内容概要
- ES 基础介绍,重点是其中的核心概念。
- 基础 API 实践操作。
1. 基础介绍
Elasticsearch (ES) 是一个数据库,提供了分布式的、准实时搜索和分析。
基于 Apache Lucene,可以操作结构化数据、非结构化数据、数字类型数据、地理空间数据。
数据存储使用松散结构的 JSON 文档。
主要特性
- 轻量快速的全文搜索。
- 安全分析和基础设施监控。
- 支持海量规模,数千台服务器、PB级数据量。
- 可以集成可视化数据分析工具,用于例如应用性能分析、日志监控、基础设施度量指标监控。
- 可以用于机器学习,对数据实时进行自动化模型处理。
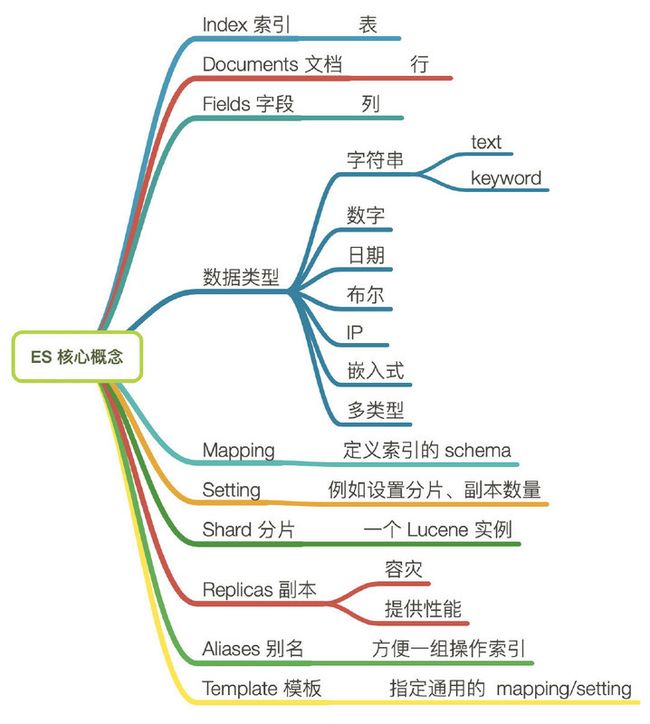
核心概念
- Index 索引
关系数据库中的表,存储文档。
6.0.0 版本之前,一个索引中可以存放不同类型的文档,例如 Car 和 Bike 这2种文档可以在一个索引中。
6.0.0 版本之后,不可以了,需要为每种类型的文档建立不同的索引。
- Documents 文档
关系数据库中的 行。
每个文档有一个唯一 _id。
- Fields 字段
关系数据库中的 列。
- 数据类型
1)字符串
有2种类型:text 和 keyword。
text 用户存储产品描述、文章内容之类的文本,可以根据关键字在其中查找。
ES 会把内容解析成一个字符串列表,然后创建倒排索引,描述每个单词都在哪些文档中出现了。
例如一个文档有一个字段 “Description”,值为 “This phone has dual sim capability”。
这个值会被解析为一个列表:
[“this”, “phone”, “has”, “dual”, “sim”, “capability”]
倒排索引中,会指出每个词所在的文档列表,如:
“this” -> doc_1,doc_3
Keyword 用于存储用户名、邮件地址、邮编这类的明确的内容。
这类内容不会被分割解析,适用于精确匹配。
2)数字
存储例如标识码、百分比、电话号等。
支持:long, integer, short, byte, double, float。
3)日期
形式包括:“2015/01/01 12:10:30” 此类的字符串、微秒级 long 型数字、秒级 integer 型数字。
内部使用 UTC long 型存储。
4)布尔
5)IP
6)嵌入式
一个属性可以是一个 JSON 数组。
例如:
{
"name":"ABC United",
"homeGround":"Old Trafford",
"players":[
{
"firstName":"James",
"lastName":"Cohen",
"position":"Goal Keeper"
},
{
"firstName":"Paul",
"lastName":"Pogba",
"position":"Midfielder"
}
]
}对于嵌入类型,每个数组对象都会被作为一个隐藏文档进行索引。
7)多类型
例如有一个字段 “student_name”,我们希望可以通过部分匹配的方式进行查找,也希望通过完全匹配的方式查找。
这就相当于同时有2种类型:text和 keyword。
可以这样设置:
{
"student_name":{
"type":"text",
"fields":{
"keyword":{
"type":"keyword"
}
}
}
}- Mapping
用于定义一个索引的 schema。
定义索引中有哪些字段、字段类型,配置类型相关的元数据。
- Setting
通过 Setting 可以自定义一些索引的行为,还允许我们自定义分析器和标准化器,以分析索引的不同文本字段。
重要的 Setting 例如:
1)number_of_shards:定义索引分片数量,默认为 1。
2)number_of_replicas:定义分片的副本数量,默认 1。
3)refresh_interval:用于指定文档索引的时间与可供搜索的时间之间的间隔,默认 1秒。
- Shard 分片
一个分片是一个 Lucene 实例,是一个被 ES 自动管理的工作单元。
我们只需要指定分片及其副本的数量,无需对分片进行操作。
ES 自动在所有节点中分布所有分片,当节点故障时,会把分片移到其他节点,当有新节点添加进来时,也会自动把一些分片移过来。
- Replicas 副本
主分片的拷贝,副本的作用:
1)当主分片故障后,其副本可以提升为主分片。
2)主分片及其副本都可以处理查询请求,可以提升性能。
- Aliases 别名
用于指定索引或索引集的替代名称。
当我们想从多个索引中获取文档时非常有用。
- Template 模板
用户对多个索引指定通用的 mapping 和 Setting。
每当创建与模板中定义的特定模式匹配的新索引时,模板将应用于该索引。
创建索引时特别定义的任何 mapping/Setting 都将优先于模板中的定义。
2. API 操作
测试环境搭建
使用的 ES 版本为 7.5.1。
下面使用docker启动一个单节点环境:
docker run -p 9200:9200 -p 9300:9300 -e "discovery.type=single-node" docker.elastic.co/elasticsearch/elasticsearch:7.5.1测试:
$ curl -X GET "localhost:9200/_cat/nodes?v&pretty"
ip heap.percent ram.percent cpu load_1m load_5m load_15m node.role master name
172.17.0.2 7 97 2 0.96 0.61 0.25 dilm * 245e340eba97
$ curl localhost:9200
{
"name" : "245e340eba97",
"cluster_name" : "docker-cluster",
"cluster_uuid" : "mq_bxY5zTjCpmJU0xOLSbA",
"version" : {
"number" : "7.5.1",
"build_flavor" : "default",
"build_type" : "docker",
"build_hash" : "3ae9ac9a93c95bd0cdc054951cf95d88e1e18d96",
"build_date" : "2019-12-16T22:57:37.835892Z",
"build_snapshot" : false,
"lucene_version" : "8.3.0",
"minimum_wire_compatibility_version" : "6.8.0",
"minimum_index_compatibility_version" : "6.0.0-beta1"
},
"tagline" : "You Know, for Search"
}参考文档:
https://www.elastic.co/guide/...
实践操作
- 创建索引
curl -X PUT "localhost:9200/traveler?pretty" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d'
{
"settings":{
"number_of_shards":5,
"number_of_replicas":2
},
"mappings":{
"properties":{
"name":{
"type":"keyword"
},
"age":{
"type":"integer"
},
"background":{
"type":"text"
},
"nationality":{
"type":"keyword"
}
}
}
}
'- 插入文档
curl -X PUT "localhost:9200/traveler/_doc/1?pretty" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d'
{
"name":"John Doe",
"age":"23",
"background":"Born and brought up in California. Engineer by profession. Loves to cook",
"nationality":"British"
}
'- 读取文档
curl -X GET "localhost:9200/traveler/_doc/1?pretty"- 删除文档
curl -X DELETE "localhost:9200/traveler/_doc/1?pretty"- 删除索引
curl -X DELETE "localhost:9200/traveler?pretty"- 所有索引列表
curl -X GET "localhost:9200/_cat/indices"- 查看集群健康情况
curl -X GET "localhost:9200/_cat/health?v"- 查看某个索引的信息
# mapping + setting
curl -X GET "localhost:9200/traveler?pretty"
# mapping
curl -X GET "localhost:9200/traveler/_mapping?pretty"
# setting
curl -X GET "localhost:9200/traveler/_settings?pretty"- 为索引设置别名
curl -X POST "localhost:9200/_aliases" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d'
{
"actions":[
{
"add":{
"index":"traveler",
"alias":"read_alias"
}
}
]
}
'- 获取索引中的所有文档
curl -X GET "localhost:9200/traveler/_search?pretty"结果中的关键项:took - 此次查询耗时,毫秒。
timed_out - 查询是否超时。
_shards - 查询了分片的情况,如一共查询了几个分片、成功了几个。
hits - 查询结果。
hits.total - 结果文档数。
hits.hits - 结果数组,默认只显示前10个文档。
hits.max_score - 匹配度最高的文档的分值。
hits.hits._score - 此文档匹配度分值。
- 获取所有中的文档总数
curl -X GET "localhost:9200/traveler/_count?pretty"- 匹配查询
curl -X GET "localhost:9200/traveler/_search?pretty" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d'
{
"query":{
"match":{
"background":"brought up California Loves cook"
}
}
}
'匹配条件是 "background",其值会被处理为数组:[“brought”, “up”, “california”, “loves”, “cook”]。
只要其中的某一个与文档中的 "background" 值相匹配,文档就会被返回。
- term 查询
curl -X GET "localhost:9200/traveler/_search?pretty" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d'
{
"query":{
"term":{
"name":{
"value":"John Doe"
}
}
}
}
'这用于获取在提供的字段中包含确切术语的文档。
适用于 keyword, numeric, date, boolean 类型的字段。
- terms 查询
curl -X GET "localhost:9200/traveler/_search?pretty" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d'
{
"query":{
"terms":{
"name":[
"John Doe",
"Jack Ripper",
"Buzz Aldrin"
]
}
}
}
'类似 IN 查询,匹配一个或多个。
- 前缀匹配查询
curl -X GET "localhost:9200/traveler/_search?pretty" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d'
{
"query":{
"prefix":{
"name":"Joh"
}
}
}
'- 正则查询
curl -X GET "localhost:9200/traveler/_search?pretty" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d'
{
"query":{
"regexp":{
"name":{
"value":"J.*e"
}
}
}
}
'- 单次多查询
在一个请求中执行多个查询操作。
curl -X GET "localhost:9200/_msearch?pretty" -H 'Content-Type: application/x-ndjson' -d'
{"index":"traveler"}
{"query":{"terms":{"name":["John Doe","Jack Ripper","Barack Obama"]}}}
{}
{"query":{"prefix":{"name":"Buzz"}}}
{"index":"traveler"}
{"query":{"match_all":{}}}
'推荐阅读: