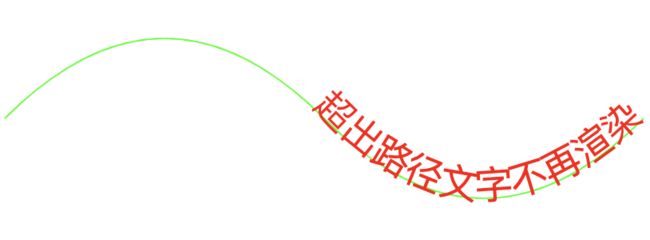
路径文本
DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8"/>
<title>textpathtitle>
head>
<body>
<svg xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg" width="600" height="300">
<path id="path1" d="M 100 200 Q 200 100 300 200 T 500 200" stroke="rgb(0,255,0)" fill="none">path>
<text style="font-size:24px;">
<textpath xlink:href="#path1" fill="red">超出路径文字不再渲染textpath>
text>
svg>
html>
dx,dy属性:切线和法线方向的偏移量
例如修改x属性,可以让文字右移动
DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8"/>
<title>textpathtitle>
head>
<body>
<svg xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg" width="600" height="300">
<path id="path1" d="M 100 200 Q 200 100 300 200 T 500 200" stroke="rgb(0,255,0)" fill="none">path>
<text style="font-size:24px;" x="100">
<textpath xlink:href="#path1" fill="red">超出路径文字不再渲染textpath>
text>
svg>
html>
示例2 修改dy属性 可以往下移动
DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8"/>
<title>textpathtitle>
head>
<body>
<svg xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg" width="600" height="1000">
<path id="path1" d="M 100 200 Q 200 100 300 200 T 500 200" stroke="rgb(0,255,0)" fill="none">path>
<text style="font-size:24px;" dy="20">
<textpath xlink:href="#path1" fill="red">超出路径文字不再渲染textpath>
text>
svg>
html>
其中 text-anchor="middle" 指的是 文本长度的中间位置处于底部path的头部位置;
但是使用 startOffset="50%" 偏移量,可以把这个位置再调整回来,如:
DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8"/>
<title>textpathtitle>
head>
<body>
<svg xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg" width="600" height="1000">
<path id="path1" d="M 100 200 Q 200 100 300 200 T 500 200" stroke="rgb(0,255,0)" fill="none">path>
<text style="font-size:24px;" text-anchor="middle">
<textpath xlink:href="#path1" fill="red" startOffset="50%">超出路径文字不再渲染textpath>
text>
svg>
html>
因此,同时设置了尾部对齐 text-anchor="end" 和 偏移量startOffset="100%" ,就会看到文字的末尾和路径的末尾对齐
DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8"/>
<title>textpathtitle>
head>
<body>
<svg xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg" width="600" height="1000">
<path id="path1" d="M 100 200 Q 200 100 300 200 T 500 200" stroke="rgb(0,255,0)" fill="none">path>
<text style="font-size:24px;" text-anchor="end">
<textpath xlink:href="#path1" fill="red" startOffset="100%">超出路径文字不再渲染textpath>
text>
svg>
html>
使用超链接