2.1 软件安装
待监测服务器centos系统主要安装的软件是:nagios-plugins-1.4.16.tar.gz和nrpe-2.14.tar.gz。
其他的插件视待监测服务器需要监测的内容而定,如要监测oracle表空间,则需要安装check_oracle_health-1.7.8.1.tar.gz、DBD-Oracle-1.64.tar.gz和DBI-1.627.tar.gz。
待监测服务器是windows系统的话,则需要安装NSCP-0.4.1.101-Win32.msi在(32位操作系统)或NSCP-0.4.1.101-x64.msi(64位操作系统)。NSCP在以往的版本中称为NSClient++。安装方法也很简单,在下面具体进行讲解。
待检测的centos5.5或相近版本的系统需要安装nagios-plugins-1.4.16.tar.gz和nrpe-2.14.tar.gz。安装方法如下:
一、创建用户
# useradd nagios
二、安装插件nagios-plugins-1.4.16.tar.gz
# tar -zxvf nagios-plugins-1.4.16.tar.gz
#cd nagios-plugins-1.4.16
#./configure --prefix=/usr/local/nagios --with-nagios-user=nagios --with-nagios-group=nagios
make && make install
chown -R nagios.nagios /usr/local/nagios/
chown -R nagios.nagios /usr/local/nagios/libexec/
三、安装nrpe-2.14.tar.gz
1, 安装nrpe-2.14.tar.gz
先测试openssl和openssl-devel是否已经安装,如果没有安装则首先需要进行安装。否则configure就有问题。安装包可以在centos安装盘中找到:
# rpm -qa|grep openssl
# lsof -i:5666 //查询端口5666是否未被使用
#cd ..
#tar -zxvf nrpe-2.14.tar.gz
#cd nrpe-2.14
#./configure --enable-ssl --with-ssl-lib
#make all && make install-plugin && make install-daemon && make install-daemon-config
2, 修改nrpe配置文件
修改配置文件/usr/local/nagios/etc/nrpe.cfg:
#vi /usr/local/nagios/etc/nrpe.cfg
1) allow_hosts 加上nagios服务器IP地址,允许与nagios服务器进行通讯:
allowed_hosts=127.0.0.1,192.168.50.22
或使用命令:
# sed -i '/^allowed_/s/$/,192.168.50.22/' /usr/local/nagios/etc/nrpe.cfg
sed -i '/^allowed_/s/$/,192.168.50.191/' /usr/local/nagios/etc/nrpe.cfg
killall nrpe
ps -ef|grep nrpe
/usr/local/nagios/bin/nrpe -c /usr/local/nagios/etc/nrpe.cfg -d
exit
向 /etc/rc.d/rc.local 文件最后增加一行空行,然后加入一行自动启动监听程序。然后显示下文件内容,看看添加是否正确:
sed -i '$ a\ ' /etc/rc.d/rc.local
sed -i '$ a\/usr/local/nagios/bin/nrpe -c /usr/local/nagios/etc/nrpe.cfg -d' /etc/rc.d/rc.local
more /etc/rc.d/rc.local
介绍一个常用的命令:nagios服务器上,各类似的被监测设备的cfg配置文件都可以复制使用。而service项中有hosts属性,而且server项又很多,因此,可以使用以下命令全部替换。例如:我们将50.31_cdn1.cfg复制为50.32_cdn2.cfg后,需要将50.32_cdn2.cfg文件的host_name的50.31_cdn1全部要修改成50.32_cdn2,则可以使用以下语句:
sed -i "s/50.31_cdn1/50.32_cdn2/g" `grep 50.31_cdn1 -rl /usr/local/nagios/etc/server/50.32_cdn2.cfg`
sed -i "s/被替换字/替换后字/g" `grep 被替换字 -rl 文件路径`
2) 增加command项,以下增加的command需要根据所在被监测服务器需要监测的项目以及被监测服务器上的环境而定。如有些服务器的根分区是/dev/sda2,有些是/dev/sda3,而有些是 /dev/mapper/VolGroup00-LogVol00 。例如:
command[check_users]=/usr/local/nagios/libexec/check_users -w 5 -c 10
command[check_load]=/usr/local/nagios/libexec/check_load -w 15,10,5 -c 30,25,20
command[check_sda2]=/usr/local/nagios/libexec/check_disk -w 20% -c 10% -p /dev/sda2
以下各小节会根据被监测服务器的具体情况进行说明。由于服务器众多,不可能一一全部写出,下面会尽可能多的找一些比较典型的被监测服务器和设备进行说明。
3, 启动NRPE进程
启动NRPE进程有两种方法,一种是直接使用命令,本人是采用这种方法。
1) 使用命令启动
/usr/local/nagios/etc/nrpe.cfg配置完毕后,在被监测服务器上启动NRPE进程:
#/usr/local/nagios/bin/nrpe -c /usr/local/nagios/etc/nrpe.cfg -d
如果想让被监测服务器启动后自动启动这个进程,则可以将这个命令写入/etc/rc.d/rc.local文件中。
NRPE服务启动后,可以参考nrpe.cfg中的command命令项,在本机测试下各命令是否可以执行,如:
# /usr/local/nagios/libexec/check_nrpe -H 127.0.0.1 -c check_users
USERS OK - 3 users currently logged in |users=3;5;10;0
然后可以到nagios服务器上去测试下命令是否可用,如:
# /usr/local/nagios/libexec/check_nrpe -H 192.168.50.10 -c check_users
USERS OK - 3 users currently logged in |users=3;5;10;0
测试通过。
2) 使用xinetd服务加载
有些资料上叙述的可以使用xinetd进程加载启动NRPE:
#cd nrpe-2.14
#make install-xinetd
在/etc/services文件中增加一行后,重启xinetd:
#vi /etc/services
nrpe 5666/tcp # NRPE
#service xinetd restart
4, 关闭NRPE进程
如果是使用第一种命令行方式启动的,则可以通过kill -9 进程号,或者也可以使用 #killall nrpe 命令关闭NRPE进程。
5, 测试启动是否成功:
1) 查看端口号
netstat -at | grep nrpe
如果出现以下行,则测试通过
tcp 0 0 *:nrpe *:* LISTEN
2) 也可以使用check_nrpe命令
# /usr/local/nagios/libexec/check_nrpe -H localhost
如果出现以下信息,则测试也通过
NRPE v2.14
3) 也可以在nagios服务器上进行测试:
比如在192.168.50.22上测试192.168.50.10:
# /usr/local/nagios/libexec/check_nrpe -H 192.168.50.10
如果此时出现 NRPE v2.14 则表示成功;反之,如果出现 CHECK_NRPE: Error - Could not complete SSL handshake. 则可能50.22或者50.10上没有启动nrpe或者其中之一没有安装openssl。
2.2 数据库192.168.50.10
2.2.1 Oracle服务器监测
1, 在安装完nagios-plugin和nrpe插件后,我们来安装监控oracle表空间的插件。
1) 查看是否安装了perl:
输入 perl -v,出现以下信息则说明已安装。否则先安装perl,因为这个监测脚本是使用perl编写的。可以使用yum,也可以在centos安装盘上找相应的rpm包:
#perl -v
This is perl, v5.8.8 built for x86_64-linux-thread-multi
Copyright 1987-2006, Larry Wall
... ... ... ...
2) 安装 DBI-1.627.tar.gz
#tar zxvf DBI-1.627.tar.gz
cd DBI-1.627
perl Makefile.PL
make all
make install
3) 没有报错我们进行下一步安装DBD-Oracle
#tar zxvf DBD-Oracle-1.64.tar.gz
cd DBD-Oracle-1.64
perl Makefile.PL
执行上述命令肯定会遇到找不到ORACLE_HOME或LD_LIBRARY_PATH错误:
可以先设置临时ORACLE_HOME变量,参考oracle用户的环境变量:
#export ORACLE_HOME=/u01/oracle/product/11.2.0/db_1
export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=$ORACLE_HOME/lib:/lib64:/usr/lib64:/usr/local/lib64:/usr/X11R6/lib64/
再执行perl Makefile.PL就OK了
make
make install
4) 最后一步安装主角check_oracle_health
#tar zxvf check_oracle_health-1.7.8.1.tar.gz
cd check_oracle_health-1.7.8.1
./configure --prefix=/usr/local/nagios --with-nagios-user=nagios --with-nagios-group=nagios --with-mymodules-dir=/usr/local/nagios/libexec --with-mymodules-dyndir=/usr/local/nagios/libexec
make all
make install
完成后,查看/usr/local/nagios/libexec目录下插件check_oracle_health已经有了。
2, 切换到oracle用户,试运行一下这个插件
/usr/local/nagios/libexec/check_oracle_health --connect=你oracle的SID --user=oracle用户 --password=oracle密码 --mode=tnsping
或者可以把最后的--mode=tnsping换成--mode=tablespace-usage试试看是否能查看所有表空间了:
#su - oracle
$/usr/local/nagios/libexec/check_oracle_health --connect=voddb --user=sys --password=111111 --mode=tnsping
OK - connection established to voddb. 输出OK了
$
$/usr/local/nagios/libexec/check_oracle_health --connect=voddb --user=sys --password=111111 --mode=tablespace-usage
OK - tbs USERS usage is 2.32%, tbs UNDOTBS1 usage is 0.11%,,,,,,,,,,,,后面一大堆表空间信息
如果测试的时候,报:
CRITICAL - cannot connect to voddb. install_driver(Oracle) failed: Can't load '/usr/lib64/perl5/site_perl/5.8.8/x86_64-linux-thread-multi/auto/DBD/Oracle/Oracle.so' for module DBD::Oracle: libclntsh.so.11.1: cannot open shared object file: No such file or directory at /usr/lib64/perl5/5.8.8/x86_64-linux-thread-multi/DynaLoader.pm line 230.
at (eval 13) line 3
的错误,则进行如下处理:
vi /etc/ld.so.conf
include ld.so.conf.d/*.conf
/u01/oracle/product/11.2.0/db_1/lib #增加这一句后执行:
#ldconfig /etc/ld.so.conf
#让这个文件生效后,再次执行以上check_oracle_health就能通过
#/usr/local/nagios/libexec/./check_oracle_health --connect=voddb --user=sys --password=111111 --mode=tnsping
OK - connection established to voddb.
#
还有一种解决这个问题的方法是 http://blog.csdn.net/russle/article/details/4542662 :
Another solution to this problem is to modify the Makefile file (which is created when you run perl Makefile.PL ) as follows:
1.Search for the line LD_RUN_PATH=
2.Replace it with LD_RUN_PATH=my_oracle_home/lib
where my_oracle_home is, of course, the home path to your Oracle installation. In particular, the file libclntsh.so.8.0 should exist in the lib subdirectory.
Then just type make install , and all should go well.
Note that setting LD_RUN_PATH has the effect of hardcoding the path to my_oracle_home/lib in the file Oracle.so , which is generated by DBD::Oracle . This is an efficiency mechanism, so that at runtime it doesn't have to search through LD_LIBRARY_PATH or the default directories used by ld .
3, 在root用户的.bash_profile文件中添加以下oracle_home等参数(参考oracle用户的.bash_profile文件):
vi .bash_profile
export ORACLE_HOME=/u01/oracle/product/11.2.0/db_1
export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=$ORACLE_HOME/lib:/lib64:/usr/lib64:/usr/local/lib64:/usr/X11R6/lib64/
root重新登录后执行
#/usr/local/nagios/libexec/./check_oracle_health --connect=voddb --user=system --password=111111 --mode=tablespace-usage
如果能够测试出oracle系统的各个表空间的情况,则以上操作都已经通过。
如果还是不行,可以尝试将oracle用户的.bash_profile文件中有关oracle的参数都添加上去:
export ORACLE_BASE=/u01/oracle/
export ORACLE_HOME=$ORACLE_BASE/product/11.2.0/db_1
export PATH=$PATH:$ORACLE_HOME/bin
export ORACLE_SID=voddb
在64bit的centos5.8中还会出现以下错误:
则需要在 .bash_profile文件中再增加参数:
export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=$ORACLE_HOME/lib:/lib64:/usr/lib64:/usr/local/lib64:/usr/X11R6/lib64/
之后,就能成功执行:
# /usr/local/nagios/libexec/check_oracle_health --connect=voddb --user=sys --password=111111 --mode=tnsping
4, 被监控测试自己是没问题了,如何让监控机去调用这个脚本呢?在被监控机上的nrpe.cfg文件加入如下内容(完整的内容请看第5小点):
vi /usr/local/nagios/etc/nrpe.cfg
command[check_oracle_health]=/usr/local/nagios/libexec/check_oracle_health --connect=voddb --user=sys --password=111111 --mode=tablespace-usage
5) 保存后退出,然后我们重启被监控机的nrpe服务
#killall nrpe
#/usr/local/nagios/bin/nrpe -c /usr/local/nagios/etc/nrpe.cfg -d
6) 下面我们到nagios服务器50.22上去测试这个插件
/usr/local/nagios/libexec/check_nrpe -H 你的被监控机IP地址 -c check_oracle_health
#/usr/local/nagios/libexec/check_nrpe -H 192.168.50.10 -c check_oracle_health
这里192.168.50.10是数据库服务器的ip地址。
如果正常,就会输出所有的表空间使用情况。
5, 修改nrpe.cfg配置文件
#vi /usr/local/nagios/etc/nrpe.cfg
#允许与50.22进行通讯
... ...
allowed_hosts=127.0.0.1,192.168.50.22
... ...
command[check_users]=/usr/local/nagios/libexec/check_users -w 5 -c 10
command[check_load]=/usr/local/nagios/libexec/check_load -w 15,10,5 -c 30,25,20
#监测根分区目录 / 的硬盘容量使用情况
command[check_sda2]=/usr/local/nagios/libexec/check_disk -w 20% -c 10% -p /dev/sda2
#监测oracle数据库安装表空间的分区目录 /u01 的硬盘容量使用情况
command[check_sda5]=/usr/local/nagios/libexec/check_disk -w 20% -c 10% -p /dev/sda5
command[check_swap]=/usr/local/nagios/libexec/check_swap -w 20% -c 10%
command[check_zombie_procs]=/usr/local/nagios/libexec/check_procs -w 5 -c 10 -s Z
command[check_total_procs]=/usr/local/nagios/libexec/check_procs -w 300 -c 400
#监测oracle sid
command[check_oracle_sid]=/usr/local/nagios/libexec/check_oracle --db voddb
#监测oracle tns
command[check_oracle_tns]=/usr/local/nagios/libexec/check_oracle --tns voddb
#监测oracle 表空间,这里的check_oracle_tbs为经过修改的check_oracle_health。check_oracle_health为监控oracle表空间的插件
command[check_oracle_health]=/usr/local/nagios/libexec/check_oracle_tbs --connect=voddb --user=system --password=111111 --m
ode=tablespace-usage --warning=80 --critical=90
其他参数都默认。
这里的command在本机可以使用以下命令进行测试,如:
# /usr/local/nagios/libexec/check_nrpe -H 127.0.0.1 -c check_swap
# /usr/local/nagios/libexec/check_nrpe -H 127.0.0.1 -c check_oracle_health
Nagios服务器192.168.50.22服务器可以直接在shell下验证该命令是否能够成功执行,如:
# /usr/local/nagios/libexec/./check_nrpe -H 192.168.50.10 -c check_swap
SWAP OK - 97% free (9829 MB out of 10236 MB) |swap=9829MB;2047;1023;0;10236
#
一定要在nagios的服务器上验证下到被监测机器的监测项是否可执行,是否能获取到监测数据。
6, 在进行命令执行测试时,可能会出现以下问题:
1) 在数据库机器直接使用以下命令测试能够成功:
/usr/local/nagios/libexec/check_oracle --db voddb
/usr/local/nagios/libexec/check_oracle --tns voddb
/usr/local/nagios/libexec/check_oracle_tbs --connect=voddb --user=system --password=111111 --m
ode=tablespace-usage --warning=80 --critical=90
2) 在数据库机器使用check_nrpe测试oracle sid 正常,但是oracle tns和tbs的两个命令会出现以下错误:
[root@db1 libexec]# ./check_nrpe -H 127.0.0.1 -c check_oracle_sid
adpdb OK - 1 PMON process(es) running
[root@db1 libexec]# ./check_nrpe -H 127.0.0.1 -c check_oracle_tns
No TNS Listener on adpdb
[root@db1 libexec]# ./check_nrpe -H 127.0.0.1 -c check_oracle_health
CRITICAL - cannot connect to adpdb. ORA-12154: TNS:could not resolve the connect identifier specified (DBD ERROR: OCIServerAttach)
[root@db1 libexec]#
3) 解决方法
出现这个问题,是权限不足,将nagios加入到oinstall组,并重启nrpe(一定要重启下)。这样,错误就能解决:
[root@db1 libexec]#usermod -a -G oinstall nagios
[root@db1 libexec]#id nagios
uid=504(nagios) gid=504(nagios) groups=504(nagios),501(oinstall)
[root@db1 libexec]# killall nrpe
[root@db1 libexec]# /usr/local/nagios/bin/nrpe -c /usr/local/nagios/etc/nrpe.cfg -d
[root@db1 libexec]# ./check_nrpe -H 127.0.0.1 -c check_oracle_tns
OK - reply time 0 msec from adpdb
[root@db1 libexec]# ./check_nrpe -H 127.0.0.1 -c check_oracle_health
OK - tbs USERS usage is 20.00%
tbs UNDOTBS1 usage is 1.09%
tbs TEMP usage is 0.00%
tbs SYSTEM usage is 67.41%
tbs SYSAUX usage is 74.84%
'tbs_users_alloc'=5MB;;;0;5 'tbs_undotbs1_usage_pct'=1.09%;80;90 'tbs_undotbs1_usage'=10MB;740;832;0;925 'tbs_undotbs1_alloc'=925MB;;;0;925 'tbs_temp_usage_pct'=0.00%;80;90 'tbs_temp_usage'=0MB;819;921;0;1024 'tbs_temp_alloc'=1024MB;;;0;1024 'tbs_system_usage_pct'=67.41%;80;90 'tbs_system_usage'=690MB;819;921;0;1024 'tbs_system_alloc'=1024MB;;;0;1024 'tbs_sysaux_usage_pct'=74.84%;80;90 'tbs_sysaux_usage'=766MB;819;921;0;1024 'tbs_sysaux_alloc'=1024MB;;;0;1024 'tbs_adp_ts_usage_pct'=0.49%;80;90
[root@db1 libexec]#
注意事项:
check_oracle_health这个监测脚本,对表空间的使用率百分比计算方式是:
已经使用的表空间大小 / 最大能够达到的表空间大小 ×100%
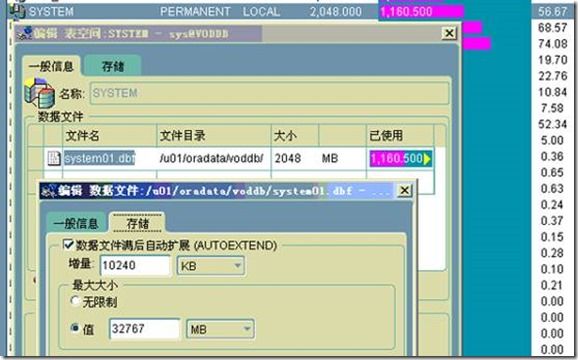
这里的“最大能够达到的表空间大小”不是当前表空间的大小,而是表空间能够扩大的最大表空间文件大小,oracle11g默认的最大表空间文件大小都是:32767MB。
以上面的system表空间为例,我们分配的表空间文件为2G,目前已经使用了1160.5M,oracle console计算出来的已经使用的百分比为56.67。
而check_oracle_health计算的方法是:1160.5M / 32767M = 3.5%
这个不是我们希望的数据,如果所有的表空间文件都自动增加到32767M,服务器都要爆掉了。我们希望的使用百分比应该是56.57,当数据使用率超过80%的时候,人为的去扩大表空间,而不是让oracle系统自己去扩大。
因此,对check_oracle_health脚本进行了修改,将2913行的:
-- a.maxbytes bytes_max,
改成了:
a.bytes bytes_max,
将2966行的:
-- SUM(DECODE(d.autoextensible, 'YES', d.maxbytes, 'NO', d.bytes)) bytes_max,
改成了
SUM(d.bytes) bytes_max,
并将这个脚本另存为check_oracle_tbs。修改后的那一段代码为:
if (DBD::Oracle::Server::return_first_server()->version_is_minimum("9.x")) {
@tablespaceresult = $params{handle}->fetchall_array(q{
SELECT
a.tablespace_name "Tablespace",
b.status "Status",
b.contents "Type",
b.extent_management "Extent Mgmt",
a.bytes bytes,
-- a.maxbytes bytes_max, -- modified by sandish 20130619
a.bytes bytes_max,
c.bytes_free + NVL(d.bytes_expired,0) bytes_free
FROM
(
-- belegter und maximal verfuegbarer platz pro datafile
-- nach tablespacenamen zusammengefasst
-- => bytes
............
............
UNION ALL
SELECT
d.tablespace_name "Tablespace",
b.status "Status",
b.contents "Type",
b.extent_management "Extent Mgmt",
sum(a.bytes_free + a.bytes_used) bytes, -- allocated
-- SUM(DECODE(d.autoextensible, 'YES', d.maxbytes, 'NO', d.bytes)) bytes_max, --modified by sandish 20130619
SUM(d.bytes) bytes_max,
SUM(a.bytes_free + a.bytes_used - NVL(c.bytes_used, 0)) bytes_free
FROM
sys.v_$TEMP_SPACE_HEADER a,
sys.dba_tablespaces b,
sys.v_$Temp_extent_pool c,
dba_temp_files d
WHERE
c.file_id(+) = a.file_id
and c.tablespace_name(+) = a.tablespace_name
and d.file_id = a.file_id
and d.tablespace_name = a.tablespace_name
and b.tablespace_name = a.tablespace_name
GROUP BY
b.status,
b.contents,
b.extent_management,
d.tablespace_name
ORDER BY
1
});
修改后的脚本,基本上符合了对表空间监测的要求,但对于临时表空间的监测出来的数据都还是0。
----查找临时表空间使用情况:
SELECT a.tablespace_name, a.BYTES total, a.bytes - nvl(b.bytes, 0) free,
nvl(b.bytes, 0)/a.BYTES *100 "used(%)"
FROM (SELECT tablespace_name, SUM (bytes) bytes FROM dba_temp_files GROUP BY tablespace_name) a,
(SELECT tablespace_name, SUM (bytes_cached) bytes FROM v$temp_extent_pool GROUP BY tablespace_name) b
WHERE a.tablespace_name = b.tablespace_name(+);
可以根据以上的查询临时表空间的方法修改监测脚本。
1.2.2 nagios服务器192.168.50.22上的配置
拷贝objects 文件夹中的localhost.cfg到/servers下,重命名为50.10_voddb.cfg:
#/usr/local/nagios/etc/objects/localhost.cfg -p /usr/local/nagios/etc/servers/50.10_voddb.cfg
#vi /usr/local/nagios/etc/servers/50.10_voddb.cfg
###############################################################################
###############################################################################
#
# HOST DEFINITION
#
###############################################################################
###############################################################################
# Define a host for the local machine
define host{
use linux-vod-sw ;从这个模板进行继承,交换机为父类
host_name 50.10_voddb ;host名字,以下所有的service的host_name都要改成这个
alias voddb centos5.5 64bit ; A longer name for the server
address 192.168.50.10 ; IP address of the server
icon_p_w_picpath database.gif ; nagios map上显示的两张图
statusmap_p_w_picpath database.gd2
}
#模板中的这里有hostgroup一项,这里全部删除,我们已经创建了hostgroup.cfg文件,在hostgroup.cfg文件中,将本机的host_name加入其members就行。
###############################################################################
###############################################################################
#
# SERVICE DEFINITIONS
#
###############################################################################
###############################################################################
# Define a service to "ping" the local machine
define service{
use generic-service ; Name of service template to use
host_name 50.10_voddb
service_description PING
check_command check_ping!100.0,20%!500.0,60%
}
define service{
use generic-service ; Name of service template to use
host_name 50.10_voddb
service_description ftp
check_command check_ftp ;本机上启动了ftp服务,也需要监测
}
# Define a service to check the number of currently logged in
# users on the local machine. Warning if > 20 users, critical
# if > 50 users.
define service{
use generic-service ; Name of service template to use
host_name 50.10_voddb
service_description Current Users
check_command check_nrpe!check_users
}
# Define a service to check the number of currently running procs
# on the local machine. Warning if > 250 processes, critical if
# > 400 users.
define service{
use generic-service ; Name of service template to use
host_name 50.10_voddb
service_description Total Processes
check_command check_nrpe!check_total_procs
}
define service{
use generic-service
host_name 50.10_voddb
service_description Current Load
check_command check_nrpe!check_load
}
# Define a service to check the swap usage the local machine.
# Critical if less than 10% of swap is free, warning if less than 20% is free
define service{
use generic-service ; Name of service template to use
host_name 50.10_voddb
service_description Swap Usage
check_command check_nrpe!check_swap
}
define service{
use generic-service
host_name 50.10_voddb
service_description Space Usage /
check_command check_nrpe!check_sda2
}
define service{
use generic-service
host_name 50.10_voddb
service_description Space Usage /u01/
check_command check_nrpe!check_sda5
}
define service{
use generic-service
host_name 50.10_voddb
service_description Zombie Processes
check_command check_nrpe!check_zombie_procs
}
define service{
use generic-service
host_name 50.10_voddb
service_description oracle_sid
check_command check_nrpe!check_oracle_sid
}
define service{
use generic-service
host_name 50.10_voddb
service_description oracle_tns
check_command check_nrpe!check_oracle_tns
}
define service{
use generic-service
host_name 50.10_voddb
service_description oracle_tablespace
check_command check_nrpe!check_oracle_health
}
最后验证配置文件是否正确,并重启nagios服务:
# /usr/local/nagios/bin/nagios -v /usr/local/nagios/etc/nagios.cfg
#service nagios start
然后可以查看nagios的ie:http://192.168.50.22/nagios/,点击左面列表看的host,然后选择50.10_voddb右边的放大镜,等几十秒就能查看到监测信息了:
![]()
2.3 其他centos机器监测
2.3.1 被监测机器配置
我们再找一台作为例子来说明如何监测。centos机器的监测项除了cpu负载,内存、硬盘空间,主要的监测项为进程和端口。
进程有tomcat,dhcp,dns,httpd,ftp,mysql等;端口如80,8080等。
如果要监测某个进程,我们可以通过命令先查看下系统中的进程以及它的数量;
如果要监测端口,我们可以使用命令“lsof -i:端口号”查看端口是否已经打开。
如果监测硬盘容量,可以使用df先查看下硬盘的设备文件名。
一般,我们都使用插件check_nrpe来监测。如果是自定义的监测项,需要在被监测机器中进行配置。查看下我已经配置好的一台dhcp服务器的nrpe.cfg文件:
#[root@dhcp root]# vi /usr/local/nagios/etc/nrpe.cfg
... ...
command[check_users]=/usr/local/nagios/libexec/check_users -w 5 -c 10
command[check_load]=/usr/local/nagios/libexec/check_load -w 15,10,5 -c 30,25,20
command[check_disk]=/usr/local/nagios/libexec/check_disk -w 20% -c 10% -p /dev/mapper/VolGroup00-LogVol00
command[check_zombie_procs]=/usr/local/nagios/libexec/check_procs -w 5 -c 10 -s Z
command[check_total_procs]=/usr/local/nagios/libexec/check_procs -w 300 -c 400
command[check_swap]=/usr/local/nagios/libexec/check_swap -w 20% -c 10%
command[check_dns_proc]=/usr/local/nagios/libexec/check_procs -c 1:1 -C named
command[check_dhcpd_proc]=/usr/local/nagios/libexec/check_procs -c 1:1 -C dhcpd
这里,command[check_disk]是监测根分区的使用情况。通过df命令,查得根分区的设备文件为/dev/mapper/VolGroup00-LogVol00。
command[check_dns_proc]为监测dns服务启是否启动,如果有一个dns进程,则表示状态正常,否则都是异常;
command[check_dhcpd_proc] 为监测dns服务启是否启动,如果有一个dhcp进程,则表示状态正常,否则都是异常;
另外,检查下allowed_hosts是否将nagios服务器ip写入了,正确的应该为:
allowed_hosts=127.0.0.1,192.168.50.22
允许本机和nagios服务器通过nrpe协议进行通讯。
测试tcp端口不需要定义监测命令。修改好后重启下nrpe:
#killall nrpe
#/usr/local/nagios/bin/nrpe -c /usr/local/nagios/etc/nrpe.cfg -d
2.3.2 nagios服务器192.168.50.22上的配置
拷贝objects 文件夹中的localhost.cfg到/servers下,由于被监测机器的ip地址为192.168.50.11,我们重命名localhost.cfg为50.11_portal.cfg:
#/usr/local/nagios/etc/objects/localhost.cfg -p /usr/local/nagios/etc/servers/50.11_portal.cfg
vi /usr/local/nagios/etc/servers/50.11_portal.cfg
###############################################################################
###############################################################################
#
# HOST DEFINITION
#
###############################################################################
###############################################################################
# Define a host for the local machine
define host{
use linux-vod-sw ; Inherit default values from a template
host_name 50.11_portal ; The name we're giving to this server
alias portal centos5.5 32bit ; A longer name for the server
address 192.168.50.11 ; IP address of the server
}
###############################################################################
###############################################################################
#
# SERVICE DEFINITIONS
#
###############################################################################
###############################################################################
# Define a service to "ping" the local machine
define service{
use generic-service ; Name of service template to use
host_name 50.11_portal
service_description PING
check_command check_ping!100.0,20%!500.0,60%
}
# Define a service to check the number of currently logged in
# users on the local machine. Warning if > 20 users, critical
# if > 50 users.
define service{
use generic-service ; Name of service template to use
host_name 50.11_portal
service_description Current Users
check_command check_nrpe!check_users
}
# Define a service to check the number of currently running procs
# on the local machine. Warning if > 250 processes, critical if
# > 400 users.
define service{
use generic-service ; Name of service template to use
host_name 50.11_portal
service_description Total Processes
check_command check_nrpe!check_total_procs
}
# Define a service to check the swap usage the local machine.
# Critical if less than 10% of swap is free, warning if less than 20% is free
define service{
use generic-service ; Name of service template to use
host_name 50.11_portal
service_description Swap Usage
check_command check_nrpe!check_swap
}
# Define a service to check HTTP on the local machine.
# Disable notifications for this service by default, as not all users may have HTTP enabled.
define service{
use generic-service ; Name of service template to use
host_name 50.11_portal
service_description tomcat_portal
check_command check_tcp!8080 ;监测8080端口
}
define service{
use generic-service ; Name of service template to use
host_name 50.11_portal
service_description tomcat_ web
check_command check_tcp!8082 ;监测8082端口
}
define service{
use generic-service ; Name of service template to use
host_name 50.11_portal
service_description portal_aaa ;
check_command check_tcp!3000 ;监测3000端口
}
define service{
use generic-service
host_name 50.11_portal
service_description Space Usage/
check_command check_nrpe!check_disk
}
define service{
use generic-service
host_name 50.11_portal
service_description Current Load
check_command check_nrpe!check_load
}
define service{
use generic-service
host_name 50.11_portal
service_description Zombie Processes
check_command check_nrpe!check_zombie_procs
}
最后验证配置文件是否正确,如果正确,则重启nagios服务:
# /usr/local/nagios/bin/nagios -v /usr/local/nagios/etc/nagios.cfg
#service nagios start
然后可以刷新ie:http://192.168.50.22/nagios/,等几十秒就能查看到监控信息了:
2.4 windows机器监测
2.4.1 客户windows服务器配置
30几台服务器中,其中2、3台的操作系统为windows2003server 32位操作系统,因此需要安装NSCP-0.4.1.101-Win32.msi。如果是windows2008R2系统,由于是64位,因此,可以安装NSCP-0.4.1.101-x64.msi。
安装的时候,需要填写nagios服务器的ip地址,允许与nagios服务器进行通讯。密码可以填111111,或者不填。这里我们填了6个1,因此,在nagios服务器的command.cfg配置文件的check_nt命令行中需要增加 -s 111111 的参数,否则,通讯会失败。
Enable NSCAclient不选择。
其他的都默认,点击下一步进行安装。
NSClient++ 默认安装在C:\Program Files\NSClient++,其配置文件为:nsclient.ini。如果安装时候,密码忘了写,可以在安装完后,直接修改这个配置文件。
这里,需要监测的内容除了一般的服务器的信息外,还包括的windows服务有:
mysql
sqlserver
tomcat
监测的进程有cmd.exe,explorer.exe
1.4.2 nagios服务器192.168.50.22上的配置
拷贝objects 文件夹中的windows.cfg到/servers下,重命名为50.15_win1.cfg:
#/usr/local/nagios/etc/objects/windows.cfg -p /usr/local/nagios/etc/servers/50.15_win1.cfg
#vi /usr/local/nagios/etc/servers/50.15_win1
###############################################################################
# WINDOWS.CFG - SAMPLE CONFIG FILE FOR MONITORING A WINDOWS MACHINE
#
# Last Modified: 06-13-2007
#
# NOTES: This config file assumes that you are using the sample configuration
# files that get installed with the Nagios quickstart guide.
#
###############################################################################
###############################################################################
###############################################################################
#
# HOST DEFINITIONS
#
###############################################################################
###############################################################################
# Define a host for the Windows machine we'll be monitoring
# Change the host_name, alias, and address to fit your situation
define host{
use linux-vod-sw ; Inherit default values from a template
host_name 50.15_win1 ; The name we're giving to this host
alias win2k3 ; A longer name associated with the host
address 192.168.50.15 ; IP address of the host
icon_p_w_picpath win40.gif
statusmap_p_w_picpath win40.gd2
}
###############################################################################
###############################################################################
#
# SERVICE DEFINITIONS
#
###############################################################################
###############################################################################
# Create a service for monitoring the uptime of the server
# Change the host_name to match the name of the host you defined above
define service{
use generic-service
host_name 50.15_win1
service_description Uptime
check_command check_nt!UPTIME
}
# Create a service for monitoring CPU load
# Change the host_name to match the name of the host you defined above
define service{
use generic-service
host_name 50.15_win1
service_description CPU Load
check_command check_nt!CPULOAD!-l 5,80,90
}
# Create a service for monitoring memory usage
# Change the host_name to match the name of the host you defined above
define service{
use generic-service
host_name 50.15_win1
service_description Memory Usage
check_command check_nt!MEMUSE!-w 80 -c 90
}
# Create a service for monitoring C:\ disk usage
# Change the host_name to match the name of the host you defined above
define service{
use generic-service
host_name 50.15_win1
service_description C:\ Drive Space
check_command check_nt!USEDDISKSPACE!-l c -w 80 -c 90
}
# Create a service for monitoring the W3SVC service
# Change the host_name to match the name of the host you defined above
define service{
use generic-service
host_name 50.15_win1
service_description MySQL55
check_command check_nt!SERVICESTATE!-d SHOWALL -l MySQL55
}
#windows服务名中如果带有空格,需要用双引号引起来
define service{
use generic-service
host_name 50.15_win1
service_description Tomcat6
check_command check_tcp!8899
}
define service{
use generic-service
host_name 50.15_win1
service_description FTP
check_command check_tcp!21
}
define service{
use generic-service
host_name 101.27_win
service_description MSSQLSERVER
check_command check_nt!SERVICESTATE!-d SHOWALL -l MSSQLFDLauncher,MSSQLSERVER,MSSQLServerOLAPService,MsDtsServer100,ReportServer,SQLWriter,SQLSERVERAGENT #需要监测多个服务,依次写上
}
# Create a service for monitoring the Explorer.exe process
# Change the host_name to match the name of the host you defined above
define service{
use generic-service
host_name 50.15_win1
service_description Explorer
check_command check_nt!PROCSTATE!-d SHOWALL -l Explorer.exe
}
define service{
use generic-service
host_name 50.15_win1
service_description CMD
check_command check_nt!PROCSTATE!-d SHOWALL -l cmd.exe
}
监测的windows服务的服务名称可查看windows服务中的“服务名称”(注意不是“显示名称”),如下图中为Tomcat6
修改
vi /usr/local/nagios/etc/objects/commands.cfg
# 'check_nt' command definition
define command{
command_name check_nt
command_line $USER1$/check_nt -H $HOSTADDRESS$ -p 12489 -v $ARG1$ $ARG2$ -s 111111 #把密码加进来
}
我这里几台windows安装的NSClient++密码都是6个1。如果两台windows安装的NSClient++密码不一样,我也想不出什么好办法来,因此,尽量用同样的密码,或者都不输入密码。
最后验证配置文件是否正确,并重启nagios服务:
# /usr/local/nagios/bin/nagios -v /usr/local/nagios/etc/nagios.cfg
#service nagios start
然后可以刷新ie:http://192.168.50.22/nagios/,等几十秒就能查看到监控信息了:
2.5 交换机配置
查看nagios的交换机默认监测配置文件:/usr/local/nagios/etc/object/swicth.cfg,可以看到交换机监测的常规项似乎监控端口以及端口的带宽,我们将这两项配置起来。
监测端口状态使用命令check_snmp!-C public -o ifOperStatus.1 -r 1 -m RFC1213-MIB,因此需要知道需要监测的端口号的OID;
监测端口带宽利用率使用命令check_local_mrtgtraf!/var/www/html/mrtg/192.168.50.252_1.log!AVG!1000000,1000000!5000000,5000000!10 ,这里,需要使用mrtg获取监测端口的log文件。因此,需要在服务器端安装mrtg包。启动mrtg获取端口带宽数据日志文件,然后nagios通过分析日志文件,将带宽数据反映到nagios的web上。
2.5.1 交换机配置
1, 启动交换机SNMP
这里的交换机型号为思科的3650。查询交换机SNMP是否启动,可以通过命令查看。如果交换机已经打开了ie的配置页面功能,也可以打开IE登录后查看:
User Access Verification
Password:
Vod-SW>en
Password:
Vod-SW#show snmp
%SNMP agent not enabled
Vod-SW#
在交换机中启动snmp,我们通过ie界面进行配置。打开ie,输入“http://交换机ip地址”,输入交换机的登录用户名密码后,找到“Advanced Settings”,将SNMP选择Enable,并输入SNMP Read Community为public,后,点击提交。
Vod-SW#show snmp
Chassis: FOC1509Z5JL
0 SNMP packets input
0 Bad SNMP version errors
0 Unknown community name
0 Illegal operation for community name supplied
0 Encoding errors
0 Number of requested variables
0 Number of altered variables
0 Get-request PDUs
0 Get-next PDUs
0 Set-request PDUs
0 Input queue packet drops (Maximum queue size 1000)
0 SNMP packets output
0 Too big errors (Maximum packet size 1500)
0 No such name errors
0 Bad values errors
0 General errors
0 Response PDUs
0 Trap PDUs
SNMP global trap: disabled
SNMP logging: disabled
SNMP agent enabled
Vod-SW#
2, 获取交换机端口信息(可以在50.22上进行如下获取OID操作)
(这里顺便提一下,如果使用mrtg插件监测交换机的话,在mrtg配置成功后,可以在mrtg的html主页面上就能知道各个端口的OID,因此,也不需要通过以下的方法获取交换机端口的OID号。不过,很多的硬件设备还是需要自行搜索OID号,并根据硬件产商官方有关文档进行对比甄别所要监测的OID信息。)
获取端口信息的命令为:check_snmp!-C public -o ifOperStatus.1 -r 1 -m RFC1213-MIB。其中:
"-o ifOperStatus.1"指取出交换机的端口编号为1的OID状态。"-r 1"选项是让check_snmp插件检查返回一个正常(OK)状态,如果是在SNMP查询结果中存在"1"(1说明交换机端口处于运行状态)如果没找到1就是紧急(CRITICAL)状态。"-m RFC1213-MIB"是可选的,它告诉check_snmp插件只加载"RFC1213-MIB"库而不是加载每个在系统里的MIB库,这可以加快插件运行速度。
监测交换机的端口需要OID,即端口号。交换机的端口号1往往就是1,而其他的端口号就不是2,3,4等等了。可以通过以下命令获取端口信息(信息中包含端口号):
snmpwalk -c public -v 1 -t 120 [交换机ip地址] >>switch.txt
查看switch.txt文件:
IF-MIB::ifOperStatus.1 = INTEGER: up(1)
IF-MIB::ifOperStatus.301 = INTEGER: up(1)
IF-MIB::ifOperStatus.302 = INTEGER: up(1)
IF-MIB::ifOperStatus.303 = INTEGER: up(1)
IF-MIB::ifOperStatus.304 = INTEGER: up(1)
IF-MIB::ifOperStatus.305 = INTEGER: up(1)
IF-MIB::ifOperStatus.5001 = INTEGER: up(1)
IF-MIB::ifOperStatus.10101 = INTEGER: up(1)
IF-MIB::ifOperStatus.10102 = INTEGER: up(1)
... ... ... ...
IF-MIB::ifOperStatus.10147 = INTEGER: down(2)
IF-MIB::ifOperStatus.10148 = INTEGER: down(2)
IF-MIB::ifOperStatus.10149 = INTEGER: up(1)
IF-MIB::ifOperStatus.10150 = INTEGER: up(1)
IF-MIB::ifOperStatus.10151 = INTEGER: down(2)
IF-MIB::ifOperStatus.10152 = INTEGER: down(2)
IF-MIB::ifOperStatus.10501 = INTEGER: up(1)
然后根据查到的端口对应的OID设置端口监控
这里我们可以找几个端口号进行监测,普通的端口为1到48;49和50是聚合口,连到核心交换机上。因此我们可以监测端口1,49和50:ifOperStatus.1,ifOperStatus.10149和ifOperStatus.10150
其中,配置文件:
check_ping!200.0,20%!600.0,60%
表示:
紧急(CRITICAL)-条件是RTA大于600ms或丢包率大于等于60%;
告警(WARNING)-条件是RTA大于200ms或是丢包率大于等于20%;
正常(OK)-条件是RTA小于200ms或丢包率小于20%
check_snmp!-C public -o ifOperStatus.1 -r 1 -m RFC1213-MIB
表示:
"-o ifOperStatus.1"指出取出交换机的端口编号为1的OID状态。"-r 1"选项是让check_snmp插件检查返回一个正常(OK)状态,如果是在SNMP查询结果中存在"1"(1说明交换机端口处于运行状态)如果没找到1就是紧急(CRITICAL)状态。"-m RFC1213-MIB"是可选的,它告诉check_snmp插件只加载"RFC1213-MIB"库而不是加载每个在系统里的MIB库,这可以加快插件运行速度。
check_local_mrtgtraf!/var/www/html/mrtg/192.168.50.252_10150.log!AVG!10000000,10000000!50000000,50000000!10
表示:
读取日志文件/var/www/html/mrtg/192.168.50.252_10150.log中的平均速度,当超过10M时状态改为warning;如果超过50M状态改为critical。
"/var/www/html/mrtg/192.168.50.252_10150.log "参数传给check_local_mrtgtraf,意思是插件的MRTG日志文件在这个文件里读写,"AVG"参数的意思是取带宽的统计平均值,"10000000, 10000000"参数是指流入的告警门限 (以字节为单位),"50000000,50000000"是输出流量紧急状态门限(以字节为单位),"10"是指如果MRTG日志如果超过10分钟没有数据 返回一个紧急状态(应该每5分钟更新一次)。
2.5.2 nagios服务器192.168.50.22上的配置
在交换机上打开snmp通讯就行了,大部分的工作是在nagios服务器上进行配置。
一、 MRTG插件安装(http://www.xianren.org/net/centos-mrtg.html)
监测端口流量需要使用MRTG插件,在服务器上先安装MRTG插件:
1, 下载MRTG安装包
从http://oss.oetiker.ch/mrtg/pub/?M=D下载mrtg-2.17.4.tar.gz
2, 前提条件
在安装mrtg之前,请确保您有安装GD的libpng,zlib的包。如果尚未安装,则先安装这两个包;
#rpm -qa|grep libpng
#rpm -qa|grep zlib
3, 安装MRTG
#tar -zxvf mrtg-2.17.4.tar.gz
cd mrtg-2.17.4
./configure --prefix=/usr/local/mrtg --sysconfdir=/etc/mrtg --with-gd=/usr/local/gd2/include --with-gd-lib=/usr/local/gd2/lib --with-gd-inc=/usr/local/gd2/include --with-png=/usr/local/include --with-png-lib=/usr/local/lib --with-png-inc=/usr/local/include --with-zlib=/usr/local/zlib/include --with-zlib-lib=/usr/local/zlib/include --with-zlib-inc=/usr/local/zlib/include
如果configure出现什么warning或者error,可以尝试下下面的configre命令:
./configure --prefix=/usr/local/mrtg --with-gd=/usr/local/gd2/ --with-gd-lib=/usr/local/gd2/lib/ --with-gd-inc=/usr/local/gd2/include/ --with-z=/usr/local/zlib/ --with-z-lib=/usr/local/zlib/lib/ --with-z-inc=/usr/local/zlib/include/ --with-png=/usr/local/lib
make
make install
到这里Mrtg已被成功的安装到系统上了。
4, 生成cfg文件
我们要监控的交换机IP为:192.168.50.252 ,Apache主目录是/var/www/html。将mrtg的log数据日志放在/var/www/html/mrtg/文件夹中,
首先来生成cfg文件:
#mkdir /var/www/html/mrtg/
/usr/local/mrtg/bin/cfgmaker --global 'WorkDir: /var/www/html/mrtg' --global 'Options[_]: bits,growright' --output /var/www/html/mrtg/mrtg252.cfg [email protected]
5, 修改mrtg252.cfg文件(如果以下设置已经有了,则不需要更改):
打开mrtg252.cfg,查看以下信息是否正确:
更改WorkDir为/var/www/html/mrtg
去掉Options[_]: growright, bits前面的#
并加入Language:Chinese使之支持中文(如果中文显示有问题,比如显示的都是四方块,那么,可能是操作系统尚未安装中文字符集。解决的方法是要么安装中文字符集,要么这个配置就不需加入)
保存并退出。
6, 接着运行env LANG=C /usr/local/mrtg/bin/mrtg /var/www/html/mrtg/mrtg252.cfg
连续执行三次以上直到不再显示错误为止
7, 生成页面文件
#/usr/local/mrtg/bin/indexmaker --output=/var/www/html/mrtg/index252.html --title="192.168.50.252 Vod-Switch Traffic MRTG on linux"
8, 如果httpd已经启动了,则可以访问如下网页:
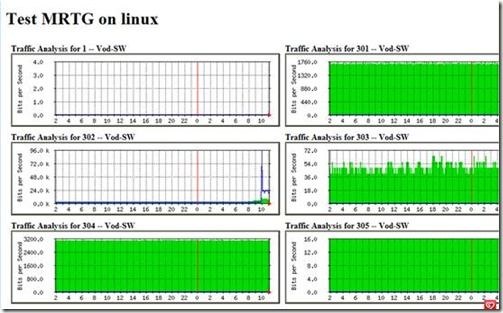
http://192.168.50.22/mrtg ,(以下是经过1个星期左右时间启动后的图。如果是刚配置成功启动,则图上都没有数据。数据会随时间逐步生成):
9, 为了让监测数据自动更新,还需要让程序在后台定时运行,
crontab -e
在其中输入 :
*/5 * * * * /usr/bin/env LANG=C /usr/local/mrtg/bin/mrtg /var/www/html/mrtg/mrtg252.cfg --logging /var/log/mrtg252.log
即让系统在后台每五分钟执行一次env LANG=C /usr/local/mrtg/bin/mrtg /var/www/html/mrtg/mrtg252.cfg进行数据刷新。
用nagios命令测试下:
# /usr/local/nagios/libexec/./check_mrtgtraf -F /var/www/html/mrtg/192.168.50.252_1.log
Traffic OK - Avg. In = 0.0 B/s, Avg. Out = 0.0 B/s|in=0.000000B/s;;;0.000000 out=0.000000B/s;;;0.000000
#
(另外一台交换机配置也类似)
二、 nagios监测配置文件50.252_switch.cfg设置
1, 生成switch配置文件存放的路径
#mkdir /usr/local/nagios/etc/switches
2, 在nagios.cfg文件上配置switch监控文件存放的路径
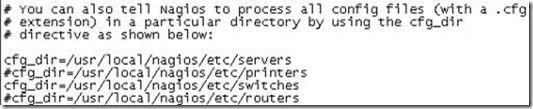
#vi /usr/local/nagios/etc/nagios.cfg
cfg_dir=/usr/local/nagios/etc/switches
3, 配置50.252_switch.cfg
#cp -p /usr/local/nagios/etc/objects/switch.cfg /usr/local/nagios/etc/switches/50.252_switch.cfg
#vi /usr/local/nagios/etc/switches/50.252_switch.cfg
###############################################################################
# SWITCH.CFG - SAMPLE CONFIG FILE FOR MONITORING A SWITCH
#
# Last Modified: 10-03-2007
#
# NOTES: This config file assumes that you are using the sample configuration
# files that get installed with the Nagios quickstart guide.
#
###############################################################################
###############################################################################
###############################################################################
#
# HOST DEFINITIONS
#
###############################################################################
###############################################################################
# Define the switch that we'll be monitoring
define host{
use generic-switch ; Inherit default values from a template
host_name 50.252_VodSw ; The name we're giving to this switch
alias 50.252 Vod Switch ; A longer name associated with the switch
address 192.168.50.252 ; IP address of the switch
hostgroups switches ; Host groups this switch is associated with
}
#这里,交换机直接继承了默认的generic-switch,并且在这里加入了下面定义的组switches。
###############################################################################
###############################################################################
#
# HOST GROUP DEFINITIONS
#
###############################################################################
###############################################################################
# Create a new hostgroup for switches
define hostgroup{
hostgroup_name switches ; The name of the hostgroup
alias Network Switches ; Long name of the group
}
#这里,定义了交换机的组,另外一台交换机的配置文件中就不能再定义了,只需要在host定义中增加“hostgroups switches”就行了
###############################################################################
###############################################################################
#
# SERVICE DEFINITIONS
#
###############################################################################
###############################################################################
# Create a service to PING to switch
define service{
use generic-service ; Inherit values from a template
host_name 50.252_VodSw ; The name of the host the service is associated with
service_description PING ; The service description
check_command check_ping!200.0,20%!600.0,60% ; The command used to monitor the service
normal_check_interval 5 ; Check the service every 5 minutes under normal conditions
retry_check_interval 1 ; Re-check the service every minute until its final/hard state is determined
}
# Monitor uptime via SNMP
define service{
use generic-service ; Inherit values from a template
host_name 50.252_VodSw
service_description Uptime
check_command check_snmp!-C public -o sysUpTime.0
}
# Monitor Port 49,50 status via SNMP
define service{
use generic-service ; Inherit values from a template
host_name 50.252_VodSw
service_description Port 1 Link Status
check_command check_snmp!-C public -o ifOperStatus.1 -r 1 -m RFC1213-MIB
}
define service{
use generic-service ; Inherit values from a template
host_name 50.252_VodSw
service_description Port 49 Link Status
check_command check_snmp!-C public -o ifOperStatus.10149 -r 1 -m RFC1213-MIB
}
define service{
use generic-service ; Inherit values from a template
host_name 50.252_VodSw
service_description Port 50 Link Status
check_command check_snmp!-C public -o ifOperStatus.10150 -r 1 -m RFC1213-MIB
}
# Monitor bandwidth via MRTG logs
define service{
use generic-service ; Inherit values from a template
host_name 50.252_VodSw
service_description Port 1 Bandwidth Usage
check_command check_local_mrtgtraf!/var/www/html/mrtg/192.168.50.252_1.log!AVG!1000000,1000000!5000000,5 000000!10
}
define service{
use generic-service ; Inherit values from a template
host_name 50.252_VodSw
service_description Port 49 Bandwidth Usage
check_command check_local_mrtgtraf!/var/www/html/mrtg/192.168.50.252_10149.log!AVG!1000000,1000000!5000000,5000000!10
}
define service{
use generic-service ; Inherit values from a template
host_name 50.252_VodSw
service_description Port 50 Bandwidth Usage
check_command check_local_mrtgtraf!/var/www/html/mrtg/192.168.50.252_10150.log!AVG!1000000,1000000!5000000,5000000!10
}
define service{
use generic-service ; Inherit values from a template
host_name 50.252_VodSw
service_description CPU Load AVG5sec
check_command check_snmp!-C public -o .1.3.6.1.4.1.9.9.109.1.1.1.1.6.1 -w 50 -c 80 -u% -l "CPU load is" -m RFC1213-MIB
}
2.5.3 CPU监测
这里,单独叙述下通过snmp监测交换机的cpu
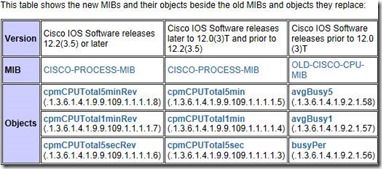
从网上http://www.cisco.com/en/US/tech/tk648/tk362/technologies_tech_note09186a0080094a94.shtml
查到监测cpu的有关信息:
telnet到交换机,看到这台交换机的版本是12.2(50):
同时,查询下cpu负载:
使用MIB图中的第一列的MID号,在192.168.50.22上监测cpu:
1) 5秒平均负载
snmpwalk -v2c -c public 192.168.50.252 .1.3.6.1.4.1.9.9.109.1.1.1.1.6.1
2) 1分钟平均负载
snmpwalk -v2c -c public 192.168.50.252 .1.3.6.1.4.1.9.9.109.1.1.1.1.7.1
3) 5分钟平均负载
snmpwalk -v2c -c public 192.168.50.252 .1.3.6.1.4.1.9.9.109.1.1.1.1.6.1
这三个命令都能成功执行。
再执行:
#cd /usr/local/nagios/libexec
./check_snmp -H 192.168.50.252 -o .1.3.6.1.4.1.9.9.109.1.1.1.1.6.1 -c public
SNMPv2-SMI::enterprises.9.9.109.1.1.1.1.6.1 = Gauge32: 7
./check_snmp -H 192.168.50.252 -o .1.3.6.1.4.1.9.9.109.1.1.1.1.7.1 -c public
SNMPv2-SMI::enterprises.9.9.109.1.1.1.1.7.1 = Gauge32: 10
./check_snmp -H 192.168.50.252 -o .1.3.6.1.4.1.9.9.109.1.1.1.1.8.1 -c public
SNMPv2-SMI::enterprises.9.9.109.1.1.1.1.8.1 = Gauge32: 11
对比以上的3个数据,基本上是一致的。
然后整理监测脚本:
./check_snmp -H 192.168.50.252 -o .1.3.6.1.4.1.9.9.109.1.1.1.1.7.1 -c public -P 1 -w 50 -c 80 -u% -l "CPU load is" -m:
生成监测服务,将以下脚本加入到/usr/local/nagios/etc/switches/50.252_switch.cfg中:
define service{
use generic-service ; Inherit values from a template
host_name 50.252_VodSw
service_description CPU Load AVG5sec
check_command check_snmp!-C public -o .1.3.6.1.4.1.9.9.109.1.1.1.1.6.1 -w 50 -c 80 -u% -l "CPU load is" -m RFC1213-MIB
}
最后验证cfg文件以及重新加载nagios服务
# /usr/local/nagios/bin/nagios -v /usr/local/nagios/etc/nagios.cfg
#service nagios reload
2.5.4 内存监测
# 获取内存当前使用情况(bytes),对应交换机查询出来的Userd(b)一列
snmpwalk -v 2c -c public 192.168.50.252 1.3.6.1.4.1.9.9.48.1.1.1.5
# 获取内存当前空闲多少(bytes),对应交换机查询出来的Free(b)一列
snmpwalk -v 2c -c public 192.168.50.252 1.3.6.1.4.1.9.9.48.1.1.1.6
# 获取内存历史最大空余多少(bytes),对应交换机查询出来的Largest (b)一列
snmpwalk -v 2c -c public 192.168.50.252 1.3.6.1.4.1.9.9.48.1.1.1.7
# snmpwalk -v 2c -c public 192.168.50.252 1.3.6.1.4.1.9.9.48.1.1.1.5
SNMPv2-SMI::enterprises.9.9.48.1.1.1.5.1 = Gauge32: 19222640
SNMPv2-SMI::enterprises.9.9.48.1.1.1.5.2 = Gauge32: 3606412
SNMPv2-SMI::enterprises.9.9.48.1.1.1.5.16 = Gauge32: 40
#
# snmpwalk -v 2c -c public 192.168.50.252 1.3.6.1.4.1.9.9.48.1.1.1.6
SNMPv2-SMI::enterprises.9.9.48.1.1.1.6.1 = Gauge32: 68694184
SNMPv2-SMI::enterprises.9.9.48.1.1.1.6.2 = Gauge32: 4782196
SNMPv2-SMI::enterprises.9.9.48.1.1.1.6.16 = Gauge32: 1048536
#
Vod-SW>show mem
Head Total(b) Used(b) Free(b) Lowest(b) Largest(b)
Processor 3480DD4 87916844 19222984 68693860 54383028 30100460
I/O 6800000 8388608 3606544 4782064 4729364 4758216
Driver te 2600000 1048576 44 1048532 1048532 1048532
--More--
最好是能够计算出百分比,然后设置阈值进行告警。。。。如果实在没什么办法,可以直接监控内存Free的总数量,自己计算一个百分比:比如低于50%×87916844,为warning;低于20%×87916844,为critical。
也可以在网上查老外写的监测脚本check_snmp_mem,如:
http://opensource.is/trac/browser/nagios-plugins/check_snmp/trunk?rev=8f404c77185fa7589fb7fbb51cd569b2344c394e&order=name
https://github.com/surcouf/nagios-snmp-plugins/blob/master/check_snmp_mem.pl
http://opensource.ok.is/trac/browser/nagios-plugins/check_snmp/check_snmp_mem.pl
对脚本的oid进行适当的修改后,就应该能使用了。
配置文件创建成功后,使用命令验证下配置文件,如果没有问题,则重启nagios,然后就能查看到交换机的监测项。
另外一台交换机配置类似。
2.6 4台ipqam
4台ipqam地址为192.168.50.101到104。登录管理控制台,可看到snmp都已经开启。因此,可以对这些设备进行监测。
由于对这个设备监测项不是特别了解,因此,我们只对设备的简单几项进行监测:ping、uptime和eth0口。将交换机的配置文件复制一份进行修改。Server项改成以下三项:
define service{
use generic-service ; Inherit values from a template
host_name 50.101_ipqam ; The name of the host the service is associated with
service_description PING ; The service description
check_command check_ping!200.0,20%!600.0,60% ; The command used to monitor the service
normal_check_interval 5 ; Check the service every 5 minutes under normal conditions
retry_check_interval 1 ; Re-check the service every minute until its final/hard state is determined
}
# Monitor uptime via SNMP
define service{
use generic-service ; Inherit values from a template
host_name 50.101_ipqam
service_description Uptime
check_command check_snmp!-C public -o sysUpTime.0
}
# Monitor Port eth0 status via SNMP
define service{
use generic-service ; Inherit values from a template
host_name 50.101_ipqam
service_description eth0 Link Status
check_command check_snmp!-C public -o ifOperStatus.2 -r 1 -m RFC1213-MIB
}
#通过snapwalk查得eth0的OID为2。因此这里为ifOperStatus.2
父子设置
上面章节对父子设置简单的介绍过,这里另起一节进行说明。
Host之间可以设置父子关系,比如交换机为父,交换机之下的服务器为子;或者表示某台服务器依赖与另外一台服务器。
如果将交换机设为主机,那么交换机下应该有很多的“子”服务器,此时,可以设置一个模板,如在/usr/local/nagios/etc/object/templates.cfg最后新增:
define host{
name linux-vod-sw ; Name of this template
use generic-host ; Inherit default values
check_period 24x7
check_interval 5
retry_interval 1
max_check_attempts 10
check_command check-host-alive
icon_p_w_picpath redhat.gif
statusmap_p_w_picpath redhat.gd2
parents 50.252_VodSw #使用这个模板的设备都是 50.252_VodSw 的子设备
# notification_period 24x7
# notification_interval 30
# notification_options d,r
notifications_enabled 0
contact_groups admins
register 0 ; DONT REGISTER THIS - ITS A TEMPLATE
}
然后将所有的服务器配置文件中的host定义段中的use设置为use linux-vod-sw。如:
define host{
use linux-vod-sw ; Inherit default values from a template
host_name 50.10_voddb ; The name we're giving to this server
alias voddb centos5.5 64bit ; A longer name for the server
address 192.168.50.10 ; IP address of the server
icon_p_w_picpath database.gif
statusmap_p_w_picpath database.gd2
}
MAP图片显示设置
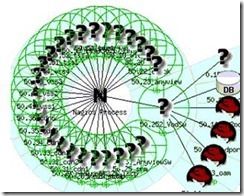
图片定义
在nagios的ie监测项Map界面,如果没有设置好图片,则显示的图片都为“?”。以下大部分都还没有配置图片,右面的一些服务器已经配置了图片:
图片文件在host定义中,如:
define host{
use linux-box-SZ-vod-sw ; Inherit default values from a template
host_name 50.10_voddb ; The name we're giving to this server
alias voddb centos5.5 64bit ; A longer name for the server
address 192.168.50.10 ; IP address of the server
icon_p_w_picpath database.gif
statusmap_p_w_picpath database.gd2
}
这里定义了两个变量icon_p_w_picpath和statusmap_p_w_picpath。statusmap_p_w_picpath在上图中进行显示,文件名后缀为.gd2。
如果鼠标移动到某个服务器上,又会显示一个框,这个框中的左上角图片为icon_p_w_picpath参数指定的图片文件名:
图片参数包括(摘录网上的解释):
icon_p_w_picpath : 可以使用GIF、PNG或者是JPG文件,推荐图像尺寸为40x40
icon_p_w_picpath_alt: 即为HTML语法中关于p_w_picpath元素的ALT属性值
vrml_p_w_picpath : Nagios提供使用VRML语言绘制三维图像功能,这里不要使用透明图片(PNG, GIF),最好使用JPG
statusmap_p_w_picpath: 提供给statusmap CGI脚本使用的图片,服务器要支持GD,这个文件的类型为gd2
(icon_p_w_picpath_alt,vrml_p_w_picpath尚未研究是怎么用的。)
图片配置完后的nagios Map应该是这样的:
上面的Map图中,有些图是nagios自带的,有些图是我用windows的画图版画出40×40像素的图后,通过下一小节的方法转成gd2。
Gd2图片文件生成
http://www.net527.com/caozuoxitong/Linux/6374.html
可以通过以下方法将png或者gif生成gd2文件
1, 可以从厂商下载visio或者PPT的图标库,一般可以得到JPG格式的文件,调整大小到40x40。
This variable is used to define the name of an p_w_picpath that should be associated with this host in the statusmap CGI. You can specify a JPEG, PNG, and GIF p_w_picpath if you want, although I would strongly suggest using a GD2 format p_w_picpath, as other p_w_picpath formats will result in a lot of wasted CPU time when the statusmap p_w_picpath is generated. GD2 p_w_picpaths can be created from PNG p_w_picpaths by using the pngtogd2 utility supplied with Thomas Boutell's gd library. The GD2 p_w_picpaths should be created in uncompressed format in order to minimize CPU load when the statusmap CGI is generating the network map p_w_picpath. The p_w_picpath will look best if it is 40x40 pixels in size.
以上意思是推荐是使用GD2图片文件,因为其消耗系统资源少。不能使用压缩的GD2图片文件。可以使用Thomas Boutell's gd library的pngtogd2从png生成GD2文件。图片建议使用40×40像素。
2, 将pnp转成GD2
下载编译、安装GD库
gd-progs-2.0.33-9.4.el5_4.2.i386.rpm
#rpm -ivh gd-progs-2.0.33-9.4.el5_4.2.i386.rpm
# pngtogd2 -h
Usage: pngtogd2 filename.png filename.gd2 cs fmt
where cs is the chunk size
fmt is 1 for raw, 2 for compressed
# giftogd2 -h
Usage: giftogd2 filename.gif filename.gd2 cs fmt
where cs is the chunk size
fmt is 1 for raw, 2 for compressed
#./pngtogd2 /usr/local/nagios/share/p_w_picpaths/logos/H3cSwitch.png H3cSwitch.gd2 cs 1
cp H3cSwitch.gd2 /usr/local/nagios/share/p_w_picpaths/logos/
3, 定义define hostextinfo,define serviceextinfo使用自定义的图标
define hostextinfo{
host_name host_name
notes note_string
notes_url url
action_url url
icon_p_w_picpath p_w_picpath_file
icon_p_w_picpath_alt alt_string
vrml_p_w_picpath p_w_picpath_file
statusmap_p_w_picpath p_w_picpath_file
2d_coords x_coord,y_coord
3d_coords x_coord,y_coord,z_coord
}
define serviceextinfo{
host_name host_name
service_description service_description
notes note_string
notes_url url
action_url url
icon_p_w_picpath p_w_picpath_file
icon_p_w_picpath_alt alt_string
}
define hostextinfo{
host_name H3C-S5100
# notes_url http://webserver/hostinfo.pl?host=you_can_edit_this
icon_p_w_picpath H3cSwitch.png
# icon_p_w_picpath_alt
vrml_p_w_picpath H3cSwitch.png
statusmap_p_w_picpath H3cSwitch.gd2
# 2d_coords 100,250
# 3d_coords 100.0,50.0,75.0
}
----------------本章完--------------------