一、磁盘及分区
1.检测并确认新硬盘
# fdisk -l
Disk /dev/sda:21.5 GB, 21474836480 bytes
255 heads, 63 sectors/track, 2610 cylinders
Units = cylinders of 16065 * 512 = 8225280bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes /512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512bytes
Disk identifier: 0x00078511
Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System
/dev/sda1 * 1 64 512000 83 Linux
Partition 1 does not end on cylinderboundary.
/dev/sda2 64 2611 20458496 8e Linux LVM
Disk /dev/sdb:21.5 GB, 21474836480 bytes
255 heads, 63 sectors/track, 2610 cylinders
Units = cylinders of 16065 * 512 = 8225280bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes /512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512bytes
Disk identifier: 0x00000000
Disk /dev/sdc:26.8 GB, 26843545600 bytes
255 heads, 63 sectors/track, 3263 cylinders
Units = cylinders of 16065 * 512 = 8225280bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes /512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512bytes
Disk identifier: 0x00000000
2.规划硬盘中的分区
# fdisk /dev/sdb
Device contains neither a valid DOSpartition table, nor Sun, SGI or OSF disklabel
Building a new DOS disklabel with diskidentifier 0xae03f6ac.
Changes will remain in memory only, untilyou decide to write them.
After that, of course, the previous contentwon't be recoverable.
Warning:invalid flag 0x0000 of partition table 4 will be corrected by w(rite)
WARNING:DOS-compatible mode is deprecated. It's strongly recommended to
switch off the mode (command 'c') and change display units to
sectors (command 'u').
Command (m forhelp): p ←查看分区信息,看是否创建过分区,以免重复
Disk /dev/sdb:21.5 GB, 21474836480 bytes
255 heads, 63 sectors/track, 2610 cylinders
Units = cylinders of 16065 * 512 = 8225280bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes /512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512bytes
Disk identifier: 0xae03f6ac
Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System
Command (m forhelp): n ←新建分区
Command action
e extended
p primary partition (1-4)
p ←选择主分区
Partition number (1-4): 1 ←选择分区号
First cylinder (1-2610, default 1):
Using defaultvalue 1
Last cylinder, +cylinders or +size{K,M,G}(1-2610, default 2610): +100M ←分区的大小
Command (m forhelp): p ←查看是否创建成功
Disk /dev/sdb:21.5 GB, 21474836480 bytes
255 heads, 63 sectors/track, 2610 cylinders
Units = cylinders of 16065 * 512 = 8225280bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes /512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512bytes
Disk identifier: 0xae03f6ac
Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System
/dev/sdb1 1 14 112423+ 83 Linux
Command (m forhelp): w ←保存并退出
The partition table has been altered!
Calling ioctl() to re-read partition table.
Syncing disks.
3.删除分区
# fdisk /dev/sdb
WARNING:DOS-compatible mode is deprecated. It's strongly recommended to
switch off the mode (command 'c') and change display units to
sectors (command 'u').
Command (m forhelp): p ←查看分区信息
Disk /dev/sdb:21.5 GB, 21474836480 bytes
255 heads, 63 sectors/track, 2610 cylinders
Units = cylinders of 16065 * 512 = 8225280bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes /512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512bytes
Disk identifier: 0xae03f6ac
Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System
/dev/sdb1 1 14 112423+ 83 Linux
/dev/sdb2 15 21 56227+ 83 Linux
Command (m forhelp): d ←删除分区
Partition number (1-4): 2 ←选择要删除的分区
Command (m forhelp): w ←保存并退出
The partition table has been altered!
Calling ioctl() to re-read partition table.
Syncing disks.
二、LVM
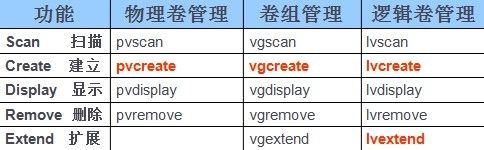
l 介绍最常用的几个命令:
1)pvcreate用于将分区或整个硬盘转换成物理卷,主要是添加LVM属性信息并划分PE存储单位。该命令需要使用分区或硬盘设备名作为参数
2)vgcreate用于将一个或多个物理卷创建为一个卷组,第一个命令参数指定定义的新卷组名称,其后依次指定需要加入到该卷组的物理卷作为参数
3)lvcreate用于从指定的卷组中分割空间,以创建新的逻辑卷。需要指定逻辑卷大小、名称及所在的卷组名作为参数
4)lvextend用于动态扩展逻辑卷的空间,当目前使用的逻辑卷空间不足时,可以从所在卷组中分割额外的空间进行扩展
# pvcreate /dev/sdb1 ←转化物理卷
Physical volume "/dev/sdb1"successfully created
# pvcreate /dev/sdc1 ←转化物理卷
Physical volume "/dev/sdc1"successfully created
# vgcreate group /dev/sdb1 /dev/sdc1 ←创建组group
Volume group "group" successfullycreated
# lvcreate -L 50M -n lv_data group ←创建逻辑卷lv_data
Rounding up size to full physical extent 52.00 MiB
Logical volume "lv_data" created
# lvextend -L +100M /dev/group/lv_data ←扩展逻辑卷
Extending logical volume lv_data to 152.00 MiB
Logical volume lv_data successfully resized
格式化文件系统有3中方法:
mkfs -t ext4 /dev/卷组名/逻辑卷名
mkfs.ext4 /dev/卷组名/逻辑卷名
mke2fs -t ext4 /dev/卷组名/逻辑卷名
# mkfs.ext4 /dev/group/lv_data
mke2fs 1.41.12 (17-May-2010)
Filesystem label=
OS type: Linux
Block size=1024 (log=0)
Fragment size=1024 (log=0)
Stride=0 blocks, Stripe width=0 blocks
38912 inodes, 155648 blocks
7782 blocks (5.00%) reserved for the superuser
First data block=1
Maximum filesystem blocks=67371008
19 block groups
8192 blocks per group, 8192 fragments pergroup
2048 inodes per group
Superblock backups stored on blocks:
8193, 24577, 40961, 57345, 73729
Writing inodetables: done
Creating journal (4096 blocks): done
Writing superblocks and filesystemaccounting information: done
This filesystemwill be automatically checked every 37 mounts or
180 days, whichever comes first. Use tune2fs -c or -i to override.
三、挂载
Linux系统中,文件系统创建后,还需将其安装到Linux目录树的某个位置上才能使用,这个过程称为挂载,文件系统所挂载到的目录称为挂载点。文件系统使用完毕,还可对其进行卸载
1.挂载文件系统
在Linux系统中,磁盘设备被挂接到一个已存在的目录上,以后的磁盘的存取就变成了对该挂接目录的读写访问。通常选择已存在的空目录作为挂接目录,因为如果挂接目录已经包含文件,在挂接操作完成后,原文件将临时被挂接磁盘中的文件覆盖,直到从系统中卸载该磁盘为止。文件系统的挂载,可以在系统引导过程中自动加载,也可以使用命令手工挂载
# mkdir /data ←创建挂载点目录
# mount /dev/group/lv_data /data ←挂载
# cd /data
# ll
total 12
drwx------ 2 root root 12288 Aug 20 04:47lost+found
2.卸载文件系统
如果系统已挂接的磁盘不再使用,为了节省系统资源,可以将该磁盘从系统中卸下。与挂载相比,卸载文件系统简单很多,卸载文件系统使用umount命令
# umount /dev/group/lv_data ←卸载
# cd /data
# ll
total 0