运维核心工作:
操作系统安装(物理机、虚拟机)--> 应用程序包部署(安装、配置、服务启动)--> 批量操作 --> 业务系统程序部署(安装,运行以及发布)--> 监控
系统安装(OS Provisioning):
(a) bare metal:裸机上安装系统,pxe预执行环境:cobbler是二次封装的pxe;
(b) virtual machine:在虚拟机上安装系统;Configuration:程序配置
(1) puppet(ruby语言研发):学习入门曲线陡峭;早先问世,稳定,重量级;
(2) saltstack(python语言研发):与puppet相似,要有强大的二次研发能力才能填坑,重量级;
(3) chef:轻量级,使用简单,早期问世;
(4) cfengine:
(5) ansible:
注意:puppet和saltstack都是重量级应用在上百台服务器以上的运维环境,需要长时间学习才能灵活运用,如果数量较少,支出会大于收益;
这就产生了一些较轻量级、简单入门学习的运维工具来负责较少量的服务器运维;
如chef、cfengine、ansible等;
Command and Control:批量执行命令控制
(1) fabric轻量级,python语言研发;可编写fabric脚本完成强大功能;
(2) func 重量级
(3) ansible预发布验证:
新版本的代码先发布到服务器(跟线上环境配置完全相同,只是未接入到调度器);程序发布:
不能影响用户体验;
系统不能停机;
不能导致系统故障或造成系统完全不可用;灰度发布:
发布路径:
/webapp/tuangou-1.1
/web/app/tuangou
/webapp/tuangou-1.2
在调度器上下线一批主机(maintanance)--> 关闭服务 --> 部署新版本的应用程序 --> 启动服务 --> 在调度器上启用这一批服务器;
- 自动化灰度发布: 脚本、发布平台;
轻量级的运维工具:Ansible
Ansible的特性
- 模块化:调用特定的模块,完成特定任务
- 基于Python语言实现,有Paramiko,PyYAML,Jinja2(模板语言)三个关键模块;
- 部署简单:agentless
- 支持自定义模块
- 支持playbook编排任务
- 有幂等性:一个任务执行一遍一执行n遍效果不一样,不因为重复执行带来意外情况
- 安全,基于OpenSSH
- 无需代理不依赖PKI(无需ssl)
- YAML格式编排任务,支持丰富的数据结构
- 较强大的多层解决方案
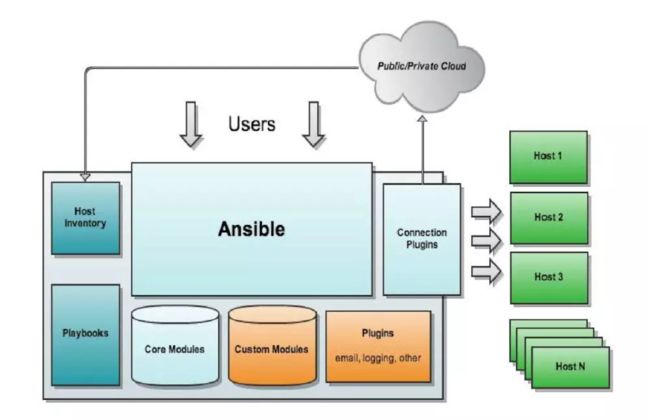
Ansible的架构
- Core Modules:核心模块
- Custom Modules:自定义模块
- Connection Plugins:连接插件
- Host Inventory:ansible管理主机的清单
/etc/ansible/hosts - Plugins:模块功能的补充,如记录日志发送通知等
- Playbooks 核心组件;任务剧本,编排定义ansible任务集的配置文件,ansible顺序依次执行,通常是json格式的yaml文件
Ansible的安装使用
- ansible是基于epel仓库,因此安装之前先要配置epel的yum源仓库
[root@server1 ~]# yum info ansible
Loaded plugins: fastestmirror, langpacks
Loading mirror speeds from cached hostfile
* base: mirror.jdcloud.com
* extras: mirrors.shu.edu.cn
* updates: mirrors.shu.edu.cn
Available Packages
Name : ansible
Arch : noarch
Version : 2.7.7
Release : 1.el7
Size : 11 M
Repo : epel
Summary : SSH-based configuration management, deployment, and task execution system
URL : http://ansible.com
License : GPLv3+
Description : Ansible is a radically simple model-driven configuration management,
: multi-node deployment, and remote task execution system. Ansible works
: over SSH and does not require any software or daemons to be installed
: on remote nodes. Extension modules can be written in any language and
: are transferred to managed machines automatically.
[root@server1 ~]# rpm -ql ansible | less
/etc/ansible/ansible.cfg #ansible主配置文件
/etc/ansible/hosts #主机清单配置文件
/etc/ansible/roles #角色配置文件
...
ansible的使用方式:
(1) 在命令行中直接给出
(2) 在riles中定义好ansible语法格式:
ansible[options] ansible的简单格式:
ansible HOST-PATTERN -m MOD_NAME -a MOD_ARGS -f FORKS -C -u USERNAME -c CONNECTION基于密钥的方式连接两台host主机node1和node2
[root@server1 ~]# ssh-keygen -t rsa -P "" #生成密钥
[root@server1 ~]# ssh-copy-id -i ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub [email protected]
# 使用密钥连接node1
[root@server1 ~]# ssh-copy-id -i ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub [email protected]
# 使用密钥连接node2
[root@server1 ~]# vim /etc/ansible/hosts # 编辑主机清单文件添加主机
[websrvs]
192.168.1.128
192.168.1.129
[dbsrvs]
192.168.1.128
[root@server1 ~]# ansible all -m ping -C # 使用ping命令测试两台主机node1,node2;-C:测试模式,干跑;
192.168.1.129 | SUCCESS => {
"changed": false,
"ping": "pong"
}
192.168.1.128 | SUCCESS => {
"changed": false,
"ping": "pong"
}
- ansible的常用模块:
- group模块
[root@server1 ~]# ansible-doc -s group # 查看group模块的帮助文档 示例: [root@server1 ~]# ansible all -m group -a "gid=3000 name=mygro state=present system=no" 192.168.1.129 | CHANGED => { "changed": true, "gid": 3000, "name": "mygro", "state": "present", "system": false } 192.168.1.128 | CHANGED => { "changed": true, "gid": 3000, "name": "mygro", "state": "present", "system": false } # 在node1和node2上查看/etc/group文件确认操作是否成功 [root@node1 ~]# tail -1 /etc/group mygro:x:3000:- user模块
- *name= 指定要管理的用户;
- state= 为present | absent;
- system= 是否创建系统帐号;
- uid= 指定UID;
- shell= 默认shell类型;
- group= 基于组;
- groups= 额外(附加)组;
- comment= 注释信息;
- home= 用户的家目录;
- move_home= 移动已存在用户的家目录;
- password 添加密码,应该指定是的openssl加密后的密码;
- remove 当state=absent时,删除用户时同时删除家目录;
示例:
[root@server1 ~]# ansible all -m user -a "uid=5000 name=testuser state=present groups=mygro shell=/bin/tcsh"
192.168.1.128 | CHANGED => {
"changed": true,
"comment": "",
"create_home": true,
"group": 5000,
"groups": "mygro",
"home": "/home/testuser",
"name": "testuser",
"shell": "/bin/tcsh",
"state": "present",
"system": false,
"uid": 5000
}
192.168.1.129 | CHANGED => {
"changed": true,
"comment": "",
"create_home": true,
"group": 5000,
"groups": "mygro",
"home": "/home/testuser",
"name": "testuser",
"shell": "/bin/tcsh",
"state": "present",
"system": false,
"uid": 5000
}
# 在node1和node2上查看用户创建结果
[root@node1 ~]# tail -1 /etc/passwd
testuser:x:5000:5000::/home/testuser:/bin/tcsh
- copy模块:
ansible-doc -s copy;用来复制文件到远程主机
2种用法:
1)src= dest=
2)content= dest=
owner,group,mode可同时指明文件的属主、组及权限;
一般有=号的选项为必有选项;
src=为本地文件或目录;
dest=为远程被管理主机文件或目录;
content=表示把此处的内空直接当做源文件;
[root@server1 ~]# ansible all -m copy -a "src=/etc/fstab dest=/tmp/fstab.ansible mode=600"
192.168.1.128 | CHANGED => {
"changed": true,
"checksum": "f5dec7037c1be2d9c54110114ffb00b9efb834ba",
"dest": "/tmp/fstab.ansible",
"gid": 0,
"group": "root",
"md5sum": "03ef74ad995b394c5265817e23ee086e",
"mode": "0600",
"owner": "root",
"secontext": "unconfined_u:object_r:admin_home_t:s0",
"size": 541,
"src": "/root/.ansible/tmp/ansible-tmp-1550649775.34-194820899443510/source",
"state": "file",
"uid": 0
}
192.168.1.129 | CHANGED => {
"changed": true,
"checksum": "f5dec7037c1be2d9c54110114ffb00b9efb834ba",
"dest": "/tmp/fstab.ansible",
"gid": 0,
"group": "root",
"md5sum": "03ef74ad995b394c5265817e23ee086e",
"mode": "0600",
"owner": "root",
"secontext": "unconfined_u:object_r:admin_home_t:s0",
"size": 541,
"src": "/root/.ansible/tmp/ansible-tmp-1550649775.36-53381265559986/source",
"state": "file",
"uid": 0
}
# 在node1和node2上查看结果
[root@node1 ~]# ll -d /tmp/fstab.ansible
-rw-------. 1 root root 541 Feb 20 16:02 /tmp/fstab.ansible
- command模块:
ansible-doc -s command;在被管理远程主机上执行命令;省略模块时,默认为command模块;- chdir:指定在哪个目录下运行命令;
- creates:命令运行前创建文件;如果文件存在就不执行命令;
- removes:命令运行后移除文件;如果文件不存在就不执行命令;
- executable:指定shell程序来运行命令;
示例:
[root@server1 ~]# ansible all -m command -a "ifconfig"
192.168.1.129 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
ens33: flags=4163 mtu 1500
inet 192.168.1.129 netmask 255.255.255.0 broadcast 192.168.1.255
...
lo: flags=73 mtu 65536
inet 127.0.0.1 netmask 255.0.0.0
...
virbr0: flags=4099 mtu 1500
inet 192.168.122.1 netmask 255.255.255.0 broadcast 192.168.122.255
...
192.168.1.128 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
ens33: flags=4163 mtu 1500
inet 192.168.1.128 netmask 255.255.255.0 broadcast 192.168.1.255
...
lo: flags=73 mtu 65536
inet 127.0.0.1 netmask 255.0.0.0
...
virbr0: flags=4099 mtu 1500
inet 192.168.122.1 netmask 255.255.255.0 broadcast 192.168.122.255
...
注意:command执行时不适用shell解析,是裸执行;比如传递参数`-a "echo mageedu | passwd --stdin testuser"`不能传递密码给testuser,需要使用下面的shell模块
- shell模块:
ansible-doc -s shell;在被管理远程主机上执行命令;但是为调用shell进程,然后把命令在子进程中运行;在执行的命令中可使用管道符;
示例:
[root@server1 ~]# ansible all -m shell -a "echo mageedu | passwd --stdin testuser"
192.168.1.128 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
Changing password for user testuser.
passwd: all authentication tokens updated successfully.
192.168.1.129 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
Changing password for user testuser.
passwd: all authentication tokens updated successfully.
- file 模块:
ansible-doc -s file
用法:- 创建链接文件:
path= 指明操作的文件
src= 要链接的源文件;
state= link - 修改属性:
path=
owner=
mode=
group= - 创建目录:
path=
state= directory
- 创建链接文件:
示例:
[root@server1 ~]# ansible all -m file -a "path=/var/tmp/hello.dir state=directory"
192.168.1.128 | CHANGED => {
"changed": true,
"gid": 0,
"group": "root",
"mode": "0755",
"owner": "root",
"path": "/var/tmp/hello.dir",
"secontext": "unconfined_u:object_r:user_tmp_t:s0",
"size": 6,
"state": "directory",
"uid": 0
}
192.168.1.129 | CHANGED => {
"changed": true,
"gid": 0,
"group": "root",
"mode": "0755",
"owner": "root",
"path": "/var/tmp/hello.dir",
"secontext": "unconfined_u:object_r:user_tmp_t:s0",
"size": 6,
"state": "directory",
"uid": 0
}
node1:
[root@node1 ~]# ls -d /var/tmp/hello.*
/var/tmp/hello.dir
#设定文件属性
[root@server1 ~]# ansible all -m copy -a "src=/etc/fstab dest=/var/tmp/fstab.ansible"
[root@server1 ~]# ansible all -m file -a "src=/var/tmp/fstab.ansible path=/var/tmp/fstab.link state=link"
192.168.1.128 | CHANGED => {
"changed": true,
"dest": "/var/tmp/fstab.link",
"gid": 0,
"group": "root",
"mode": "0777",
"owner": "root",
"secontext": "unconfined_u:object_r:user_tmp_t:s0",
"size": 22,
"src": "/var/tmp/fstab.ansible",
"state": "link",
"uid": 0
}
192.168.1.129 | CHANGED => {
"changed": true,
"dest": "/var/tmp/fstab.link",
"gid": 0,
"group": "root",
"mode": "0777",
"owner": "root",
"secontext": "unconfined_u:object_r:user_tmp_t:s0",
"size": 22,
"src": "/var/tmp/fstab.ansible",
"state": "link",
"uid": 0
}
node1:
[root@node1 ~]# ll -d /var/tmp/fstab.*
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 541 Feb 20 16:25 /var/tmp/fstab.ansible
lrwxrwxrwx. 1 root root 22 Feb 20 16:30 /var/tmp/fstab.link -> /var/tmp/fstab.ansible
- cron模块:定义任务计划
- minute= 几分钟,范围0-59
- day= 一个月的那一天,范围1-31,例如:1-5,/2等
- month= 哪个月,范围1-12;
- hour= 哪个小时,范围0-23;
- weekday= 星期几,范围0-6;
- job= 表示 state为present时,要执行的命令;
- name= 必须指定计划任务条目;
- state=
present:创建cron计划任务;默认;
absent:删除cron计划任务;
示例:
[root@server1 ~]# ansible all -m cron -a "minute=*/3 job='/usr/sbin/update 192.168.1.254 &> /dev/null' name=text1"
192.168.1.128 | CHANGED => {
"changed": true,
"envs": [],
"jobs": [
"text1"
]
}
192.168.1.129 | CHANGED => {
"changed": true,
"envs": [],
"jobs": [
"text1"
]
}
node1:
[root@node1 ~]# crontab -l
#Ansible: text1
*/3 * * * * /usr/sbin/update 192.168.1.254 &> /dev/null
[root@server1 ~]# ansible all -m cron -a "name=text1 state=absent" #删除定时任务
192.168.1.129 | CHANGED => {
"changed": true,
"envs": [],
"jobs": []
}
192.168.1.128 | CHANGED => {
"changed": true,
"envs": [],
"jobs": []
}
- yum模块:安装程序模块
[root@server1 ~]# ansible all -m yum -a "name=nginx state=installed"
192.168.1.128 | SUCCESS => {
"changed": true,
"msg": "",
"rc": 0,
"results": [
...
192.168.1.129 | SUCCESS => {
"changed": true,
"msg": "",
"rc": 0,
"results": [
...
node1:
[root@node1 ~]# rpm -q nginx
nginx-1.12.2-2.el7.x86_64
- service模块:
- name= 指明管理的服务
- state=
started 启动服务;
stopped 停止服务;
restarted重启服务; - enabled= 开机自动启动;1或0
- runlevel= 在指定级别下为开机自动启动;默认为2345,或345级别;
- arguments 向命令行传参数;
示例:
[root@server1 ~]# ansible all -m service -a "name=nginx state=started"
192.168.1.128 | CHANGED => {
"changed": true,
"name": "nginx",
"state": "started",
"status": {
...
192.168.1.129 | CHANGED => {
"changed": true,
"name": "nginx",
"state": "started",
"status": {
...
node1:
[root@node1 ~]# ss -tnl
State Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address:Port Peer Address:Port
LISTEN 0 128 *:80 *:*
...
注意:service有2个选项:
enabled设定开机自动启动
runlevel在哪个级别设定开机自动启动
- spripts模块:脚本模块
示例:
[root@server1 ~]# vim /tmp/text.sh
#!/bin/bash
#
echo "ansible script" > /tmp/ansible.txt
[root@server1 ~]# ansible all -m script -a "/tmp/text.sh"
192.168.1.129 | CHANGED => {
"changed": true,
"rc": 0,
"stderr": "Shared connection to 192.168.1.129 closed.\r\n",
"stderr_lines": [
"Shared connection to 192.168.1.129 closed."
],
"stdout": "",
"stdout_lines": []
}
192.168.1.128 | CHANGED => {
"changed": true,
"rc": 0,
"stderr": "Shared connection to 192.168.1.128 closed.\r\n",
"stderr_lines": [
"Shared connection to 192.168.1.128 closed."
],
"stdout": "",
"stdout_lines": []
}
- Playbook的核心元素:
- hosts:主机(关联到的主机);可以是一个或多个用冒号分隔的主机组;可以是一个主机组,也可以是一个主机;这些主机必须定义在hosts iventory中;
- remoute_user:在远程主机上执行任务的用户;即以哪个用户的身份运行此任务,可以全局指定,也可以在tasks中单独指定执行任务的用户;即不同的任务指明不同的用户;
- sudo_user:在使用sudo方式时执行任务时,指明临时切换哪个用户执行;只是在指明以sudo的方式运行时才使用;- tasks:任务列表;定义任务的方式主要就是调用模块和模块参数;
- variables:变量(多次引用任务使用)
- templates:模板(包含了模板语法的文本文件)
- handlers:从处理器(由特定条件触发的任务)任务,在特定条件下触发;在handlers所关注的资源发生改变时才触发任务;一般使用notify机制通知来触发;
生效方式:接收到其他任务的通知时被触发; - roles:角色
playbook的主要作用:
就是能够把多个相关联的任务,通过读取YAML格式的配置文件一次编完;要把任务、变量、模板、处理器放在一个YAML格式文件中进行指定,然后任务就可一次批量执行;
例如:
playbook的基础组件hosts和tasks演示:
[root@server1 ~]# mkdir playbook
[root@server1 ~]# cd playbook/
[root@server1 playbook]# vim first.yaml
- hosts: all
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: install redis
yum: name=redis state=latest
- name: start redis
service: name=redis state=started
[root@server1 playbook]# ansible-playbook --check first.yaml
PLAY [all] ********************************************************************************************************
TASK [Gathering Facts] #只要收集参数成功都显示ok; ********************************************************************************************
ok: [192.168.1.128]
ok: [192.168.1.129]
TASK [install redis] #在playbook中定义的第一个任务**********************************************************************************************
changed: [192.168.1.128]
changed: [192.168.1.129]
TASK [start redis] #在playbook中定义的第二个任务************************************************************************************************
changed: [192.168.1.129]
changed: [192.168.1.128]
PLAY RECAP #返回的报告********************************************************************************************************
192.168.1.128 : ok=3 changed=2 unreachable=0 failed=0
192.168.1.129 : ok=3 changed=2 unreachable=0 failed=0
[root@server1 playbook]# ansible-playbook --list-hosts first.yaml
#查看这个playbook运行在哪些主机
playbook: first.yaml
play #1 (all): all TAGS: []
pattern: [u'all']
hosts (2):
192.168.1.128
192.168.1.129
[root@server1 playbook]# ansible-playbook -C first.yaml #干跑一遍测试
[root@server1 playbook]# ansible-playbook first.yaml #真正执行
- 注意:
GATHERING FACTS第一个任务,是默认的,在每一个目标主机上运行之前,需要知道目标主机的状态,例如主机名、ip地址等,这些都是内建变量,叫主机的facts变量,是ansible可调用的变量之一;这个过程就是收集变量的过程,也可以手动收集; - 如果指明了三个任务,在三台主机上运行,执行次序是,把第一个任务在三台主机运行,没问题则在三台主机上再运行第二个任务,如果在运行其中某一主机出现故障,后面的任务会终止;
所以,任务列表,是自上而下,每个任务依次进行的;
指明任务的格式:2种
(1) action:module arguments 较新版本支持
(2) module:arguments 所有版本通用 - shell和command模块参数独特,后面直接跟命令,而非key=value类的参数列表;
(1) 某任务的状态在运行后为changed时,可通过notify通知给相应的handlers处理器;
(2) 任务可以通过tags打标签,而后可在ansibles-playbook命令上使用-t指定进行调用,可调用多个标签; - setup模块:手动收集指定远程主机的变量
ansible 192.168.1.128 -m setup
示例1:安装httpd,安装配置文件,启动httpd服务
[root@server1 playbook]# mkdir working
[root@server1 playbook]# cd working/
[root@server1 working]# cp /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf ./
[root@server1 working]# vim httpd.conf
Listen 8080
[root@server1 working]# cd ..
[root@server1 playbook]# vim web.yaml
- hosts: websrvs
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: install httpd package
yum: name=httpd state=present
- name: install configure file
copy: src=working/httpd.conf dest=/etc/httpd/conf/
- name: start httpd service
service: name=httpd state=started
- name: excute ss command
shell: ss -tnl | grep 8080
[root@server1 playbook]# ansible-playbook --check web.yaml #测试语法
[root@server1 playbook]# ansible-playbook web.yaml #真正执行
注意:在ansible-playbook中执行ss -tnl | grep :8080,这种查询是不显示,所以,一般不在ansible-playbook里执行有关查询显示的命令;
示例2:演示使用handlers,触发执行;
如果把监听端改为808,再执行,则不会生效,因为,服务已经启动了,除非重启服务,这时,就应该用到handlers处理器
[root@server1 playbook]# vim web-2.yaml
- hosts: websrvs
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: install httpd package
yum: name=httpd state=present
- name: install configure file
copy: src=working/httpd.conf dest=/etc/httpd/conf/
- name: start httpd service
service: name=httpd state=started
handlers:
- name: restart httpd
service: name=httpd state=restarted
[root@server1 playbook]# vim working/httpd.conf
Listen 808
[root@server1 playbook]# ansible-playbook --check web-2.yaml
[root@server1 playbook]# ansible-playbook web-2.yaml
[root@server1 playbook]# ansible websrvs -m shell -a "ss -tnl | grep 808"
192.168.1.129 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
LISTEN 0 128 :::808 :::*
192.168.1.128 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
LISTEN 0 128 :::808 :::*
示例3:
根据上例,如果仅修改了配置文件,却还要从第一步,执行安装程序包,这样是没必要的,所以,可使用tag,给任务加标签,不指定标签时,执行所有任务,加标签时,只执行标签所在的任务;
[root@server1 playbook]# cp web-2.yaml web-3.yaml
[root@server1 playbook]# vim web-3.yaml
- hosts: websrvs
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: install httpd package
yum: name=httpd state=present
tags: insthttpd
- name: install configure file
copy: src=working/httpd.conf dest=/etc/httpd/conf/
tags: instconf
- name: start httpd service
service: name=httpd state=started
tags: starthttpd
handlers:
- name: restart httpd
service: name=httpd state=restarted
[root@server1 playbook]# vim working/httpd.conf
Listen 80
[root@server1 playbook]# ansible-playbook -t insthttpd --check web-3.yaml
[root@server1 playbook]# ansible-playbook -t instconf,insthttpd --check web-3.yaml #调用多个标签;
- variables:变量
- 1) facts:任何facts变量都由正在通信的目标主机发回的信息,ansible自动获取变量,可直接调用;在setup模块中查看变量;
- 2)ansible-playbook命令的命令行中的自定义变量;
-e VARS, --extra-vars=VARS - 3)通过roles传递变量;
- 4)Host Inventory
- a)向不同的主机传递不同的变量;
- b)向组中的主机传递相同的变量;
[groupname:vars]
variable=value
- 注意:invertory参数:
用于定义ansible远程路径目标主机时使用的参数,而非传递给playbook的变量;
ansible_ssh_host
ansible_ssh_port
ansible_ssh_user
ansible_ssh_pass
ansible_sudo_pass
...
通常ansible中的inventory还有专门参数,不叫变量,因为它不是传递给playbook使用的,而是通过ansible连接每个被管理主机时使用的;
示例1:演示ansible-playbook命令行调用变量
[root@server1 playbook]# vim forth.yaml
- hosts: websrvs
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: install {{ pkname }}
yum: name={{ pkname }} state=present
[root@server1 playbook]# ansible-playbook -e pkname=memcached --check forth.yaml
[root@server1 playbook]# ansible-playbook -e pkname=memcached forth.yaml
- playbook的其它组件:
- 变量:5种
ansible facts可使用setup模块获取;收集远程主机变量;
ansible-playbook -e "var=value"自定义变量
host variable:host iventory主机变量
group variable(主机组上的变量)
roles - 变量调用方法:{{ variable }}
- 变量:5种
在playbook中定义变量的方法:
vars:
- var1: value1
- var2: valure2
注意:这种变量有个缺陷,要想改变变量值时都要改变配置文件,不过可在调用时覆盖其变量的值;
- templates模块:基于模板方式生成一个文件复制到远程主机;
src= 指定本地jinja2的模板文件路径
dest= 远程主机路径
owner= 属主
group= 属组
mode= 权限-
模板:templates
就是文本文件,内部嵌套有脚本(这个脚本使用模板编程语言编写)
python只有在实现web框架时进行嵌入,将自己基于模板编程语言嵌入到其它文本中的机制,它的模板编程语言叫jinja2嵌入式的编程语言;类似于playbook,在python中叫resource资源和清单facts;在清单中定义资源时或定义使用的模板时会用到rubby的模板编程语言;
jinja2模板编程语言所实现的功能是,可以在文本文件中,使用一个所谓的嵌入的标记语法,引入一段模板编程语言所编写的脚本;而这种脚本无法就是支持比较简单的编程元素,如条件判断、(迭代)循环、变量;- jinja2:模板编程语言
字面量:是常见的python对象
字符串:一般使用单引号或双引号;
数字:整数,浮点数;
列表:使用[item1,tiem2,..],是可变的数据结构;
元组:(item1,item2,...),是不可变的数据结构;
字典:{key1:value1,key2:value2,...},就是键值对的组合;
key一般为字符串所以要用引号;
布尔型:true/false- 算术运算:
+,-,,/, //只留商,%只留余数,*
比较操作:
==, !=, >, >=, <, <=
逻辑运算:
and,or,not
- 算术运算:
- jinja2:模板编程语言
-
演示模板使用:使用ansible在二台主机上,安装nginx,提供配置文件,但其中的worker_processores的值要与主机的cpu核心数相同;此时,就可把配置文件基于模板方式提供,而这个worker_processores的值,放的是jinja2所支持的变量,直接使用变量的方式放在那个位置,而本机的template模块会自动套用这里面变量的值,给ansible facts所报告的结果,并把它生成在这个文件中,而后复制到目标主机上去;这就是模板的作用;
示例:
[root@server1 ~]# ansible all -m yum --check -a "name=nginx state=latest" #测试安装nginx
[root@server1 ~]# ansible all -m yum -a "name=nginx state=latest" #安装nginx
[root@server1 ~]# mkdir files
[root@server1 ~]# cp /etc/nginx/nginx.conf /root/files/nginx.conf.j2
[root@server1 ~]# cd files
[root@server1 files]# vim nginx.conf.j2
修改:
worker_processes {{ ansible_processor_vcpus }};
[root@server1 files]# vim nginx.yaml
- hosts: websrvs
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: Install nginx
yum: name=nginx state=present
- name: Install config file
template: src=/root/files/nginx.conf.j2 dest=/etc/nginx/nginx.conf
notify: restart nginx
- name: start service
service: name=nginx state=started
handlers:
- name: restart nginx
service: name=nginx state=restarted
[root@server1 files]# ansible-playbook nginx.yaml --check
[root@server1 files]# ansible-playbook nginx.yaml
可使用主机变量,让不同主机监听不同端口:
[root@server1 files]# vim /etc/ansible/hosts
[websrvs]
192.168.1.128 http_port=80 #定义主机变量
192.168.1.129 http_port=8080
[root@server1 files]# vim nginx.conf.j2
修改:
listen {{ http_port }};
[root@server1 files]# ansible-playbook nginx.yaml --check
[root@server1 files]# ansible-playbook nginx.yaml
条件测试:when示例
]# scp [email protected]:/etc/nginx/nginx.conf files/nginx.conf.c6.j2 复制一个centos6上的nginx配置文件;
]# vim files/nginx.conf.c6.j2
worker_processes {{ ansible_processor_vcpus }};
]# vim nginx.yaml
- hosts: all
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: install nginx
yum: name=nginx state=present
- name: install conf file to c7
template: src=files/nginx.conf.j2 dest=/etc/nginx/nginx.conf
when: ansible_distribution_major_version == "7"
notify: restart nginx
tags: instconf
- name: install conf file to c6
template: src=files/nginx.conf.c6.j2 dest=/etc/nginx/nginx.conf
when: ansible_distribution_major_version == "6"
notify: restart nginx
tags: instconf
- name: start nginx service
service: name=nginx state=started
handlers:
- name: restart nginx
service: name=nginx state=restarted
示例:
同时安装nginx、memcached、php-fpm等程序包,使用循环
]# vim iter.yaml
- hosts: all
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: install some packages
yum: name={{ item }} state=present
with_items:
- nginx
- memcached
- php-fpm
- role 角色
有3组服务器web、db、ha都用到时间同步服务,当编写三个yaml文件分别适用于这3组服务器时,每个文件都要写一遍时间同步的功能;或另有一种情况,假如第一组服务器即是web又是db,第二组服务器只是db,第三组服务器只是web,此时要写yaml文件,如果要写一个db的,再写一行web的,还要写一个db和web合并的,如果还要memcached服务器,而有些在db上,有些在web上,在这种场景中,代码在不同的主机角色间灵活组合,而这对于此前固化在yaml中的格式显然是不适用的;
如果把每一种配置的定义的功能独立化,而且谁用到时谁去调用即可;这种可独立化的配置通常按照功能为基准进行划分的;如果服务器安装了某种功能就扮演成了某种角色;即把db功能的定义一个角色,web功能的配置定义一个角色,memcached功能配置定义一个角色等等;需要什么就事先定义好什么,放在特定目录下,当主机需要进行配置时,写一个yaml配置文件,在其里面指明用在哪个主机上、使用remote_user基于哪个运行、调用角色即可;
这就是角色机制,是自包含的,为了让服务器能够调用其中的角色实现某种功能,所需要的一切代码、文件的集合都放在一个特定位置,这个组件就称为角色;
角色的好处是跟主机是分离的,谁用谁调用;
对于playbook而言,角色就是在playbook中所应该定义各种组件的集合;但此前是写在playbook一个文件中的,而如果要变成角色,要扮演成一个单独的目录,角色名就是目录名;
每一个角色一般按固定格式定义,任何角色都不能引用自己目录以外的资源,这样把这个目录复制到任何主机上都可以用,这就是自包含应该指明file子目录;所有的模板放在templates子目录下;所有的任务放在tasks子目录下,所有的处理器放在handlers子目录下;所有变量放在vars子目录下;还有一个补充meta子目录;
不是所有目录必须得有,一般用到哪些目录,就给出哪些目录即可;这就是角色的目录组织形式;
角色(role);/etc/ansible/roles也可在ansible.cfg中定义;
一般为目录,每一个角色就是一个子目录;
角色集合:
roles/
mysql/
httpd/
nginx/
memcached/每个角色,以特定的层级目录结构进行组织:
mysql/
files/:存放由copy或script模块等调用的文件;
templates/:存放为template模块查找所需的模板文件目录;
tasks/:至少应该包含一个名为main.yml的文件;其它文件需要在此文件中通过include进行包含;
handlers/:至少应该包含一个名为main.yml的文件;其它文件需要在此文件中通过include进行包含;
vars/:至少应该包含一个名为main.yml的文件;其它文件需要在此文件中通过include进行包含;
meta/:定义当前角色的特殊设定及其依赖关系;至少应该包含一个名为main.yml的文件;其它文件需要在此文件中通过include进行包含;
default/:设定默认变量时使用此目录中的main.yml文件;在playbook调用角色方法1:
- hosts: websrvs
remote_user: root
roles:
- mysql
- memcached
- nginx
- 在playbook调用角色方法2:在角色调用时,传递变量给角色
- hosts:
remote_user:
roles:
- { role: nginx, username: nginx }
#键role用于指定角色名称,后续的k/v用于传递变量给角色;
#还可以基于条件测试实现角色调用;
roles:
- { role: nginx, when: "ansible_distribution_major_version == '7'" }
Ansible实现主/备模式主可用
安装ansible
[root@localhost ~]# yum -y install ansible keepalive编辑主机清单
[root@localhost ~]# vim /etc/ansible/host
[websrvs]
192.168.1.115
192.168.1.116
[hasrvs]
192.168.1.10
192.168.1.11
- 创建固定目录结构
[root@localhost ~]# mkdir -pv /etc/ansible/roles/{keepalived,nginx}/{files,tasks,templates,handlers,vars,default,meta}
[root@localhost ~]# tree /etc/ansible/roles/
/etc/ansible/roles/
├── keepalived
│ ├── default
│ ├── files
│ ├── handlers
│ ├── meta
│ ├── tasks
│ ├── templates
│ └── vars
└── nginx
├── default
├── files
├── handlers
├── meta
├── tasks
│ └── main.yml
├── templates
│ └── index.html.j2
└── vars
- 基于密钥连接node1、node2、r1、r2、
[root@localhost ~]# ssh-keygen -t rsa -P ""
[root@localhost ~]# ssh-copy-id -i ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub [email protected]
[root@localhost ~]# ssh-copy-id -i ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub [email protected]
[root@localhost ~]# ssh-copy-id -i ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub [email protected]
[root@localhost ~]# ssh-copy-id -i ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub [email protected]
- 编辑roles
[root@localhost ~]# vim /etc/ansible/roles/keepalived/tasks/main.yml
#编辑如下内容
- name: install keepalived
yum: name=keepalived state=latest
when: ansible_os_family == "RedHat"
- name: install conf
template: src=kl.conf.j2 dest=/etc/keepalived/keepalived.conf
tags: conf
notify: restart keepalived
- name: start keepalived
service: name=keepalived state=started enabled=yes
[root@localhost ~]# vim /etc/ansible/roles/keepalived/handlers/main.yml
- name: restart keepalived
service: name=keedpalived state=restarted
- 编辑keepalived配置文件,并定义变量
[root@localhost ~]# vim /etc/ansible/roles/keepalived/templates/kl.conf.j2
! Configuration: command not found
global_defs {
notification_email {
root@localhost
}
notification_email_from keepalived@localhost
smtp_server 127.0.0.1
smtp_connect_timeout 30
router_id {{ ansible_fqdn }}
vrrp_mcast_group4 224.1.105.33
}
vrrp_instance VI_1 {
state {{ kl_status }}
interface ens33
virtual_router_id 33
priority {{ kl_priority }}
advert_int 1
authentication {
auth_type PASS
auth_pass XXXX1111
}
virtual_ipaddress {
192.168.1.99 dev ens33 label ens33:0
}
notify_master "/etc/keepalived/notify.sh master"
notify_backup "/etc/keepalived/notify.sh backup"
notify_fault "/etc/keepalived/notify.sh fault"
}
virtual_server 192.168.1.99 80 {
delay_loop 1
lb_algo wrr
lb_kind DR
protocol TCP
sorry_server 127.0.0.1 80
real_server 192.168.1.115 80 {
weight 1
HTTP_GET {
url {
path /index.html
status_code 200
}
nb_get_retry 3
delay_before_retry 2
connect_timeout 3
}
}
real_server 192.168.1.116 80 {
weight 1
HTTP_GET {
url {
path /index.html
status_code 200
}
nb_get_retry 3
delay_before_retry 2
connect_timeout 3
}
}
}
[root@localhost files]# vim /etc/ansible/hosts
[hasrvs]
192.168.1.10 kl_status=MASTER kl_priority=100
192.168.1.11 kl_status=BACKUP kl_priority=96
- 配置nginx的roles
[root@localhost files]# vim /etc/ansible/roles/nginx/tasks/main.yml
- name: Install nginx
yum: name=nginx state=latest
- name: Install conf
template: src=index.html.j2 dest=/usr/share/nginx/html/index.html
notify: reload nginx
- name: start script
script: /root/files/setkl.sh start
notify: reload nginx
- name: start nginx
service: name=nginx state=started
[root@localhost files]# vim /etc/ansible/roles/nginx/templates/index.html.j2
{{ ansible_fqdn }}
[root@localhost files]# vim /etc/ansible/roles/nginx/handlers/main.yml
- name: reload nginx
service: name=nginx state=reload
- 编辑keepalived和nginx的playbook
[root@localhost ~]# cd files
[root@localhost files]# vim kl.yml
- hosts: hasrvs
remote_user: root
roles:
- keepalived
[root@localhost files]# vim nginx.yml
- hosts: websrvs
remote_user: root
roles:
- nginx
- 测试并执行
[root@localhost files]# ansible-playbook --check kl.yml
[root@localhost files]# ansible-playbook --check kl.yml
[root@localhost files]# ansible-playbook --check nginx.yml
[root@localhost files]# ansible-playbook nginx.yml
- 访问测试
[root@localhost files]# curl http://192.168.1.99
rs1.ilinux.com
[root@localhost files]# curl http://192.168.1.99
rs2.ilinux.com
[root@localhost files]# curl http://192.168.1.99
rs1.ilinux.com
[root@localhost files]# curl http://192.168.1.99
rs2.ilinux.com
[root@localhost files]# curl http://192.168.1.99
rs1.ilinux.com
node1:规则已生成
[root@node1 ~]# ipvsadm -ln
IP Virtual Server version 1.2.1 (size=4096)
Prot LocalAddress:Port Scheduler Flags
-> RemoteAddress:Port Forward Weight ActiveConn InActConn
TCP 192.168.1.99:80 wrr
-> 192.168.1.115:80 Route 1 0 3
-> 192.168.1.116:80 Route 1 0 2
[root@node1 ~]# ifconfig
ens33: ...
ens33:0: flags=4163 mtu 1500
inet 192.168.1.99 netmask 255.255.255.255 broadcast 0.0.0.0
ether 00:0c:29:6d:e2:f7 txqueuelen 1000 (Ethernet)
[root@node1 ~]# systemctl stop keepalived.service
node2:
[root@node2 ~]# ipvsadm -ln
IP Virtual Server version 1.2.1 (size=4096)
Prot LocalAddress:Port Scheduler Flags
-> RemoteAddress:Port Forward Weight ActiveConn InActConn
TCP 192.168.1.99:80 wrr
-> 192.168.1.115:80 Route 1 0 0
-> 192.168.1.116:80 Route 1 0 0
#使用客户端访问:
[root@localhost files]# curl http://192.168.1.99
rs2.ilinux.com
[root@localhost files]# curl http://192.168.1.99
rs1.ilinux.com
[root@localhost files]# curl http://192.168.1.99
rs2.ilinux.com
[root@localhost files]# curl http://192.168.1.99
rs1.ilinux.com
[root@localhost files]# curl http://192.168.1.99
rs2.ilinux.com