1.UDP端口扫描
前提:基于已发现的存活主机
假设ICMP port unreachable响应代表端口关闭
目标系统不响应ICMP port unreachable时,可能产生误判
- 完整的UDP应用层请求
- 准确性高
- 耗时巨大
1.1 scapy udp scan
- 端口关闭:通过ICMP port unreachable
- 端口开放:没有回包
- 存在误判
(1)编写udp_scan脚本
#!/usr/bin/python
import logging
import subprocess
logging.getLogger("scapy.runtime").setLevel(logging.ERROR)
from scapy.all import *
if len(sys.argv) != 4:
print "Usage - ./udp_scan.py[start port && end port]"
print "Example - ./udp_scan.py 1.1.1.1 1-200"
print "Example will preform an ICMP scan of the 1.1.1.0 is assigned"
sys.exit()
ip = sys.argv[1]
start = int(sys.argv[2])
end = int(sys.argv[3])
for port in range (start,end):
a = sr1(IP(dst=ip)/UDP(dport=port),timeout=3,verbose=0)
time.sleep(1)
if a == None:
print port
else:
pass
查看扫描后结果(以metasploitable2为目标主机):
1.2 nmap udp scan
nmap -sU 192.168.50.183
nmap 192.168.50.183 -sU -p53 //指定端口扫描
- nmap默认扫描1000个常用端口
- 利用ICMP host unreachable
2.TCP端口扫描
所有的TCP扫描方式都是基于三次握手的变化来判断目标端口状态
- 基于连接的协议
- 三次握手
- 全连接扫描
- 2.1 隐蔽扫描
- 不建立完整连接 syn---syn/ack---rst
- 应用日志不记录扫描行为--隐蔽
- 2.1.1隐蔽扫描-scapy脚本实现
>>>a=sr1(IP(dst="192.168.50.183")/TCP(flags="S"),timeout=0,verbose=0) //发送标志位为SYN的tcp包
>>> a.display()
###[ IP ]###
version= 4L
ihl= 5L
tos= 0x0
len= 44
id= 0
flags= DF
frag= 0L
ttl= 64
proto= tcp
chksum= 0x5451
src= 192.168.50.183
dst= 192.168.50.115
\options\
###[ TCP ]###
sport= http //默认是80端口
dport= ftp_data
seq= 2348057631
ack= 1
dataofs= 6L
reserved= 0L
flags= SA //返回包为syn+ack,标明端口是开放的
window= 5840
chksum= 0x8a52
urgptr= 0
options= [('MSS', 1460)]
从下面的抓包可以看见,返回了syn+ack,但是下面的RST并不是由于scapy产生的,而是由主机系统内核自己发出的rst
#!/usr/bin/python
import logging
import subprocess
logging.getLogger("scapy.runtime").setLevel(logging.ERROR)
from scapy.all import *
if len(sys.argv) != 4:
print "Usage - ./syn_scan.py[start port && end port]"
print "Example - ./syn_scan.py 1.1.1.1 1-200"
print "Example will preform an ICMP scan of the 1.1.1.0 is assigned"
sys.exit()
ip = sys.argv[1]
start = int(sys.argv[2])
end = int(sys.argv[3])
for port in range (start,end):
a = sr1(IP(dst=ip)/TCP(dport=port),timeout=1,verbose=0)
if a == None:
pass
else:
if int(a[TCP].flags) == 18: //syn+ack位为1时,值为18
print port
else:
pass
- 2.1.2 隐蔽扫描-nmap
nmap -sS 1.1.1.1 -p 80,21,25,443 //多个指定端口扫描
nmap -sS 1.1.1.1 -p 1-65535 --open
nmap -sS 1.1.1.1 -p - --open //扫描1-65535并处于open状态的端口
nmap -sS -iL iplist.txt -p 80,21,23,53
- 2.1.2 隐蔽扫描-hping3
hping3 1.1.1.1 --scan 80 -S //发送syn包
hping3 1.1.1.1 --scan 80,21,25,443 -S
hping3 1.1.1.1 --scan 0-65535 -S
hping3 -c 100 -S --spoof 1.1.1.2 -p ++1 1.1.1.3 //发送100以内端口,++1逐个递加,并以伪造原地址为1.1.1.2去发送给1.1.1.3
伪造源地址扫描
- 2.2 僵尸扫描
- 极度隐蔽
- 实施条件苛刻
- 可伪造源地址
- 选择僵尸机
- 闲置系统
- 系统使用递增的IPID(ip包头中的Identification,而0或随机产生的情况是无法实现僵尸扫描的)
- 2.2.1 原理
①原理图--目标主机端口开放状态下
②原理图--目标主机端口关闭状态下
- 2.2.2 实验1
*192.168.50.115(scanner扫描机)---------192.168.50.185(zombie僵尸机)---------192.168.50.183(target靶机) *
注:windows xp、windows server2003及以下可以用于zombie僵尸机,而linux或是更高版本的windows的ipid是随机的,无法用来完成此次实验。
>>> i=IP()
>>> t=TCP()
>>> rz=(i/t)
>>> rt=(i/t)
>>> rz[IP].dst="192.168.50.185"
>>> rz[TCP].dport=445
>>> rz[TCP].flags="SA" //向zombie机发送syn+ack,此时zombie后返回reset
>>> rt[IP].src="192.168.50.185"
>>> rt[IP].dst="192.168.50.183"
>>> rt[TCP].dport=21
>>> rt[TCP].flags="S" //以伪造zombie源地址发送syn给target,target会返回给zombie一个syn+ack,而zombie会返回给target一个reset
***观察结果***
>>>az1=sr1(rz) //发送给zombie,返回ipidentification为1
###[ IP ]###
version= 4L
ihl= 5L
tos= 0x0
len= 40
id= 166 //id为166
flags=
frag= 0L
ttl= 128
proto= tcp
chksum= 0x53ad
src= 192.168.50.185
dst= 192.168.50.115
>>>at=sr1(rt,timeout=1) //发送给taget,返回ipididentification为2
>>>az2=sr1(rz) //再次发送给zombie,返回ipididentification为3
###[ IP ]###
version= 4L
ihl= 5L
tos= 0x0
len= 40
id= 168 //id为168
flags=
frag= 0L
ttl= 128
proto= tcp
chksum= 0x53ab
src= 192.168.50.185
dst= 192.168.50.115
查看抓包结果:
当target端口(rt[TCP].dport=20325)不开放时,其id值相差为1
- 2.2.3脚本实现僵尸扫描
上述是通过scapy命令行的方式实现的扫描,下面使用脚本的方式对其进行僵尸扫描,代码如下:
#!/usr/bin/python
import logging
logging.getLogger("scapy.runtime").setLevel(logging.ERROR)
from scapy.all import *
def ipid(zombie):
reply1 = sr1(IP(dst=zombie)/TCP(flags="SA"),timeout=2,verbose=0)
send(IP(dst=zombie)/TCP(flags="SA"),verbose=0)
reply2 = sr1(IP(dst=zombie)/TCP(flags="SA"),timeout=2,verbose=0)
if reply2[IP].id == (reply1[IP].id + 2): //探测是否满足zombie僵尸机
print "IPID sequence is incremental and target appears to be idle,ZOMBIE located"
response = raw_input("Do you want to use this zombie to perform a scan?(Y or N):")
if response == "Y":
target = raw_input("Enter the IP address of the target system:")
zombiescan(target,zombie)
else:
print " Either the IPID sequence is not incremental or the target is not idle,not a good zombie"
def zombiescan(target,zombie): //对target进行僵尸扫描
print "\nScanning target" + target +"with zombie" + zombie
print "\n-------------Open Port on Target ----------------\n"
for port in range(1,100):
try:
start_val = sr1(IP(dst=zombie)/TCP(flags="SA",dport=port),timeout=1,verbose=0)
send(IP(src=zombie,dst=target)/TCP(flags="S",dport=port),verbose=0)
end_val = sr1(IP(dst=zombie)/TCP(flags="SA",dport=port),timeout=1,verbose=0)
if end_val[IP].id == (start_val[IP].id + 2):
print port
except:
pass
print "--------------Zombie Scan Suite------------------\n" //程序执行组件/入口
print "1 - Identify Zombie Host\n"
print "2 - Perform Zombie Scan\n"
ans = raw_input("Select an Option (1 or 2):")
if ans == "1":
zombie = raw_input("Enter IP address to test IPID sequence:")
ipid(zombie)
else:
if ans == "2":
zombie = raw_input("Enter IP address for zombie system:")
target = raw_input("Enter IP address for scan target:")
zombiescan(target,zombie)
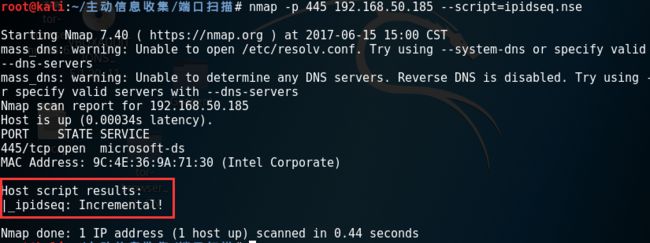
- 2.2.4 nmap实现僵尸扫描
(1)发现僵尸机
namp -p445 192.168.50.185 --script=ipidseq.nse
(2)扫描目标
nmap 192.168.50.183 -sI 192.168.50.185 -Pn -p 0-100
2.3全连接端口扫描
2.3.1 scapy:
①syn扫描不需要raw packets
②内核认为syn/ack是非法包,直接发送rst终端连接
③全连接扫描对scapy比较困难 //需要iptables屏蔽reset脚本1:
#!/usr/bin/python
import logging
logging.getLogger("scapy.runtime").setLevel(logging.ERROR)
from scapy.all import *
reponse=sr1(IP(dst="192.168.50.183")/TCP(dport=80,flags="S"))
reply=sr1(IP(dst="192.168.50.183")/TCP(dport=80,flags="A",ack=(reponse[TCP].seq+1))) //发送一个ack确认包,并且seq以返回的+1
通过抓包发现,在对方返回syn+ack时,系统会给对方发送rst,此时在给对方发送ack确认包,对方会认为这不是连接,会返回一个rst
- 脚本2:
将上述的脚本完善一下,同时由于系统会自动返回reset,因此将其系统的reset屏蔽掉,再看结果 :
#!/usr/bin/python
import logging
logging.getLogger("scapy.runtime").setLevel(logging.ERROR)
from scapy.all import *
SYN=IP(dst="192.168.50.183")/TCP(dport=21,flags="S")
SYN.display()
print "\n\n-- RECEIVED --"
response=sr1(SYN,timeout=1,verbose=0)
response.display()
if int(response[TCP].flags) ==18:
print "\n\n -- SENT --"
A=IP(dst="192.168.50.183")/TCP(dport=21,flags="A",ack=(response[TCP].seq+1))
A.display()
print "\n\n-- RECEIVED --"
response2=sr1(A,timeout=1,verbose=0)
response2.display()
else:
print "SYN.ACK not returned"
** 设置iptables,将宿主机的rst包在output方向上drop**
# iptables -A OUTPUT -p tcp --tcp-flags RST RST -d 192.168.50.183 -j DROP
此时在抓包查看:
- 2.3.2 nmap
nmap -sT 192.168.50.183 -p1-500
- 2.3.3 dmitry
dmitry -p 192.168.50.183
- 2.3.4 NC
# nc -nv -w 1 -z 192.168.50.183 1-500 //-w表示扫描一个端口的等待时间为1s,-z表示使用扫描