foreach用法和之前的数组遍历是一样的,只不过这里遍历的key是属性名,value是属性值。在类外部遍历时,只能遍历到public属性的,因为其它的都是受保护的,类外部不可见。
class HardDiskDrive {
public $brand;
public $color;
public $cpu;
public $workState;
protected $memory;
protected $hardDisk;
private $price;
public function __construct($brand, $color, $cpu, $workState, $memory, $hardDisk, $price) {
$this->brand = $brand;
$this->color = $color;
$this->cpu = $cpu;
$this->workState = $workState;
$this->memory = $memory;
$this->hardDisk = $hardDisk;
$this->price = $price;
}
}
$hardDiskDrive = new HardDiskDrive('希捷', 'silver', 'tencent', 'well', '1T', 'hard', '$456');
foreach ($hardDiskDrive as $property => $value) {
var_dump($property, $value);
echo '
';
}输出结果为:
string(5) "brand" string(6) "希捷"
string(5) "color" string(6) "silver"
string(3) "cpu" string(7) "tencent"
string(9) "workState" string(4) "well" 通过输出结果我们也可以看得出来常规遍历是无法访问受保护的属性的。
如果我们想遍历出对象的所有属性,就需要控制foreach的行为,就需要给类对象,提供更多的功能,需要继承自Iterator的接口:
为什么一个类只要实现了Iterator迭代器,其对象就可以被用作foreach的对象呢?其实原因很简单,在对PHP实例对象使用foreach语法时,会检查这个实例有没有实现Iterator接口,如果实现了,就会通过内置方法或使用实现类中的方法模拟foreach语句。
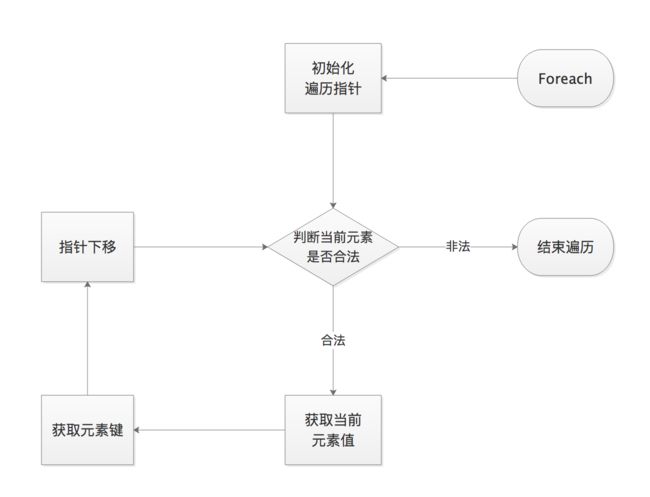
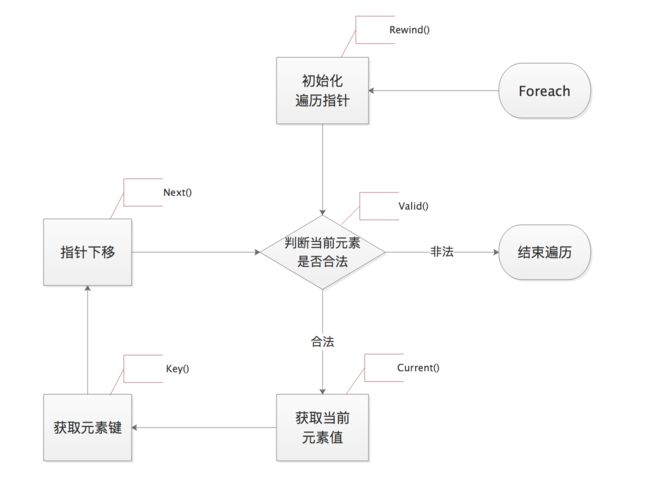
该接口,实现了foreach需要的每个操作。foreach的执行流程如下图:
看图例中,foreach中有几个关键步骤:5个。
而Iterator迭代器中所要求的实现的5个方法,就是用来帮助foreach,实现在遍历对象时的5个关键步骤:
当foreach去遍历对象时, 如果发现对象实现了Ierator接口, 则执行以上5个步骤时, 不是foreach的默认行为, 而是调用对象的对应方法即可:
示例代码:
class Team implements Iterator {
//private $name = 'itbsl';
//private $age = 25;
//private $hobby = 'fishing';
private $info = ['name' => 'itbsl', 'age' => 25, 'hobby' => 'fishing'];
public function rewind()
{
reset($this->info); //重置数组指针
}
public function valid()
{
//如果为null,表示没有元素,返回false
//如果不为null,返回true
return !is_null(key($this->info));
}
public function current()
{
return current($this->info);
}
public function key()
{
return key($this->info);
}
public function next()
{
return next($this->info);
}
}
$team = new Team();
foreach ($team as $property => $value) {
var_dump($property, $value);
echo '
';
}输出结果为:
string(4) "name" string(5) "itbsl"
string(3) "age" int(25)
string(5) "hobby" string(7) "fishing"