在第一阶段将未处理完的ClassSymbol放入uncompleted队列后,循环队列中的ClassSymbol并调用complete()方法,从而调用了MemberEnter类的complete(Symbol symbol)方法。
在这个类中主要对ClassSymbol中的ClassType进行了属性的填充,不过也会有其它的一些逻辑。
1、访问MemberEnter类的visitTopLevel(JCCompilationUnit jcCompilationUnit):
public void visitTopLevel(JCCompilationUnit jcCompilationUnit) {
// 如果运行完importAll()方法后,那么starImportScope中的elements就不为null
if (jcCompilationUnit.starImportScope.elements != null) { // starImportScope为A scope for all import-on-demands.
// we must have already processed this toplevel
return;
}
// check that no class exists with same fully qualified name as toplevel package
if (checkClash && jcCompilationUnit.packageIdentifier != null) {
Symbol packageSymbol = jcCompilationUnit.packageSymbol;
while (packageSymbol.ownerSymbol != symbolTable.rootPackage) { // 进行循环检测
packageSymbol.ownerSymbol.complete(); // enter all class members of packageSymbol
if (symbolTable.classes.get(packageSymbol.getQualifiedName()) != null) {
log.error(jcCompilationUnit.position, "pkg.clashes.with.class.of.same.name", packageSymbol); // 程序包{0}与带有相同名称的类冲突
}
packageSymbol = packageSymbol.ownerSymbol;
}
}
// process package annotations
annotateLater(jcCompilationUnit.packageAnnotations, environment, jcCompilationUnit.packageSymbol);
// Import-on-demand java.lang.
PackageSymbol pkgSymbol = classReader.enterPackage(names.java_lang);
importAll(jcCompilationUnit.position, pkgSymbol , environment);
// Process all import clauses. jcCompilationUnit.defs中包含JCImport也包含JCClassDecl
memberEnter(jcCompilationUnit.defs, environment);
}
重点来查看importAll()方法的逻辑。
2、调用importAll()方法后,会将PackageSymbol中members_field中存储的所有符号(java.lang包下定义的类符号)导入到当前environment.toplevel.starImportScope中。
调用importAll()方法,这个方法的具体代码如下:
private void importAll( int position,
final TypeSymbol typeSymbol,
Environment environment) {
// Check that packages imported from exist (JLS ???).
if ( typeSymbol.kind == _PCK_1 &&
typeSymbol.members().elements == null && // PackageSymbol的members()方法中还会调用ClassReader的complete()方法
!typeSymbol.exists() // PackageSymbol中的exists()方法 (flags_field & EXISTS) != 0
){
// If we can't find java.lang, exit immediately.
if (((PackageSymbol)typeSymbol).fullname.equals(names.java_lang)) {
JCDiagnostic msg = diags.fragment("fatal.err.no.java.lang"); // 致命错误: 在类路径或引导类路径中找不到程序包 java.lang
throw new FatalError(msg);
} else {
log.error(DiagnosticFlag.RESOLVE_ERROR, position, "doesnt.exist", typeSymbol); // 程序包{0}不存在
}
}
Scope membersField = typeSymbol.members();
environment.toplevel.starImportScope.importAll(membersField);
}
调用typeSymbol.members()方法会触发了java.lang名称的PackageSymbol的complete()方法,complete()方法主要调用ClassReader方法来完成主要逻辑,代码如下:
/**
* Completion for classes to be loaded. Before a class is loaded we make
* sure its enclosing class (if any 如果有的话) is loaded.
*
* 在完成类 将被加载之前,要确保它的封闭类已经被加载了
*/
public void complete(Symbol symbol) throws CompletionFailure {
if (symbol.kind == _TYP_2) {
ClassSymbol classSymbol = (ClassSymbol) symbol;
classSymbol.members_field = new ErrorScope(classSymbol); // make sure it's always defined
boolean saveSuppressFlush = suppressFlush;
suppressFlush = true;
try {
completeOwners(classSymbol.owner);
completeEnclosing(classSymbol);
} finally {
suppressFlush = saveSuppressFlush;
}
fillIn(classSymbol);
} else if (symbol.kind == _PCK_1) {
PackageSymbol packageSymbol = (PackageSymbol) symbol;
try {
fillIn(packageSymbol); // 为这个符号填充一些信息,如members_field,并且为Scope中的Entry添加符号
} catch (IOException ex) {
throw new CompletionFailure(symbol, ex.getLocalizedMessage()).initCause(ex);
}
}
if (!filling && !suppressFlush) {
annotate.flush(); // finish attaching annotations
}
}
(1)symbol.kind=_TYP_2的逻辑,主要调用了两个方法完成classSymbol的处理。
/** complete up through the enclosing package. */
private void completeOwners(Symbol ownerSymbol) {
if (ownerSymbol.kind != _PCK_1) { // 处理的是非PackageSymbol
completeOwners(ownerSymbol.owner); // 递归调用
}
ownerSymbol.complete();
}
/**
* Tries to complete lexically enclosing classes if classSymbol looks like a
* nested class. This is similar to completeOwners but handles the situation
* when a nested class is accessed directly as it is possible with the Tree
* API or javax.lang.model.*.
*/
private void completeEnclosing(ClassSymbol classSymbol) {
if (classSymbol.owner.kind != _PCK_1) { // 处理的是PackageSymbol
return;
}
Symbol owner = classSymbol.owner;
Name shortName = Convert.shortName(classSymbol.name);
List names = Convert.enclosingCandidates(shortName);
for (Name name : names) {
Symbol enclosingClass = owner.members().lookup(name).symbol;
if (enclosingClass == null) {
enclosingClass = classes.get(TypeSymbol.formFlatName(name, owner));
}
if (enclosingClass != null) {
enclosingClass.complete();
}
}
}
调用完如上的两个方法后继承调用fillIn()方法,代码如下:
/**
* Fill in definition of class `c' from corresponding class or source file.
*/
private void fillIn(ClassSymbol classSymbol) {
if (completionFailureName == classSymbol.fullname) {
throw new CompletionFailure(classSymbol, "user-selected completion failure by class name");
}
currentOwner = classSymbol;
warnedAttrs.clear();
JavaFileObject classfile = classSymbol.classfile;
if (classfile != null) {
JavaFileObject previousClassFile = currentClassFile;
try {
if (filling) {
Assert.error("Filling " + classfile.toUri() + " during " + previousClassFile);
}
currentClassFile = classfile;
if (verbose) {
log.printVerbose("loading", currentClassFile.toString());
}
if (sourceCompleter != null) {
sourceCompleter.complete(classSymbol);
} else {
throw new IllegalStateException("Source completer required to read " + classfile.toUri());
}
return;
} finally {
currentClassFile = previousClassFile;
}
} else {
JCDiagnostic diag = diagFactory.fragment("class.file.not.found", classSymbol.flatname);
throw newCompletionFailure(classSymbol, diag);
}
}
ClassReader中定义了一个接口,如下:
public interface SourceCompleter {
void complete(ClassSymbol sym) throws CompletionFailure;
}
其实现类只有一个JavaCompiler,如下:
/** Complete compiling a source file that has been accessed
* by the class file reader.
* @param c The class the source file of which needs to be compiled.
* @param filename The name of the source file.
* @param f An input stream that reads the source file.
*/
public void complete(ClassSymbol c) throws CompletionFailure {
// System.err.println("completing " + c);//DEBUG
if (completionFailureName == c.fullname) {
throw new CompletionFailure(c, "user-selected completion failure by class name");
}
JCCompilationUnit tree;
JavaFileObject filename = c.classfile;
JavaFileObject prev = log.useSource(filename);
try {
tree = parse(filename, filename.getCharContent(false));
} catch (IOException e) {
log.error("error.reading.file", filename, JavacFileManager.getMessage(e));
tree = make.TopLevel(List.nil(), null, List.nil());
} finally {
log.useSource(prev);
}
enter.complete(List.of(tree), c);
if (enter.getEnvironment(c) == null) {
boolean isPkgInfo = tree.sourcefile.isNameCompatible("package-info", JavaFileObject.Kind.SOURCE);
if (isPkgInfo) {
if (enter.getEnvironment(tree.packageSymbol) == null) {
JCDiagnostic diag = diagFactory.fragment("file.does.not.contain.package", c.location());
throw reader.new BadClassFile(c, filename, diag);
}
} else {
JCDiagnostic diag = diagFactory.fragment("file.doesnt.contain.class", c.getQualifiedName());
throw reader.new BadClassFile(c, filename, diag);
}
}
implicitSourceFilesRead = true;
}
(2)symbol.kind=_PCK_1的逻辑,主要调用了fillIn()方法,主要就是往packageSymbol的members_field属性(Scope类型)中填充java.lang包下的所有类符号ClassSymbol,具体代码实现如下:
/**
* Load directory of package into members scope.
*/
private void fillIn(PackageSymbol packageSymbol) throws IOException {
if (packageSymbol.members_field == null) {
packageSymbol.members_field = new Scope(packageSymbol);
}
String packageName = packageSymbol.fullname.toString();
Set kinds = getPackageFileKinds();
// Lists all file objects matching the given criteria in the given location.
// List file objects in "subpackages" if recurse is true.
if (packageName == null || EnumSet.of(JavaFileObject.Kind.CLASS) == null || fileManager == null) {
return;
}
Iterable files = fileManager.list(PLATFORM_CLASS_PATH, packageName,
EnumSet.of(JavaFileObject.Kind.CLASS), false);
/**
* Location to search for platform classes. Sometimes called the boot
* class path.
*/
fillIn(packageSymbol, PLATFORM_CLASS_PATH, files);
Set classKinds = EnumSet.copyOf(kinds);
classKinds.remove(JavaFileObject.Kind.SOURCE);
boolean wantClassFiles = !classKinds.isEmpty();
Set sourceKinds = EnumSet.copyOf(kinds);
sourceKinds.remove(JavaFileObject.Kind.CLASS);
boolean wantSourceFiles = !sourceKinds.isEmpty();
/**
* Location to search for existing source files.
*/
boolean haveSourcePath = fileManager.hasLocation(SOURCE_PATH);
// 省略一部分代码
}
又调用了fillIn()私有方法,代码如下:
private void fillIn(PackageSymbol packageSymbol, Location location, Iterable files) {
currentLoc = location;
for (JavaFileObject javaFileObject : files) {
switch (javaFileObject.getKind()) {
case CLASS:
case SOURCE: {
// TODO pass binaryName to includeClassFile
String binaryName = fileManager.inferBinaryName(currentLoc, javaFileObject);
String simpleName = binaryName.substring(binaryName.lastIndexOf(".") + 1);
if (SourceVersion.isIdentifier(simpleName) || simpleName.equals("package-info")) { // simpleName不为java定义的关键字或者不为package-info时
includeClassFile(packageSymbol, javaFileObject);
}
break;
}
default: {
extraFileActions(packageSymbol, javaFileObject);
}
}
}
}
调用includeClassFile()方法,具体代码如下:
/**
* Include class corresponding to given class file in package, unless (1) we
* already have one the same kind (.class or .java), or (2) we have one of
* the other kind, and the given class file is older.
*/
protected void includeClassFile(PackageSymbol packageSymbol, JavaFileObject file) {
if ((packageSymbol.flags_field & EXISTS) == 0) {
for (Symbol q = packageSymbol; q != null && q.kind == _PCK_1; q = q.owner) {
q.flags_field |= EXISTS;
}
}
JavaFileObject.Kind kind = file.getKind();
int seen;
if (kind == JavaFileObject.Kind.CLASS) {
seen = CLASS_SEEN;
} else {
seen = SOURCE_SEEN;
}
String binaryName = fileManager.inferBinaryName(currentLoc, file);
int lastDot = binaryName.lastIndexOf(".");
Name classname = names.fromString(binaryName.substring(lastDot + 1));
boolean isPkgInfo = (classname == names.package_info);
ClassSymbol classSymbol = null;
if (isPkgInfo) {
classSymbol = packageSymbol.package_info;
} else {
Entry entry = packageSymbol.members_field.lookup(classname);
classSymbol = (ClassSymbol) entry.symbol;
}
if (classSymbol == null) {
classSymbol = enterClass(classname, packageSymbol);
if (classSymbol.classfile == null) { // only update the file if's it's newly created
classSymbol.classfile = file;
}
if (isPkgInfo) {
packageSymbol.package_info = classSymbol;
} else {
if (classSymbol.owner == packageSymbol) { // it might be an inner class
packageSymbol.members_field.enter(classSymbol);
}
}
} else if (classSymbol.classfile != null && (classSymbol.flags_field & seen) == 0) {
// if c.classfile == null, we are currently compiling this class and
// no further action is necessary.
// if (c.flags_field & seen) != 0, we have already encountered a
// file of the same kind; again no further action is necessary.
if ((classSymbol.flags_field & (CLASS_SEEN | SOURCE_SEEN)) != 0) {
classSymbol.classfile = preferredFileObject(file, classSymbol.classfile);
}
}
classSymbol.flags_field |= seen;
}
创建file对应的类符号并且输入到packageSymbol的members_field属性中。同时也填充了classSymbol的classfile、flags_field属性。如有必要,需要调用enterClass()方法来完成对classSymbol的创建。
enterClass()方法如下:
/**
* Create a new toplevel or member class symbol with given name and owner
* and enter in `classes' unless already there.
*/
public ClassSymbol enterClass(Name name, TypeSymbol ownerTypeSymbol) {
Name flatName = TypeSymbol.formFlatName(name, ownerTypeSymbol);
ClassSymbol classSymbol = classes.get(flatName);
if (classSymbol == null) {
classSymbol = defineClass(name, ownerTypeSymbol);
classes.put(flatName, classSymbol);
} else {
boolean a = (classSymbol.name != name || classSymbol.owner != ownerTypeSymbol);
boolean b = ownerTypeSymbol.kind == _TYP_2;
boolean c = classSymbol.owner.kind == _PCK_1;
if (a && b && c) {
// reassign fields of classes that might have been loaded with
// their flat names.
// TODO 为什么要提前通过类全名进行加载呢?
classSymbol.owner.members().remove(classSymbol);
classSymbol.name = name;
classSymbol.owner = ownerTypeSymbol;
classSymbol.fullname = ClassSymbol.formFullName(name, ownerTypeSymbol);
}
}
return classSymbol;
}
defineClass()方法代码如下:
/**
* Define a new class given its name and owner.
*/
public ClassSymbol defineClass(Name name, Symbol owner) {
ClassSymbol c = new ClassSymbol(0, name, owner);
if (owner.kind == _PCK_1) {
Assert.checkNull(classes.get(c.flatname), c);
}
c.completer = this; // 将ClassReader对象赋值给新的ClassSymbol的completer属性
return c;
}
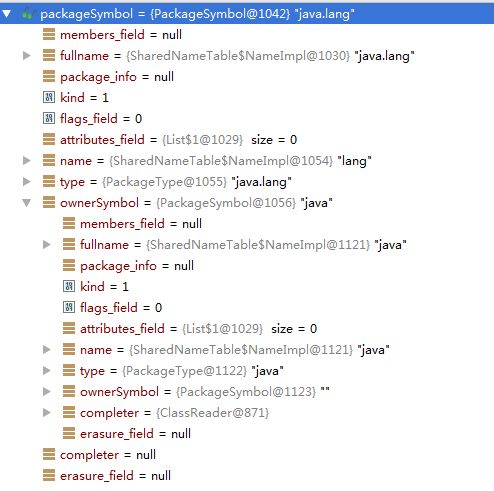
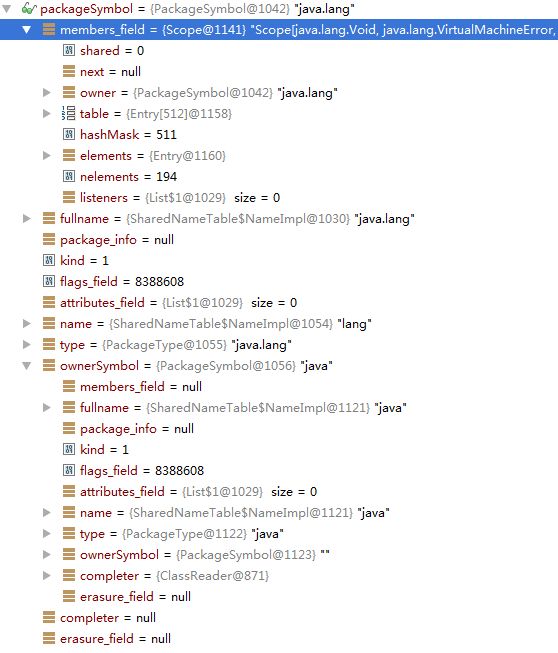
调用之前与这后的截图如下:
在执行过某个Symbol的complete()方法后,其中的属性completer会被置为null。而调用某个符号Symbol的complete()方法也主要是对members_field进行符号的填充。只有TypeSymbol,也就是PackageSymbol与ClassSymbol有members_field属性。
3、调用memberEnter()方法后处理JCImport语法节点。查看MemberEnter类的visitImport()方法,最重要的逻辑如下:
// process the non-static imports and the static imports of types. 处理类型的静态和非静态引入
public void visitImport(JCImport jcImport) {
JCTree jcTree = jcImport.qualified;
Name name = TreeInfo.name(jcTree); // identifier/field/a parameterized type
TypeSymbol typeSymbol;
// Create a local environment pointing to this tree to disable
// effects of other imports in Resolve.findGlobalType
Environment localEnvironment = environment.duplicate(jcImport); // 更新tree属性为JCImport
// Attribute qualifying package or class.
JCFieldAccess jcFieldAccess = (JCFieldAccess) jcTree;
int protoKind;
if(jcImport.staticImport){
// import static java.lang.Math.*;
// import static java.lang.Math.sin;
protoKind = _TYP;
}else{
// import java.lang.* _PCK
// import java.lang.Object _TYP
protoKind = _TYP | _PCK;
}
// 在符号输入的过程中也可能进行标记,如下:
Type type = attr.attribTree(jcFieldAccess.selected, localEnvironment, protoKind, Type.noType);
typeSymbol = type.typeSymbol;
if (name == names.asterisk) {
// Import on demand.
check.checkCanonical(jcFieldAccess.selected);
if (jcImport.staticImport){
importStaticAll(jcImport.position, typeSymbol, environment);
}else{
importAll(jcImport.position, typeSymbol, environment);
}
} else {
// Named type import.
if (jcImport.staticImport) {
importNamedStatic(jcImport.position(), typeSymbol, name, localEnvironment);
check.checkCanonical(jcFieldAccess.selected);
} else {
Type type1 = attributeImportType(jcTree, localEnvironment);
TypeSymbol typeSymbol1 = type1.typeSymbol;
check.checkCanonical(jcTree); // 是否是合乎规范的?
importNamed(jcImport.position(), typeSymbol1, environment); // Import given class.
}
}
}
如上代码要处理import java.util.ArrayList;语句。
(1)标记java.util,获取PackageType与typeSymbol,如下截图。
(2)处理java.util.ArrayList,也就是调用attributeImportType()方法,返回ClassType类型
(3)调用importNamed()方法为当前环境的Scope中导入符号。
4、对于JCClassDefinition节点调用MemberEnter的visitTree()后不做任何处理。但是在MemberEnter的complete(Symbol symbol)方法中对JCClassDefinition语法节点进行填充。
(1) 填充classType属性的supertype_field属性
Type superType = null;
if(jcClassDeclaration.extending != null){
superType = attr.attribBase(jcClassDeclaration.extending, baseEnvironment, true, false, true);
}else{
if( (jcClassDeclaration.modifiers.flags & Flags.ENUM) != 0 && !target.compilerBootstrap(classSymbol) ){
JCExpression jcExpression = enumBase(jcClassDeclaration.position, classSymbol);
superType = attr.attribBase(jcExpression, baseEnvironment,true, false, false);
}else{
if(classSymbol.fullname == names.java_lang_Object){
superType = Type.noType;
}else{
superType = symbolTable.objectType;
}
}
}
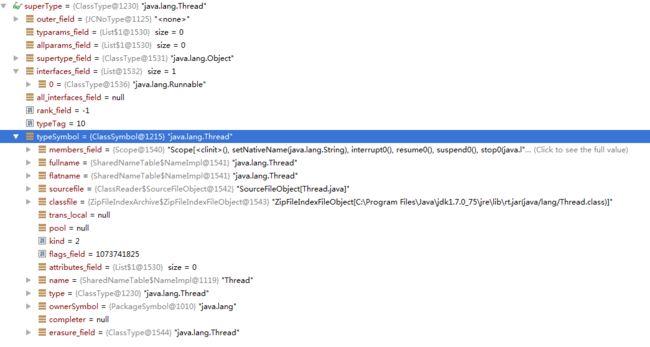
如果使用了extends关键字来明确继承一个类,如继承Thead类时,其superType如下截图。
(2) 填充classType属性的interfaces_field和all_interfaces_field属性
// Determine interfaces.
ListBuffer interfaces = new ListBuffer();
ListBuffer all_interfaces = null; // lazy initializer
Set interfaceSet = new HashSet();
List interfaceTrees = jcClassDeclaration.implementing;
// 为枚举类型添加了两个接口,Comparable和Serializable
if ((jcClassDeclaration.modifiers.flags & Flags.ENUM) != 0 && target.compilerBootstrap(classSymbol)) {
// add interface Comparable
// ClassType(Type outer, List typeParameters, TypeSymbol typeSymbol)
ClassType ct = new ClassType(
symbolTable.comparableType.getEnclosingType(), // java.lang.Comparable
List.of(classSymbol.type),
symbolTable.comparableType.typeSymbol
);
JCExpression jcExpression = treeMaker.Type(ct);
interfaceTrees = interfaceTrees.prepend(jcExpression);
// add interface Serializable
JCExpression serializableExpr = treeMaker.Type(symbolTable.serializableType);
interfaceTrees = interfaceTrees.prepend(serializableExpr);
}
for (JCExpression iface : interfaceTrees) {
Type interfaceType = attr.attribBase(iface, baseEnvironment, false, true, true);
if (interfaceType.typeTag == CLASS) {
interfaces.append(interfaceType);
if (all_interfaces != null){
all_interfaces.append(interfaceType);
}
check.checkNotRepeated(iface.position(), types.erasure(interfaceType), interfaceSet);
} else { // 如果进入这个循环,可能已经出错了?
if (all_interfaces == null){
all_interfaces = new ListBuffer().appendList(interfaces);
}
all_interfaces.append(modelMissingTypes(interfaceType, iface, true));
}
}
// 处理annotation注解
// java.lang.annotation.Annotation
if ( (classSymbol.flags_field & ANNOTATION) != 0 ) {
classType.interfaces_field = List.of(symbolTable.annotationType);
classType.all_interfaces_field = classType.interfaces_field;
} else {
classType.interfaces_field = interfaces.toList();
classType.all_interfaces_field = (all_interfaces == null) ? classType.interfaces_field : all_interfaces.toList();
}
// 如果类是Object,则进一步其父类和接口
if (classSymbol.fullname == names.java_lang_Object) {
if (jcClassDeclaration.extending != null) {
check.checkNonCyclic(jcClassDeclaration.extending.position(), superType);
classType.supertype_field = Type.noType;
}
else if (jcClassDeclaration.implementing.nonEmpty()) {
check.checkNonCyclic(jcClassDeclaration.implementing.head.position(), classType.interfaces_field.head);
classType.interfaces_field = List.nil();
}
}
(3) 标记类的类型变量
attr.attribTypeVariables(jcClassDeclaration.typeParameters, baseEnvironment);
(4) 添加默认的构造函数
// Add default constructorSymbol if needed.
// 在非接口且没有默认构造函数的情况下,添加默认的构造函数
if ((classSymbol.flags() & INTERFACE) == 0 && !TreeInfo.hasConstructors(jcClassDeclaration.defs)) {
// 默认如下三项都为空
List argumentTypes = List.nil();
List typeParameters = List.nil();
List thrown = List.nil();
long ctorFlags = 0;
boolean based = false;
if (classSymbol.name.isEmpty()) { // 如果符号的name为空的话
JCNewClass jcNewClass = (JCNewClass)environment.next.tree;
if (jcNewClass.constructorSymbol != null) {
Type superConstructorType = types.memberType(classSymbol.type,jcNewClass.constructorSymbol);
argumentTypes = superConstructorType.getParameterTypes();
typeParameters = superConstructorType.getTypeArguments();
ctorFlags = jcNewClass.constructorSymbol.flags() & VARARGS;
if (jcNewClass.enclosingExpression != null) {
argumentTypes = argumentTypes.prepend(jcNewClass.enclosingExpression.type);
based = true;
}
thrown = superConstructorType.getThrownTypes();
}
}
JCTree constructorDef = DefaultConstructor(treeMaker.at(jcClassDeclaration.position), classSymbol, typeParameters, argumentTypes, thrown, ctorFlags,based);
jcClassDeclaration.defs = jcClassDeclaration.defs.prepend(constructorDef);
}
(5) 输入this与super关键字到当前的作用域
// If this is a class, enter symbols for this and super into current scope.
// 如果为一个类,输入this和super关键字到当前的作用域
if ((classSymbol.flags_field & INTERFACE) == 0) {
// 输入this符号
VarSymbol thisSymbol = new VarSymbol(FINAL | HASINIT, names._this, classSymbol.type, classSymbol);
thisSymbol.pos = Position.FIRSTPOS; // firstpos
environment.info.scope.enter(thisSymbol);
// 有直接的父类才会输入super符号???
if (classType.supertype_field.typeTag == CLASS) { // 对于接口,supertype_field的typeTag为INTERFACE
VarSymbol superSymbol = new VarSymbol(FINAL | HASINIT, names._super, classType.supertype_field, classSymbol);
superSymbol.pos = Position.FIRSTPOS;
environment.info.scope.enter(superSymbol);
}
}
在complete()方法的结尾处有如下代码,是通过循环取出halfcompleted队列中的值来继承进行符号填充的。
try {
while (halfcompleted.nonEmpty()) {
Environment temp = halfcompleted.next();
finish(temp);
}
} finally {
isFirst = true;
}
5、处理JCMethodDeclaration
如上的实例中有两个方法,一个为test方法,另外一个为编译器默认添加的构造方法
public void visitMethodDefinition(JCMethodDeclaration jcMethodDeclaration) {
Scope enclosingScope = enter.enterScope(environment);
// MethodSymbol(long flags, Name name, Type type, Symbol owner)
MethodSymbol methodSymbol = new MethodSymbol(0, jcMethodDeclaration.name, null, enclosingScope.owner);
// Check that given modifiers are legal for given symbol and
// return modifiers together with any implicit modifiers for that symbol.
// checkFlags(DiagnosticPosition pos, long flags, Symbol symbol, JCTree jcTree)
methodSymbol.flags_field = check.checkFlags(jcMethodDeclaration.position(), jcMethodDeclaration.modifiers.flags, methodSymbol, jcMethodDeclaration);
jcMethodDeclaration.methodSymbol = methodSymbol; // 为methodSymbol赋值
Environment localEnvironment = methodEnvironment(jcMethodDeclaration, environment);
DeferredLintHandler prevLintHandler = check.setDeferredLintHandler(deferredLintHandler.setPos(jcMethodDeclaration.position()));
try {
// Compute the method type
methodSymbol.type = signature(jcMethodDeclaration.typeParameters, jcMethodDeclaration.parameters,
jcMethodDeclaration.returnType, jcMethodDeclaration.thrown, localEnvironment);
} finally {
check.setDeferredLintHandler(prevLintHandler);
}
// Set methodSymbol.parameters
ListBuffer parameters = new ListBuffer();
JCVariableDeclaration lastParameter = null;
for (List l = jcMethodDeclaration.parameters; l.nonEmpty(); l = l.tail) {
JCVariableDeclaration param = lastParameter = l.head;
parameters.append(Assert.checkNonNull(param.varSymbol));
}
methodSymbol.parameters = parameters.toList();
// mark the method varargs, if necessary
if (lastParameter != null && (lastParameter.modifiers.flags & Flags.VARARGS) != 0){
methodSymbol.flags_field |= Flags.VARARGS;
}
// method scope为什么要和class scope共享hashtable呢?
localEnvironment.info.scope.leave(); // ??
if (check.checkUnique(jcMethodDeclaration.position(), methodSymbol, enclosingScope)) {
enclosingScope.enter(methodSymbol);
}
annotateLater(jcMethodDeclaration.modifiers.annotations, localEnvironment, methodSymbol);
if (jcMethodDeclaration.defaultValue != null){ // 对于注解定义类中定义的方法可以有default默认值
annotateDefaultValueLater(jcMethodDeclaration.defaultValue, localEnvironment, methodSymbol);
}
}
可以看到主要填充了JCMethodDeclaration的methodSymbol属性,并且对methodSymbol的flags_field、parameters、type等属性进行值进行了填充。
6、JCVariableDeclaration语法节点