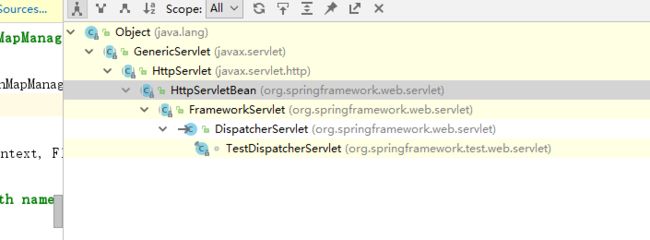
先看看关键servlet:DispatcherServlet的继承结构图
我们先从GenericServlet这个类看起。
1.这个类实现了servlet接口
2.看关键代码
public void init(ServletConfig config) throws ServletException {
this.config = config;
this.init();
}
public void init() throws ServletException {
}
这里init(ServletConfig config)是实现servlet的方法,init()是新建的方法。
而由于实现的方法里面,调用了init()这个方法,所以后续继承了GenericServlet 这个类的类,只要重写init()方法,即可对servlet的初始化部分进行修改。
我们再来看HttpServletBean这个类。
1.看关键代码
public final void init() throws ServletException {
if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
this.logger.debug("Initializing servlet '" + this.getServletName() + "'");
}
try {
PropertyValues pvs = new HttpServletBean.ServletConfigPropertyValues(this.getServletConfig(), this.requiredProperties);
BeanWrapper bw = PropertyAccessorFactory.forBeanPropertyAccess(this);
ResourceLoader resourceLoader = new ServletContextResourceLoader(this.getServletContext());
bw.registerCustomEditor(Resource.class, new ResourceEditor(resourceLoader, this.getEnvironment()));
this.initBeanWrapper(bw);
bw.setPropertyValues(pvs, true);
} catch (BeansException var4) {
this.logger.error("Failed to set bean properties on servlet '" + this.getServletName() + "'", var4);
throw var4;
}
this.initServletBean();
if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
this.logger.debug("Servlet '" + this.getServletName() + "' configured successfully");
}
}
这里用final修饰了init()方法(表示方法不可以被重写),那么继承了当前类的servlet,初始化的时候,必须调用这里的init()方法。也就是说,DispatcherServlet初始化的时候,是调用这个方法进行初始化的。
这里的关键代码是:this.initServletBean();
方法在frameServlet类里重写。
protected final void initServletBean() throws ServletException { this.getServletContext().log("Initializing Spring FrameworkServlet '" + this.getServletName() + "'"); if (this.logger.isInfoEnabled()) { this.logger.info("FrameworkServlet '" + this.getServletName() + "': initialization started"); } long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); try { this.webApplicationContext = this.initWebApplicationContext(); this.initFrameworkServlet(); } catch (ServletException var5) { this.logger.error("Context initialization failed", var5); throw var5; } catch (RuntimeException var6) { this.logger.error("Context initialization failed", var6); throw var6; } if (this.logger.isInfoEnabled()) { long elapsedTime = System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime; this.logger.info("FrameworkServlet '" + this.getServletName() + "': initialization completed in " + elapsedTime + " ms"); } }
然后看这个方法:initWebApplicationContext
源码:
1 protected WebApplicationContext initWebApplicationContext() { 2 WebApplicationContext rootContext = WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(this.getServletContext()); 3 WebApplicationContext wac = null; 4 if (this.webApplicationContext != null) { 5 wac = this.webApplicationContext; 6 if (wac instanceof ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) { 7 ConfigurableWebApplicationContext cwac = (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext)wac; 8 if (!cwac.isActive()) { 9 if (cwac.getParent() == null) { 10 cwac.setParent(rootContext); 11 } 12 13 this.configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(cwac); 14 } 15 } 16 } 17 18 if (wac == null) { 19 wac = this.findWebApplicationContext(); 20 } 21 22 if (wac == null) { 23 wac = this.createWebApplicationContext(rootContext); 24 } 25 26 if (!this.refreshEventReceived) { 27 this.onRefresh(wac); 28 } 29 30 if (this.publishContext) { 31 String attrName = this.getServletContextAttributeName(); 32 this.getServletContext().setAttribute(attrName, wac); 33 if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) { 34 this.logger.debug("Published WebApplicationContext of servlet '" + this.getServletName() + "' as ServletContext attribute with name [" + attrName + "]"); 35 } 36 } 37 38 return wac; 39 }
看27行的this.onRefresh(wac); 这个方法在DispatcherServlet类里被重写。
看代码:
1 protected void onRefresh(ApplicationContext context) { 2 this.initStrategies(context); 3 } 4 5 protected void initStrategies(ApplicationContext context) { 6 this.initMultipartResolver(context); 7 this.initLocaleResolver(context); 8 this.initThemeResolver(context); 9 this.initHandlerMappings(context); 10 this.initHandlerAdapters(context); 11 this.initHandlerExceptionResolvers(context); 12 this.initRequestToViewNameTranslator(context); 13 this.initViewResolvers(context); 14 this.initFlashMapManager(context); 15 }
这个refresh里面,有一个initStrategies方法,初始化策略,这里就讲所有处理需要的准备工具准备完毕。
前面所有的代码部分都是servlet的init()相关的,也就是DispatcherServlet的初始化过程,这个初始化过程是tomcat容器加载应用的时候进行的。
应用部署完毕,客户端向服务器请求的时候,则tomcat会将用户的请求封装成httpServletRequest,然后找到service()方法进行处理,下面来说说service方法。
service方法在FrameworkServlet重写。
代码:
1 protected void service(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { 2 if (HttpMethod.PATCH.matches(request.getMethod())) { 3 this.processRequest(request, response); 4 } else { 5 super.service(request, response); 6 } 7 8 }
protected final void processRequest(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
Throwable failureCause = null;
LocaleContext previousLocaleContext = LocaleContextHolder.getLocaleContext();
LocaleContext localeContext = this.buildLocaleContext(request);
RequestAttributes previousAttributes = RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes();
ServletRequestAttributes requestAttributes = this.buildRequestAttributes(request, response, previousAttributes);
WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request);
asyncManager.registerCallableInterceptor(FrameworkServlet.class.getName(), new FrameworkServlet.RequestBindingInterceptor());
this.initContextHolders(request, localeContext, requestAttributes);
try {
this.doService(request, response);
} catch (ServletException var17) {
failureCause = var17;
throw var17;
} catch (IOException var18) {
failureCause = var18;
throw var18;
} catch (Throwable var19) {
failureCause = var19;
throw new NestedServletException("Request processing failed", var19);
} finally {
this.resetContextHolders(request, previousLocaleContext, previousAttributes);
if (requestAttributes != null) {
requestAttributes.requestCompleted();
}
if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
if (failureCause != null) {
this.logger.debug("Could not complete request", (Throwable)failureCause);
} else if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
this.logger.debug("Leaving response open for concurrent processing");
} else {
this.logger.debug("Successfully completed request");
}
}
this.publishRequestHandledEvent(request, response, startTime, (Throwable)failureCause);
}
}
从这里可以看到processRequest方法有调用this.doService(request, response); ,而doService()方法,在DispatcherServlet里面实现。
servlet初始化init()方法只在应用加载的时候,调用一次,而service方法,用户每次请求的时候,都会调用,所以,doService方法,才是关键。