一、沙盒机制
1.什么是沙盒
通俗的说,就是将一个应用程序的所有的非代码文件放在一个文件夹里(沙盒),应用程序只能从该文件系统读取文件,不能去其他地方访问。
每一个iOS应用程序都会为自己创建一个文件系统目录。这个独立封闭、安全的空间,叫做沙盒。
2.打开模拟器的沙盒目录
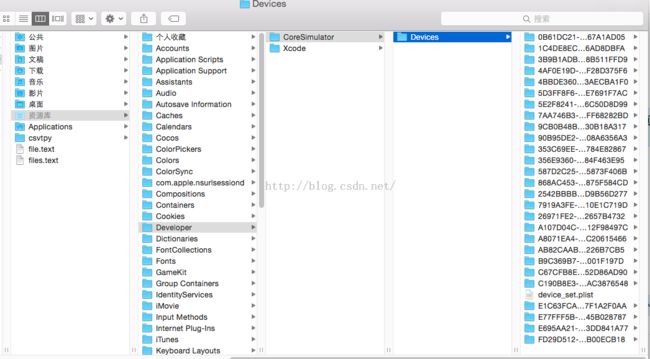
点击finder----点击菜单栏的前往----按住alt,出现了隐藏的资源库选项----点击资源库----developer----CoreSimulator----Devices,然后发现这里有很多的一长串字母的文件,
根据时间找到最新的一个文件打开。
或者在终端写 : defaults write com.apple.finder AppleShowAllFiles -bool true ,也可以显示隐藏文件
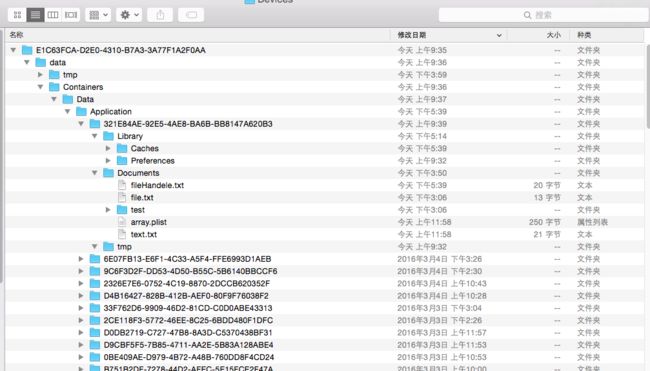
看到里面有三个并列文件夹 Library,Documents,tmp
Document:
只有用户生成的文件、其他数据及其他程序不能重新创建的文件,应该保存在/Documents 目录下面,并将通过iCloud自动备份,应该将所有的应用程序数据文件写入到这个目录下。
Library
iTunes不会自动备份此目录
这个目录下有两个子目录:Caches 和 Preferences
Caches
可以重新下载或者重新生成的数据应该保存在/Library/Caches 目录下面。举个例子,比如杂志、新闻、地图应用使用的数据库缓存文件和可下载内容应该保存到这个文件夹。此目录下不会再应用退出时删除。
Preferences
目录包含应用程序的偏好设置文件。您不应该直接创建偏好设置文件,而是应该使用NSUserDefaults类来取得和设置应用程序的偏好
tmp
只是临时使用的数据应该保存到/tmp 文件夹。尽管 iCloud 不会备份这些文件,但在应用在使用完这些数据之后要注意随时删除,避免占用用户设备的空间,保存应用程序再次启动过程中不需要的信息
二、文件的写入与读取
得到沙盒路径的方法
写在SandBoxPaths中,外部可调用
//得到docments路径
+(NSString *)documentsPath
{
NSArray *docArray = NSSearchPathForDirectoriesInDomains(NSDocumentDirectory, NSUserDomainMask, YES);
return docArray[0];
}
//library
+(NSString *)libraryPath
{
NSArray *libArray = NSSearchPathForDirectoriesInDomains(NSLibraryDirectory, NSUserDomainMask, YES);
return libArray[0];
}
//library/cache
+(NSString *)cachePath
{
NSArray *cacheArray = NSSearchPathForDirectoriesInDomains(NSCachesDirectory, NSUserDomainMask, YES);
return cacheArray[0];
}
//library/perfrence 系统维护的,一般人为不会去动这个文件夹
+(NSString *)perfrencePath
{
NSArray *perfrenceArr = NSSearchPathForDirectoriesInDomains(NSPreferencePanesDirectory, NSUserDomainMask, YES);
return perfrenceArr[0];
}
//也可以通过拼接方式得到library/perfrence
NSArray *libPath = NSSearchPathForDirectoriesInDomains(NSLibraryDirectory, NSUserDomainMask, YES);
NSLog(@"%@",libPath[0]);
NSString *perPath = [libPath[0]stringByAppendingString:@"Preferences"];
//tmp路径
+(NSString *)tmpPath
{
NSString *tmpStr = NSTemporaryDirectory();
return tmpStr;
}
//app路径
NSString *appPath = [NSBundle mainBundle].resourcePath;
//程序包中的一个图片资源
NSString *imagePath = [[NSBundle mainBundle]pathForResource:@"myImage" ofType:@"png"];
```
通过拼接方式获得路径
//沙盒主路径
NSString *homeStrPath = NSHomeDirectory();
NSLog(@"homePath = %@",homeStrPath);
//得到沙盒下的lib路径
NSString *libPath = [homeStrPath stringByAppendingPathComponent:@"Library"];
NSLog(@"lib : %@",libPath);
//得到沙盒下document路径
NSString *docPath = [homeStrPath stringByAppendingPathComponent:@"Documents"];
写入和读取文件
//写入文件
-(void)writeString
{
NSString *str = @"将要写入的数据";
//拼接字符串,构造数据将要存储的位置
NSString *path = [[SandBoxPaths documentsPath]stringByAppendingString:@"/text.txt"];
//将数据写入路径下
//核心方法writeToFile,可以写入字符串,数组,字典等
//atomically:YES,会先写入一个中间临时文件,完成后再存入目标文件
BOOL isWrite = [str writeToFile:path atomically:YES encoding:NSUTF8StringEncoding error:nil];
if (isWrite) {
NSLog(@"写入成功,%@",path);
}
else
NSLog(@"写入失败");
}
//读取文件
-(void)readFile:(NSString*)path
{
//path的文件里面是什么格式,就用什么格式去取
//路径就是定位到文件的路径
//NSArray *arr = [NSArray arrayWithContentsOfFile:path];
NSString *str = [NSString stringWithContentsOfFile:path encoding:NSUTF8StringEncoding error:nil];
NSLog(@"读取:%@",str);
}
##三、文件管理器NSFileManger与文件对接器NSFileHandle,还有归档
#####1.文件管理器
文件管理器主要是对文件进行创建、删除、改名、获取文件信息等操作
文件连接器主要对文件内容进行读取和写入
//FILEmanager使用
-(void)myFilemanager
{
//得到路径
NSString* path = [[SandBoxPaths documentsPath]stringByAppendingPathComponent:@"test"];
NSString *pathTest = [[SandBoxPaths documentsPath]stringByAppendingPathComponent:@"text.txt"];
NSString *pathDst = [[SandBoxPaths documentsPath]stringByAppendingPathComponent:@"test/text1.txt"];
NSString *pathStrFile = [[SandBoxPaths documentsPath]stringByAppendingPathComponent:@"file.txt"];
NSString *str = @"sssssssssssss";
NSData *data = [str dataUsingEncoding:NSUTF8StringEncoding];
//创建文件管理器
NSFileManager *fileM = [NSFileManager defaultManager];
//创建目录
//路径Path
//是否自动创建
//attributes权限设置
BOOL isCreate = [fileM createDirectoryAtPath:path withIntermediateDirectories:YES attributes:nil error:nil];
if (isCreate) {
NSLog(@"成功:,%@",path);
}
else
NSLog(@"失败");
//创建文件并写入数据
[fileM createFileAtPath:pathStrFile contents: data attributes:nil];
//从文件中读取
NSData *getData = [fileM contentsAtPath:pathStrFile];
NSLog(@"%@",[[NSString alloc]initWithData:getData encoding:NSUTF8StringEncoding]);
//移动文件位置
BOOL isMove = [fileM moveItemAtPath:pathTest toPath:pathDst error:nil];
if (isMove) {
NSLog(@"成功移动");
}
else
NSLog(@"移动失败");
//复制文件
BOOL isCopy = [fileM copyItemAtPath:pathDst toPath:pathTest error:nil];
if (isCopy) {
NSLog(@"复制成功");
}
else
NSLog(@"复制失败");
//比较文件是否相同
BOOL isEqual = [fileM contentsEqualAtPath:pathTest andPath:pathDst];
if (isEqual) {
NSLog(@"文件内容相同");
}
else
NSLog(@"文件内容不同");
//移除文件
BOOL isRemove = [fileM removeItemAtPath:pathDst error:nil];
if (isRemove) {
NSLog(@"移除成功");
}
else
NSLog(@"移除失败");
//文件是否存在
BOOL isExist = [fileM fileExistsAtPath:pathDst];
if (isExist) {
NSLog(@"文件存在");
}
else
NSLog(@"文件不存在");
}
#####2.文件对接器,NSFileHandle
//NSfileHandle的使用
//首次使用时,要先创建需要操作的文件
NSString *path = [[SandBoxPaths documentsPath]stringByAppendingPathComponent:@"fileHandele.txt"];
NSString *contentStr = @"12345678901234567890";
NSData *contentData = [contentStr dataUsingEncoding:NSUTF8StringEncoding];
NSFileManager *manager = [NSFileManager defaultManager];
//先判断文件是否存在,如果不存在再创建
if ([manager fileExistsAtPath:path]) {
NSLog(@"文件已经存在");
}
else
{
//创建文件
[manager createFileAtPath:path contents:contentData attributes:nil];
}
//创建准备读取的handle对象
NSFileHandle *readHandle =[NSFileHandle fileHandleForReadingAtPath:path];
//得到可读的内容的长度,节点移动到末尾
NSUInteger length = [[readHandle availableData]length];
NSLog(@"%ld",length);
//跳到指定的偏移量
[readHandle seekToFileOffset:5];
//读取特定长度,从当前节点到指定长度,节点移动到读取末尾
NSData *lengthData = [readHandle readDataOfLength:11];
NSString *lengthStr = [[NSString alloc]initWithData:lengthData encoding:NSUTF8StringEncoding];
NSLog(@"lengthStr = %@",lengthStr);
//得到从当前节点到最后的可读取的内容,节点移动到最后
NSData *availableData = [readHandle availableData];
NSString *availableStr = [[NSString alloc]initWithData:availableData encoding:NSUTF8StringEncoding];
NSLog(@"avStr = %@",availableStr);
//跳到指定的偏移量,移动回2处,也就是从第三个位置开始读
[readHandle seekToFileOffset:2];
//完整的读取文件,从当前节点读到末尾
NSData *endData = [readHandle readDataToEndOfFile];
NSString *endStr = [[NSString alloc]initWithData:endData encoding:NSUTF8StringEncoding];
NSLog(@"endStr = %@",endStr);
//创建一个可以写入的fileHandle
NSFileHandle *writeHandle = [NSFileHandle fileHandleForWritingAtPath:path];
//改变偏移量
[writeHandle seekToFileOffset:4];
//写入
NSString *writeStr = @"abc";
NSData *writeData = [writeStr dataUsingEncoding:NSUTF8StringEncoding];
[writeHandle writeData:writeData];
//跳到指定的偏移量
[readHandle seekToFileOffset:0];
//读取
NSString *allStr = [NSString stringWithContentsOfFile:path encoding:NSUTF8StringEncoding error:nil];
NSLog(@"allStr = %@",allStr);
#####3.归档与反归档
归档的作用,就是将复杂对象存储进文件,复杂对象就是如我们自己定义的person类,student类,不能用writeToFile写入文件中。
我们需要先将复杂对象转换为NSData类型,用writeToFile存入文件
取出时再通过反归档,把NSData类型恢复成复杂对象
归档时,person类等要遵守协议,实现归档和反归档的方法
import "Person.h"
@implementation Person
//序列化操作,归档
//实际上是对当前类对象所有的属性进行归档
//协议方法在我们归档的时候自动调用
-(void)encodeWithCoder:(NSCoder *)aCoder
{
[aCoder encodeObject:self.name forKey:@"name"];
[aCoder encodeObject:self.sex forKey:@"sex"];
}
//反归档
-(instancetype)initWithCoder:(NSCoder *)aDecoder
{
self = [super init];
if (self) {
self.name = [aDecoder decodeObjectForKey:@"name"];
self.sex = [aDecoder decodeObjectForKey:@"sex"];
}
return self;
}
pragma mark -- 归档,反归档
-(void)archiver
{
Person *firstPer = [[Person alloc]init];
firstPer.name = @"wna";
firstPer.sex = @"m";
//创建一个mutableData,用于保存归档后的对象
NSMutableData *mutableData = [NSMutableData data];
//创建归档工具
NSKeyedArchiver *archiver = [[NSKeyedArchiver alloc]initForWritingWithMutableData:mutableData];
//归档
[archiver encodeObject:firstPer forKey:@"person"];
//结束
//只有调用了此方法,才会将归档好的对象装换为NSData
[archiver finishEncoding];
//拼接写入沙盒路径
NSString *cachesPath2 = [[NSSearchPathForDirectoriesInDomains(NSCachesDirectory, NSUserDomainMask, YES)objectAtIndex:0]
stringByAppendingPathComponent:@"person.txt"];
//写入沙盒
[mutableData writeToFile:cachesPath2 atomically:YES];
}
//反归档
-(void)unArchiver
{
//拼接写入沙盒路径
NSString *cachesPath2 = [[NSSearchPathForDirectoriesInDomains(NSCachesDirectory, NSUserDomainMask, YES)objectAtIndex:0]
stringByAppendingPathComponent:@"person.txt"];
//反归档
//从文件路径读取
NSData *fileData = [NSData dataWithContentsOfFile:cachesPath2];
//反归档工具
NSKeyedUnarchiver *unArchiver = [[NSKeyedUnarchiver alloc]initForReadingWithData:fileData];
//反归档成对象,key要对应
Person *secondPer = [unArchiver decodeObjectForKey:@"person"];
//反归档结束
[unArchiver finishDecoding];
NSLog(@"person = %@",secondPer.name);
}
这里再附加一个把UIImage转换为NSString的方法
//UIImage转换为NSString
-(NSString)imageToStringWithImage:(UIImage)image
{
//先将image转换为data类型,后面参数是品质
NSData imageData = UIImageJPEGRepresentation(image, 1.0);
//再讲NSData转换为NSString
NSString string = [imageData base64EncodedStringWithOptions:NSDataBase64Encoding64CharacterLineLength];
return string;
}
//将base64的字符串转换为图片
-(UIImage)base64StringToImage:(NSString)base64Str
{
//将字符串转换为NSData
NSData *imageData = [[NSData alloc]initWithBase64EncodedString:base64Str
options:NSDataBase64DecodingIgnoreUnknownCharacters];
//NSData到图片
UIImage *image = [UIImage imageWithData:imageData];
return image;
}