一 、封装使用
封装:
#封装 变量和函数都放在类中,广义
#狭义的封装:吧一些变量或者方法隐藏起来,不对外公开,只提供内部使用
#共有的
#私有的:__名字
class Person:
__country = '中国'
# print(Person.__country)#AttributeError: type object 'Person' has no attribute '__country'
#私有属性,只能在类的内部使用,不能在类的外部使用
print(Person.__dict__)# '_Person__country'
#_Person__country
print(Person._Person__country)#中国
#如果非要在类的外部调用一个私有的名字,name必须是在私有的名字前加_类名__私有的名字
#不能使用上面这种方式去调用私有的变量
#私有的变量:
在类的内部如果使用__变量的形式会发生变形,python会自动加上_类名
class Person:
__country = '中国'
# print(Person.__country)#AttributeError: type object 'Person' has no attribute '__country'
#私有属性,只能在类的内部使用,不能在类的外部使用
# print(Person.__dict__)# '_Person__country'
# #_Person__country
# print(Person._Person__country)#中国
#如果非要在类的外部调用一个私有的名字,name必须是在私有的名字前加_类名__私有的名字
#不能使用上面这种方式去调用私有的变量
Person.__name = 'XXX'
print(Person.__name) #在类的外部不能定义一个私有的变量
print(Person.__dict__)
class Person:
__country = '中国' #私有静态属性
def __init__(self,name,pwd):
self.name = name
self.__pwd = pwd #私有的对象属性
def login(self):
print(self.__dict__)
if self.name =='alex' and self.__pwd =='alex3714':
print('ok')
alex = Person('alex','alex3714')
alex.login()
print(alex.__dict__)
内部方法:
class Person:
def __init__(self):pass
def __eat(self):
print('thins is eating')
alex = Person()
alex.__eat()
#静态属性、对象属性、方法(动态属性)前面加上双下划线会变成私有的
#私有的特定就是只能在类的内部调用,不能再类的外部使用
二、类中的装饰器方法
classmethod staticmethod property
#三个装饰器函数
from math import pi
class Circle:
def __init__(self,r):
self.r = r
@property
def area(self):
return self.r **2 * pi
@property
def perimeter(self):
return self.r *2 * pi
#将一个函数伪装成一个属性@property
c = Circle(3)
print(c.area)
print(c.perimeter)
验证一个苹果价格折扣例子:
class Goods:
def __init__(self,price,discount):
self.__price = price
self.discount = discount
@property
def price(self):
return self.__price * self.discount
@price.setter
def price(self,newprice):
self.__price = newprice
@price.deleter
def price(self):
del self.__price
apple = Goods(8,0.7)
print(apple.price)
apple.price = 10
del apple.price
print(apple.__dict__)
print(apple.price)
Calssmethod模块
class Person:
country = '中国人'
@classmethod
def func(cls):
print('当前角色国籍是%s'%cls.country)
Person.func()
#如果某一个类中的方法,并没有用到这个类的实例中的具体属性
#只是用到了类中的静态变量,就是用类方法
staticmethod 模块
class Student:
@staticmethod
def login():
name = input(">>name")
pwd = input(">>pwd")
if name ==' ' and pwd ==' ':
print('实例化')
Student.login()
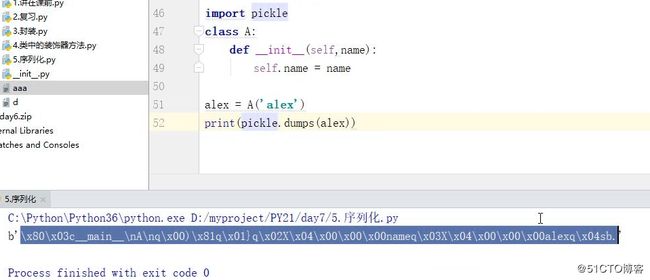
序列化模块:
#什么交序列化呢?
#{'11111:{'name:'xx,'age:24}}
#数据类型---字符串的过程
#为什么要用序列化
#数据从内存到文件
#数据在网络上传输 字节--字符串 - 字典
#python序列化模块有哪些
#json 通用的,支持的数据类型也少 list tuple dict
#pickle python中通用的 支持几乎所有的数据类型
#shelve python中使用的边界的序列话工具
# dumps loads
#dump load
多次写读数据
Pickle:
两个必须会:
#登陆
#数据库
#存储用户密码的时候: 不适用明文
#对用户密码进行计算,得到一个新的固定的字符串
#hashlib模块 摘要算法
#包含了多种算法
#将一个字符串进行摘要运算 拿到一个固定的值
import hashlib
hashlib.md5()
#能够让一个字符串唯一的对应一个固定的值
#sha/md5()
Md5算法
import hashlib
md5obj = hashlib.md5() #实例化一个md5的摘要算法的对象
md5obj.update('alex3714'.encode('utf-8'))#使用md5算法的对象来操作一个字符串
ret = md5obj.hexdigest() #hex+digest 16进制+消化
print(ret,type(ret),len(ret))
1、Sha算法
import hashlib
md5obj = hashlib.sha512() #实例化一个md5的摘要算法的对象
md5obj.update('alex3714'.encode('utf-8'))#使用md5算法的对象来操作一个字符串
ret = md5obj.hexdigest() #hex+digest 16进制+消化
print(ret,type(ret),len(ret))
#撞库
#Md5
#加盐
import hashlib
md5obj = hashlib.md5() #实例化一个md5的摘要算法的对象
md5obj.update('alex3714'.encode('utf-8'))#使用md5算法的对象来操作一个字符串
ret = md5obj.hexdigest() #hex+digest 16进制+消化
print(ret,type(ret),len(ret))
2、#撞库
#Md5
#加盐
md5obj = hashlib.md5('tesla'.encode('utf-8')) #实例化一个md5的摘要算法的对象
md5obj.update('alex3714'.encode('utf-8'))#使用md5算法的对象来操作一个字符串
ret = md5obj.hexdigest() #hex+digest 16进制+消化
print(ret,type(ret),len(ret))
3、#动态加盐
username = 'alex' #用户加盐
md5obj = hashlib.md5(username.encode('utf-8')) #实例化一个md5的摘要算法的对象
md5obj.update('alex3714'.encode('utf-8'))#使用md5算法的对象来操作一个字符串
ret = md5obj.hexdigest() #hex+digest 16进制+消化
print(ret,type(ret),len(ret))
拆分读字节,防止太大5个G
md5obj = hashlib.md5() #实例化一个md5的摘要算法的对象
md5obj.update('alex'.encode('utf-8'))#使用md5算法的对象来操作一个字符串# 等同于alex3714
md5obj.update('3714'.encode('utf-8'))#使用md5算法的对象来操作一个字符串#等同于alex3714
print(md5obj.hexdigest())
Configparse模块:
import configparser
config = configparser.ConfigParser()
config["DEFAULT"] = {'ServerAliveInterval': '45',
'Compression': 'yes',
'CompressionLevel': '9',
'ForwardX11':'yes'
}
config['bitbucket.org'] = {'User':'hg'}
config['topsecret.server.com'] = {'Host Port':'50022','ForwardX11':'no'}
with open('example.ini', 'w') as f:
config.write(f)
import logging
#日志
#程序出错---日志对内看的
#对外给用户看的
#简单配置
logging.basicConfig(level=logging.DEBUG)
logging.debug('debug message') #非常细节的日志---排查错误
logging.info('info message') #正常的日志信息
logging.warning('warning message')#小问题可以运行 警告
logging.error('error message') #错误
logging.critical('critical message')#严重错误
#logger对象的方式配置
import logging
logger = logging.getLogger()
# 吸星大法
#创造一个格式
format=logging.Formatter('%(asctime)s %(filename)s[line:%(lineno)d] %(levelname)s %(message)s')
format1=logging.Formatter('%(asctime)s %(filename)s[line:%(lineno)d] %(levelname)s %(message)s')
#文件里输入
fh = logging.FileHandler('LOG.log') #创造了一个操作文件的对象fh
fh.setFormatter(format)
logger.addHandler(fh)
#往屏幕上写
sh = logging.StreamHandler()
sh.setFormatter(format1)
logger.addHandler(sh)
#内容
logger.warning('www message')
#反射
#通过字符串数据类型的变量名 来访问变量的值
name = 'value'
#类名 反射 静态属性 和方法
#模块 反射模块中的名字
#反射 自己搜在文件中的名字
#xx.yy这种形式 都可以用反射
#'startswith'
print('aaa'.startswith('a'))
ret = getattr('aaa','startswith')
print(ret('a'))
有点问题
:
class Person:
role = 'Person'
def __init__(self,name):
self.name = name
def eat(self):print('eating')
def drink(self):print('drinking')
def play(self):print('playing')
def sleep(self):print('sleepping')
alex = Person('alex')
alex.name
print(getattr(alex,'name'))
print(getattr(Person,'role'))
while True:
inp = input('>>>')
if hasattr(alex,inp):
getattr(alex,inp)()
#首先使用getattr获取一个名字,如果在这个对象的命名空间中没有这个名字 会报错
#getattr的反射好伴侣 hasattr
#如果使用getattr获取一个方法,那么只能拿到一个方法的内存地址
#如果getattr获取一个属性,那么直接使用反射就可以获取到值
#__new__ 构造方法 创建一个对象
#__init__ 初始化方法
class Foo:
def __new__(cls, *args, **kwargs):
print('执行我了')
return object.__new__(cls)
def __init__(self):
print('22222222')
Foo()
#先执行new方法,objectf.new()
#在执行init
#单列模式
class Persion:
__isinstace = None
def __new__(cls, *args, **kwargs):
if not cls.__isinstace:
obj = object.__new__(cls)
cls.__isinstace = obj
return cls.__isinstace
def __init__(self,name):
self.name = name
alex = Persion('alex')
egon = Persion('egon')
print(id(alex))
print(id(egon))
#__new__ 生小孩
#类: 生一个小孩__new__ 给小孩穿衣服__init__
#单类模式下的类: 只有一个小孩
#len 方法
class A:
def __len__(self):
return 10
print(len([1,2,3]))
a = A()
print(len(a))
#类中的内置方法 很多都和 内置函数相关
class Person:
def __init__(self,name):
self.name = name
def __str__(self):
return 'a object of Person named %s'%self.name
# def __hash__(self):
# return 1231212
# def __len__(self):
# return 10
a = Person('alex')
b = Person('egon')
# print(len(a))
# print(hash(a))
print(a)
print(b)