项目位置 https://github.com/deepsadness/SDLCmakeDemo
系列内容导读
- SDL2-移植Android Studio+CMakeList集成
- Android端FFmpeg +SDL2的简单播放器
- SDL2 Android端的简要分析(VideoSubSystem)
- SDL2 Android端的简要分析(AudioSubSystem)
Android 部分源码分析
Android部分的初始化和视频部分基本相同。
这里简单看一下。
在SDLActivity中调用了
SDL.setupJNI()。SDL.setupJNI()中SDLAudioManager.nativeSetupJNI()开始对JNI方法进行初始化。在
SDL_android.c中,nativeSetupJNI初始化JNI回调java方法的指针。
/* Audio initialization -- called before SDL_main() to initialize JNI bindings */
JNIEXPORT void JNICALL SDL_JAVA_AUDIO_INTERFACE(nativeSetupJNI)(JNIEnv* mEnv, jclass cls)
{
__android_log_print(ANDROID_LOG_VERBOSE, "SDL", "AUDIO nativeSetupJNI()");
Android_JNI_SetupThread();
mAudioManagerClass = (jclass)((*mEnv)->NewGlobalRef(mEnv, cls));
midAudioOpen = (*mEnv)->GetStaticMethodID(mEnv, mAudioManagerClass,
"audioOpen", "(IIII)[I");
midAudioWriteByteBuffer = (*mEnv)->GetStaticMethodID(mEnv, mAudioManagerClass,
"audioWriteByteBuffer", "([B)V");
midAudioWriteShortBuffer = (*mEnv)->GetStaticMethodID(mEnv, mAudioManagerClass,
"audioWriteShortBuffer", "([S)V");
midAudioWriteFloatBuffer = (*mEnv)->GetStaticMethodID(mEnv, mAudioManagerClass,
"audioWriteFloatBuffer", "([F)V");
midAudioClose = (*mEnv)->GetStaticMethodID(mEnv, mAudioManagerClass,
"audioClose", "()V");
midCaptureOpen = (*mEnv)->GetStaticMethodID(mEnv, mAudioManagerClass,
"captureOpen", "(IIII)[I");
midCaptureReadByteBuffer = (*mEnv)->GetStaticMethodID(mEnv, mAudioManagerClass,
"captureReadByteBuffer", "([BZ)I");
midCaptureReadShortBuffer = (*mEnv)->GetStaticMethodID(mEnv, mAudioManagerClass,
"captureReadShortBuffer", "([SZ)I");
midCaptureReadFloatBuffer = (*mEnv)->GetStaticMethodID(mEnv, mAudioManagerClass,
"captureReadFloatBuffer", "([FZ)I");
midCaptureClose = (*mEnv)->GetStaticMethodID(mEnv, mAudioManagerClass,
"captureClose", "()V");
if (!midAudioOpen || !midAudioWriteByteBuffer || !midAudioWriteShortBuffer || !midAudioWriteFloatBuffer || !midAudioClose ||
!midCaptureOpen || !midCaptureReadByteBuffer || !midCaptureReadShortBuffer || !midCaptureReadFloatBuffer || !midCaptureClose) {
__android_log_print(ANDROID_LOG_WARN, "SDL", "Missing some Java callbacks, do you have the latest version of SDLAudioManager.java?");
}
checkJNIReady();
}
简单的看一下播放的几个方法,都做了什么
audioOpen
SDLAudioManager->audioOpen
传入的参数
- sampleRate
采样率。表示每秒需要的采样字节数 - is16Bit
表示是否采用16位的深度进行采样 - isStereo
表示是否使用双声道进行采样 - desiredFrames
预期的每次采样的音频帧数
public static int audioOpen(int sampleRate, boolean is16Bit, boolean isStereo, int desiredFrames) {
int channelConfig = isStereo ? AudioFormat.CHANNEL_CONFIGURATION_STEREO : AudioFormat.CHANNEL_CONFIGURATION_MONO;
int audioFormat = is16Bit ? AudioFormat.ENCODING_PCM_16BIT : AudioFormat.ENCODING_PCM_8BIT;
//计算每一帧的大小
int frameSize = (isStereo ? 2 : 1) * (is16Bit ? 2 : 1);
Log.v(TAG, "SDL audio: wanted " + (isStereo ? "stereo" : "mono") + " " + (is16Bit ? "16-bit" : "8-bit") + " " + (sampleRate / 1000f) + "kHz, " + desiredFrames + " frames buffer");
//得到预期的帧数,来计算buffer。
//我们预期的帧数,也不能小于getMinBufferSize得到的帧数
// Let the user pick a larger buffer if they really want -- but ye
// gods they probably shouldn't, the minimums are horrifyingly high
// latency already
desiredFrames = Math.max(desiredFrames, (AudioTrack.getMinBufferSize(sampleRate, channelConfig, audioFormat) + frameSize - 1) / frameSize);
if (mAudioTrack == null) {
//打开AudioTrack
mAudioTrack = new AudioTrack(AudioManager.STREAM_MUSIC, sampleRate,
channelConfig, audioFormat, desiredFrames * frameSize, AudioTrack.MODE_STREAM);
// Instantiating AudioTrack can "succeed" without an exception and the track may still be invalid
// Ref: https://android.googlesource.com/platform/frameworks/base/+/refs/heads/master/media/java/android/media/AudioTrack.java
// Ref: http://developer.android.com/reference/android/media/AudioTrack.html#getState()
if (mAudioTrack.getState() != AudioTrack.STATE_INITIALIZED) {
Log.e(TAG, "Failed during initialization of Audio Track");
mAudioTrack = null;
return -1;
}
mAudioTrack.play();
}
Log.v(TAG, "SDL audio: got " + ((mAudioTrack.getChannelCount() >= 2) ? "stereo" : "mono") + " " + ((mAudioTrack.getAudioFormat() == AudioFormat.ENCODING_PCM_16BIT) ? "16-bit" : "8-bit") + " " + (mAudioTrack.getSampleRate() / 1000f) + "kHz, " + desiredFrames + " frames buffer");
return 0;
}
audioWriteXXXBuffer
写入不同的Buffer格式。这方法比较简单。我们就看一种
public static void audioWriteByteBuffer(byte[] buffer) {
if (mAudioTrack == null) {
Log.e(TAG, "Attempted to make audio call with uninitialized audio!");
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < buffer.length; ) {
//把buffer写入,进行播放
int result = mAudioTrack.write(buffer, i, buffer.length - i);
if (result > 0) {
i += result;
} else if (result == 0) {
try {
Thread.sleep(1);
} catch(InterruptedException e) {
// Nom nom
}
} else {
Log.w(TAG, "SDL audio: error return from write(byte)");
return;
}
}
}
audioClose
进行关闭和释放
public static void audioClose() {
if (mAudioTrack != null) {
mAudioTrack.stop();
mAudioTrack.release();
mAudioTrack = null;
}
}
SDL流程
SDL初始化
SDL_Init(): 初始化SDL。
SDL_OpenAudio(): 打开音频播放器。
SDL_PauseAudio(): 开始播放。
SDL循环渲染数据
调用callback,将正确的数据喂入
初始化SDL_AudioInit
在视频初始化的过程,我们就看到了。SDL_Init方法,传入SDL_INIT_AUDIO标志位,就会走到SDL_AudioInit方法,对音频系统进行初始化。
SDL_AudioInit方法比较简单,就是将JNI的方法指针给audio.impl。同时设置变量的标志位。
static int
ANDROIDAUDIO_Init(SDL_AudioDriverImpl * impl)
{
/* Set the function pointers */
impl->OpenDevice = ANDROIDAUDIO_OpenDevice;
impl->PlayDevice = ANDROIDAUDIO_PlayDevice;
impl->GetDeviceBuf = ANDROIDAUDIO_GetDeviceBuf;
impl->CloseDevice = ANDROIDAUDIO_CloseDevice;
impl->CaptureFromDevice = ANDROIDAUDIO_CaptureFromDevice;
impl->FlushCapture = ANDROIDAUDIO_FlushCapture;
/* and the capabilities */
impl->HasCaptureSupport = SDL_TRUE;
impl->OnlyHasDefaultOutputDevice = 1;
impl->OnlyHasDefaultCaptureDevice = 1;
return 1; /* this audio target is available. */
}
在上面Android方法的初始化中,可以看到这些JNI回调java 的方法的实现,都在SDLAudioManager里面。
打开音频播放器SDL_OpenAudio
- 方法签名
extern DECLSPEC int SDLCALL SDL_OpenAudio(SDL_AudioSpec * desired,
SDL_AudioSpec * obtained);
我们可以看到,SDL_OpenAudio需要传入两个参数,一个是我们想要的音频格式。一个是最后实际的音频格式。
这里的SDL_AudioSpec,是SDL中记录音频格式的结构体。
typedef struct SDL_AudioSpec
{
int freq; /**< DSP frequency -- samples per second */
SDL_AudioFormat format; /**< Audio data format */
Uint8 channels; /**< Number of channels: 1 mono, 2 stereo */
Uint8 silence; /**< Audio buffer silence value (calculated) */
Uint16 samples; /**< Audio buffer size in sample FRAMES (total samples divided by channel count) */
Uint16 padding; /**< Necessary for some compile environments */
Uint32 size; /**< Audio buffer size in bytes (calculated) */
SDL_AudioCallback callback; /**< Callback that feeds the audio device (NULL to use SDL_QueueAudio()). */
void *userdata; /**< Userdata passed to callback (ignored for NULL callbacks). */
} SDL_AudioSpec;
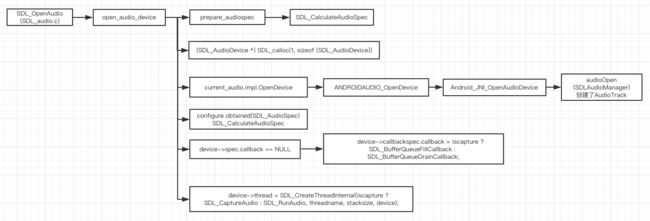
对照函数调用图。
- 对结果的音频格式参数,先进行初步的初始化。
- 分配
SDL_AudioDevice,并初始化 - 对音频的状态进行初始化
//目前是非关闭
SDL_AtomicSet(&device->shutdown, 0); /* just in case. */
//暂停
SDL_AtomicSet(&device->paused, 1);
//可用状态
SDL_AtomicSet(&device->enabled, 1);
- 调用
current_audio.impl.OpenDevice,开启打开音频设备。
这个方法最终会调用到SDLAudioManager的open方法。
public static int[] audioOpen(int sampleRate, int audioFormat, int desiredChannels, int desiredFrames) {
return open(false, sampleRate, audioFormat, desiredChannels, desiredFrames);
}
protected static int[] open(boolean isCapture, int sampleRate, int audioFormat, int desiredChannels, int desiredFrames) {
int channelConfig;
int sampleSize;
int frameSize;
Log.v(TAG, "Opening " + (isCapture ? "capture" : "playback") + ", requested " + desiredFrames + " frames of " + desiredChannels + " channel " + getAudioFormatString(audioFormat) + " audio at " + sampleRate + " Hz");
/* On older devices let's use known good settings */
if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT < 21) {
if (desiredChannels > 2) {
desiredChannels = 2;
}
if (sampleRate < 8000) {
sampleRate = 8000;
} else if (sampleRate > 48000) {
sampleRate = 48000;
}
}
if (audioFormat == AudioFormat.ENCODING_PCM_FLOAT) {
int minSDKVersion = (isCapture ? 23 : 21);
if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT < minSDKVersion) {
audioFormat = AudioFormat.ENCODING_PCM_16BIT;
}
}
switch (audioFormat)
{
case AudioFormat.ENCODING_PCM_8BIT:
sampleSize = 1;
break;
case AudioFormat.ENCODING_PCM_16BIT:
sampleSize = 2;
break;
case AudioFormat.ENCODING_PCM_FLOAT:
sampleSize = 4;
break;
default:
Log.v(TAG, "Requested format " + audioFormat + ", getting ENCODING_PCM_16BIT");
audioFormat = AudioFormat.ENCODING_PCM_16BIT;
sampleSize = 2;
break;
}
if (isCapture) {
switch (desiredChannels) {
case 1:
channelConfig = AudioFormat.CHANNEL_IN_MONO;
break;
case 2:
channelConfig = AudioFormat.CHANNEL_IN_STEREO;
break;
default:
Log.v(TAG, "Requested " + desiredChannels + " channels, getting stereo");
desiredChannels = 2;
channelConfig = AudioFormat.CHANNEL_IN_STEREO;
break;
}
} else {
switch (desiredChannels) {
case 1:
channelConfig = AudioFormat.CHANNEL_OUT_MONO;
break;
case 2:
channelConfig = AudioFormat.CHANNEL_OUT_STEREO;
break;
case 3:
channelConfig = AudioFormat.CHANNEL_OUT_STEREO | AudioFormat.CHANNEL_OUT_FRONT_CENTER;
break;
case 4:
channelConfig = AudioFormat.CHANNEL_OUT_QUAD;
break;
case 5:
channelConfig = AudioFormat.CHANNEL_OUT_QUAD | AudioFormat.CHANNEL_OUT_FRONT_CENTER;
break;
case 6:
channelConfig = AudioFormat.CHANNEL_OUT_5POINT1;
break;
case 7:
channelConfig = AudioFormat.CHANNEL_OUT_5POINT1 | AudioFormat.CHANNEL_OUT_BACK_CENTER;
break;
case 8:
if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= 23) {
channelConfig = AudioFormat.CHANNEL_OUT_7POINT1_SURROUND;
} else {
Log.v(TAG, "Requested " + desiredChannels + " channels, getting 5.1 surround");
desiredChannels = 6;
channelConfig = AudioFormat.CHANNEL_OUT_5POINT1;
}
break;
default:
Log.v(TAG, "Requested " + desiredChannels + " channels, getting stereo");
desiredChannels = 2;
channelConfig = AudioFormat.CHANNEL_OUT_STEREO;
break;
}
/*
Log.v(TAG, "Speaker configuration (and order of channels):");
if ((channelConfig & 0x00000004) != 0) {
Log.v(TAG, " CHANNEL_OUT_FRONT_LEFT");
}
if ((channelConfig & 0x00000008) != 0) {
Log.v(TAG, " CHANNEL_OUT_FRONT_RIGHT");
}
if ((channelConfig & 0x00000010) != 0) {
Log.v(TAG, " CHANNEL_OUT_FRONT_CENTER");
}
if ((channelConfig & 0x00000020) != 0) {
Log.v(TAG, " CHANNEL_OUT_LOW_FREQUENCY");
}
if ((channelConfig & 0x00000040) != 0) {
Log.v(TAG, " CHANNEL_OUT_BACK_LEFT");
}
if ((channelConfig & 0x00000080) != 0) {
Log.v(TAG, " CHANNEL_OUT_BACK_RIGHT");
}
if ((channelConfig & 0x00000100) != 0) {
Log.v(TAG, " CHANNEL_OUT_FRONT_LEFT_OF_CENTER");
}
if ((channelConfig & 0x00000200) != 0) {
Log.v(TAG, " CHANNEL_OUT_FRONT_RIGHT_OF_CENTER");
}
if ((channelConfig & 0x00000400) != 0) {
Log.v(TAG, " CHANNEL_OUT_BACK_CENTER");
}
if ((channelConfig & 0x00000800) != 0) {
Log.v(TAG, " CHANNEL_OUT_SIDE_LEFT");
}
if ((channelConfig & 0x00001000) != 0) {
Log.v(TAG, " CHANNEL_OUT_SIDE_RIGHT");
}
*/
}
frameSize = (sampleSize * desiredChannels);
// Let the user pick a larger buffer if they really want -- but ye
// gods they probably shouldn't, the minimums are horrifyingly high
// latency already
int minBufferSize;
if (isCapture) {
minBufferSize = AudioRecord.getMinBufferSize(sampleRate, channelConfig, audioFormat);
} else {
minBufferSize = AudioTrack.getMinBufferSize(sampleRate, channelConfig, audioFormat);
}
desiredFrames = Math.max(desiredFrames, (minBufferSize + frameSize - 1) / frameSize);
int[] results = new int[4];
if (isCapture) {
if (mAudioRecord == null) {
mAudioRecord = new AudioRecord(MediaRecorder.AudioSource.DEFAULT, sampleRate,
channelConfig, audioFormat, desiredFrames * frameSize);
// see notes about AudioTrack state in audioOpen(), above. Probably also applies here.
if (mAudioRecord.getState() != AudioRecord.STATE_INITIALIZED) {
Log.e(TAG, "Failed during initialization of AudioRecord");
mAudioRecord.release();
mAudioRecord = null;
return null;
}
mAudioRecord.startRecording();
}
results[0] = mAudioRecord.getSampleRate();
results[1] = mAudioRecord.getAudioFormat();
results[2] = mAudioRecord.getChannelCount();
results[3] = desiredFrames;
} else {
if (mAudioTrack == null) {
mAudioTrack = new AudioTrack(AudioManager.STREAM_MUSIC, sampleRate, channelConfig, audioFormat, desiredFrames * frameSize, AudioTrack.MODE_STREAM);
// Instantiating AudioTrack can "succeed" without an exception and the track may still be invalid
// Ref: https://android.googlesource.com/platform/frameworks/base/+/refs/heads/master/media/java/android/media/AudioTrack.java
// Ref: http://developer.android.com/reference/android/media/AudioTrack.html#getState()
if (mAudioTrack.getState() != AudioTrack.STATE_INITIALIZED) {
/* Try again, with safer values */
Log.e(TAG, "Failed during initialization of Audio Track");
mAudioTrack.release();
mAudioTrack = null;
return null;
}
mAudioTrack.play();
}
results[0] = mAudioTrack.getSampleRate();
results[1] = mAudioTrack.getAudioFormat();
results[2] = mAudioTrack.getChannelCount();
results[3] = desiredFrames;
}
Log.v(TAG, "Opening " + (isCapture ? "capture" : "playback") + ", got " + results[3] + " frames of " + results[2] + " channel " + getAudioFormatString(results[1]) + " audio at " + results[0] + " Hz");
return results;
}
这个方法,对应SDL传递过来的参数。初始化播放使用时对应使用的AudioTrack。并将最后AudioTrack配置的后的参数,返回给SDL的desireSpec。
- 接着使用返回的
audioSpec和当前的进行对比,重新复制,并且如果发生了改变,则重新创建SDL_AudioStream。
if (build_stream) {
if (iscapture) {
device->stream = SDL_NewAudioStream(device->spec.format,
device->spec.channels, device->spec.freq,
obtained->format, obtained->channels, obtained->freq);
} else {
device->stream = SDL_NewAudioStream(obtained->format, obtained->channels,
obtained->freq, device->spec.format,
device->spec.channels, device->spec.freq);
}
if (!device->stream) {
close_audio_device(device);
return 0;
}
}
结构体SDL_AudioStream
struct _SDL_AudioStream
{
SDL_AudioCVT cvt_before_resampling;
SDL_AudioCVT cvt_after_resampling;
SDL_DataQueue *queue;
SDL_bool first_run;
Uint8 *staging_buffer;
int staging_buffer_size;
int staging_buffer_filled;
Uint8 *work_buffer_base; /* maybe unaligned pointer from SDL_realloc(). */
int work_buffer_len;
int src_sample_frame_size;
SDL_AudioFormat src_format;
Uint8 src_channels;
int src_rate;
int dst_sample_frame_size;
SDL_AudioFormat dst_format;
Uint8 dst_channels;
int dst_rate;
double rate_incr;
Uint8 pre_resample_channels;
int packetlen;
int resampler_padding_samples;
float *resampler_padding;
void *resampler_state;
SDL_ResampleAudioStreamFunc resampler_func;
SDL_ResetAudioStreamResamplerFunc reset_resampler_func;
SDL_CleanupAudioStreamResamplerFunc cleanup_resampler_func;
};
这个结构体。保存src和dst 的对应的参数,并通过保存的CVT方法,可以进行方便的转换。
- 设置callback
如果我们不能设置callback(音频数据的回调)的话,SDL会默认给设置一个数据队列的管理。
因为通常,我们不会直接播放 PCM的数据,所以都会自己设置callback,在callback当中进行音频数据的格式转换和数据设置。
if (device->spec.callback == NULL) { /* use buffer queueing? */
/* pool a few packets to start. Enough for two callbacks. */
device->buffer_queue = SDL_NewDataQueue(SDL_AUDIOBUFFERQUEUE_PACKETLEN, obtained->size * 2);
if (!device->buffer_queue) {
close_audio_device(device);
SDL_SetError("Couldn't create audio buffer queue");
return 0;
}
device->callbackspec.callback = iscapture ? SDL_BufferQueueFillCallback : SDL_BufferQueueDrainCallback;
device->callbackspec.userdata = device;
}
- 最后通过一些配置,然后开启
SDL_RunAudio线程。(因为是播放,如果是录制,就走另外一个线程SDL_CaptureAudio)
device->thread = SDL_CreateThreadInternal(iscapture ? SDL_CaptureAudio : SDL_RunAudio, threadname, stacksize, device);
音频线程SDL_RunAudio
设置线程的优先级
SDL_SetThreadPriority(SDL_THREAD_PRIORITY_TIME_CRITICAL)音频的线程优先级必须是高。判断是否关闭了device
如果关闭了,就推出循环,否则进入循环。
SDL_AtomicGet(&device->shutdown)
可以看到SDL这里的音频播放的几个参数shutdown,pause,enable都是用了原子性的变量参数,保持其原子性和一致性。
- 确定数据的buff大小。
if (!device->stream && SDL_AtomicGet(&device->enabled)) {
SDL_assert(data_len == device->spec.size);
data = current_audio.impl.GetDeviceBuf(device);
} else {
/* if the device isn't enabled, we still write to the
work_buffer, so the app's callback will fire with
a regular frequency, in case they depend on that
for timing or progress. They can use hotplug
now to know if the device failed.
Streaming playback uses work_buffer, too. */
data = NULL;
}
if (data == NULL) {
data = device->work_buffer;
}
如果没有转换流而且有设备的话,就去取设备的许可的buf。这个变量在打开设备的时候,进行初始化。值为 samples*channels
不是的话,就用我们初始化时,传入的大小。作为buf.
- 判断是否callback数据
SDL_LockMutex(device->mixer_lock);
if (SDL_AtomicGet(&device->paused)) {
SDL_memset(data, device->spec.silence, data_len);
} else {
callback(udata, data, data_len);
}
SDL_UnlockMutex(device->mixer_lock);
如果是暂停的情况下,就是简单设置数据,就结束了。
如果不是暂停的话,就会进入callback(callback中,我们对音频数据进行读取,解码和设置)
- 播放
if (device->stream) {
/* Stream available audio to device, converting/resampling. */
/* if this fails...oh well. We'll play silence here. */
SDL_AudioStreamPut(device->stream, data, data_len);
while (SDL_AudioStreamAvailable(device->stream) >= ((int) device->spec.size)) {
int got;
data = SDL_AtomicGet(&device->enabled) ? current_audio.impl.GetDeviceBuf(device) : NULL;
got = SDL_AudioStreamGet(device->stream, data ? data : device->work_buffer, device->spec.size);
SDL_assert((got < 0) || (got == device->spec.size));
if (data == NULL) { /* device is having issues... */
const Uint32 delay = ((device->spec.samples * 1000) / device->spec.freq);
SDL_Delay(delay); /* wait for as long as this buffer would have played. Maybe device recovers later? */
} else {
if (got != device->spec.size) {
SDL_memset(data, device->spec.silence, device->spec.size);
}
current_audio.impl.PlayDevice(device);
current_audio.impl.WaitDevice(device);
}
}
} else if (data == device->work_buffer) {
/* nothing to do; pause like we queued a buffer to play. */
const Uint32 delay = ((device->spec.samples * 1000) / device->spec.freq);
SDL_Delay(delay);
} else { /* writing directly to the device. */
/* queue this buffer and wait for it to finish playing. */
current_audio.impl.PlayDevice(device);
current_audio.impl.WaitDevice(device);
}
最后就是进行播放。如果需要转换的话,就会先进行转换,再播放。转换失败的话,就不会播放声音。
最后是通过current_audio.impl.PlayDevice(device)方法播放
该方法,实际上是调用了Android_JNI_WriteAudioBuffer(SDL_android.c)方法。
因为是在子线程中,所以需要先通过Android_JNI_GetEnv,来调用
int status = (*mJavaVM)->AttachCurrentThread(mJavaVM, &env, NULL);
将当前的线程和JVM进行绑定,才可以调用JNI方法。
然后最后调用的是SDLAudioManager中的对应的 audioWriteXXXBuffer方法。使用AudioTrack,将数据进行write(实际上就是播放)
开始或者暂停音频播放器SDL_PauseAudio
void
SDL_PauseAudioDevice(SDL_AudioDeviceID devid, int pause_on)
{
SDL_AudioDevice *device = get_audio_device(devid);
if (device) {
current_audio.impl.LockDevice(device);
SDL_AtomicSet(&device->paused, pause_on ? 1 : 0);
current_audio.impl.UnlockDevice(device);
}
}
通过上面对RunAudio线程的分析,我们知道其是改变device->paused标志位。来回调callback。
callback
我们来关注一下我们如何进行callback的操作
- 传递自己的callback
//通过desired_spec 的callback来传递我们自己的callback
wanted_spec.callback = audio_callback;
if (SDL_OpenAudio(&wanted_spec, &spec) < 0) {
ALOGE("SDL_OpenAudio: %s \n", SDL_GetError());
return -1;
}
- 定义callback
void audio_callback(void *userdata, Uint8 *stream, int len) {
AVCodecContext *aCodecCtx = (AVCodecContext *) userdata;
int len1, audio_size;
static uint8_t audio_buf[(MAX_AUDIO_FRAME_SIZE * 3) / 2];
static unsigned int audio_buf_size = 0;
static unsigned int audio_buf_index = 0;
// 这里把得到的数据给重置了
SDL_memset(stream, 0, len);
ALOGI("audio_callback len=%d \n", len);
//向设备发送长度为len的数据
while (len > 0) {
//缓冲区中无数据
if (audio_buf_index >= audio_buf_size) {
//从packet中解码数据
audio_size = audio_decode_frame(aCodecCtx, audio_buf, audio_buf_size);
//ALOGI("audio_decode_frame finish audio_size=%d \n", audio_size);
if (audio_size < 0) //没有解码到数据或者出错,填充0
{
audio_buf_size = 1024;
memset(audio_buf, 0, audio_buf_size);
} else {
audio_buf_size = audio_size;
}
audio_buf_index = 0;
}
len1 = audio_buf_size - audio_buf_index;
if (len1 > len)
len1 = len;
//这种方式是可以直接把数据复制过去
memcpy(stream, (uint8_t *)audio_buf + audio_buf_index, len1);
//通过SDL_MixAudio方法,可以控制音量,如果直接使用memcpy是无法控制音量的
// SDL_MixAudio(stream, audio_buf + audio_buf_index, len1, SDL_MIX_MAXVOLUME);
//SDL_MixAudioFormat()
len -= len1;
stream += len1;
audio_buf_index += len1;
}
}
关闭
- 关闭
/** This method is called by SDL using JNI. */
public static void audioClose() {
if (mAudioTrack != null) {
mAudioTrack.stop();
mAudioTrack.release();
mAudioTrack = null;
}
}
最后关闭音频,就是将其stop和release