先来完成一个最简单的httprequest和httpresponse的实现。
客户端
NioEventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
Bootstrap bootstrap = new Bootstrap();
bootstrap.group(workerGroup)
.channel(NioSocketChannel.class)
.option(ChannelOption.SO_KEEPALIVE, true)
.handler(new ChannelInitializer() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel socketChannel) throws Exception {
socketChannel.pipeline().addLast(new HttpRequestEncoder());//客户端对发送的httpRequest进行编码
socketChannel.pipeline().addLast(new HttpResponseDecoder());//客户端需要对服务端返回的httpresopnse解码
// socketChannel.pipeline().addLast(new HttpClientCodec());//HttpClientCodec()包含了上面两种
socketChannel.pipeline().addLast(new HttpClientDealing());
}
});
Channel channel = bootstrap.connect("127.0.0.1", 8080).sync().channel();
URI uri = new URI("http://127.0.0.1:8080");
DefaultFullHttpRequest httpRequest = new DefaultFullHttpRequest(HttpVersion.HTTP_1_1, HttpMethod.GET, uri.toASCIIString(), Unpooled.wrappedBuffer(msg.getBytes("UTF-8")));//生成一个默认的httpRequest。
httpRequest.headers().set(HttpHeaders.Names.HOST, "127.0.0.1");
httpRequest.headers().set(HttpHeaders.Names.CONNECTION, HttpHeaders.Values.KEEP_ALIVE);
httpRequest.headers().set(HttpHeaders.Names.CONTENT_LENGTH, httpRequest.content().readableBytes());//可以在httpRequest.headers中设置各种需要的信息。
channel.writeAndFlush(httpRequest).sync();//发送
channel.closeFuture().sync();
} finally {
workerGroup.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
private static class HttpClientDealing extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter {
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
if(msg instanceof HttpResponse){
System.out.println(msg.toString());//打印服务器返回的httpResponse
}
if(msg instanceof HttpContent) {
System.out.println(msg.toString());
}
}
}
服务端
NioEventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
NioEventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
ServerBootstrap serverBootstrap = new ServerBootstrap();
serverBootstrap.group(bossGroup, workerGroup)
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)
.handler(new LoggingHandler(LogLevel.INFO))
.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel socketChannel) throws Exception {
// socketChannel.pipeline().addLast(new HttpServerCodec());
socketChannel.pipeline().addLast(new HttpRequestDecoder());//服务器添加httpRequest解码
socketChannel.pipeline().addLast(new HttpResponseEncoder());//服务器添加httpResponse编码
socketChannel.pipeline().addLast(new HttpServerDataDealing());
}
});
Channel channel = serverBootstrap.bind(8080).sync().channel();
channel.closeFuture().sync();
} finally {
bossGroup.shutdownGracefully();
workerGroup.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
private static class HttpServerDataDealing extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter {
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
if(msg instanceof HttpRequest)
{
System.out.println(msg.toString());//打印httpRequest
}
if(msg instanceof HttpContent)
{
System.out.println(msg.toString());
}
HttpResponse httpResponse = new DefaultFullHttpResponse(HttpVersion.HTTP_1_1, HttpResponseStatus.OK, Unpooled.wrappedBuffer("hello client".getBytes()));//建立httpResponse
httpResponse.headers().add(HttpHeaders.Names.CONTENT_TYPE, "text/plain");
httpResponse.headers().add(HttpHeaders.Names.CONTENT_LENGTH, 11);
ctx.writeAndFlush(httpResponse);//返回响应的httpResponse
}
}
如果只是发送简单的http请求以及响应,其实非常简单。但是为了完成功能开发,一般会在http头中加入一定的消息列表用于表示此次请求的一些参数
| 名称 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| Accept | 用于制定客户端接收哪些类型的信息 |
| Accept-Charset | 用于指定客户端接受的字符集 |
| Accept-Encoding | 类似于Accept,但是它用于指定一种自然语言 |
| Authorization | 主要用于证明客户端有权查看某个资源。当浏览器访问一个页面时,如果收到服务器的响应代码为401(未授权),可以发送一个包含Authorization请求报头域的请求,要求服务器对其进行认证 |
| Host | 发送请求时,该报头域是必需的,用于指定被请求的资源的Internet主机和端口号,它通常是从HTTP URL中提取出来的 |
| User-Agent | 允许客户端将它的操作系统,浏览器和其他属性告诉服务器 |
| Content-Length | 请求消息体的长度 |
| Content-Type | 表示后面的文档属于什么MIME类型。Servlet默认为text/plain,但通常需要显式的指定为text/html。由于经常要设置Content-Type,因此HttpServletResponse提供了一个专用的方法setContentType |
| Connection | 连接类型 |
get方法和post方法的区别
根据名称即可得知,这两种方法在设计的时候get就是为了获取资源,而post是为了发送资源
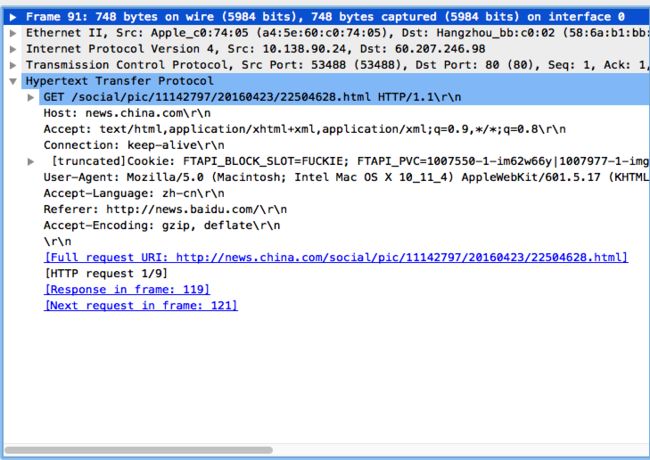
在自己机子上随便抓了一个http的get请求如下:
这里包含了get请求协议和Cookie的信息。但是没有body,Post包没想到怎么抓就没有示例了。其实get和post在内容上的区别就是post多了一个body,即在httpheaders下面还有一段内容,用于保存http提交的信息。表现在netty代码上如下所示
get方法
HttpRequest request = new DefaultHttpRequest(HttpVersion.HTTP_1_1, HttpMethod.GET, uriGet.toASCIIString());
HttpHeaders headers = request.headers();
headers.set(HttpHeaderNames.HOST, host);
headers.set(HttpHeaderNames.CONNECTION, HttpHeaderValues.CLOSE);
headers.set(HttpHeaderNames.ACCEPT_ENCODING, HttpHeaderValues.GZIP + "," + HttpHeaderValues.DEFLATE);
headers.set(HttpHeaderNames.ACCEPT_CHARSET, "ISO-8859-1,utf-8;q=0.7,*;q=0.7");
headers.set(HttpHeaderNames.ACCEPT_LANGUAGE, "fr");
headers.set(HttpHeaderNames.REFERER, uriSimple.toString());
headers.set(HttpHeaderNames.USER_AGENT, "Netty Simple Http Client side");
headers.set(HttpHeaderNames.ACCEPT, "text/html,application/xhtml+xml,application/xml;q=0.9,*/*;q=0.8");
// send request
channel.writeAndFlush(request);
post方法
HttpDataFactory factory = new DefaultHttpDataFactory(DefaultHttpDataFactory.MINSIZE); // Disk if MINSIZE exceed
// Prepare the HTTP request.
HttpRequest request = new DefaultHttpRequest(HttpVersion.HTTP_1_1, HttpMethod.POST, uriSimple.toASCIIString());
// Use the PostBody encoder
HttpPostRequestEncoder bodyRequestEncoder =
new HttpPostRequestEncoder(factory, request, false); // false => not multipart
//可以给body添加文件等
bodyRequestEncoder.addBodyFileUpload("myfile", file, "application/x-zip-compressed", false);
// it is legal to add directly header or cookie into the request until finalize
//这部分headers和get方法一样
for (Entry entry : headers) {
request.headers().set(entry.getKey(), entry.getValue());
}
// finalize request
request = bodyRequestEncoder.finalizeRequest();
// send request
channel.write(request);
post增加的内容
HttpDataFactory factory = new DefaultHttpDataFactory(DefaultHttpDataFactory.MINSIZE);
HttpPostRequestEncoder bodyRequestEncoder =
new HttpPostRequestEncoder(factory, request, false); // false => not multipart
bodyRequestEncoder.addBodyFileUpload("myfile", file, "application/x-zip-compressed", false);
request = bodyRequestEncoder.finalizeRequest();
post方法利用HttpPostRequestEncoder编码body信息,然后加入到post消息中进行发送。