上篇文章讲了编程式调用IOC,但是一般不会直接使用DefaultListableBeanFactory,而是使用其子类比如FileSystemXmlApplicationContext
FileSystemXmlApplicationContext fileSystemXmlApplicationContext = new FileSystemXmlApplicationContext("/Users/javaeeLearn/springIOC/src/main/resources/spring-mvc.xml");
User user = fileSystemXmlApplicationContext.getBean("user", User.class);
user.setName("111");
System.out.println(user.toString());
我们从上面的代码入手分析spring是如何定位到spring-mvc.xml并且将其转化为Resource的,因为spring支持从各种类型的URI获取文件(比如classpath)并将其转换为Resource,所以并不是通过路径找到文件那么简单
什么是Resource
在spring中,将各种记录信息的载体抽象为资源,比如文件对应FileSystemResource,classpath对应ClassPathResource,这里面用到了策略模式,详细参考Spring 资源访问剖析
FileSystemXmlApplicationContext里面的代码非常简单,除了构造方法就只有个getResourceByPath方法
先进入到FileSystemXmlApplicationContext的构造方法
public FileSystemXmlApplicationContext(String[] configLocations, boolean refresh, ApplicationContext parent)
throws BeansException {
super(parent);
setConfigLocations(configLocations);
if (refresh) {
refresh();
}
}
可以看到这里面最核心的就是refresh方法,spring就是从这个方法开始初始化,犹如盘古开天辟地
,这个地方使用了模板方法模式
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
// 刷新前做一些准备.
prepareRefresh();
//告诉子类刷新内部的bean factory.
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();
// Prepare the bean factory for use in this context.
prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
try {
//设置 BeanFactoy 的后置处理
postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
// 注册bean
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// 注册 Bean 的后处理器,在 Bean 创建过程中调用
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// 对上下文中的消息源进行初s化
initMessageSource();
// 初始化上下文中的事件机制
initApplicationEventMulticaster();
// 初始化其他的特殊 Bean
onRefresh();
// 检查监听 Bean 并且将这些 Bean 向容器注册
registerListeners();
// 实例化所有的(non-lazy-init)单例bean
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
// 发布容器事件,结束 Refresh 过程
finishRefresh();
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
// 为防止 Bean 资源占用,在异常处理中,销毁巳经在前面过程中生成的单件 Bean
destroyBeans();
//重置'active'标志
cancelRefresh(ex);
throw ex;
}
finally {
// Reset common introspection caches in Spring's core, since we
// might not ever need metadata for singleton beans anymore...
resetCommonCaches();
}
}
先看资源定位时序图
可以看到里面有个XmlBeanDefinitionReader,看这个名字就知道这个类是负责xml读取的,
进入XmlBeanDefinitionReader可以看到最后调用了AbstractBeanDefinitionReader#loadBeanDefinitions(java.lang.String, java.util.Set方法
public int loadBeanDefinitions(String location, Set actualResources) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
ResourceLoader resourceLoader = getResourceLoader();
if (resourceLoader == null) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(
"Cannot import bean definitions from location [" + location + "]: no ResourceLoader available");
}
if (resourceLoader instanceof ResourcePatternResolver) {
// Resource pattern matching available.
Resource[] resources = ((ResourcePatternResolver) resourceLoader).getResources(location);
int loadCount = loadBeanDefinitions(resources);
//省略部份代码
}
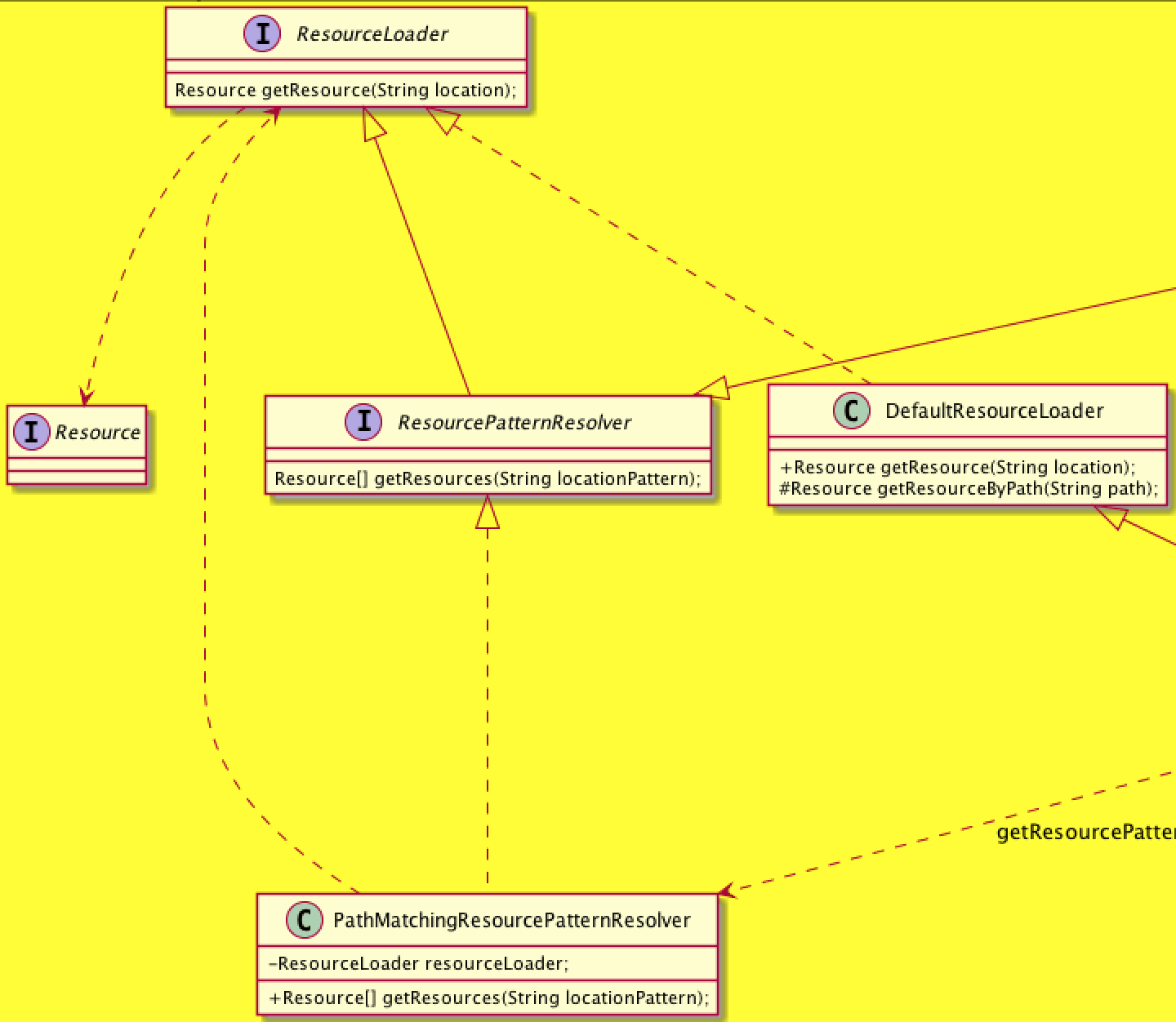
可以看到最后还是借用了ResourceLoader来处理资源的定位,下面贴上ResourceLoader基本的UML结构图
很多容器都实现了ResourceLoader,比如我们后面要说的AbstractApplicationContext,主要实现了这个接口,容器就用了资源定位的能力
进入DefaultResourceLoader#getResource方法,可以看到根据不同的路径转换为不同的资源,其中的getResourceByPath就是我们在FileSystemXmlApplicationContext看到的方法
public Resource getResource(String location) {
//省略部份代码
if (location.startsWith("/")) {
return getResourceByPath(location);
}
else if (location.startsWith(CLASSPATH_URL_PREFIX)) {
return new ClassPathResource(location.substring(CLASSPATH_URL_PREFIX.length()), getClassLoader());
}
else {
try {
// Try to parse the location as a URL...
URL url = new URL(location);
return new UrlResource(url);
}
catch (MalformedURLException ex) {
// No URL -> resolve as resource path.
return getResourceByPath(location);
}
}
}
至此spring定位资源的流程就完成了,下一步是将资源转化为BeanDefinition
附上一个资源定位相关的主要类的UML结构图