源码
message.h
message汇编源码
runtime源码
在iOS中,方法调用过程分三步
消息发送:从类及父类的缓存列表以及方法列表查找方法。
动态解析:如果消息发送阶段没有找到方法,则会进入动态解析阶段,负责动态的添加方法实现。
消息转发:如果也没有实现动态解析方法,则会进行消息转发阶段,将消息转发给可以处理消息的接受者来处理。
如果消息转发也没有实现,则会抛出常见的异常unrecognzied selector sent to instance
我们先来去掉方法调用的伪装,在main.m文件中创建一个Animal类,添加一个run实例方法
在main函数中
int main(int argc, char * argv[]) {
Animal *animal = [[Animal alloc] init];
[animal run];
return 0;
}
通过xcrun -sdk iphoneos clang -arch arm64 -rewrite-objc main.m命令转成C++代码main.cpp文件,进入文件后定位到main函数可以看到
int main(int argc, char * argv[]) {
Animal *animal = ((Animal *(*)(id, SEL))(void *)objc_msgSend)((id)((Animal *(*)(id, SEL))(void *)objc_msgSend)((id)objc_getClass("Animal"), sel_registerName("alloc")), sel_registerName("init"));
((void (*)(id, SEL))(void *)objc_msgSend)((id)animal, sel_registerName("run"));
return 0;
}
通过上面源码可以很清楚的看到C++底层将方法调用最终转换为调用objc_msgSend,并且传入参数(id)animal(消息接受者self),sel_registerName("run")(消息名_cmd),因此OC的方法调用也称为消息机制,表示给方法调用者发送消息。
接下来我们慢慢剖析一个消息发送的完整过程。
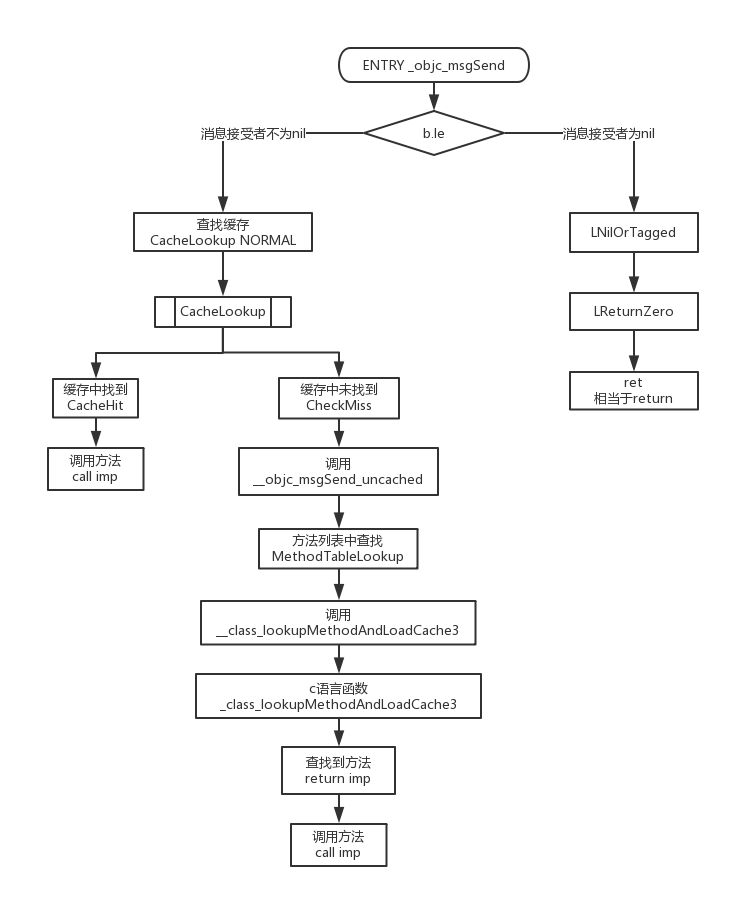
Step 1.1、 消息发送-缓存列表查找
Objective-C中方法调用从objc_msgSend开始就正式开始,objc_msgSend的申明定义在源码message.h中,实现是在Messengers.subproj/这个汇编文件夹中,以arm64的汇编源码为例(这里就只贴关键的代码)
_objc_msgSend,对消息接受者判空,是则进入LReturnZero返回nil,否则进入CacheLookup检查缓存
ENTRY _objc_msgSend
...
#if SUPPORT_TAGGED_POINTERS
b.le LNilOrTagged // 判空
#else
b.eq LReturnZero // 不为空则进入LGetIsaDone
#endif
......
LGetIsaDone:
CacheLookup NORMAL // 开始查找
......
CacheLookup开始查找缓存,查到缓存进入CacheHit并返回imp,否则进入CheckMiss
.macro CacheLookup
......
CacheHit $0
......
CheckMiss
.endmacro
CheckMiss根据传入参数跳转到__objc_msgSend_uncached or __objc_msgLookup_uncached
.macro CheckMiss
// miss if bucket->sel == 0
.if $0 == GETIMP
cbz p9, LGetImpMiss
.elseif $0 == NORMAL
cbz p9, __objc_msgSend_uncached
.elseif $0 == LOOKUP
cbz p9, __objc_msgLookup_uncached
.else
.abort oops
.endif
.endmacro
__objc_msgSend_uncached调用MethodTableLookup进入方法列表查找
STATIC_ENTRY __objc_msgSend_uncached
UNWIND __objc_msgSend_uncached, FrameWithNoSaves
MethodTableLookup // 这里是MethodTableLookup
TailCallFunctionPointer x17
END_ENTRY __objc_msgSend_uncached
MethodTableLookup内部逻辑进入方法列表查找的核心函数__class_lookupMethodAndLoadCache3,该方法在runtime.m文件中实现
.macro MethodTableLookup
......
bl __class_lookupMethodAndLoadCache3
......
.endmacro
进入到__class_lookupMethodAndLoadCache3后我们接下来看1.2的方法列表查找过程。
Step 1.2、 消息发送-方法列表查找
从核心函数_class_lookupMethodAndLoadCache3开始
IMP _class_lookupMethodAndLoadCache3(id obj, SEL sel, Class cls)
{
return lookUpImpOrForward(cls, sel, obj,
YES/*initialize*/, NO/*cache*/, YES/*resolver*/);
}
IMP lookUpImpOrForward(Class cls, SEL sel, id inst,
bool initialize, bool cache, bool resolver)
{
IMP imp = nil;
bool triedResolver = NO;
runtimeLock.assertUnlocked();
// 已经在1.1的缓存中已经查找过,所以传入的NO不再进行缓存查找
if (cache) {
imp = cache_getImp(cls, sel);
if (imp) return imp;
}
runtimeLock.lock();
checkIsKnownClass(cls);
if (!cls->isRealized()) {
cls = realizeClassMaybeSwiftAndLeaveLocked(cls, runtimeLock);
}
if (initialize && !cls->isInitialized()) {
cls = initializeAndLeaveLocked(cls, inst, runtimeLock);
// runtimeLock may have been dropped but is now locked again
// If sel == initialize, class_initialize will send +initialize and
// then the messenger will send +initialize again after this
// procedure finishes. Of course, if this is not being called
// from the messenger then it won't happen. 2778172
}
retry:
runtimeLock.assertLocked();
// 尝试查找一次缓存,如果找到直接返回
imp = cache_getImp(cls, sel);
if (imp) goto done;
// 传入对象和方法名,在方法列表中获取
{
Method meth = getMethodNoSuper_nolock(cls, sel);
if (meth) {
// 查找到后进行缓存,并直接返回
log_and_fill_cache(cls, meth->imp, sel, inst, cls);
imp = meth->imp;
goto done;
}
}
// 依次遍历父类的方法列表中或缓存进行查找
{
unsigned attempts = unreasonableClassCount();
for (Class curClass = cls->superclass;
curClass != nil;
curClass = curClass->superclass)
{
// Halt if there is a cycle in the superclass chain.
if (--attempts == 0) {
_objc_fatal("Memory corruption in class list.");
}
// 父类缓存
imp = cache_getImp(curClass, sel);
if (imp) {
if (imp != (IMP)_objc_msgForward_impcache) {
// Found the method in a superclass. Cache it in this class.
log_and_fill_cache(cls, imp, sel, inst, curClass);
goto done;
}
else {
// Found a forward:: entry in a superclass.
// Stop searching, but don't cache yet; call method
// resolver for this class first.
break;
}
}
// 父类的方法列表
Method meth = getMethodNoSuper_nolock(curClass, sel);
if (meth) {
log_and_fill_cache(cls, meth->imp, sel, inst, curClass);
imp = meth->imp;
goto done;
}
}
}
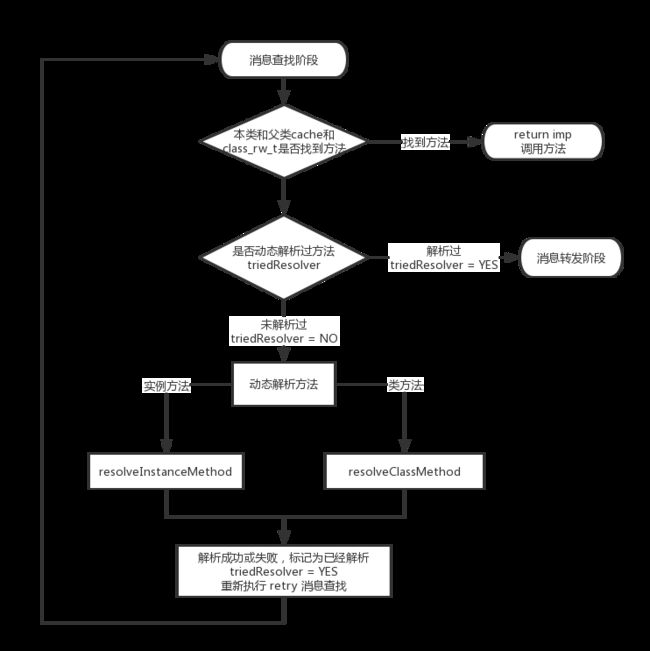
// 未找到imp,如果传入resolver为YES且triedResolver为NO(未解析过)则开始动态解析过程
if (resolver && !triedResolver) {
runtimeLock.unlock();
// 开始动态解析
resolveMethod(cls, sel, inst);
runtimeLock.lock();
// Don't cache the result; we don't hold the lock so it may have
// changed already. Re-do the search from scratch instead.
triedResolver = YES;
goto retry;
}
// 未找到imp且动态解析也未解析到,则开始消息转发
imp = (IMP)_objc_msgForward_impcache;
cache_fill(cls, sel, imp, inst);
done:
runtimeLock.unlock();
return imp;
}
realizeClass是初始化了很多数据,包括cls->ro赋值给cls->rw,添加元类version为7,cls->chooseClassArrayIndex()设置cls的索引,supercls = realizeClass(remapClass(cls->superclass)); metacls = realizeClass(remapClass(cls->ISA()))初始化superclass和cls->isa,后边针对没有优化的结构进行赋值这里不多讲,然后协调实例变量偏移布局,设置cls->setInstanceSize,拷贝flags从ro到rw中,然后添加subclass和rootclass,最后添加类别的方法,协议,和属性。
getMethodNoSuper_nolock在类对象的方法列表中查找
getMethodNoSuper_nolock(Class cls, SEL sel)
{
runtimeLock.assertLocked();
assert(cls->isRealized());
// cls->data() 得到的是 class_rw_t
// class_rw_t->methods 得到的是methods二维数组
for (auto mlists = cls->data()->methods.beginLists(),
end = cls->data()->methods.endLists();
mlists != end;
++mlists)
{
// mlists 为 method_list_t
method_t *m = search_method_list(*mlists, sel);
if (m) return m;
}
return nil;
}
search_method_list
static method_t *search_method_list(const method_list_t *mlist, SEL sel)
{
int methodListIsFixedUp = mlist->isFixedUp();
int methodListHasExpectedSize = mlist->entsize() == sizeof(method_t);
// 如果方法列表是有序的,则使用效率较高的二分法查找方法
if (__builtin_expect(methodListIsFixedUp && methodListHasExpectedSize, 1)) {
return findMethodInSortedMethodList(sel, mlist);
} else {
// 否则遍历列表查找
for (auto& meth : *mlist) {
if (meth.name == sel) return &meth;
}
}
return nil;
}
findMethodInSortedMethodList函数内二分查找实现原理
static method_t *findMethodInSortedMethodList(SEL key, const method_list_t *list)
{
assert(list);
const method_t * const first = &list->first;
const method_t *base = first;
const method_t *probe;
uintptr_t keyValue = (uintptr_t)key;
uint32_t count;
// >>1 表示将变量n的各个二进制位顺序右移1位,最高位补二进制0。
// count >>= 1 如果count为偶数则值变为(count / 2)。如果count为奇数则值变为(count-1) / 2
for (count = list->count; count != 0; count >>= 1) {
// probe 指向数组中间的值
probe = base + (count >> 1);
// 取出中间method_t的name,也就是SEL
uintptr_t probeValue = (uintptr_t)probe->name;
if (keyValue == probeValue) {
// 取出 probe
while (probe > first && keyValue == (uintptr_t)probe[-1].name) {
probe--;
}
// 返回方法
return (method_t *)probe;
}
// 如果keyValue > probeValue 则折半向后查询
if (keyValue > probeValue) {
base = probe + 1;
count--;
}
}
return nil;
}
Step 2、 动态解析
动态解析阶段源码:
static void resolveMethod(Class cls, SEL sel, id inst)
{
runtimeLock.assertUnlocked();
assert(cls->isRealized());
if (! cls->isMetaClass()) {
// try [cls resolveInstanceMethod:sel]
resolveInstanceMethod(cls, sel, inst);
}
else {
// try [nonMetaClass resolveClassMethod:sel]
// and [cls resolveInstanceMethod:sel]
resolveClassMethod(cls, sel, inst);
if (!lookUpImpOrNil(cls, sel, inst,
NO/*initialize*/, YES/*cache*/, NO/*resolver*/))
{
resolveInstanceMethod(cls, sel, inst);
}
}
}
resolveInstanceMethod函数
static void resolveInstanceMethod(Class cls, SEL sel, id inst)
{
runtimeLock.assertUnlocked();
assert(cls->isRealized());
if (! lookUpImpOrNil(cls->ISA(), SEL_resolveInstanceMethod, cls,
NO/*initialize*/, YES/*cache*/, NO/*resolver*/))
{
// 未实现动态解析方法SEL_resolveInstanceMethod
return;
}
// 调用动态解析方法也就是OC中的类方法"resolveInstanceMethod:"
BOOL (*msg)(Class, SEL, SEL) = (typeof(msg))objc_msgSend;
bool resolved = msg(cls, SEL_resolveInstanceMethod, sel);
// 动态解析后再次进行查找
IMP imp = lookUpImpOrNil(cls, sel, inst,
NO/*initialize*/, YES/*cache*/, NO/*resolver*/);
if (resolved && PrintResolving) {
if (imp) {
_objc_inform("RESOLVE: method %c[%s %s] "
"dynamically resolved to %p",
cls->isMetaClass() ? '+' : '-',
cls->nameForLogging(), sel_getName(sel), imp);
}
else {
// Method resolver didn't add anything?
_objc_inform("RESOLVE: +[%s resolveInstanceMethod:%s] returned YES"
", but no new implementation of %c[%s %s] was found",
cls->nameForLogging(), sel_getName(sel),
cls->isMetaClass() ? '+' : '-',
cls->nameForLogging(), sel_getName(sel));
}
}
}
lookUpImpOrNil
IMP lookUpImpOrNil(Class cls, SEL sel, id inst,
bool initialize, bool cache, bool resolver)
{
IMP imp = lookUpImpOrForward(cls, sel, inst, initialize, cache, resolver);
// 如果是`_objc_msgForward_impcache`则说明,动态解析添加失败,返回nil
if (imp == _objc_msgForward_impcache) return nil;
else return imp;
}
在进行过一次动态解析后,通过resolver和triedResolver两个参数的值知道,无论动态解析是否有用,都不会在lookUpImpOrForward中再次进行动态解析。
接下来我们看一下OC中动态解析的方法实现以及怎么实现动态解析
动态解析对象方法+(BOOL)resolveInstanceMethod:(SEL)sel,动态解析类方法+(BOOL)resolveClassMethod:(SEL)sel。
// 这里以`resolveInstanceMethod :`举例怎么实现动态解析
+ (BOOL)resolveInstanceMethod:(SEL)sel {
if (sel == @selector(test)) {
// 获取实例对象方法的指针
Method otherMethod = class_getInstanceMethod(self, @selector(run));
// 添加到类实例对象方法列表
class_addMethod(self, sel, method_getImplementation(otherMethod), method_getTypeEncoding(otherMethod));
// 是否动态添加
return YES;
}
NSLog(@"%s", __func__);
return [super resolveInstanceMethod:sel];
}
int main(int argc, char * argv[]) {
Animal *animal = [[Animal alloc] init];
[animal run];
[animal performSelector:@selector(test)];
return 0;
}
animal对象调用方法test,可以看到最后调的run函数,通过上面对消息发送的分析我们知道,当本类和父类cache和class_rw_t中都找不到方法时,就会进行动态解析的方法,也就是说会自动调用类的resolveInstanceMethod:方法进行动态查找。
需要注意
Method是objc_method结构体,其内部结构同method_t(内部包含SEL、type、IMP)结构体相同,可以等同转换
Step 3、 消息转发
由runtime源码中可以看出,在未进行动态解析或者动态解析失败后,就会执行imp = (IMP)_objc_msgForward_impcache;进行消息转发,但是此部分代码并未开源,我们可以从Objectiv-C提供的模板方法来进行分析。
在Objectiv-C中消息转发涉及三个函数:
1.- (id)forwardingTargetForSelector:(SEL)aSelector
2.- (NSMethodSignature *)methodSignatureForSelector:(SEL)aSelector
- (void)forwardInvocation:(NSInvocation *)anInvocation
如果forwardingTargetForSelector函数返回为nil或者没有实现的话,就会调用methodSignatureForSelector方法,用来返回一个方法签名,这也是我们正确跳转方法的最后机会。
如果methodSignatureForSelector方法返回正确的方法签名就会调用forwardInvocation方法,forwardInvocation方法内提供一个NSInvocation类型的参数,NSInvocation封装了一个方法的调用,包括方法的调用者,方法名,以及方法的参数。在forwardInvocation函数内修改方法调用对象即可。
如果methodSignatureForSelector返回的为nil,就会来到doseNotRecognizeSelector:方法内部,程序crash提示无法识别选择器unrecognized selector sent to instance。
// 3.消息转发阶段(未进行动态解析或者动态解析失败进入本阶段)
- (id)forwardingTargetForSelector:(SEL)aSelector {
if (aSelector == @selector(roar)) {
return [[Lion alloc] init];
}
return [super forwardingTargetForSelector:aSelector];
}
- (NSMethodSignature *)methodSignatureForSelector:(SEL)aSelector {
if (aSelector == @selector(hunt)) {
// 创建方法签名
// return [NSMethodSignature signatureWithObjCTypes:"v16@0:8"];
return [[[Lion alloc] init] methodSignatureForSelector:aSelector];
}
return [super methodSignatureForSelector:aSelector];
}
/// 如果上一步‘methodSignatureForSelector:’返回正确的方法签名,则执行此步。这里需要注意修改NSInvocation的target对象,由于修改前的对象是原始调用对象未实现该方法,所以一直进行消息转发,造成调用栈溢出
/// @param anInvocation anInvocation,封装了上一步分方法签名
- (void)forwardInvocation:(NSInvocation *)anInvocation {
NSLog(@"NSInvocation original target is %@", anInvocation.target);
Lion *target = [[Lion alloc] init];
anInvocation.target = target;
[anInvocation invoke];
// [anInvocation invokeWithTarget:[[Lion alloc] init]];
NSLog(@"NSInvocation destination target is %@", anInvocation.target);
}
同样上述代码,我们为动态转发方法添加返回值和参数,并在forwardInvocation方法中修改方法的返回值及参数。
// 3.消息转发阶段(未进行动态解析或者动态解析失败进入本阶段)
- (id)forwardingTargetForSelector:(SEL)aSelector {
if (aSelector == @selector(roar)) {
return [[Lion alloc] init];
}
return [super forwardingTargetForSelector:aSelector];
}
// 创建方法签名
- (NSMethodSignature *)methodSignatureForSelector:(SEL)aSelector {
if (aSelector == @selector(hunt)) {
return [[[Lion alloc] init] methodSignatureForSelector:aSelector];
}
if (aSelector == @selector(offspringCountWithAge:)) {
return [NSMethodSignature signatureWithObjCTypes:"i@:i"];
}
return [super methodSignatureForSelector:aSelector];
}
/// 如果上一步‘methodSignatureForSelector:’返回正确的方法签名,则执行此步。这里需要注意修改NSInvocation的target对象,由于修改前的对象是原始调用对象未实现该方法,所以一直进行消息转发,造成调用栈溢出
/// @param anInvocation anInvocation,封装了上一步分方法签名
- (void)forwardInvocation:(NSInvocation *)anInvocation {
if (anInvocation.selector == @selector(hunt)) {
NSLog(@"NSInvocation original target is %@", anInvocation.target);
Lion *target = [[Lion alloc] init];
anInvocation.target = target;
[anInvocation invoke];
// [anInvocation invokeWithTarget:[[Lion alloc] init]];
NSLog(@"NSInvocation destination target is %@", anInvocation.target);
} else if (anInvocation.selector == @selector(offspringCountWithAge:)) {
int age;
// 获取方法的参数,方法默认还有self和cmd两个参数,因此新添加的参数下标为2
[anInvocation getArgument:&age atIndex:2];
NSLog(@"offspringCountWithAge:修改前参数的值 = %d",age);
age = 3;
NSLog(@"offspringCountWithAge:修改后参数的值 = %d",age);
[anInvocation setArgument:&age atIndex:2];
[anInvocation invokeWithTarget:[[Lion alloc] init]];
// 获取方法的返回值
int offspringCountWithAge;
[anInvocation getReturnValue:&offspringCountWithAge];
NSLog(@"offspringCountWithAge:返回值 = %d",offspringCountWithAge); // result = 220,说明参数修改成功
offspringCountWithAge = 100;
[anInvocation setReturnValue:&offspringCountWithAge];
[anInvocation getReturnValue:&offspringCountWithAge];
NSLog(@"offspringCountWithAge:修改后返回值为 = %d",offspringCountWithAge);
}
}